lids: lumps & bumps
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
define lesion
any damage or abnormal change in tissue
state and describe the different lesions we will be looking at (3)
benign lesions - no harmful effect; may be unsightly
malignant lesions - infectious, growth, cancerous
pre malignant lesions - may become malignant
sn: Many eyelid lesions - most are innocent and innocuous (not harmful) - occasionally find a suspicious lesion - need to recognise it’s abnormal and refer
state the common benign lesions of the eye (4:3:3)
MUST know:
Xanthelasma
Papilloma - squamous cell papilloma and basal cell papilloma
Retention cysts
Milia
SHOULD know:
Skin tags
Haemangioma
Port-wine stain
EXTRA:
Dermatitis Papulosa Nigra
Naevi
Cutaneous horn (not always benign - can be pre malignant)
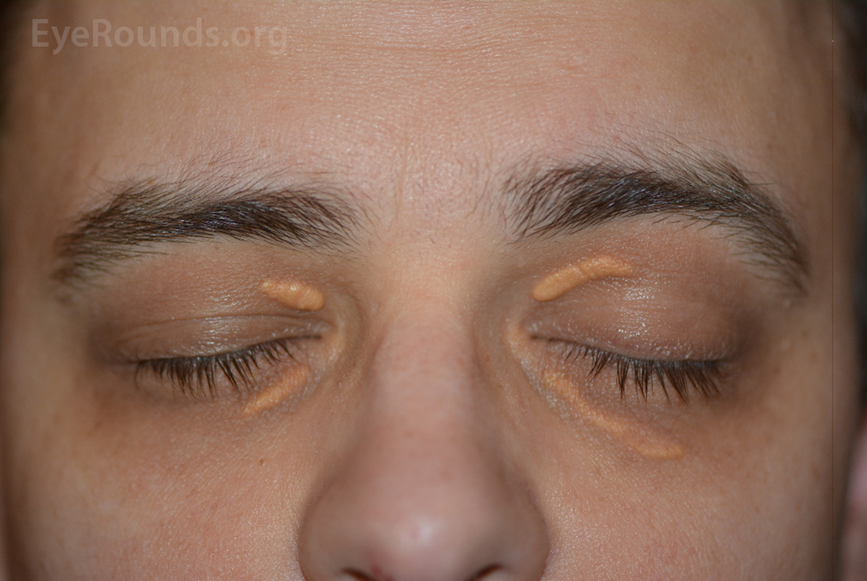
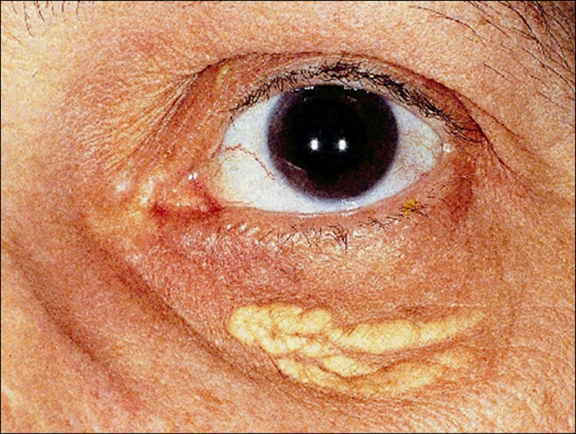
describe the signs/appearance of Xanthelasma (3)
Soft yellowish plaques, variable size
Usually medial upper and lower eyelids, often bilateral
Lipid & cholesterol deposits (50% associated with elevated serum lipid levels)
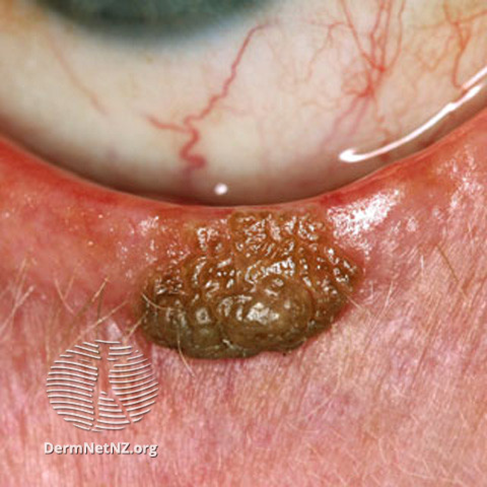
describe the appearance/signs of squamous cell papilloma (6)
Also known as viral wart
Human papilloma virus (HPV)
Common in adults
