Health Assesment Exam 2
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is special about the order of assessment in GI? Why?
Inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation; Auscultation is second because percussion and palpation can alter bowel sounds.
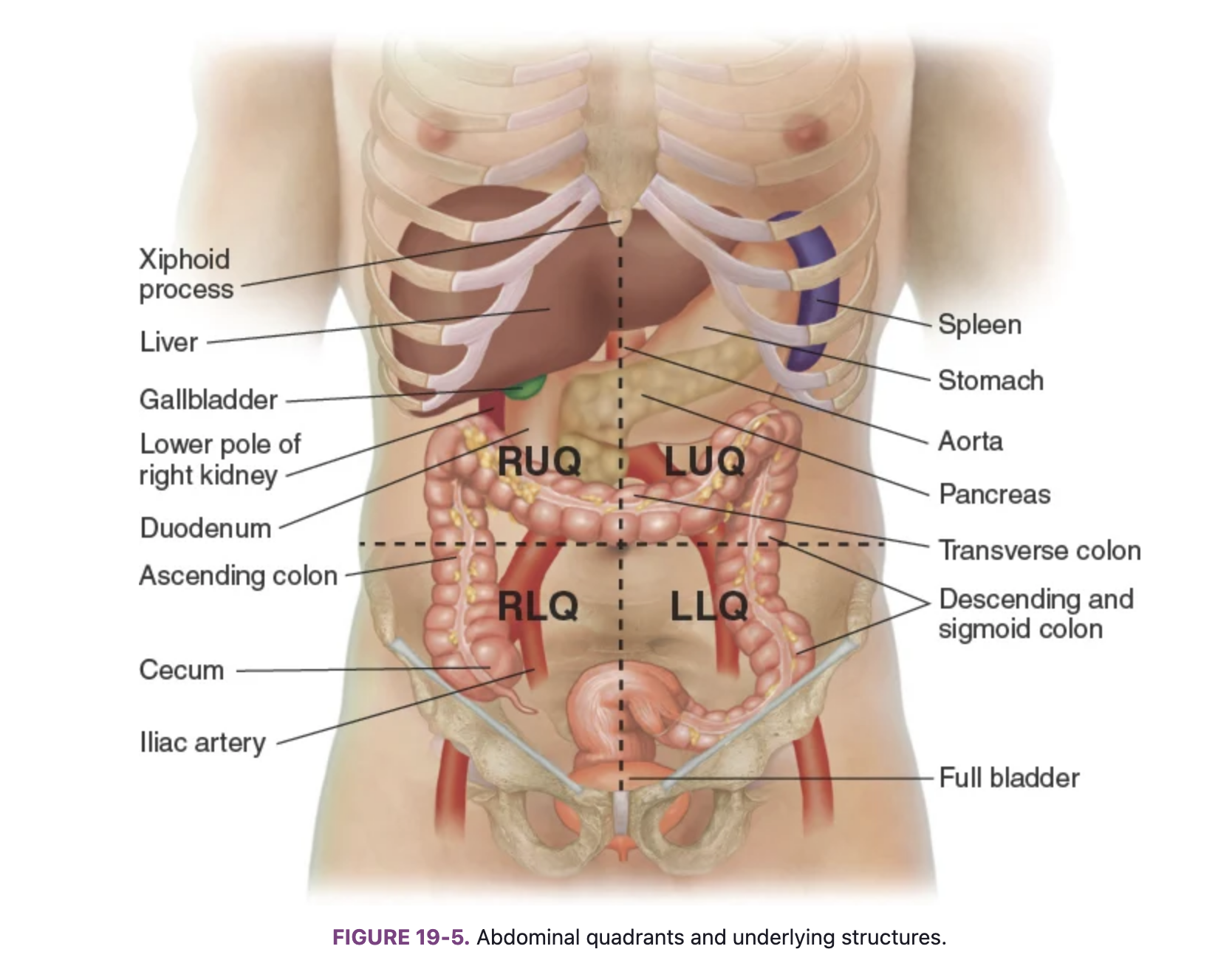
Know the locations of the abdominal organs: right upper quadrant (RUQ)
Liver, gallbladder, duodenum, head of the pancreas, right kidney and adrenal gland, hepatic flexure of the colon, and part of ascending and transverse colon.
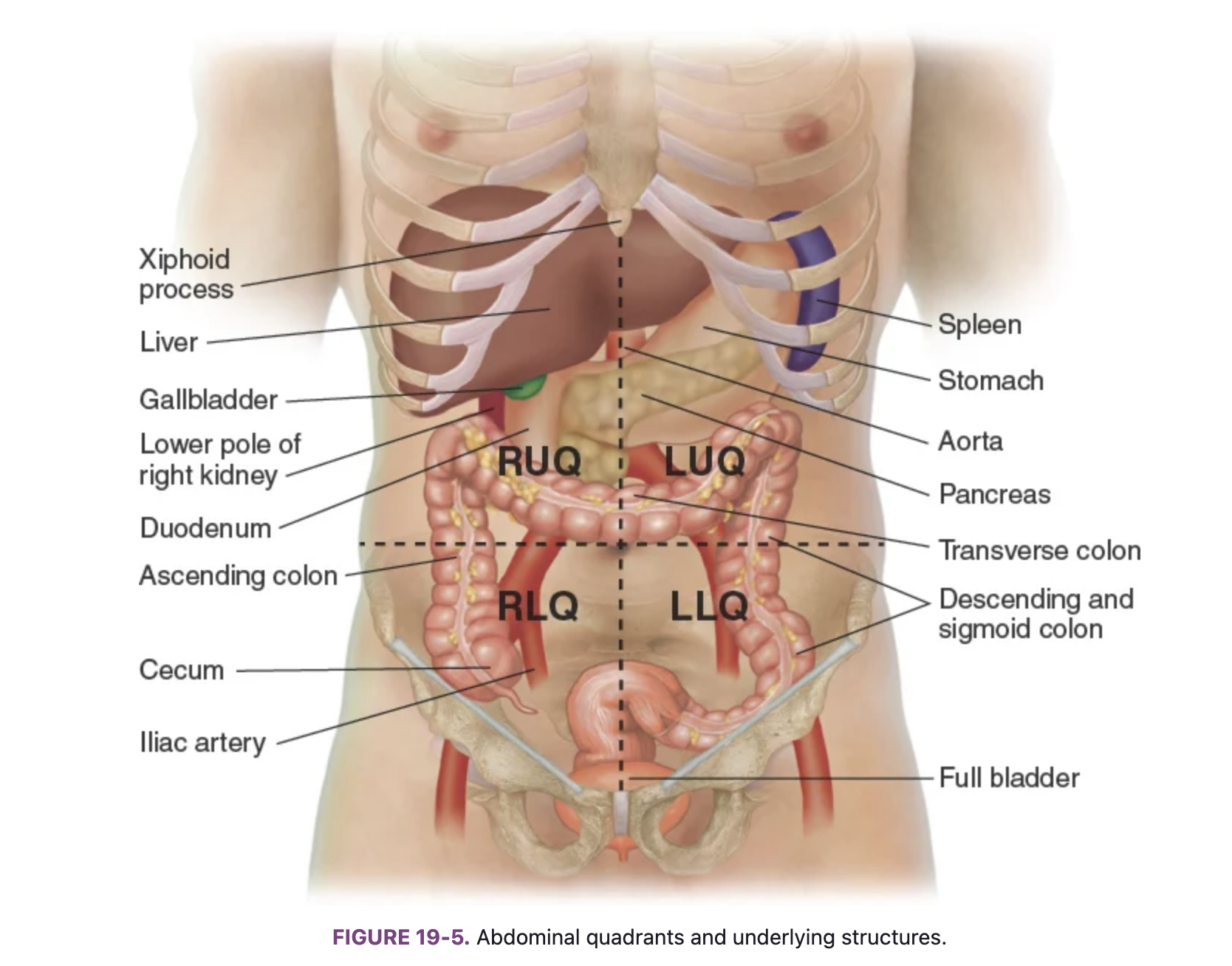
Know the locations of the abdominal organs: left upper quadrant (LUQ)
Stomach, spleen, left lobe of liver, body of pancreas, left kidney and adrenal gland, splenic fixture of colon, part of transverse and descending colon
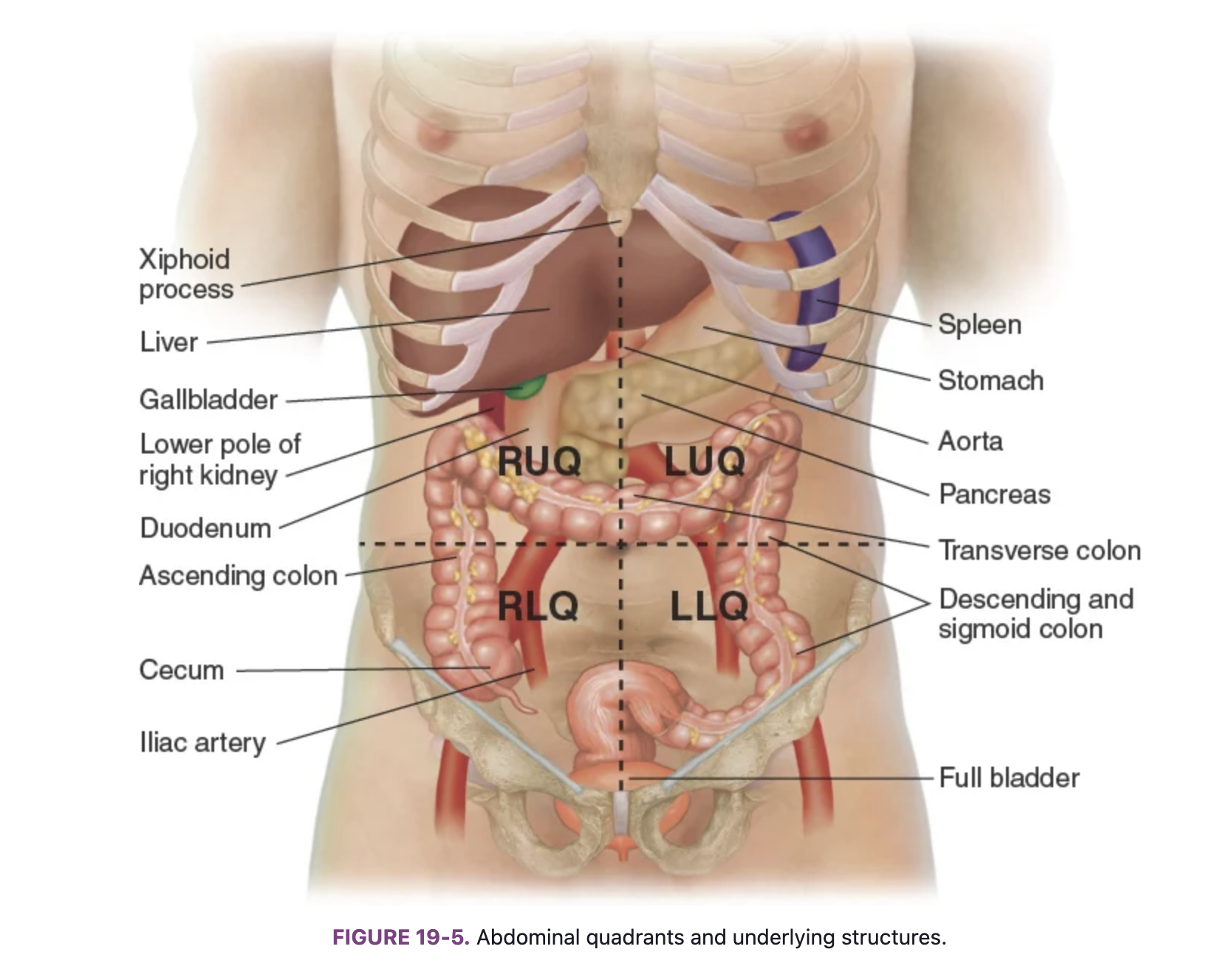
Know the locations of the abdominal organs: right lower quadrant (RLQ)
Cecum, appendix, right ovary and tube, right ureter, right spermatic cord
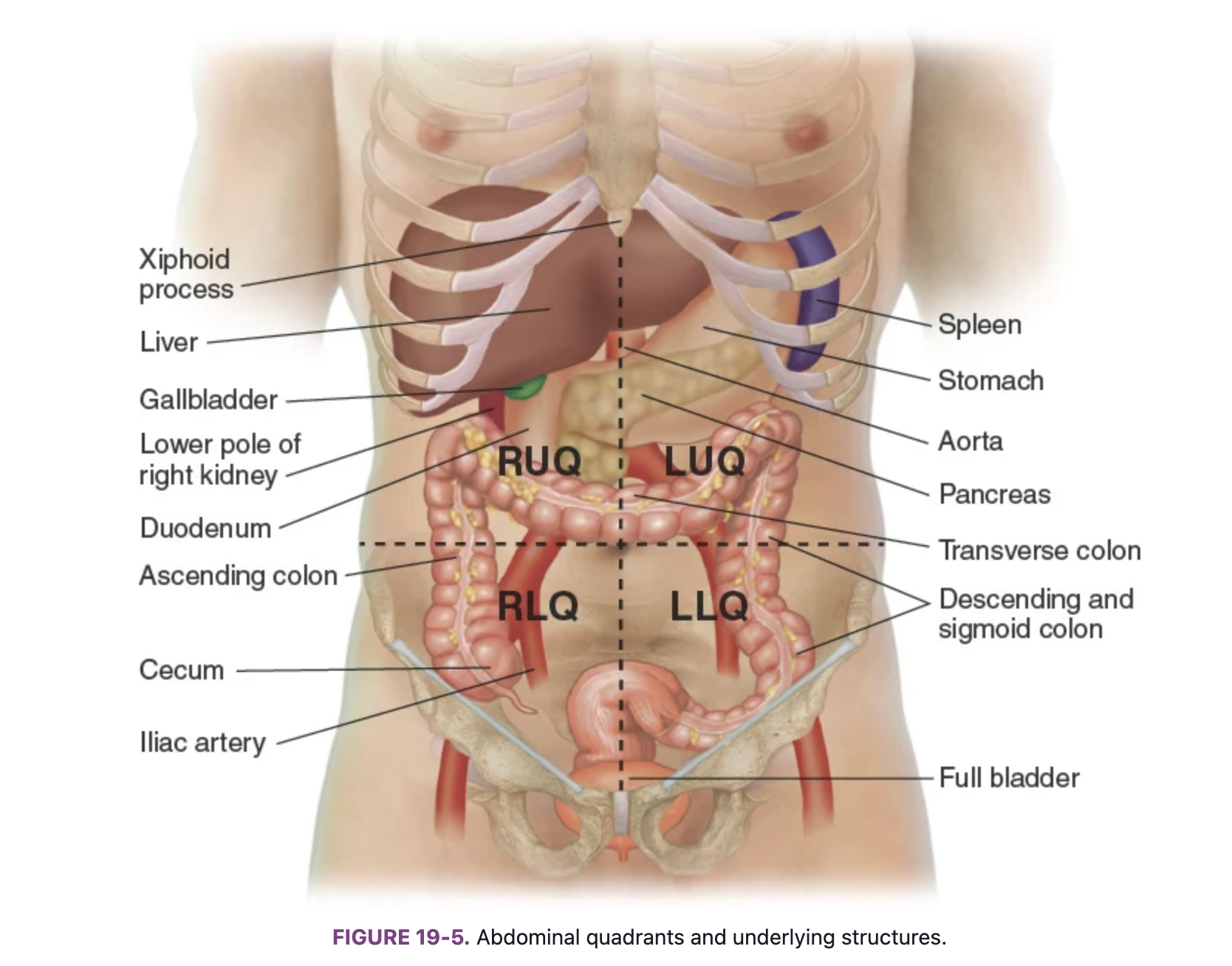
