All biology Exam Qs
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
An increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can lead to an enhanced greenhouse effect.
Describe the possible consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect. (4)
m1: global warming m2: ice caps melt m3: rises sea levels m4: climate change m5: habitat destruction m6: extinction due to disruption of food chains m7: migration → distributes organisms → distributes disease → affects plant growth
Explain the consequences of fertiliser containing nitrates polluting a river (6)
m1: nitrates soluble/dissolve m2: rain/water m3: leaching plant growth m4: block sunlight → plants die → less photosynthesis → less oxygen m5: fish/animals die m6: eutrophication
(Oryx and) humans can control water loss by making their urine very concentrated. Describe how this is done. (6)
m1: receptors present in the nephron m2: hypothalamus controls water reabsorption m3: pituitary gland releases m4: ADH m5: increases ADH m6: kidney/nephron m7: collecting duct m8: more permeable m9: reabsorption of water
Suggest why desert animals are less active in summer than in winter. (3)
m1: warmer m2: avoid sweating and water loss m3: avoid overheating as respiration produces heat m4: because there’s less water in plants
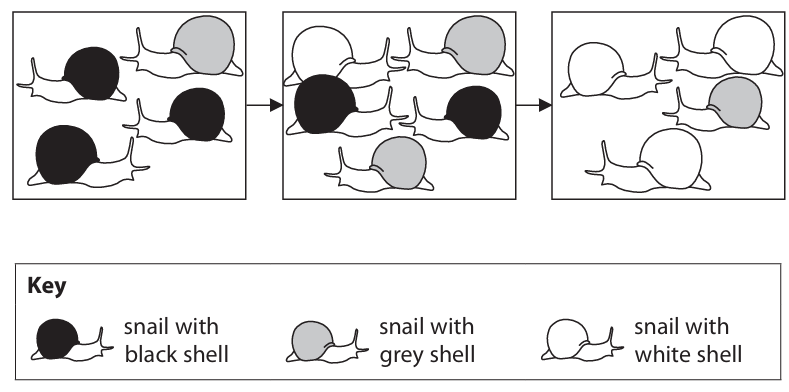
Use the information in the drawings to explain the process of natural selection (5)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: white snails survive → survival of the fittest m4: camouflaged → not eaten/killed m5: reproduce m6: pass on allele to offspring
Gazelles cannot maintain their top speed for a long time because a change in the type of respiration takes place in their muscle cells.
Explain how this change in respiration stops gazelles from running at a top speed for a long time. (3)
m1: anaerobic respiration m2: less oxygen m3: lactic acid → lower pH m4: denatures enzymes m5: less energy in the form of ATP
Zebras also try to avoid being caught by lions. It was thought that the striped coat of zebras helps to camouflage them.
A new theory suggests the striped coat evolved because it reduces the number of biting flies that feed on zebra blood.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain how a striped coat that reduces the number of flies feeding on zebra blood may have evolved. (4)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: survival of the fittest m4: reproduction m5: pass on allele
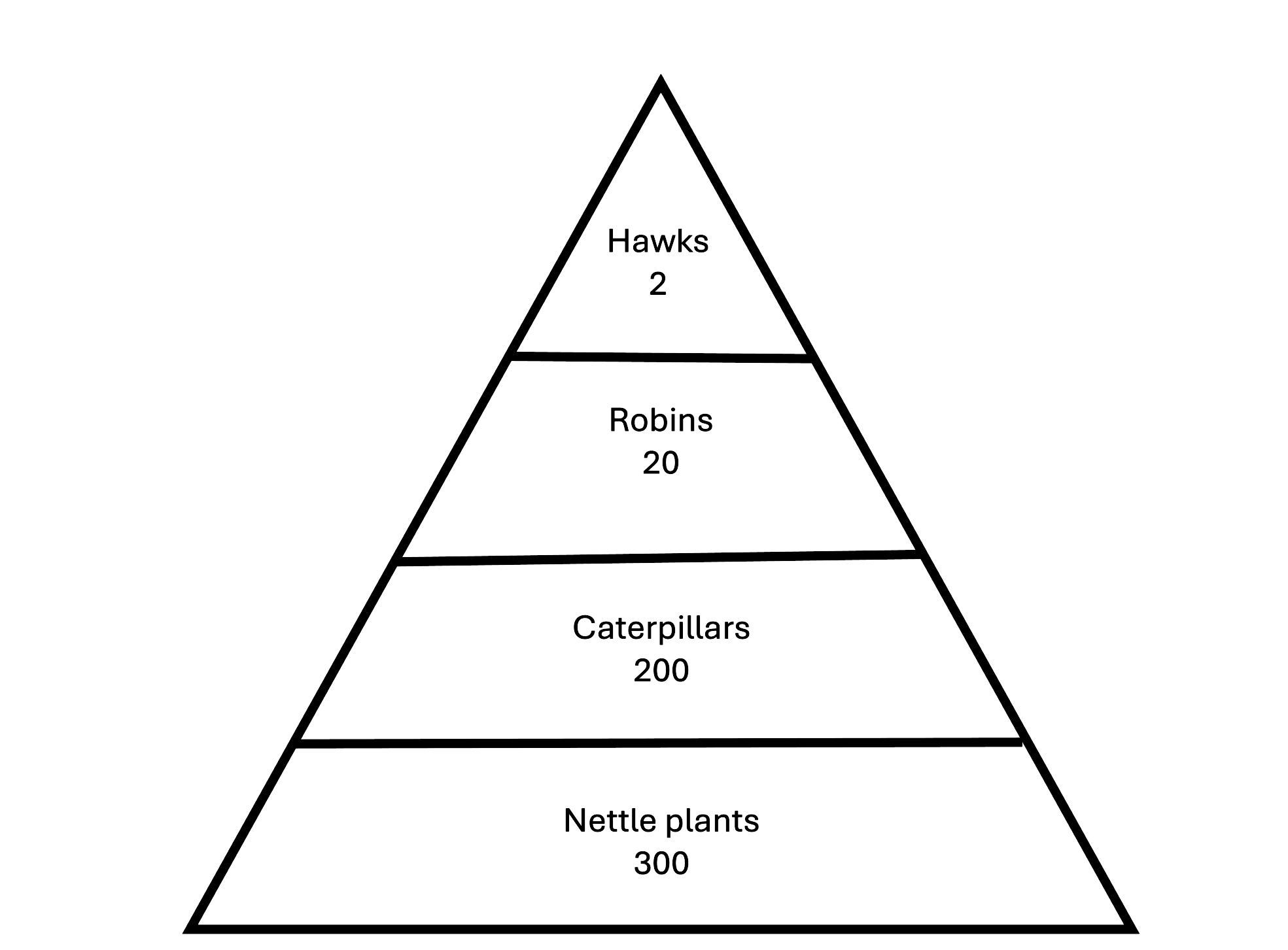
The total mass of the organisms at each level in the pyramid decreases as you move up the pyramid. Explain why. (4)