Sessile (larger immobile piece) or pedunculated (attached via a stalk)
Histopathology: excessive convoluted epithelium with central fibrovascular core
Described as looking like raspberries under magnification
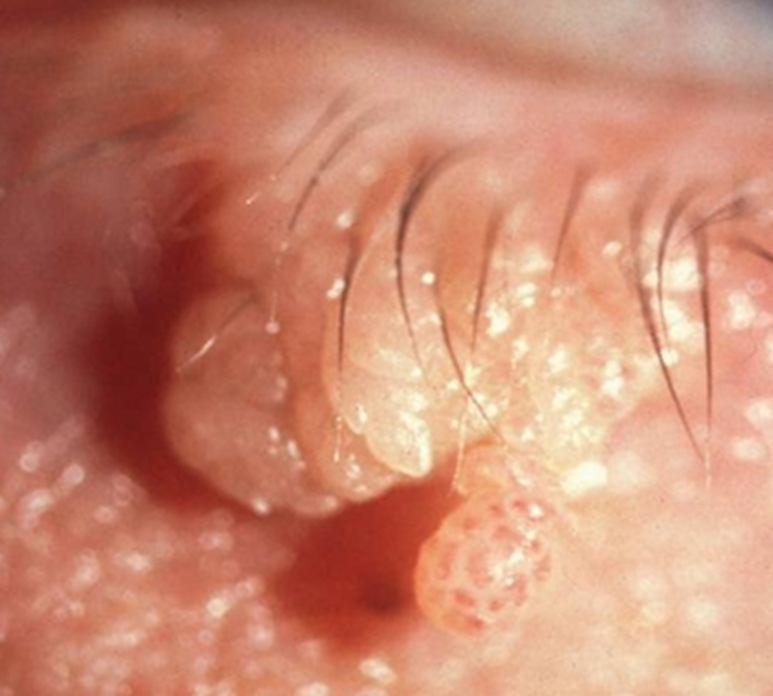
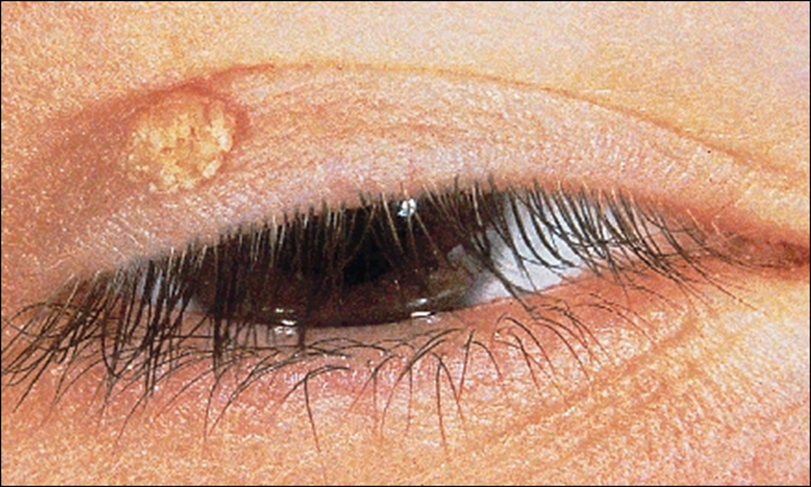
can be cosmetically removed - reassure patient
describe the appearance/signs of basal cell papilloma (7)
Also known as seborrheic keratosis or seborrheic wart
Very common (90% > 60 yrs)
Benign, harmless skin growth – build up of skin cells
Smooth, waxy or warty surface
Slow growing, not painful or tender
Flat or raised plaque
Skin coloured, yellow, grey, light brown, dark brown or mixed colours
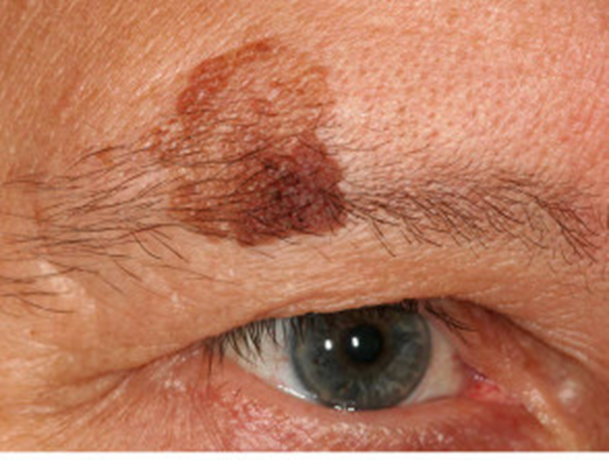
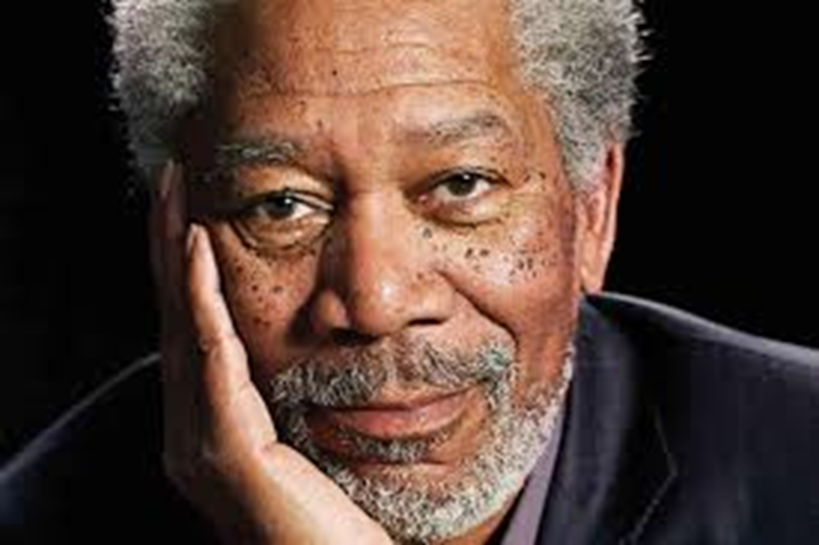
describe the appearance/signs of dermatisis papulosa nigra (4) MF
•Multiple small diameter black or dark brown papules - face and neck
•Dark skin colour
•Incidence and number increase with age
•Papules are identical to small seborrheic keratoses

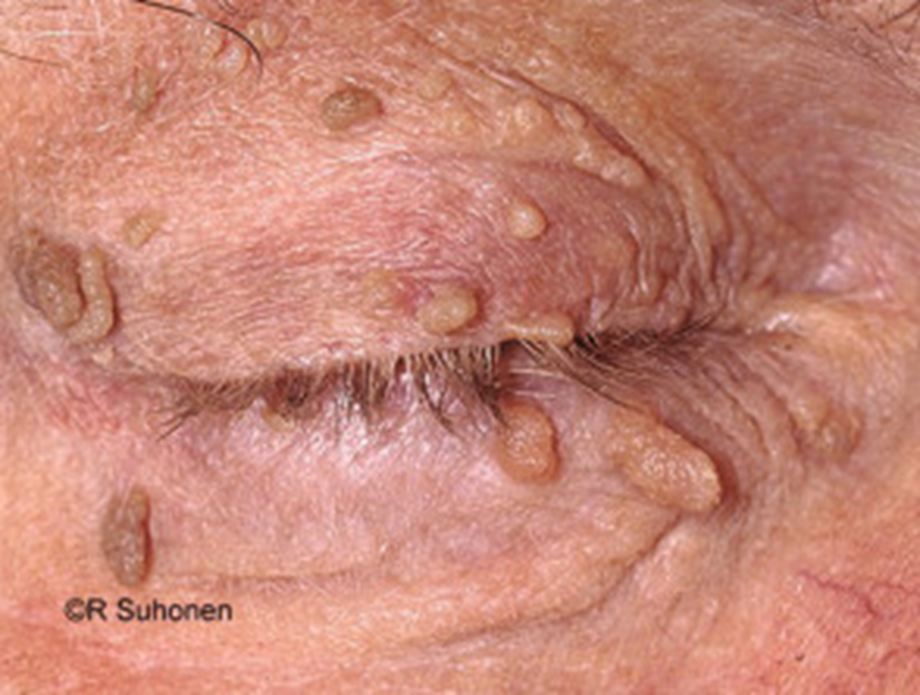
describe the appearance/signs of skin tags (6)
most common bengin lesion
Small, soft, skin coloured growth
Variable size, shape, colour and number
Cause unclear - clusters of collagen and blood vessels surrounded by skin / associated with friction when skin rubs together