Know the locations of the abdominal organs: left lower quadrant (LLQ)
Part of descending colon, sigmoid colon, left ovary and tube, left ureter, left spermatic cord
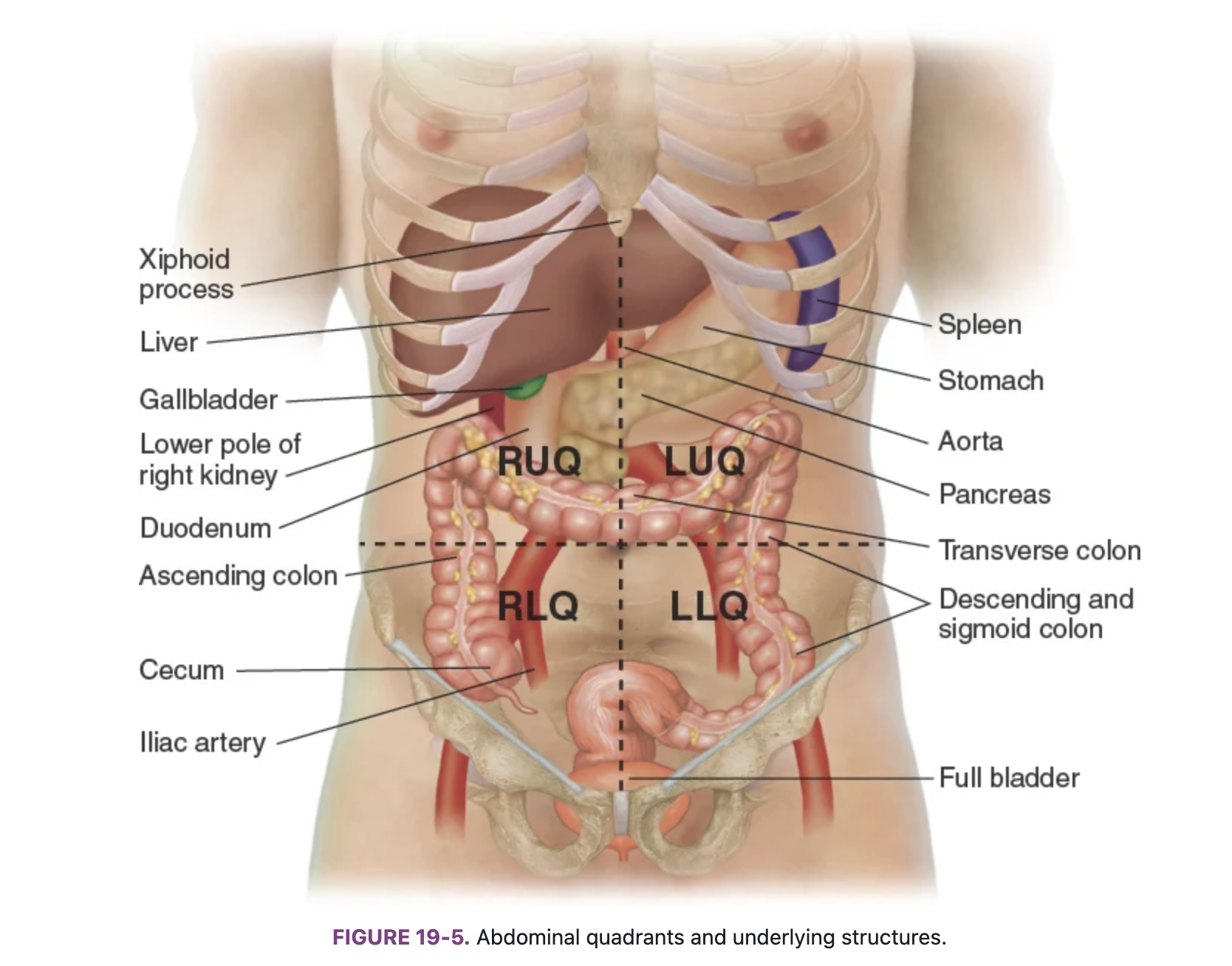
Know the locations of the abdominal organs: midline
Aorta, uterus (if enlarged), bladder (if descended)
Know how to assess for location and size using percussion
Flat hand placed on relaxed abdomen, next tap third digit on the middle phalange then fist percussion for CVA tenderness on back
Know how to assess for location and size using palpation
Light palpation detects tenderness, muscle spasm or rigidity. Use pads of fingers or the flat part of the right hand, then lift fingers from area to area; don’t slide. Next, push down about 1cm; assess 4 quadrants
Deep palpation determines organ size and any abnormal masses. Use pads of fingers or the flat part of the right hand, then lift fingers from area to area; don’t slide. Push down about 5-8cm (2-3in), assess 4 quadrants
Which organs should you be able to palpate?