m1: energy loss m2: respiration m3: egestion → not digestion m4: not all of each organism eaten m5: some organisms decompose m6: movement m7: thermoregulation → heat loss
Describe how increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the air may cause global warming and explain the possible consequences of global warming (5)
m1: greenhouse gas m2: traps heat m3: ice caps melt → flooding m4: habitats destroyed, soil erosion, desertification m5: food chain disruption → extinction m6: migration → spread of disease → affects plant growth m6: climate change
Explain how feeding on mesophyll tissue will affect tomato production (3)
m1: lower production → fewer fruit → less growth
m2: fewer chloroplasts → less chlorophyll
m3: less photosynthesis
m4: less carbohydrate
Pesticide are no longer successful in controlling the pest because the population of resistant forms of the leaf miner has increased.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain why the population of resistant forms of the leaf miner has increased. (4)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: random m4: survive → not killed m5: reproduce m6: pass on allele
Pheromone traps could also be used to control the leaf miner. Pheromones are smells that attract leaf miner males.
Design an investigation to find out if a pheromone trap would help to control the leaf miner.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences (6)
m1: increase pheromone and then remove the pheromone
m2: control species of insect, size of crops
m5: same temperature, time of year, location, size of field, etc
m3: several traps → repeat in many fields
m4: count number trapped in m6: given time period
Explain the advantages of reducing the mass of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. (5)
m1: reduces greenhouse effect m2: less global warming m3: less ice caps → melt → rise in sea level → flooding m4: less habitat destruction m5: less death/extinction m6: less migration m7: less climate change
The number of fish in the lake decreases over the 25-year period.
Explain how the changes in phosphate levels might cause the decrease in the number of fish (5)
m1: algae growth m2: block light m3: plant death → no photosynthesis m4: microbes m5: less oxygen m6: respiration
Commercial flower growers keep their plants in greenhouses under artificial light.
Describe an investigation to find out if the length of time that plants are exposed to light affects how long it takes for flowers to appear. (6)
m1: different light periods m2: same species m3: repeat m4: time to produce flowers m5: days m6: same temperature/light intensity/CO2
If waste from fish farms is released into rivers it will cause pollution.
