AP World History- Unit 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
Equal field system
Chinese system during the Tang dynasty in which the goal was to ensure an equitable distribution of land
2
New cards
Grand canal
Located in China, it was one of the world's largest waterworks projects before modern times

3
New cards
Neo-Confucianism
Philosophy that attempted to merge certain basic elements of Confucian and Buddhist thought

4
New cards
Porcelain
Lighter, thinner and adaptable ceramic

5
New cards
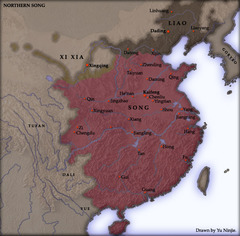
Song dynasty
Reigned during the late 10th-13th centuries and had a far-reaching impact on Chinese economy, culture, and society. It was marked by an increasingly urbanized and cosmopolitan society
6
New cards
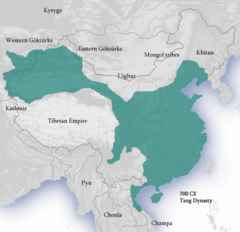
Tang dynasty
An imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui dynasty. Considered to be the Golden Age of China because of its advancements in technology, medicine, and trade. The foundation of their greatness was from the emphasis put into study which led to stronger leadership and ideas.
7
New cards
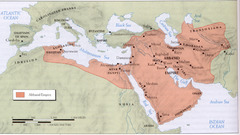
Abbasid dynasty
Cosmopolitan Arabic dynasty that replaced the Umayyads; founded by Abu al-Abbas and reached its peak under Harun al-Rashid
8
New cards
Allah
God of the monotheistic religion of Islam
9
New cards
Caliph
"Deputy," Islamic leader after the death of Muhammad
10
New cards
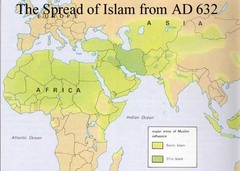
dar al-Islam
The "house of Islam", a term for the Islamic world. It refers to lands under the Islamic rule as a whole; it continued to grow during the Abbasid era.
11
New cards
Five Pillars of Islam
The foundations of Islam: 1. Profession of faith 2. prayer 3. fasting during Ramadan 4. almsgiving 5. pilgrimage or hajj
12
New cards
hajj
Pilgrimage to Mecca
13
New cards
Islam
Monotheistic religion announced by the prophet Muhammad; influenced by Judaism and Christianity, Muhammad was considered the final prophet because the earlier religions had not seen the entire picture
14
New cards
jizya
Tax in Islamic empires that was imposed on non-Muslims

15
New cards
Ka'aba
main shrine in Mecca, goal of Muslims embarking on the hajj
16
New cards
Muhammad
Prophet of Islam
17
New cards
Quran
Islamic holy book that is believed to contain the divine revelations of Allah as presented to Muhammad
18
New cards
Sunni
"Traditionalists," the most popular branch of Islam; Sunnis believe in the legitimacy of the early caliphs, compared with the Shiite belief that only a descendant of Ali can lead
19
New cards
umma
Islamic term for the "community of the faithful"
20
New cards
Ummayad dynasty
Arabic dynasty, with its capital at Damascus, that was marked by a tremendous period of expansion to Spain in the west and India in the east
21
New cards
Melaka (Malacca)
Southeast Asian kingdom that was predominantly Islamic
22
New cards
Axum
African kingdom centered in Ethiopia that became an early and lasting center of Coptic Christianity
23
New cards
caste system
class structure that is determined by birth.
24
New cards
Byzantine Empire
Long-lasting empire centered at Constantinople; it grew out of the end of the Roman empire, carried the legacy of Roman greatness, and was the only classical society to survive into the early modern age; it reached its early peak during the reign of Justinian
25
New cards
caesaropapism
Concept relating to the mixing of political and religious authority, as with the Roman emperors, that was central to the church-versus-state controversy in medieval Europe
26
New cards
Vikings
A group that raided the British Isles from their home at Vik in southern Norway