Liver, spleen, and kidneys
Which organs should you be able to percuss?
Liver, spleen, gastric bubble, kidneys
Tympany: stomach and intestines (could be empty)
Dullness: organs, solid masses, and distended bladder
What assessment findings would you expect with abnormalities in the liver? The kidneys?
Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly), enlarged kidneys (nephromegaly)
What locations and sounds are normal for the various organs?
Normal bowel sounds are gurgles & clicks. Typically heard 5 to 35 times per minute.
What should/might you see during inspection of a healthy person’s abdomen?
even temperature distribution, skin color normal for ethnicity, no edema, no lumps bumps
How are the normal and abnormal bowel sounds described?
abnormal bowel sounds include: bruits
normal bowel sounds include: gurgles and clicks
For palpation, what is the correct order and why?What is the correct technique for palpation?
RLQ to RUQ to LUQ to LLQ; if the patient reports pain, go to that quadrant last;
Light palpation detects tenderness, muscle spasm, or rigidity. Use pads of fingers or the flat part of the right hand, then lift fingers from area to area; don’t slide. Next, push down about 1cm; assess 4 quadrants.
Deep palpation determines organ size and any abnormal masses. Use the pads of fingers or the flat part of the right hand, then lift fingers from area to area; don’t slide. Push down about 5-8cm (2-3in) and assess 4 quadrants.
Concepts related to overweight, underweight, and changes across the life span
Underweight: BMI of 17.7 to 18.4
Optimal: BMI of 18.5 to 25
Overweight: BMI of 25.1 – 30
Obese: BMI of 30.1 – 40
Severely obese: BMI of >40.1
How is the heart assessed?
Inspection
Palpation
Auscultation
(Percussion – limited value)
What do the main (S1-S2) heart sounds mean?
S1 is the closing of the tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral) valves (LUB). S2 is the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valve closing (DUB).
What is PMI? Where do you check the apical pulse?
PMI: point of maximal impulse. PMI and apical pulse are felt and located in the 5th intercostal space.
How do the pulses correlate with heart sounds in a healthy person?
the “S1” sound corresponds with the pulse in a healthy person
What are signs of poor circulation?
color of skin, temperature of skin, poor pulse, decreased capillary refill
How to grade heart murmurs?
I. Only a cardiologist can hear.
II. Trained doctor can hear.
III. Students can hear. No thrill.
IV. Thrill barely palpable.
V. Thrill easily palpable.
VI. Can hear murmur by being in the room without a stethoscope