can be found on other parts of the body (neck, groin and armpits)
harmless but secondary treatment can be: freezing, strangulation (ligature), snipping and cauterisation
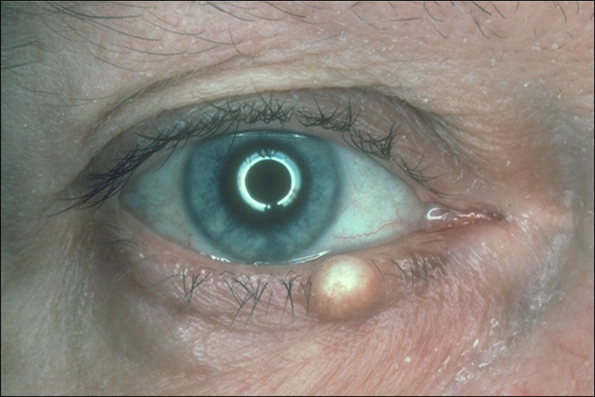
describe the appearance/signs of the different retention cysts (4)
Small, round, non-tender cysts - blocked glands
Cyst of Zeis - white cheesy (sebaceous) material - occurs on eyelid margin
Sebaceous cyst - similar to a cyst of Zeis - can occur anywhere on the skin
Cyst of Moll - clear, fluid filled, partially translucent - occurs on eyelid margin
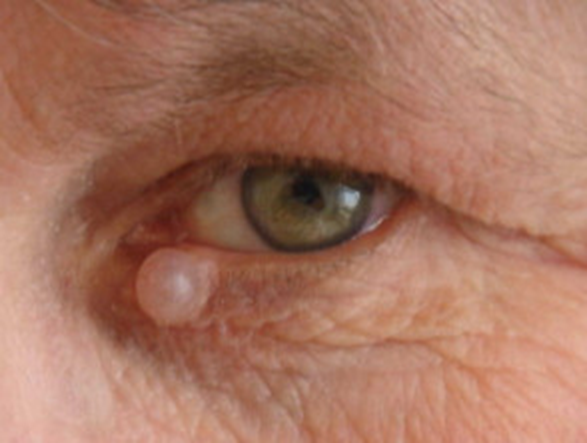
describe the appearance/signs of Milia (4)
Tiny superficial white/yellow dome-shaped cysts
usually multiple - nose, chin & cheeks
Any age - common in new born babies (40%) - and resolves as the baby grows
Trapped keratin - near the surface of the skin, derived from hair follicles
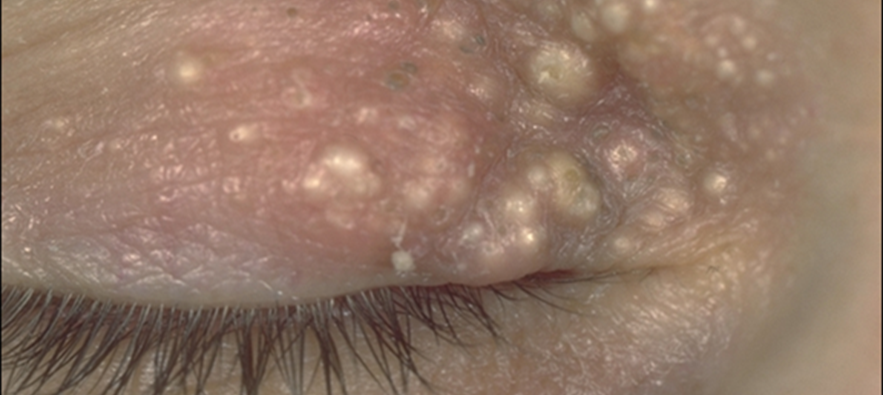
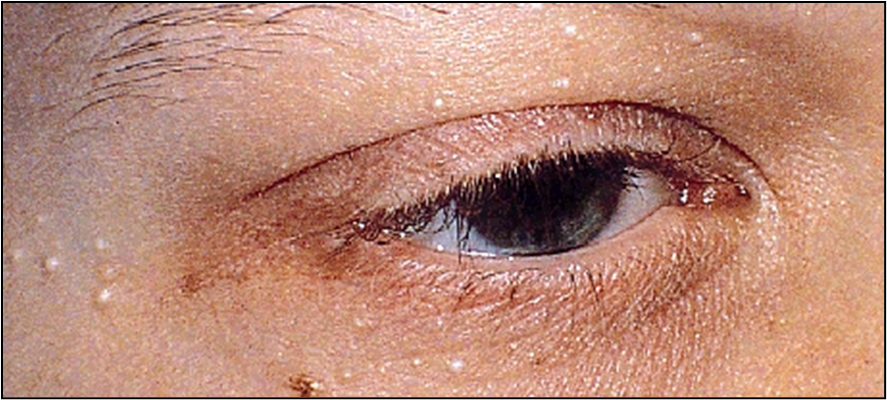
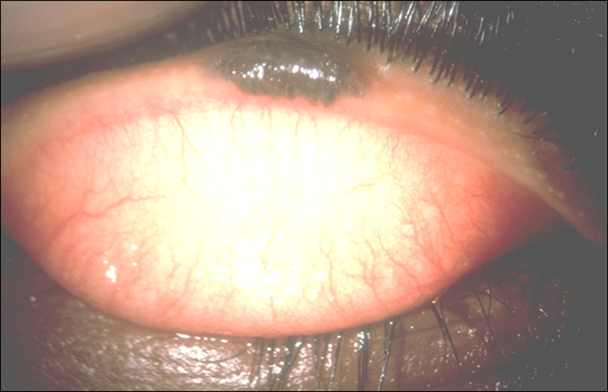
describe the appearance/signs of naevi (5)
Congenital (skin coloured markings which develop before or shortly after birth) OR acquired (benign developmental skin lesions that develop later in life)