Design an investigation to compare the pollution caused by waste released from the new type of fish farm with waste released from a traditional fish farm.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences. (6)
m1: use a traditional and a new type of farm
m2: control same species, same fish
m3: same mass of food
m4: same distance of farms/same depth in water
m5: same time of day
m6: repeat experiment
m7: measure mass of algae, mass of pondweed, O2 level, etc
An increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can lead to an enhanced greenhouse effect.
Describe the possible consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect. (4)
m1: global warming m2: ice caps melt m3: flooding m4: climate change m5: habitat destruction m6: extinction → disruption of food chains m7: migration → distribution of organisms
Fish are a good source of protein in the human diet.
Describe what happens to fish protein in the gut of a human. (5)
m1: digested m2: amino acids m3: stomach m4: protease m5: releases hydrochloric acid → low pH m6: small intestine m7: neutralises acid m8: optimum pH
Explain the consequences of fertiliser containing nitrates polluting a river (6)
m1: (nitrates) soluble m2: rain m3: leaching algal growth m4: block light m5: plants die m6: less oxygen m7: decomposers decay m8: fish/animals die m9: eutrophication
The peacock is a bird found in the jungle in India. The male has a large, colourful tail that he displays during courtship to attract a female to mate with.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to suggest how the peacock’s tail has evolved. (6)
m1: mutation m2: competition m3: selected by female m4: reproduce m5: offspring have more colourful tails m6: allele passed on m7: process continues m8: survival of the fittest → extinction of those with non colourful tails
Describe the events that take place from when pollen lands on the stigma of a flower to when seeds are formed (5)
m1: pollen tube m2: style m3: ovary m4: ovule → male gamete m4: fuses m5: female gamete m6: ovary becomes fruit
Suggest a method that could be used to estimate the population of fire ants in an area (4)
m1: using a quadrat, m2: count how many m3: multiply to get total for area m4: random m5: repeat
Describe how the tea grower could use a quadrat to estimate the total mass of tea plants growing in a large area of land. (3)
m1: use a balance m2: random m3: scale by multiplying m4: repeat
What is meant by the term selective breeding (4)
m1: human with the m2: desired characteristics m3: breed m4: repeat for many generations
Describe how you could use a quadrat to estimate the plant biomass in one of the regions. (4)
m1: use more than one m2: randomly m3: use scale m4: remove animals m5: multiply to total area
Describe an investigation to find out if keeping chickens indoors increases their growth (6)
m1: vary from indoors and outdoors m2: same species/size/age m3: control mass of food m4: control area of water m5: measure mass/length m6: of a time period m7: repeats
Describe an experiment you could do to find out the effect of pH on the growth of yeast. (6)
m1: vary pH → acid/alkali m2: same species/mass/number m3: same temp/volume of water m4: same nutrients m5: measure mass/bubbles in a given time period m6: repeat each pH
Nitrogenous waste released into the environment can cause eutrophication.
Describe the process of eutrophication and the effects that it can have on the environment. (5)
m1: plant m2: algae block light m3: less photosynthesis m4: decomposers m5: aerobic respiration m6: oxygen depletion m7: death of plants
Fish farms remove nitrogenous waste to improve the growth of fish.
Another method to improve the growth of fish is vaccination.
Explain how the process of vaccination improves the growth of fish. (4)
m1: dead m2: antigens m3: memory cells m4: secondary immune response
Fish farms remove nitrogenous waste to improve the growth of fish.
Another method to improve the growth of fish is vaccination.
Explain how the process of vaccination improves the growth of fish (4)
m1: dead m2: antigens m3: memory cells m4: immunity
Explain how a mutation in a gene can affect the phenotype of an organism. (3)
m1: mutation is random change to DNA
m2: change in nucleotides
m3: change in amino acid sequence
m4: changing enzyme
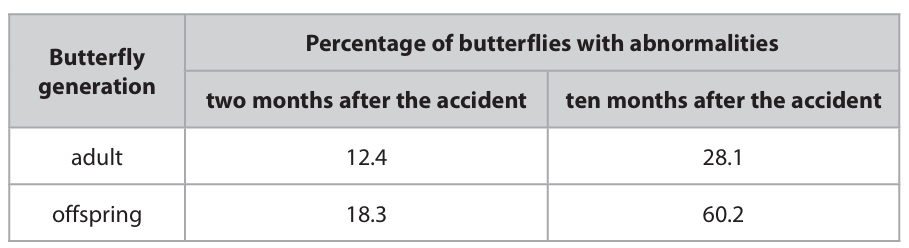
The scientists concluded that the increased level of radioactivity has led to an increased rate of mutation of DNA.