How are the 0-4+ pulse grades described?
4+ Bounding
3+ Brisk, expected (normal)
2+ Slightly diminished pulse
1+ Faint but detectable pulse
0 Absent, unable to palpate
The location of the base and the apex of the heart
Base is top of heart, apex is bottom of heart
Know about risk factors, causes, and signs/symptoms of osteoporosis and fractures.
Risk factors: biological sex (being AFAB), age (50+), body size (being slender, thin-boned), family history (of osteoporosis or hip fracture), changes in hormones (low levels of estrogen in AFAB, low levels of testosterone in AMAB), medications (long-term use of certain meds), other medical conditions (endocrine and hormonal disorders, GI diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, certain cancers, HIV/AIDS, anorexia nervosa), and lifestyle (you use it or you lose it)
Cause of osteoporosis: it is a metabolic bone disease hallmarked by a loss of mineralized bone mass.
S/S: This loss of bone mass leads to increased bone porosity as well as susceptibility to fractures
How is muscle strength assessed and charted?
Grade: 5 | ROM: Full ROM against gravity | Resistance: Full
Grade: 4 | ROM: Full ROM against gravity | Resistance: Some
Grade: 3 | ROM: Full ROM against gravity | Resistance: No
Grade: 2 | ROM: Full passive ROM with gravity eliminated | Resistance: No