Pigmented or non-pigmented - may become more pigmented post puberty
Flat or slightly raised
+/- hairs, warty surface - can be smooth
Malignant transformation is rare
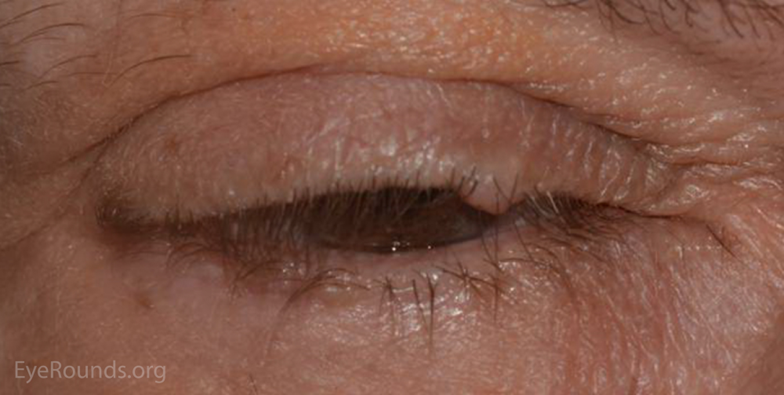
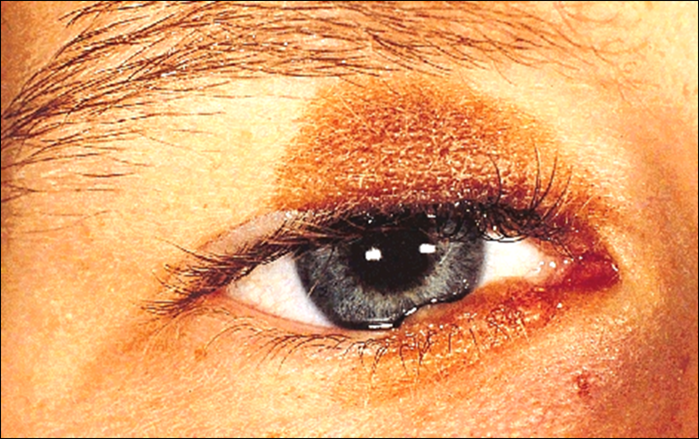
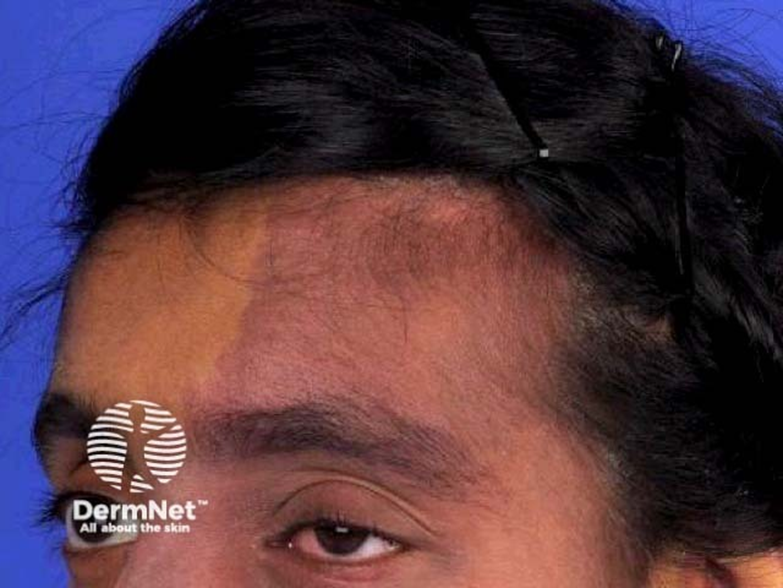
describe the appearance/signs of naevus flammeus (6)
Port-wine stain - flat red/purple mark on skin
Vascular malformation (capillaries under the skin remain dilated) - abnormal development of blood vessels
Present at birth - may become more prominent with time - about 3 in 1000 children (3F:1M) - refer children for assessment of associations
65% on head and neck
be aware that - Sturge-Weber syndrome (~8%)* & Glaucoma (~10%)*
laser treatment is available for cosmetic removal
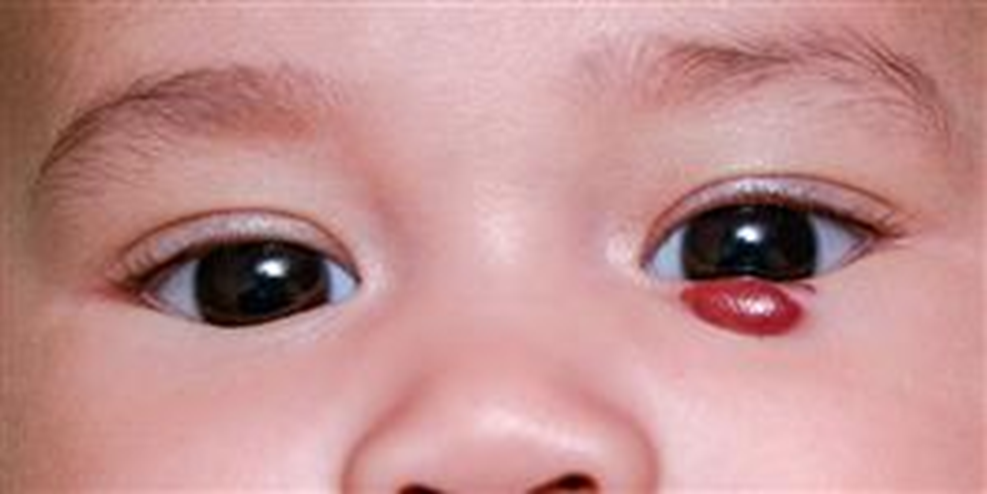
describe the appearance/signs of capillary haemangioma (5)
Strawberry naevus: evident in neonatal period - usually a few weeks after a birth but can be born with them
Grows in first year then usually regresses by 5yrs
May be cutaneous, orbital or mixed
Systemic associations - worth being investigated and aware of but can reassure parents it is harmful
can occur on upper lid - causing droopy lids - may drop visual axis and affect visual development - press on cornea - rare !