Discuss the scientists’ conclusion referring to data from the table to support your answer.
m1: increase in abnormal butterflies m2: due to longer exposure to radioactivity m3: recessive mutations may be carried by adults m4: if heterozygotes mate they produce abnormal offspring m5: there is no data before the accident m6: radioactivity is not measured
State three ways in which the structure of a DNA molecule differs from the structure of an RNA molecule (3)
m1: the sugar in DNA is deoxyribose while the sugar in RNA is ribose
m2: the base thymine is DNA is replaced by Uracil in RNA
m3: DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded
Describe the differences between the processes of transcription and translation (5)
m1: transcription occurs in the nucleus m2: transcription uses DNA to make RNA m3: transcription produces messenger RNA m4: translation takes place in the ribosome/cytoplasm m5: translation produces amino acid
The DNA molecule codes for the amino acids used to make proteins.
There are four different bases in DNA and 20 amino acids used to make proteins.
Use this information to show that a minimum of three bases on the DNA molecule is needed to code for each amino acid. (3)
m1: 43 = m2: 64 m3: 64>20 combinations required
Discuss why some farmers limit the amount of chemical fertilisers they add to their crops (5)
m1: increased soil concentration reduces water potential of soil m2: prevent water uptake m3: so plant wilts m4: damaging effect of leaching m5: causes eutrophication
Explain two reasons why a pyramid of biomass is better than a pyramid of numbers (2)
m1: biomass is quantitative
m2: biomass is usually upright
m3: numbers doesn’t take the size of the organism into account
Give three reasons why only ~10% of the energy & biomass is passed on at each stage in a food chain (3)
m1: some parts of the food are not digested by the organism
m2: some of the materials absorbed form excretory products
m3: some of the products are respired to release energy with loss of carbon dioxide and water
State 3 advantages of pesticides (3)
m1: Easily accessible and relatively cheap
m2: have an immediate effect
m3: kills the entire population of pests
State 3 disadvantages of pesticides (3)
m1: organisms they are meant to kill can develop a resistance to them
m2: non-specific chemicals and can kill other beneficial organisms
m3: they can be persistent chemicals
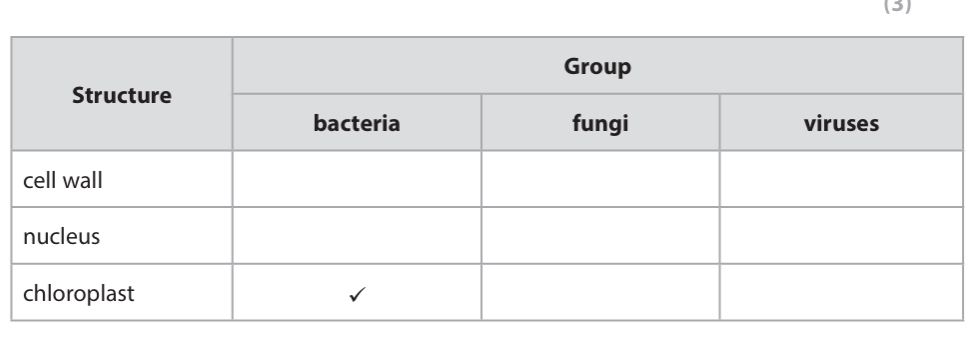
(3)
Another characteristic shown by animals is the ability to respond to their surroundings.
For example, a person may withdraw their hand from a hot object.
Describe the sequence of events that cause this response. (5)
m1: receptor m2: sensory neurone m3:impulse m4:CNS m5: synapse m6:relay neurone m7:motor neurone m8:muscle / effector m9: contract
Some antibiotics are no longer effective in killing pathogens.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain why. (5)
m1: mutation m2:.variation m3:.gene / allele / DNA m4:.survive / not killed m5: resistant m6:reproduce m7:pass on gene
The use of a pesticide may result in an increase in the number of pest organisms that are resistant to the pesticide.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain the increase in the number of pest organisms that are resistant to the pesticide.(5)
m1:variation m2: rare / random m3: mutation m4: gene m5: survive m6: reproduce m7: pass on (gene) m8: many generations / repeated over time /
Explain why no droplets are seen after bile and lipase solution is added to the oil and water mixture (4)
m1: (bile) emulsification
m2: smaller drops → increased SA
m3: optimum pH
m4: lipase is an enzyme and will break down fatty acids into glycerol
Explain how the villi is adapted to absorb glucose (5)
m1: large SA → m2: microvilli
m3: one cell thick → shorter diffusion distance
m4: diffusion occurs
m5: concentration gradient
Describe the role of chloroplasts in leaf cells (2)
m1: absorb light
m2: contains chlorophyll
m3: photosynthesis
Explain what happens to a leaf when it’s destarched (2)
m1: starch removed m2: converted to glucose m3: respiration/energy
A student is given two samples of carbohydrates
He tests to see if one is glucose and one is starch
Describe the two chemical tests he should use to identify each carbohydrate (4)
m1: use iodine m2: blue → black means starch is present
m3: Benedict’s solution, use water bath red → green means glucose is present
The small food molecules can be absorbed into the blood by villi in the small intestine.