Grade: 1 | ROM: Slight contraction | Resistance: No
Grade: 0 | ROM: No contraction | Resistance: No
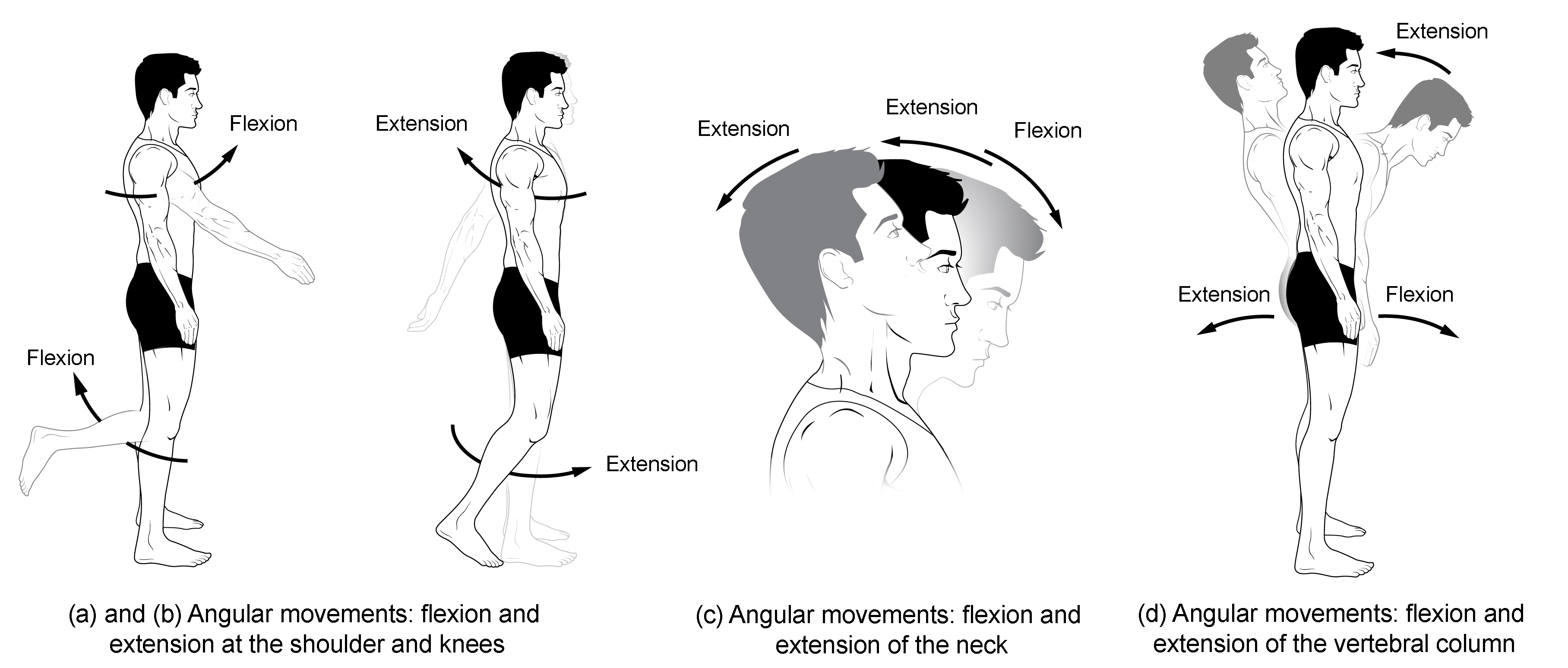
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: extention
Straightening a joint angle
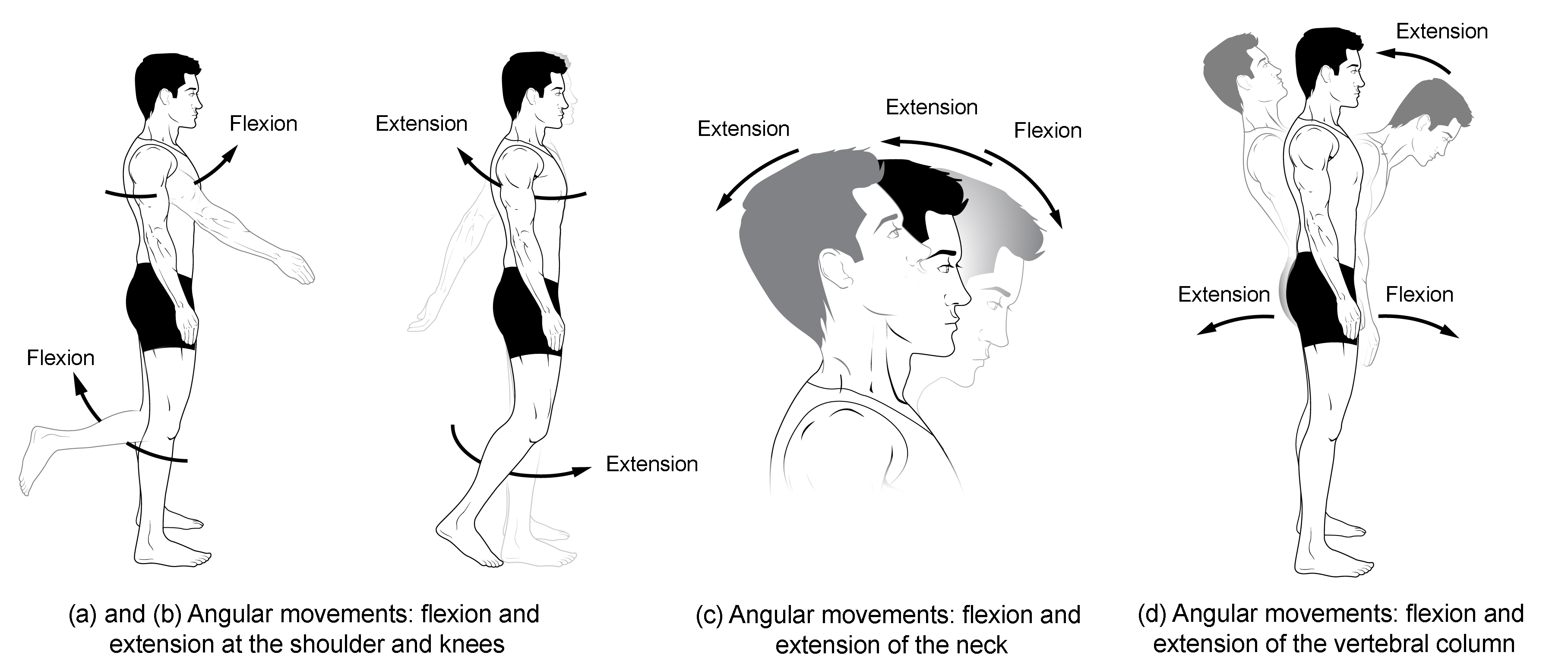
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: flexion
Shortening a joint angle
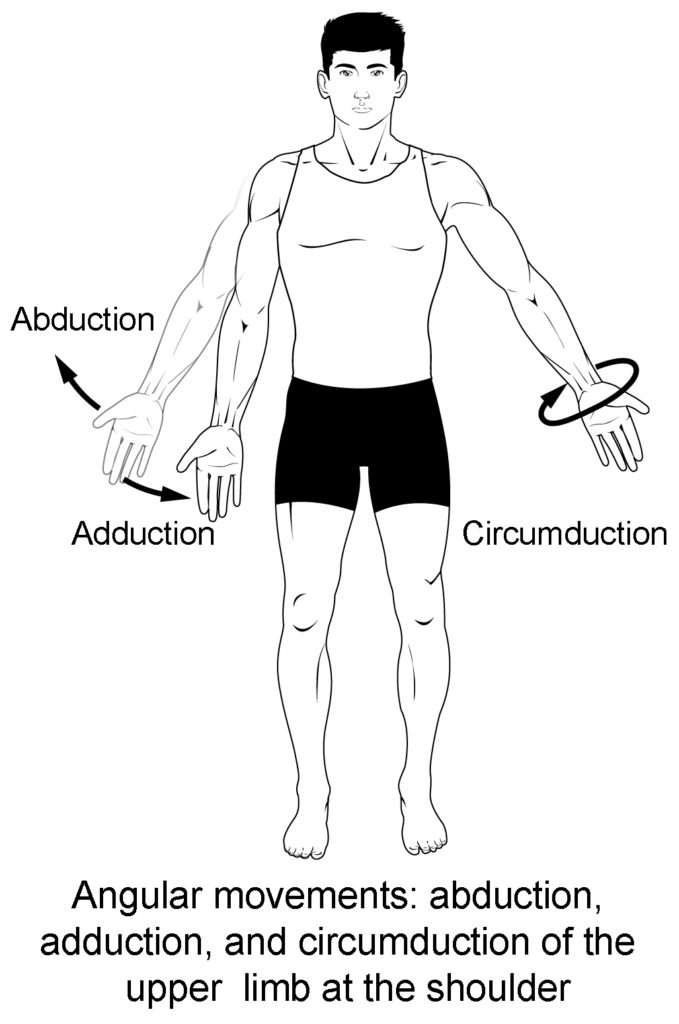
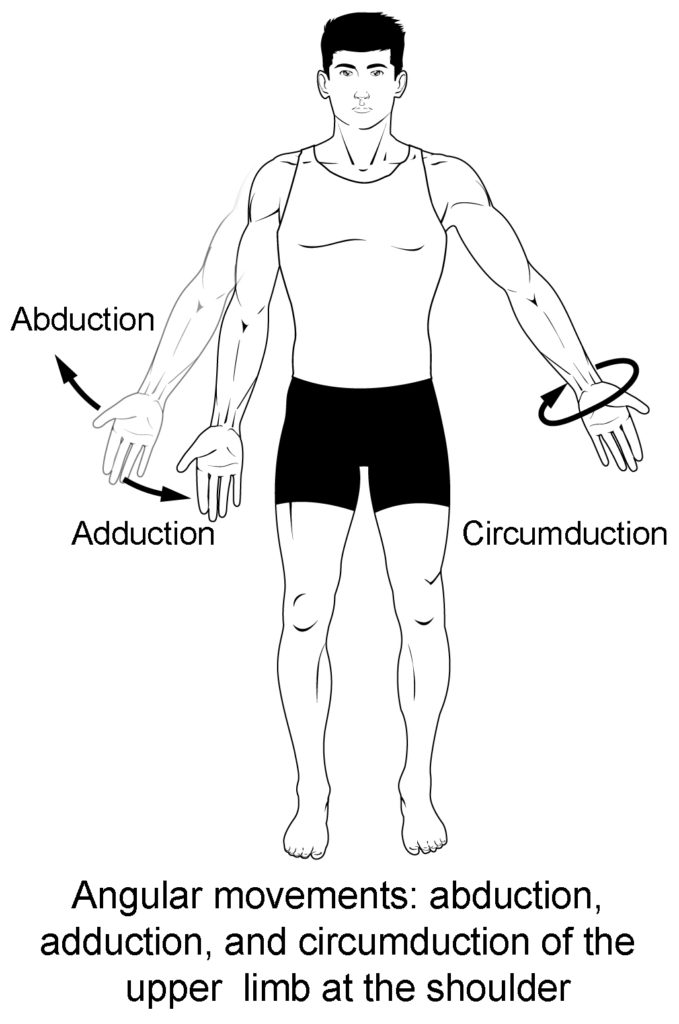
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: abduction
Moving the limb or hand laterally away from the body, or spreading the fingers or toes
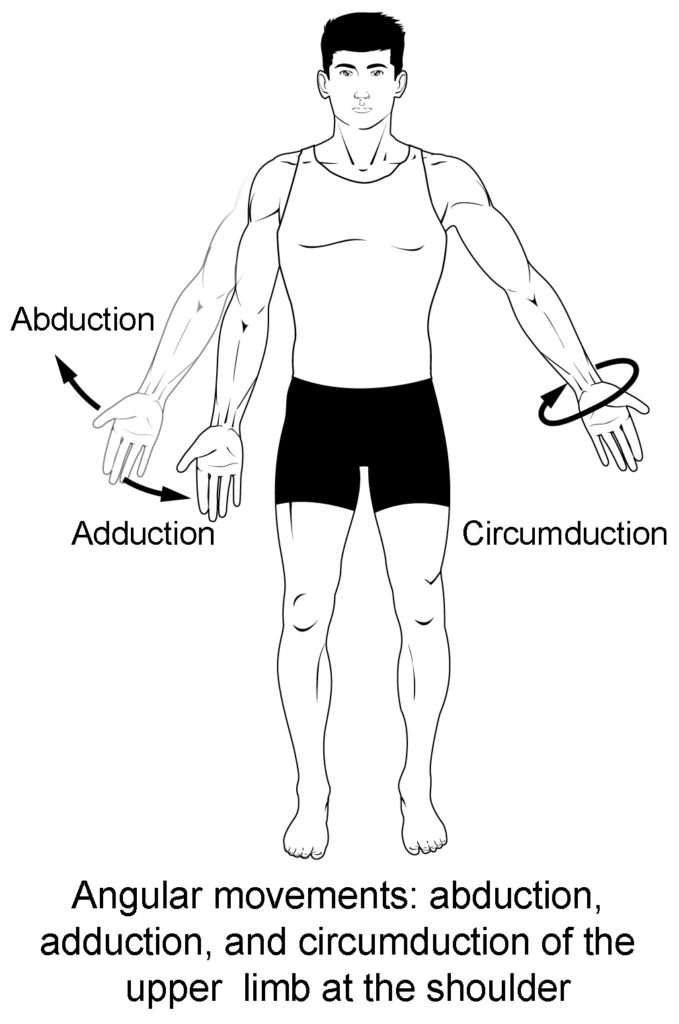
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: adduction
Brings the limb or hand toward or across the midline of the body, or brings the fingers or toes together
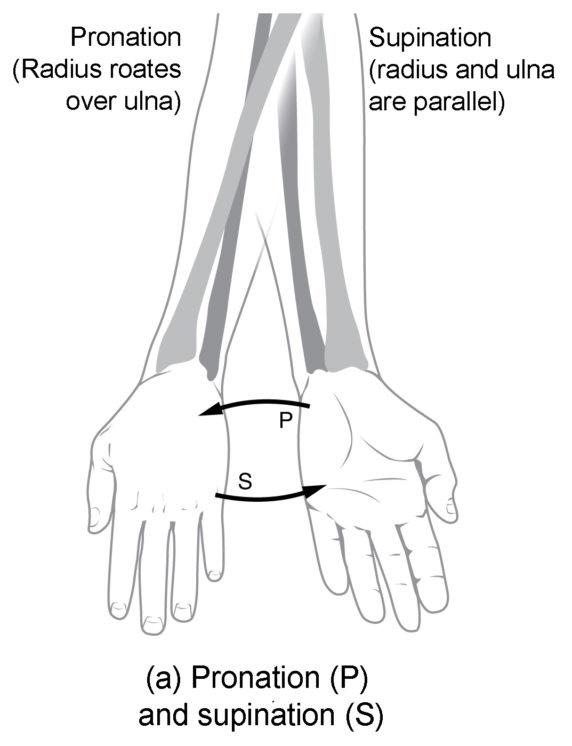
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: pronation
Turning the palms down
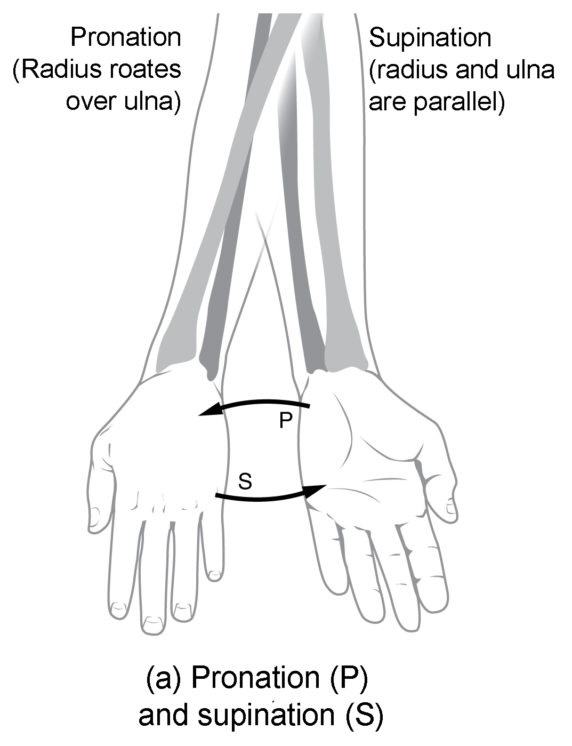
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: supination
Turning palms up
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: circumduction
Movement of the limb, hand, or fingers in a circular pattern, using the sequential combination of flexion, adduction, extension, and abduction motions.