explain what the general management/treatment of bengin lesions are (4)
Monitor & reassure
consider referral for exclusion of underlying cause - if in doubt refe
refer if problematical - urgent pathway 2 weeks in NHS for suspiscious lesions
Cosmetic excision (60% recur)
state the names of the premalignant lesions to know (2:1)
SHOULD know:
Actinic Keratosis
Keratoacanthoma
EXTRA:
cutaneous horn
describe the signs/appearance of actinic (solar) keratosis (5)
Flat scaly lesions, rough skin - multiple
Red, pink, brown or skin coloured
Older age, h/o sun exposure
May give rise to squamous cell carcinoma
Occasionally papillomatous or cutaneous horn
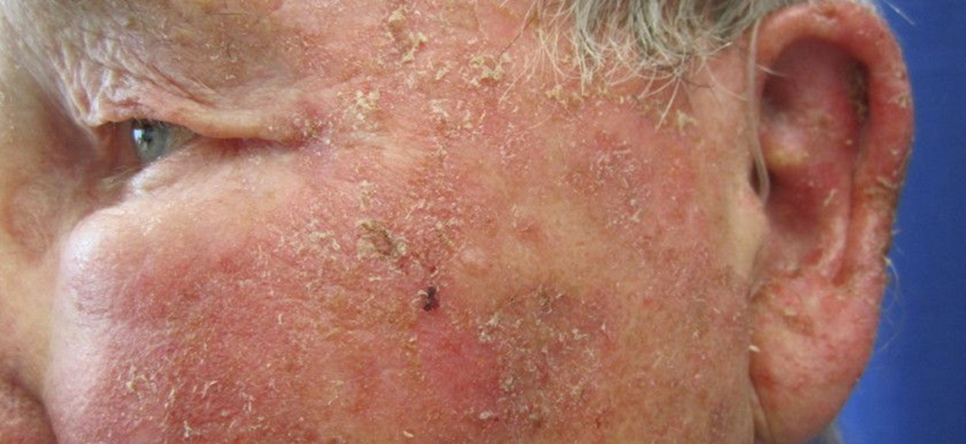
treatment/management of actinic (solar) keratosis (3)
biopsy - sample of it removed to be tested
excision
cautery - burn the skin or flesh of (a wound) with a heated instrument or caustic substance in order to stop bleeding or to prevent infection
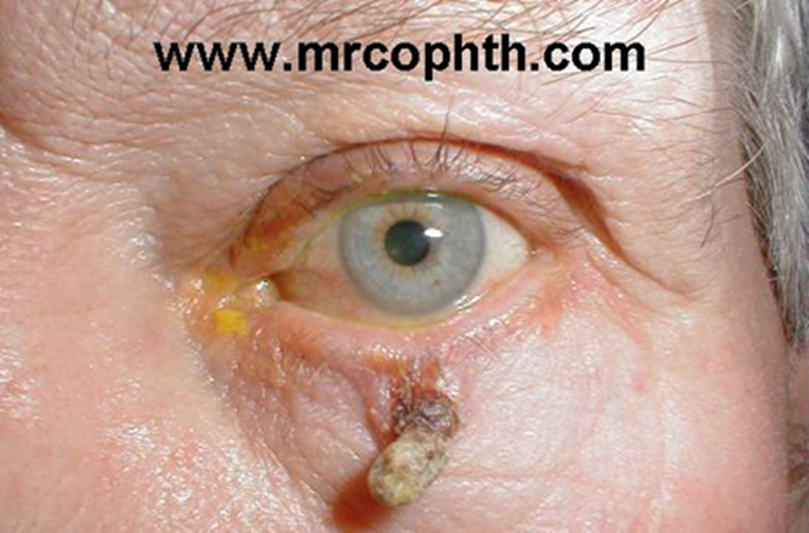
describe the signs/appearance of cutaneous horn (4)
•Keratin projection
•Arise from benign, premalignant and malignant lesions
•10% associated with squamous cell carcinoma
•Base is the point of interest - prompt referral to be removed and sent of for biopsy to see for malignancy
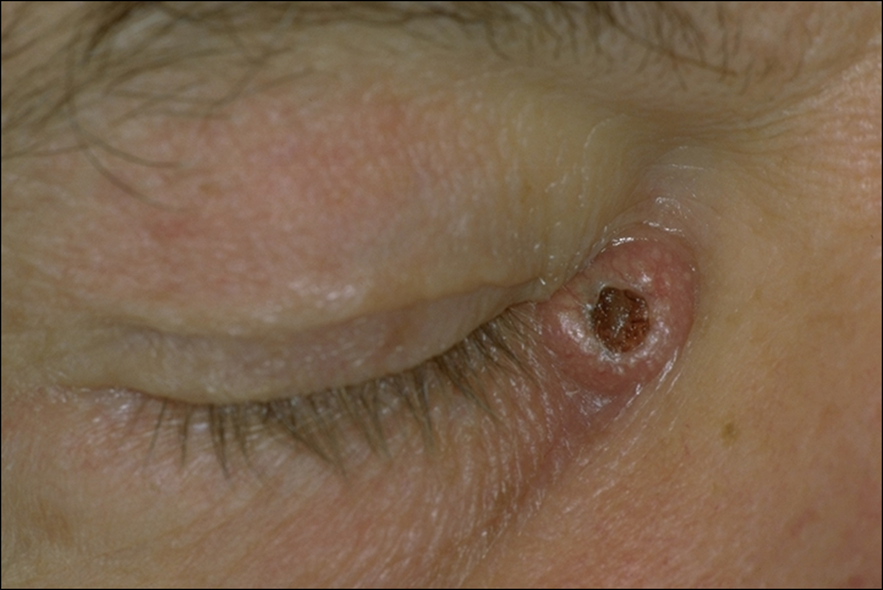
describe signs/appearance of Keratoacanthoma (5)
Rapidly enlarges (months)
Regresses or evolves into squamous cell carcinoma - be aware and prompt referral (2 weeks)