Give three ways in which villi are adapted to absorb small food molecules (3)
m1: large SA: microvilli
m2: thin, short diffusion distance
m3: blood/capillaries
m4: permeable
Describe how the green pigment in leaf cells is removed safely before testing a leaf for the presence of starch (3)
m1: boil in m2: ethanol m3: water bath
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in the blood that can increase the risk of heart disease.
Statins are drugs thought to lower blood cholesterol levels.
Design an investigation to find out the effect of statins on blood cholesterol levels.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences and paragraphs (6)
m1: range the statin levels
m2: ensure the people are the same gender/age - CONTROL
s1+s2: same diet, same stress, same exercise, same smoking
m3: of several people/group
m4: measure cholesterol level m5: at start and end → measure change
Wasps defend themselves from predators by using a sting.
This means that predators avoid attacking wasps. Ash borers look very similar to wasps.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain why ash borers have evolved to look like wasps. (4)
m1: variation in Ash borers
m2: mutation means they are not eaten m3: increases chance of survival m4: they reproduce/breed
m5: they pass on genes/alleles m6: process continues over time
Gazelles cannot maintain their top speed for a long time because a change in the type of respiration takes place in their muscle cells.
Explain how this change in respiration stops gazelles from running at a top speed for a long time. (3)
m1: anaerobic respiration m2: means less oxygen m3: which produces lactic acid m4: which affects the pH of enzymes m5: causing them to denature m6: meaning there is less energy in the form of ATP
Zebras also try to avoid being caught by lions.
It was thought that the striped coat of zebras helps to camouflage them.
A new theory suggests the striped coat evolved because it reduces the number of biting flies that feed on zebra blood.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain how a striped coat that reduces the number of flies feeding on zebra blood may have evolved. (4)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: survival of the fittest m4: produce offspring m5: which pass on gene
On a hot day there is less water in urine.
Explain how the kidney is able to reduce the water content of urine produced on a hot day (3)
m1: more ADH m2: increased permeability m3: collecting duct m4: reabsorption of water
Some people do have glucose in their urine. These people have diabetes.
Suggest why a person with diabetes has glucose in their urine. (2)
m1: not enough insulin m2: causes the glucose levels to be too high m3: and the kidney is unable to reabsorb all the glucose
micrometers and cm conversion
1cm = 1000micrometers
Describe the process of digestion in the mouth (3)
m1: chemical digestion using amylase m2: which breaks down starch m3: into glucose m4: physical/mechanical digestion as the teeth churn the food
Describe how white blood cells are used by the body to defend against infection (5)
m1: phagocyte engulfs pathogens m2: enzymes m3: breakdown m4: lymphocyte produce m5: antibodies m6: and make specific m7: antigens m8: memory cells
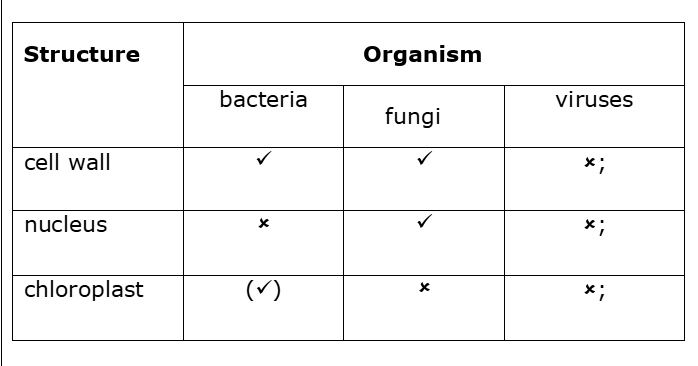
State two ways in which a bacterium differs from a virus (2)
m1: bacterium has a cell wall and no protein coat
m2: viruses do not have a cell membrane
Listeriosis is an illness caused by eating food containing the bacterium Listeria
Explain how the immune system protects most people from becoming ill with listeriosis. (5)
m1: the immune system kills/destroys bacteria m2: white blood cells m3: phagocytes m4: engulf a pathogen m4: lymphocytes m5: antibodies m6: bond to antigens m7: produce memory cells
Another characteristic shown by animals is the ability to respond to their surroundings.