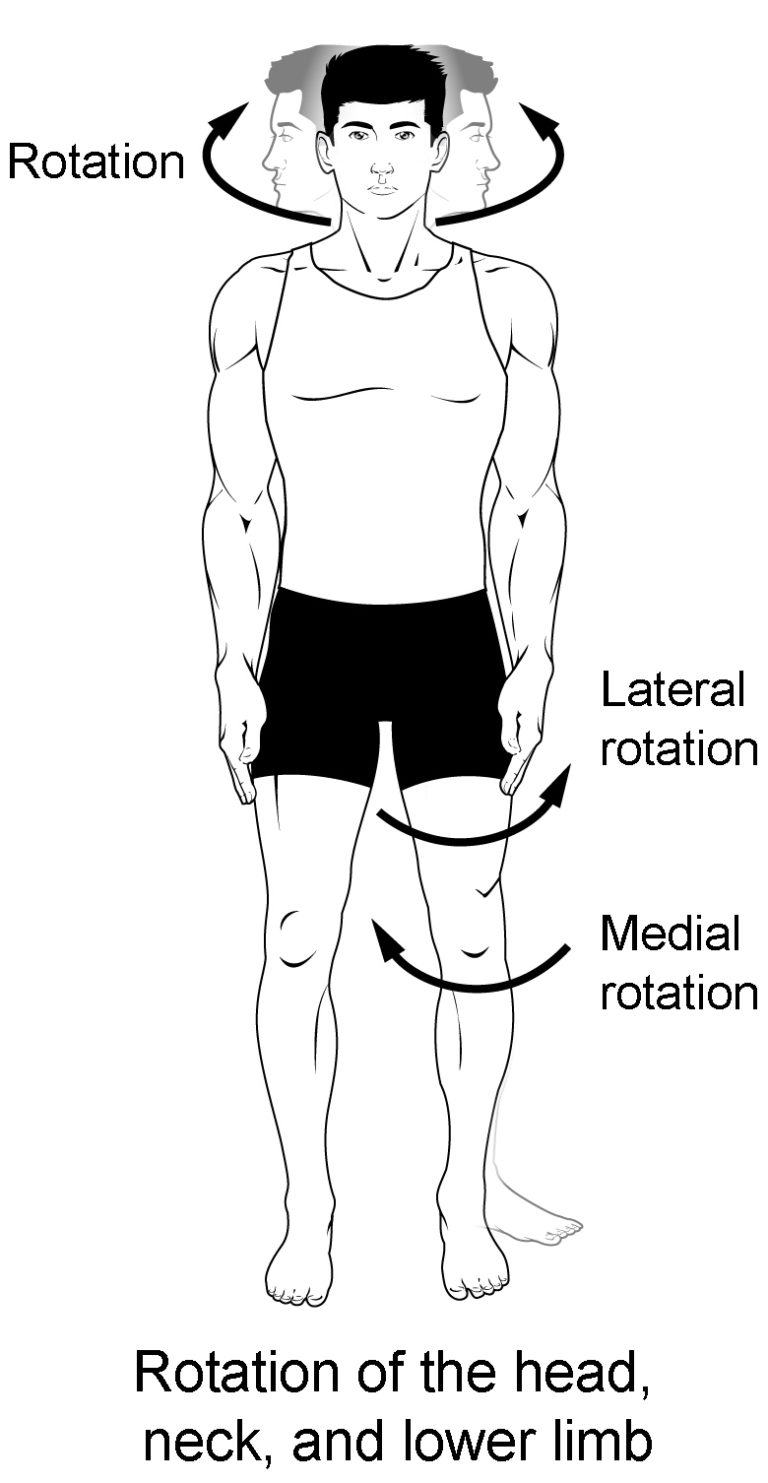
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: rotation
Moving a limb in a circular motion around a fixed joint
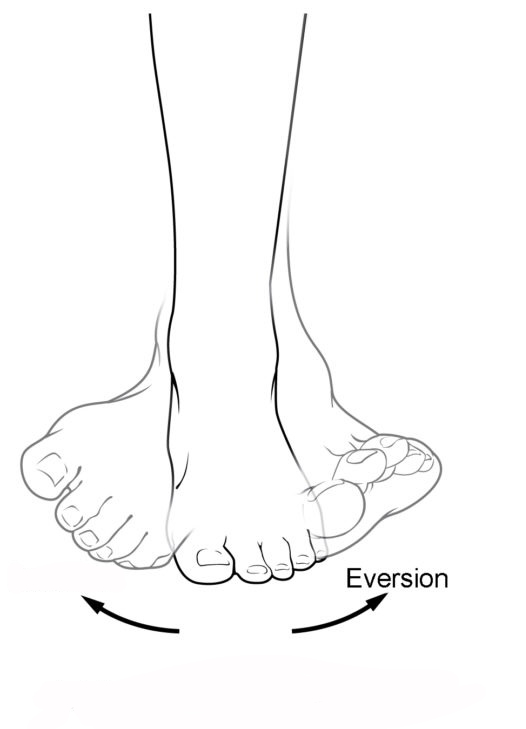
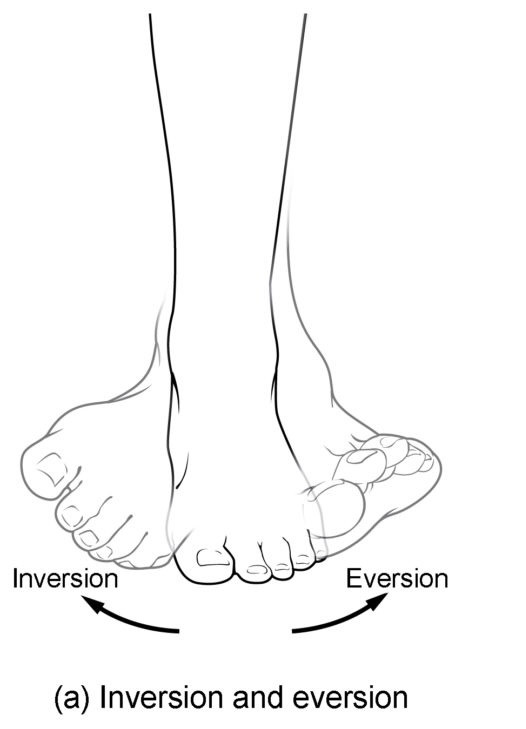
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: eversion
Turns the bottom of the foot away from the midline
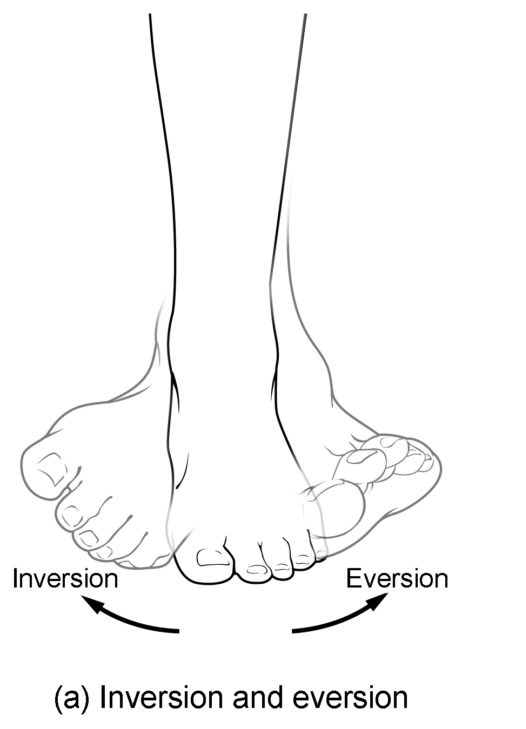
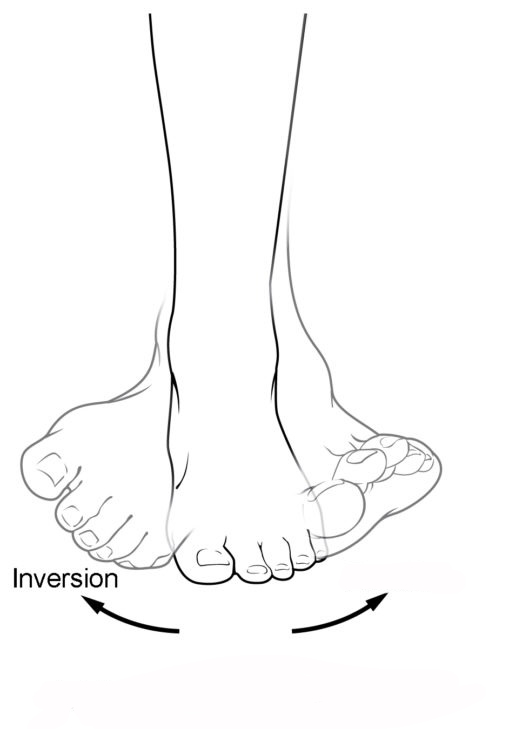
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: inversion
The turning of the foot to angle the bottom of the foot toward the midline
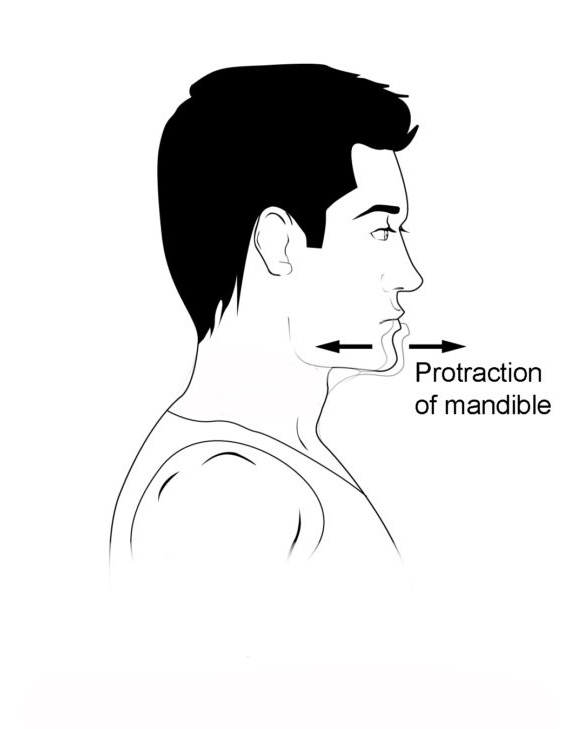
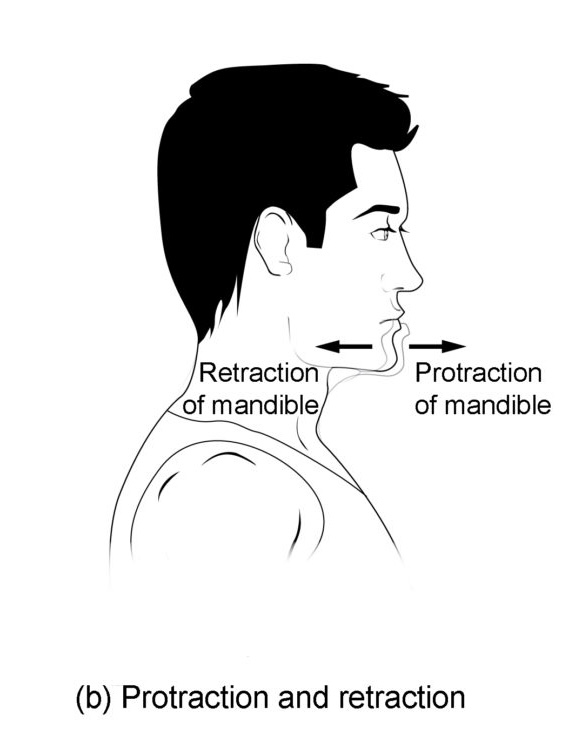
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: protraction
Pushing out or forward
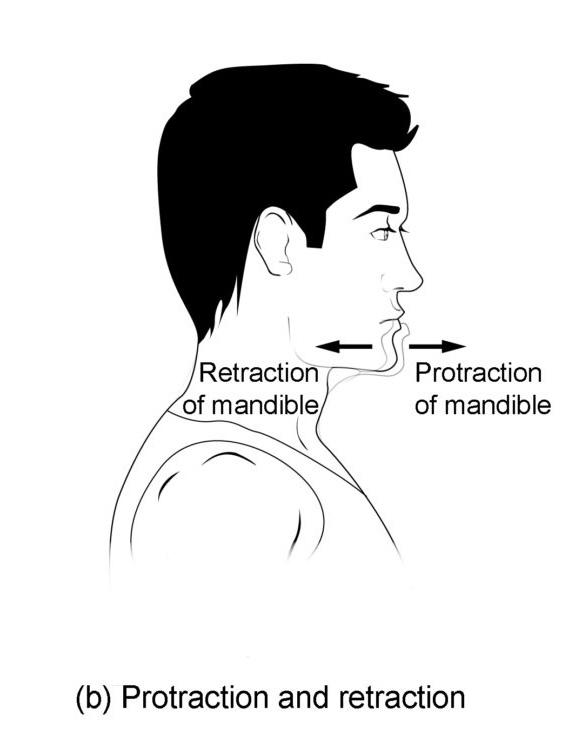
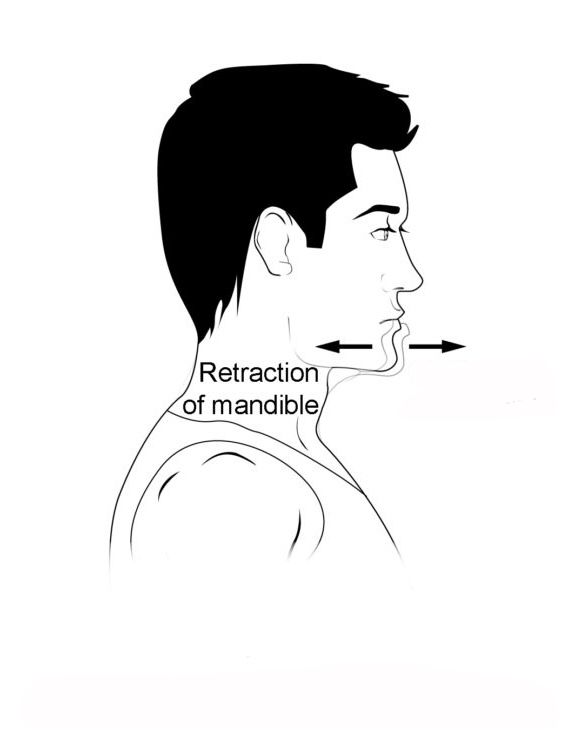
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: retraction
Pulling in or backward
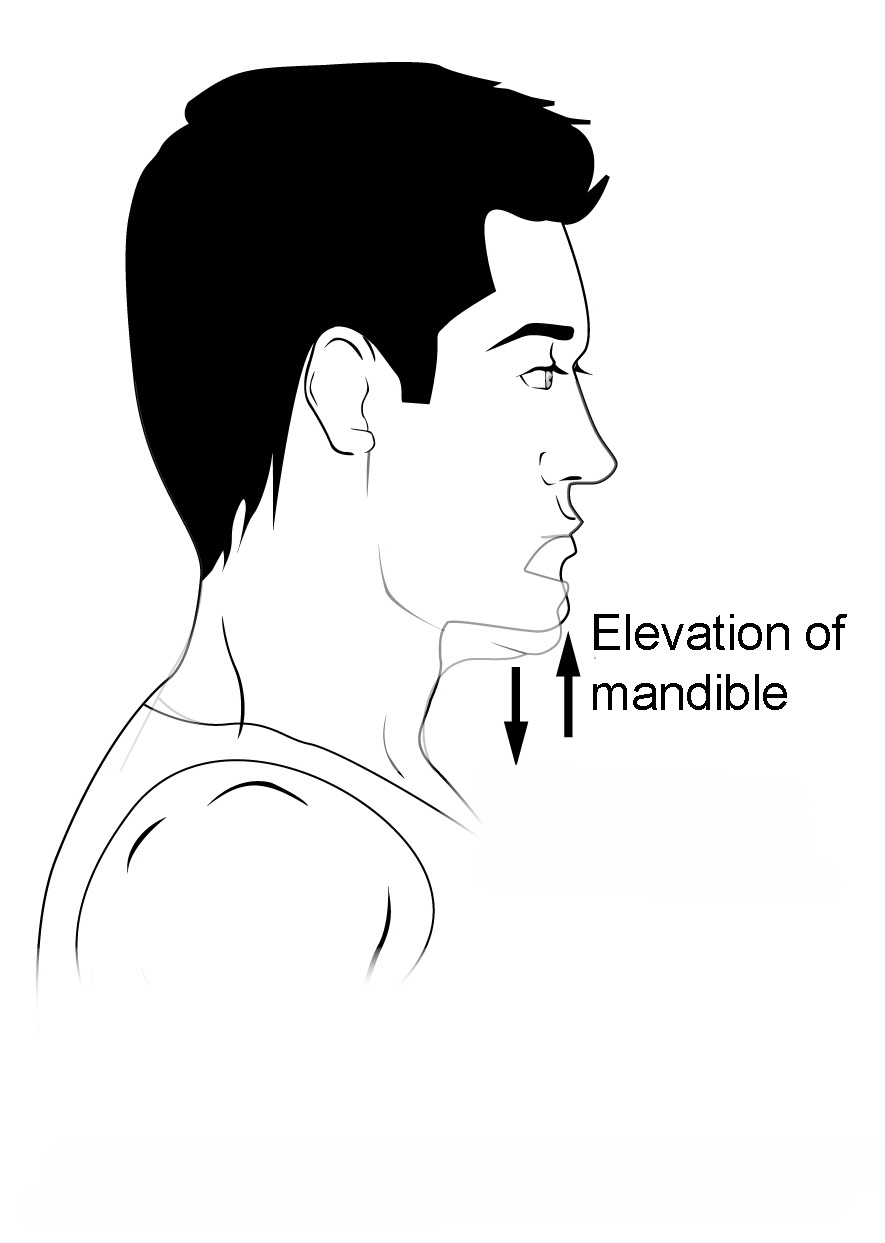
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: elevation
Upward movement
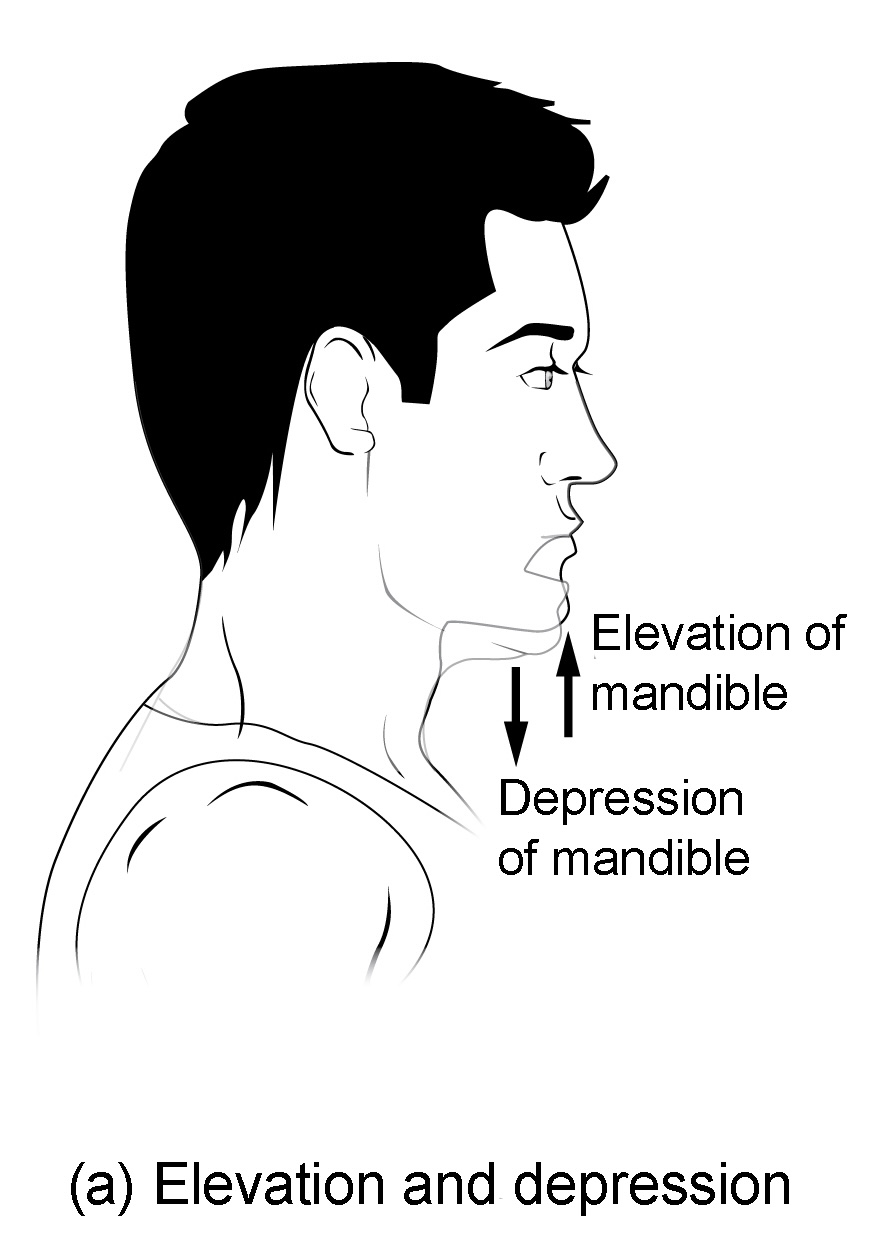
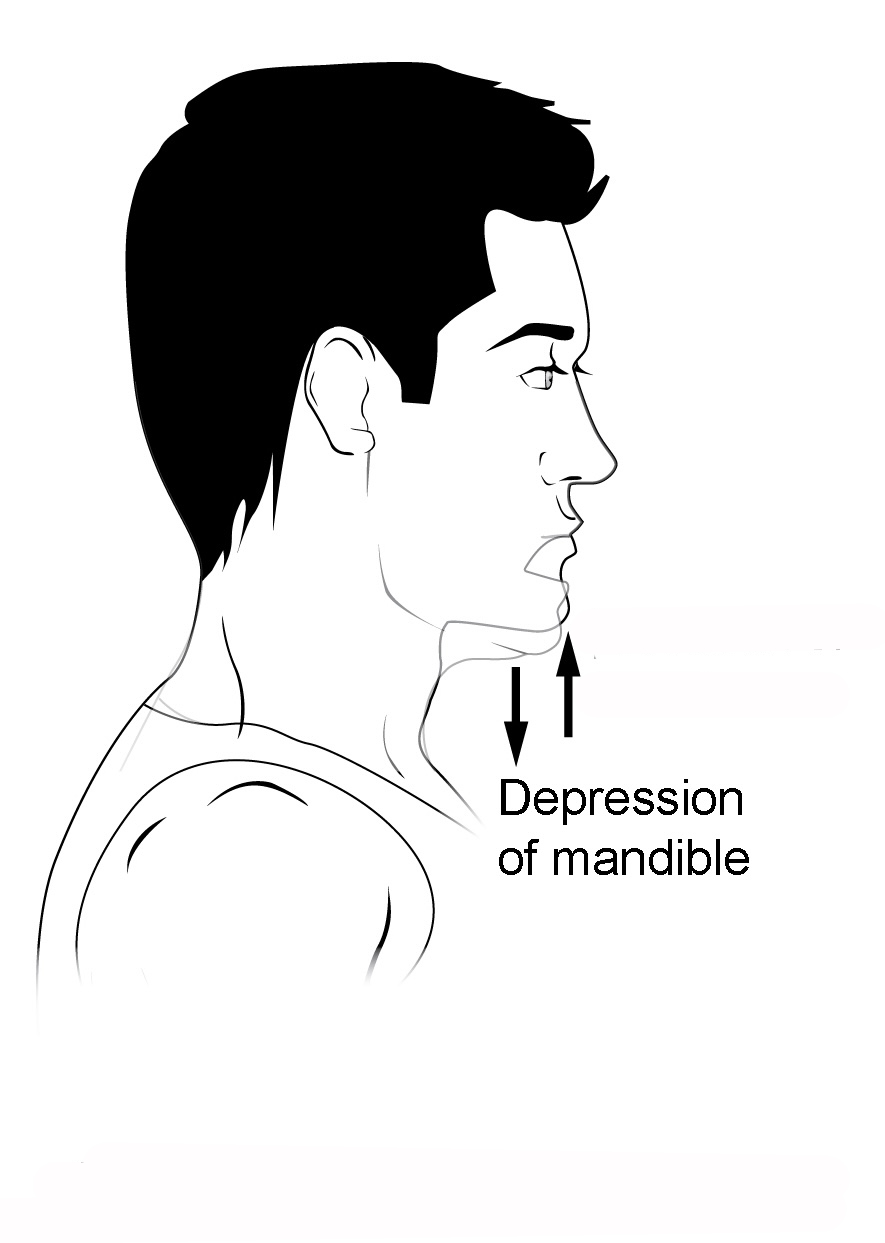
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: depression
Downward movement
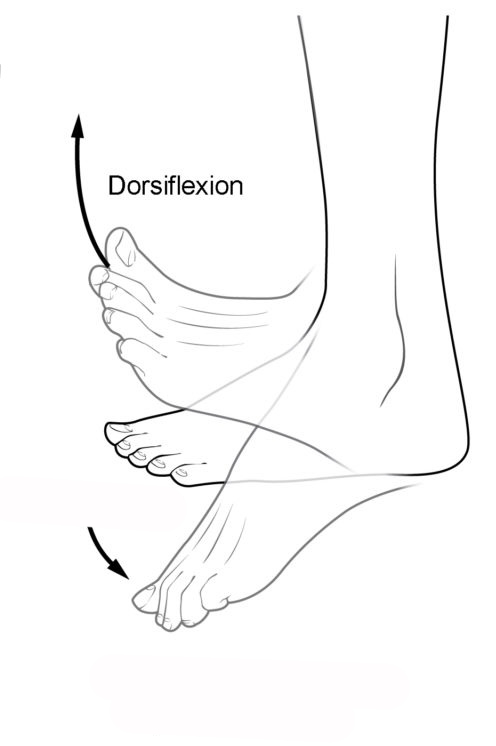
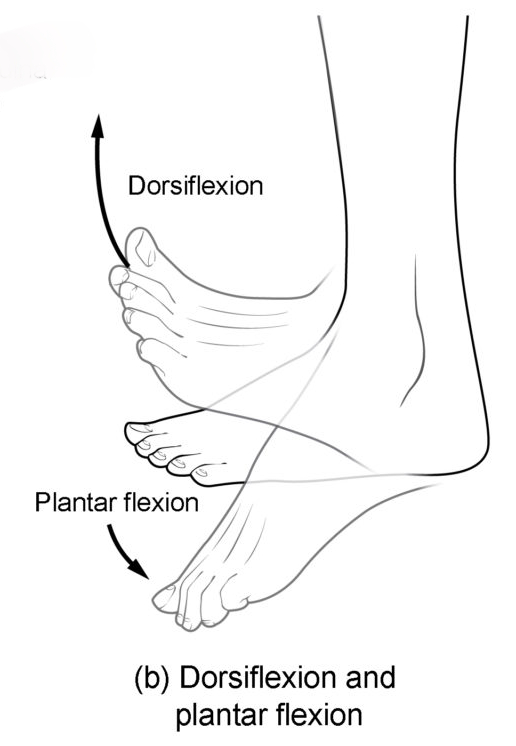