Volcano shaped with keratin plug
Visually, often difficult to distinguish from BBC or SCC
Histopathology - arises from hair follicle skin cells
state the malignant lesions to know (1:2:3)
SHOULD know:
Basal cell carcinoma
good to know:
Squamous cell carcinoma
malignant melanoma
EXTRA:
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Merkel cell carcinoma
describe the signs/appearance of basal cell carcinoma (5)
Most common periocular (around the eye/on eyelids) malignancy
Slow growing, painless, often ulcerated
Do not metastasise (spread through body) but invade locally
Change in lid contour/lash redirection or loss - lower lid is most common site
later cases sometimes pigmented
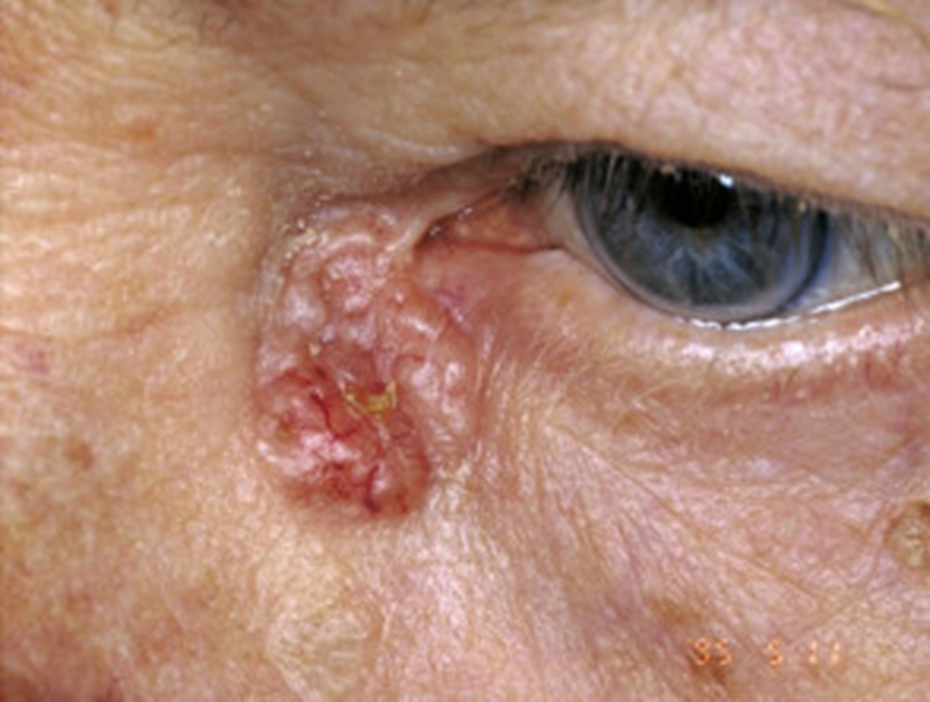
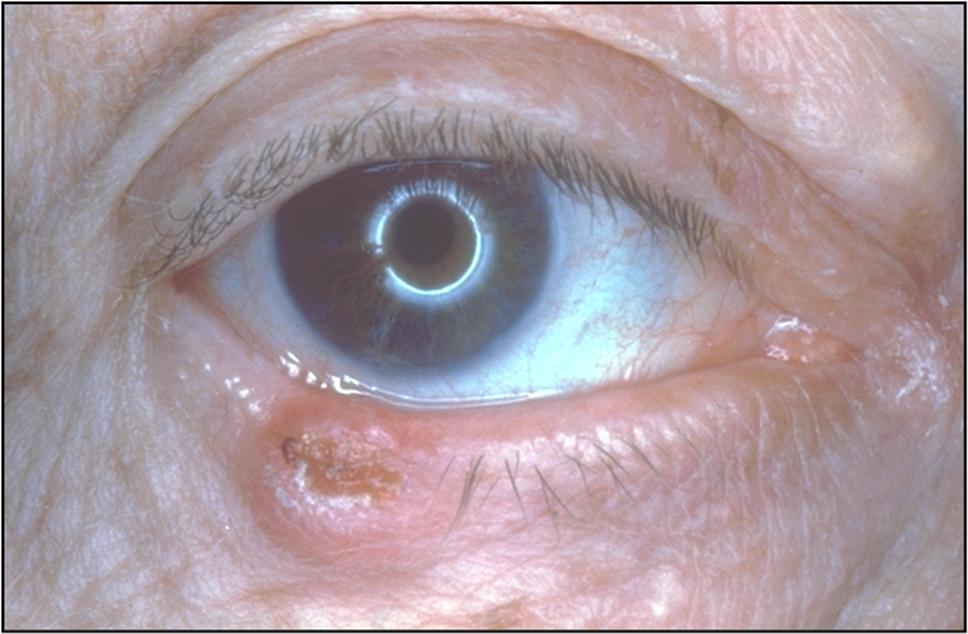
state the 3 types of basal cell carcinoma
Nodular - hard nodule, pearly appearance, abnormal (telangiectatic) vessels
Ulcerative - as nodular but with raised rolled border surrounding a central ulcer, may bleed
Sclerosing - flat hardened plaque of thickened skin without surface vascularisation, ill-defined border making it difficult to determine area of involvement
explain the management of BCC (3:2)
Optometric management
Urgent referral
Low risk skin cancer
Photographic documentation
Secondary care
Surgery
Histology
describe signs/appearance of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) (4)
May evoke inflammatory response