For example, a person may withdraw their hand from a hot object.
Describe the sequence of events that cause this response. (5)
m1: receptor m2: sensory neurone m3: impulse m4: CNS spinal cord m5: synapse m6: relay neurone m7: motor neurone m8: muscle/effector m9: contract
Fully grown penguins are large, often weighing up to 30 kg. Most other birds are much smaller.
Explain how being large helps the penguin to survive at very low temperatures. (2)
m1: smaller SA:V ratio m2: less heat loss
Penguins also have soft downy feathers and a thick layer of fat just below the skin.
Suggest how these features help penguins to survive. (2)
m1: insulation m2: trap warm air m3: less heat loss
One part of the penguin that is especially exposed to the cold is their feet.
The muscles that operate the feet are located in the penguin’s body rather than in the feet themselves.
Suggest how this benefits the penguin.
m1: muscle kept warm m2: respiration m3: enzymes
Farmers use bird scarers that make a sudden loud noise to frighten birds away from their crops.
Design an investigation to find out if noise affects the amount of crops birds eat.
m1: range noise and no noise m2: ensure the species is controlled → same species m3: mass eaten/number eaten → count birds m3: replication evident m4: time period stated m5: control weather → same time of day
Describe how the growth hormone could be destroyed in the stomach. (3)
m1: hydrochloric acid m2: enzyme m3: breakdown m4: acid denatures growth hormone
The growth hormone used in this investigation was obtained from genetically modified bacteria.
Describe how bacteria can be genetically modified and used to produce growth hormone. (4)
m1: gene/allele m2: restriction (endonuclease) m3: ligase m4: plasmid m5: vector m6: recombinant
Describe how the levels of blood glucose are kept constant in human plasma after eating a meal. (5)
m1: pancreas m2: insulin m3: lower levels m4: glycogen
Describe the effects of ADH in the body. (3)
m1: collecting duct m2: more permeable m3: more water reabsorbed into blood m4: osmosis m5: urine concentrated
Plant roots also respond to external stimuli. Describe the response of roots to gravity and explain how this response benefits the plant. (3)
m1: positively geotropic m2: hold plant m3: mineral ions
Describe how the growth hormone could be destroyed in the stomach (3)
m1: hydrochloric acid m2: enzyme m3: breakdown m4: acid denatures growth hormone
The growth hormone used in this investigation was obtained from genetically modified bacteria
Describe how bacteria can be genetically modified and used to produce growth hormone. (4)
m1: gene m2: restriction m3: ligase m4: plasmid m5: vector m6: recombinant
Many seeds contain starch.
Suggest what happens to starch in the gut of a parakeet. (3)
m1: digested m2: amylase m3: maltose
Describe how the levels of blood glucose are kept constant in human plasma after eating a meal. (3)
m1: pancreas m2: lower levels m3: glycogen
Describe how structures B and D help a person to breathe in. (5)
m1: diaphragm m2: moves down m3: ribcage moves up and out m4: increase in (thorax) volume m5: decrease in (thorax) pressure
Smoking can increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease.
Explain how coronary heart disease can cause death (5)
m1: blocked m2: coronary artery m3: clot m4: fat/cholesterol m5: less blood to heart m6: less oxygen m7: muscle cells m8: less respiration → anaerobic respiration m9: lactic acid m10: heart attack
Explain why the cells in distilled water look different when compared to the cells in salt solution. (4)
m1: water into cells m2: outside solution/distilled water more dilute m3: cell membrane against cell wall m4: turgid m5: water leaves cell m6: outside solution
Explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by changes in the environment. (5)
m1: high humidity decreases rate m2: reduced concentration gradient m3: high wind increases rate m4: increased concentration gradient m5: high temperature increases rate m6: more kinetic energy m7: high light increases rate
Explain how the structure of the leaf is adapted for its role as the organ of photosynthesis. (6)
m1: upper epidermis/cuticle is transparent m2: which lets light through as light intensity increases the rate of p/s m3: contains chloroplasts m4: palisade mesophyll layer m5: close to surface which allows it to m6: absorb light m7: stomata/guard cells open when m8: carbon dioxide levels are high
Explain how the rate of photosynthesis is affected by changes to abiotic (non-living) factors throughout the day (4)
m1: temperature m2: tends to rise in the daytime which increases the rate of p/s
m3: light intensity m4: tends to rise in the daytime which increases the rate of p/s
Explain how very high temperatures might reduce the growth of plants. (4)
m1: less photosynthesis m2: more transpiration m3: stomata closed m4: less CO2 absorbed m5: enzymes denature
Explain why reducing the blood supply to the heart muscle cells can cause a heart attack (3)
m1: less oxygen m2: anaerobic respiration occurs m3: lactic acid produced which lowers pH level m4: enzymes denature
During the production of beer the number of live yeast cells initially increases, but then decreases towards the end of the process.