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: dorsiflexion
Lifting the front of the foot, so that the top of the foot moves toward the anterior leg
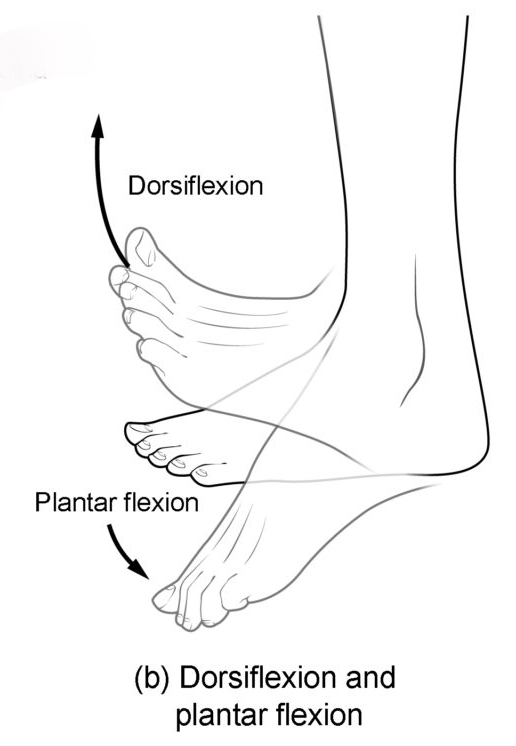
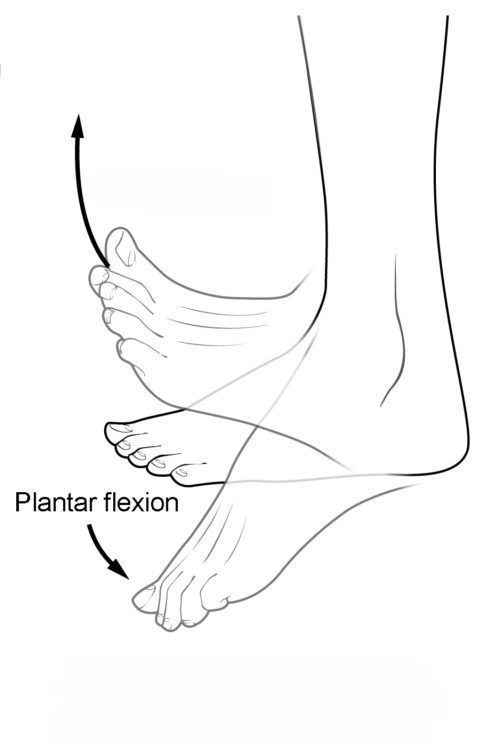
Know terminology related to the movement of joints and the spine: plantar flexion
Lifting the heel of the foot from the ground or pointing the toes downward
Know the difference between paraplegia and quadriplegia
paraplegia is waist down paralyzation; quadriplegia is neck down paralyzation
Know the expected spinal appearance in pediatrics, aging, and pregnancy.
Pediatric: babies and infants have a C-shaped spine, which will develop into the typical S-shaped spine as they learn to walk and grow
Pregnancy: Lordosis
Aging: Kyphosis
Know how to assess the joints covered in lab, and be aware of normal expectations for range of motion.
joints include: shoulder, elbow, wrist, hands, spine, hips, knees, ankles, and feet; palpate joints for any swelling, tenderness; only ask patient to do a thing that you (the nurse) can do
How do you assess for scoliosis?
Look for asymmetry in the shoulders or trunk or look for one side of the rib cage being higher than the other when the patient bends forward; ask pt to hold hands together like they are going to dive and bend forward.