symptomatic unlike BCC - patient concern about lesion, may irritate or itch, may bleed
Can look similar to BCC but more aggressive
More likely to metastasise (spread via blood) than BCC
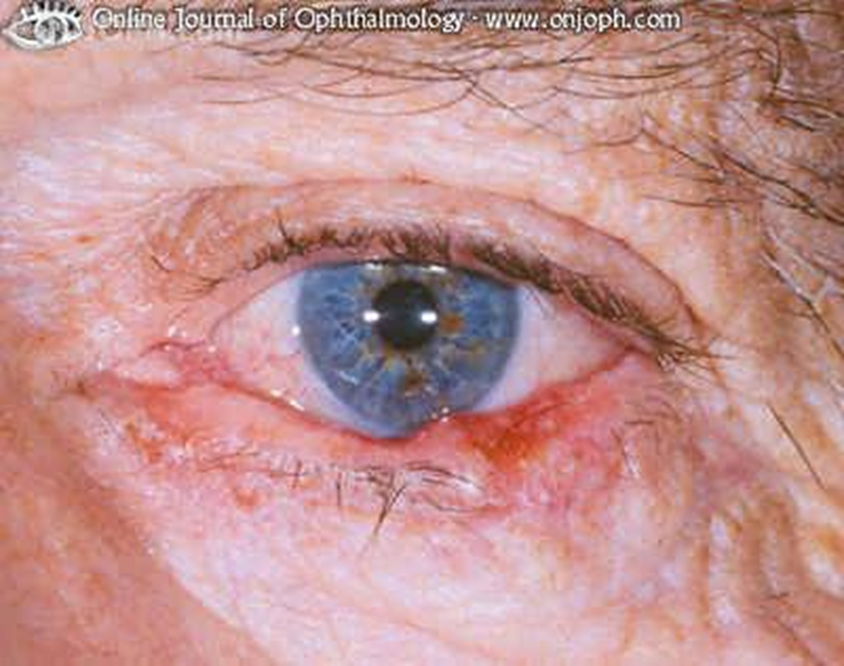
explain management/treatment of SCC (2:2)
Optometric management:
Urgent referral
Photographic documentation
Secondary care:
Surgery
Histology
describe signs/appearance of malignant melanoma (4)
•Very rare (of the eyelid)
•Can arise de novo or as a malignant transformation of a naevus
•Signs include itching, bleeding, pigmentary changes, increase in size
•50% are non-pigmented
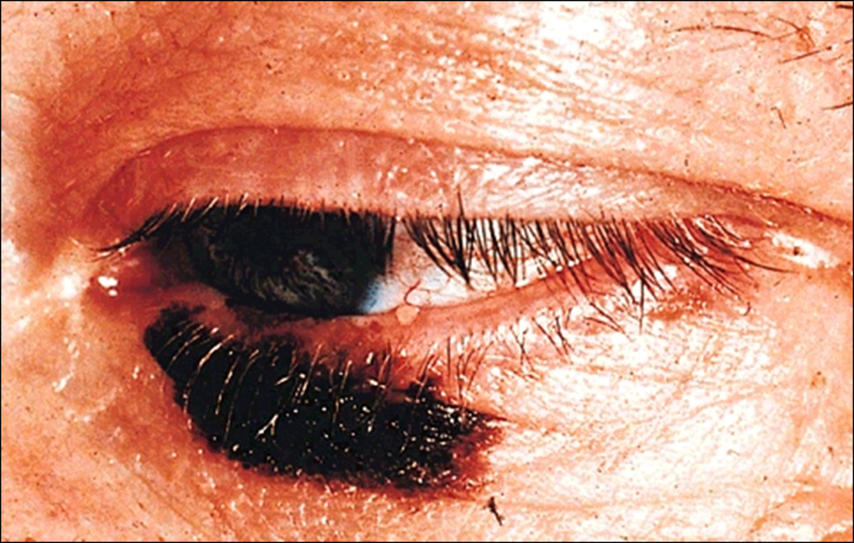
examples of other malignant lesions - extra
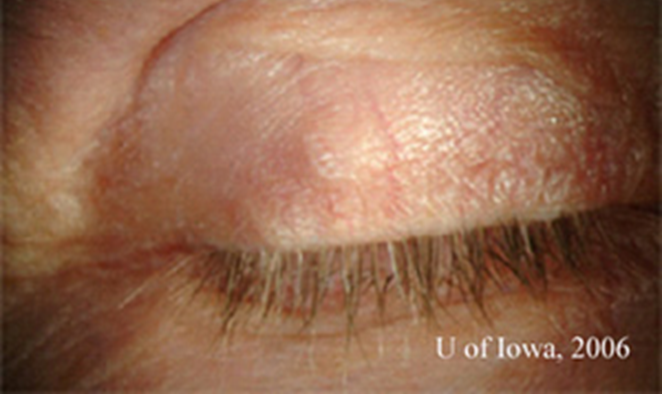
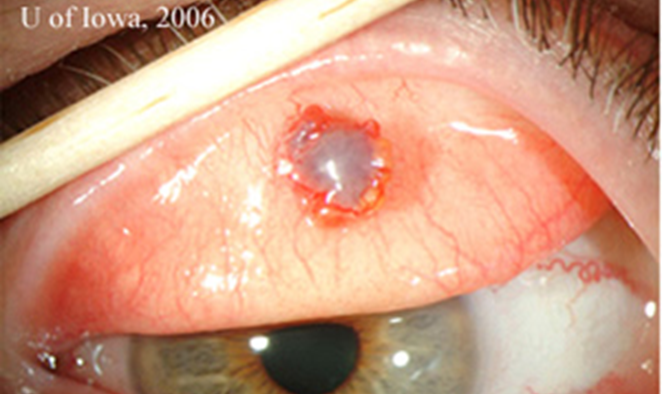
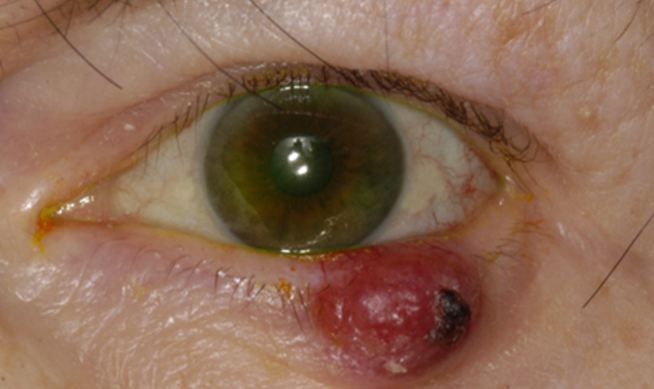
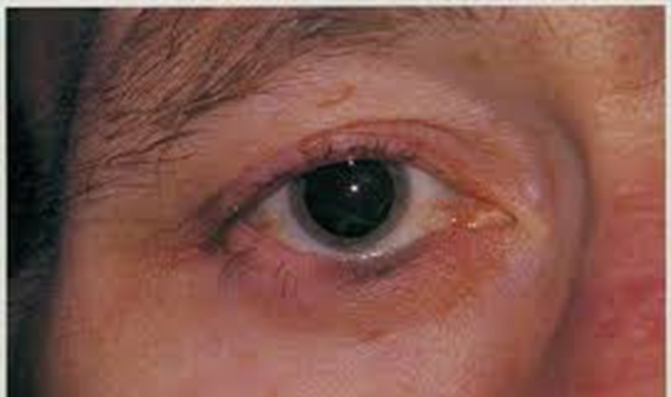
how do we distinguish between benign or malignant lesions
from patient history taking
asking key questions
state risk factors for malignancy (8)
•Prior skin cancer
•FH: skin cancer
•Previous radiation exposure (excessive UV)
•Fair skin
•Older patients
•Acute (suddenly appeared) > chronic onset
•Increasing in size
•Bleeding/crusting
state some examples of key questions we can ask patients (6)
•How long has the lesion been present?
•Has it enlarged since onset?
•Has the lesion crusted or bled?
•Has the colour changed?
•Any history of skin cancer?