Explain why the number of live yeast cells decreases towards the end of the process. (2)
m1: less food/less maltose m2: increase in ethanol/alcohol
Explain why breathing rate is higher after exercise. (4)
m1: muscles m2: respiration m3: oxygen required m4: remove lactic acid m5: oxygen debt m6: remove carbon dioxide
Describe how smoking damages the lungs. (5)
m1: bronchitis m2: ciliated cells anaesthetised m3: harmful bacteria m4: cancer m5: tar produced m6: emphysema m7: smaller SA of damaged alveoli
If a pregnant woman smokes cigarettes it will increase the risk of her producing a smaller baby. This is because cigarette smoke contains carbon monoxide.
Suggest how carbon monoxide will increase the risk of producing a smaller baby (3)
m1: red blood cells m2: oxyhaemoglobin m3: less oxygen m4: baby has less metabolism and energy in the form of ATP therefore they are smaller
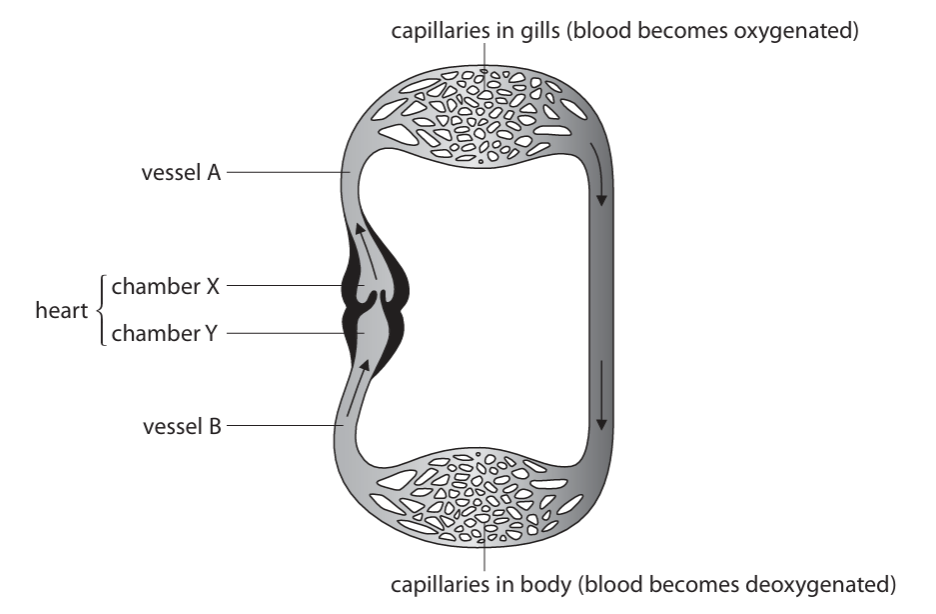
Describe how the structure of a fish heart differs from that of a human heart.(3)
m1: two chambers, one atrium one ventricle m2: less valves m3: no septum m4: chamber walls have smaller sides m5: only two blood vessels
The concentrations of the gases in the blood leaving the fish heart are different from the concentrations of the gases in the blood leaving the human heart in the aorta.