27
New cards
shamans
Religious specialists who possessed supernatural powers and who communicated with the gods and the spirits of nature
28
New cards
Yuan dynasty
Chinese dynasty that was founded by Genghis Khan's grandson
29
New cards
Bantu
Collective name of a large group of sub-Saharan African languages and of the peoples speaking these languages.
30
New cards
Great Zimbabwe
Large sub-Saharan African kingdom in the 15th century
31
New cards
Mali empire
West African kingdom founded in the 13th century by Sundiata; it reached its peak during the reign of Mansa Masu
32
New cards
Sundiata
Founder of the Mali empire, also the inspiration for the Sundiata, an African literary and mythological work
33
New cards
Swahili
East African city-state society that dominated the coast from Mogadishu to Kilwa and was active in trade. Also a Bantu language of East Africa, or a member of a group who speaks this language
34
New cards
Marco Polo
Italian merchant whose account of his travels to China and other lands became legendary
35
New cards
reconquista
Crusade, ending in 1492, to drive the Islamic forces out of Spain
36
New cards
three estates
The three classes of European society, composed of the clergy #1, the aristocrats #2 and the common people #3
37
New cards
Hangzhou
Capital of later Song dynasty; located near East China Sea; permitted overseas trading; population exceeded 1 million
38
New cards
Mecca
Original city of Islam, birthplace of Muhammad, location of the hajj

39
New cards
Mongols
Nomadic horse-people from the eastern steppe of Asia that created the largest empire in the history of the world.
40
New cards
Pax Mongolica (13th-14th centuries)
Mongols guaranteed safe passage for traders, missionaries, and travelers such as Marco Polo, trade flourished, silk, Asian artistic designs moved westward, Mongols gain incredible wealth taxing the trade, peaceful travel across Asia, cultural exchanges, exchange of ideas, medical, mathematics, finance, engineering knowledge flows between China and Middle East, printing, gunpowder transmitted from China to Europe, spread of bubonic plague.
41
New cards
Spice Roads
The trade of spices from Asia and India to Italian and Muslim merchants who would then trade it to Europeans.
42
New cards
Baghdad
Located on the Silk Roads, it was the capital city of the Abbasid Caliphate.
43
New cards
Horse collar
Harnessing method that increased the efficiency of horses by shifting the point of traction from the animal's neck to the shoulders; its adoption favors the spread of horse-drawn plows and vehicles

44
New cards
Mansa Musa
Greatest Mali king; brought Mali to its peak of power and wealth from 1312 the 1337; expanded borders, maintained peace and order, religious freedom and tolerance; hajj to Mecca; built Timbuktu

45
New cards
Timbuktu
Port city of Mali; located just off the flood plain on the great bend in the Niger River; population of 50,000; contained a library and university.
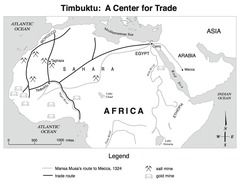
46
New cards
Ibn Battuta
Moroccan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan
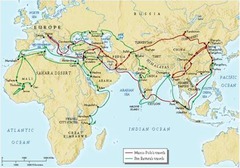
47
New cards
Caravanserai
a roadside inn where travelers (caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey; supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes covering Asia, North Africa and Southeast Europe, especially along the Silk Road.

48
New cards
Astrolabe
astronomical tool for solving problems relating to time and the position of the Sun and stars in the sky, in relation to the equator
49
New cards
Hanseatic League
a commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and their market towns in Europe before 1450s
50
New cards
Bananas
Arrived to Africa via Southeast Asia, cultivation increased the supply of food, enriched diets, and allowed the population to expand more rapidly than before.
51
New cards
bubonic plague
pathogen spread via the increased interactions amongst peoples on/around trade routes in Eurasia
52
New cards
Peasant Labor
System in Europe that kept individuals tied to land and land-owning elites
53
New cards
Foot Binding
Practice in Song Dynasty, increased patriarchal attitudes of society