•Any history of significant UV exposure (e.g. lived in a hot climate, outdoor occupation, use of sunbeds)
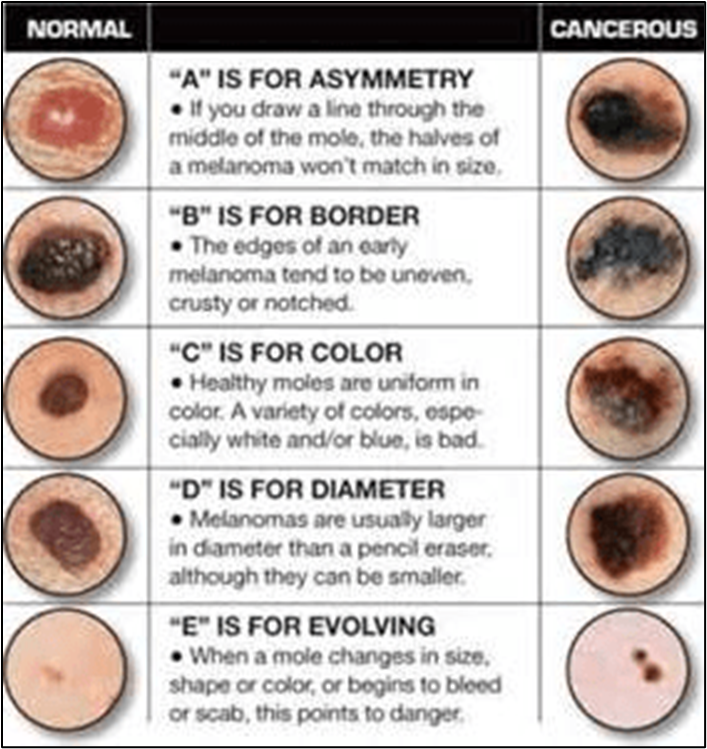
visual signs of malignant vs benign
Suspicious signs of malignancy | More reassuring signs (benign) |
New | Long standing |
Increasing in size | Remain static in size |
Surface ulceration/induration | Smooth surface - benign do not ulcerate |
Neovascularisation - new blood vessels in and around the lesion, bleeding | Does not bleed with minor trauma |
Crusts | Doesn’t form adherent crusts |
Lid margin changes - destruction of margin, loss of lashes | Does not destroy eyelash follicles (may distort them) |
Recurrent infection/inflammation |
what i need to know
Must know | Should know | Good to know | |
I: Lumps & Bumps | Common benign lesions Xanthelasma Papilloma Retention cysts Milia Basal cell carcinoma Signs of malignancy | Other benign lesions Skin tags Haemangioma Port-wine stain Premalignant lesions Actinic keratosis Keratoacanthoma | Other malignancies Squamous cell carcinoma Sebaceous gland carcinoma Malignant Melanoma Kaposi’s sarcoma Merkel cell carcinoma |
II: Eyelid Infection & Inflammation | Ectropion Entropion Acquired Ptosis Trichiasis | Blepharospasm Twitch Lagophthalmos Floppy eyelid syndrome | Madorosis & Poliosis Lash infestations |
III: Positional Abn & Eyelash Disorders | Blepharitis Hordeolum Chalazion | Molluscum contagiosum Herpes zoster ophthalmicus | Impetigo Herpes simplex |