Explain the differences in the concentrations of gases. (4)
m1: less oxygenated m2: more carbon dioxide in fish heart m3: oxygen used in respiration m4: carbon dioxide produced by respiration m5: blood oxygenated in human lungs m6: carbon dioxide removed in human lungs
Describe an investigation to find out if leaves growing at the bottom of trees are greener than leaves growing at the top of trees.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences and paragraphs. (6)
m1: choose leaves from top and bottom branch levels on each tree m2: same species controlled m3: repeat many trees m4: use chromatography to measure the rf values and the pigment of green trees m5: extract by heating with ethanol m6: also control same location/time of day
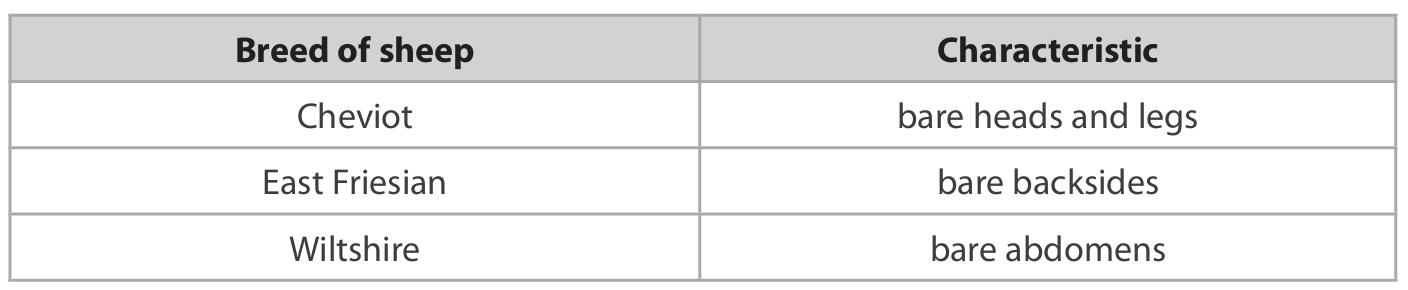
Describe how farmers could use selective breeding to develop sheep with bare legs and bare backsides. (4)
m1: choose Cheviot and East Friesian m2: parent sheep with bare backsides and parent sheep with bare legs m3: cross breed m4: select offspring with bare legs and bare backside m5: repeat for many generations
A student suggested that purple flowers are more likely to be visited by bees than white flowers.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to suggest how this might affect the number of purple and white flowers in the wild. (5)
m1: more purple pollen carried to other purple flowers m2: purple flower more likely to reproduce/purple allele is passed on in seeds m3: more purple flowers/less white flowers m5: carries on in generations
Describe how cell division by meiosis is different from cell division by mitosis. (4)
m1: mitosis produces 2 diploid cells which are m3: genetically identical whilst meiosis produces 4 haploid cells genetically different
m2: the haploid cells produced in meiosis have half the number of chromosomes
m4: meiosis produces gametes which take place in sex organs whilst mitosis occurs in almost every part of the human body
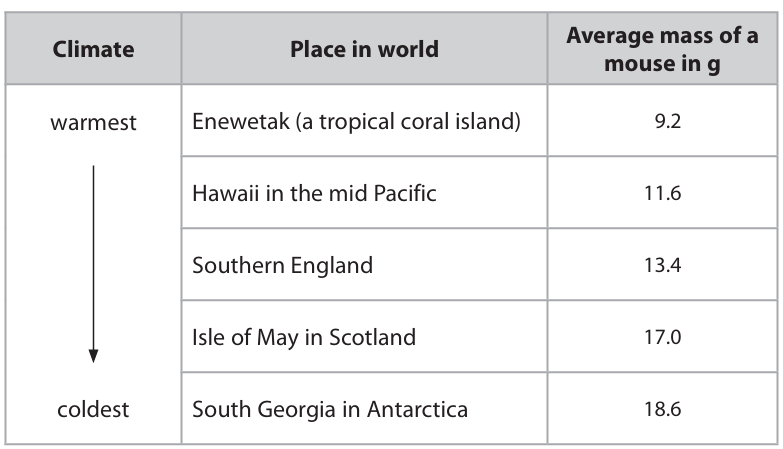
Use your understanding of natural selection to suggest why the mice in Antarctica have the biggest average mass. (5)
m1: the colder the place the bigger the mouse m2: due to mutation m3: bigger mice survive → survival of the fittest m4: reduces heat loss → insulation m5: smaller SA:V ratio to pass on allele/gene
The number of chromosomes in eggs and in sperm is less than the number of chromosomes in the body cells of animals.
Explain how the number of chromosomes in animals is maintained in their offspring (3)
m1: meiosis m2: haploid gametes m3: fuse to make a diploid
The flower in the diagram is insect-pollinated. An insect carrying pollen lands on the flower.
Describe the events that lead to seed formation. (5)
m1: stigma m2: pollen tube grows m3: into ovule m4: enters via micropyle m5: male gamete m6: fuses with m7: female gamete m8: ovule becomes seed m9: ovule wall becomes seed coat m10: ovary becomes fruit
Describe the features of an insect pollinated flower that help it to attract insects (3)
m1: large petals m2: brightly coloured
m3: scent m4: nectary