Module 3 MCB 2010 exam 3
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Why are rRNA gene sequence an excellent tool for classifying bacteria?
Genes are present in all known bacteria.
Part of the gene sequences is highly conserved
part of the gene sequences varies from species
What is extremophile?
a microbe that requires extreme conditions.
ex. temperature ,PH and/or salinity to survive
An organism that requires an environment containing greater than 9% NaCI would be considered a...
Halophile
A______ is slightly curved rod
vibrio
which of the following is a unique characteristic of Mycoplasmas?
Lacks a cell wall and smallest free living cell
Autotrophic bacterium
Produces organic compounds from carbon dioxide.
Which of the following is NOT a taxonomic domain?
Protista
How would you classify a microbe that require temperatures over 80 C for growth?
Hyperthermophile
Scientists classify prokaryotes primarily based on similarities in ...
DNA
RNA
Protein sequences
What is nitrogen fixation?
The reduction of nitrogen gas to ammonia
Which statement regarding algal morphology is MOST accurate?
Algae can be unicellular ,colonial, or multicellular
Green algae are similar to plants in all except which of the following ways?
They have similar 16S rRNA sequences
which terms BEST describes a cell that contains only one single copy of each chromosome?
Haploid
What do you call the free-living motile feeding stage of protozoa?
trophozoite
How are insects different from arachnids?
insects have three body regions
What is the name given to the process of cytoplasmic division?
Cytokinesis
Plasmodium species reproduce asexually via a process called?
Schizogony
A virion is composed of a (n)
capsid and nucleic acid core
All prion disease result in what symptoms?
fatal neurological degeneration
Which statement MOST accurately describe lytic vital replication?
Viral replication usually results in the death and lysis of the host cell
What is the name of the proteinaceous subunit that makes up the viral capsid?
capsomere
How are viroid different from viruses?
viroids lack capsids
which of the following is NOT a way that viruses can cause human cancer?
Viruses can cause abnormalities in the host cytoplasmic membrane
What is the BEST method to use when attempting to culture bacteriophages?
Mix the phages with bacteria and liquid media and pour over a plate
How do disease-causing prions produce more disease-causing prions?
They change the shape of cellular PrP
All of the following are characteristic of life EXCEPT...
the ability to live in the presence of oxygen
What are viroids?
viroid lack capsids
What is a prion?
a proteinaceous infective particle
What is a capsid?
proteins coat (outer covering)
what is a envelope?
is portion of membrane system of host
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
lytic replication
viral replication usually results in death and lysis of host cell( inserting its DNA and killing the host fast)
lysogenic replication
extended period of dormancy initiated by certain bacteriophages
(the virus's gets in to the cells and stays a while)
Retrovirus
virus that contains RNA as its genetic information.
dont use there own genomes mRNA
Latency
domains
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya
Prokaryote
unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus.
thrive in various habitats
exist in a variety of shapes
Endsopores
gram positive bacteria bacillus and clostridium
defensive strategy against unfavorable conditions
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in which one cell divides to form two identical cells.
snapping division
is a type of reproduction in prokaryotes that results in a palisade arrangement of cells
Budding
Asexual reproduction in which a part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism
extremophiles
live in extreme environments
Thermophiles
temperature environment
(heat loving over 80c)
Halophiles
saline habitats (salt lover)
red or orange pigment protects from the sun
Methanogens
Convert carbon dioxide, hydrogen gas and organic acids to methane gas. (land field).
live in colons of animals
What is a pleomorphic prokaryote?
a prokaryote whose cell morphology varies in shape and size
bacteria reproduce asexually.Name the different processess they use?
Binary fission (most common).
Snapping division.
Budding
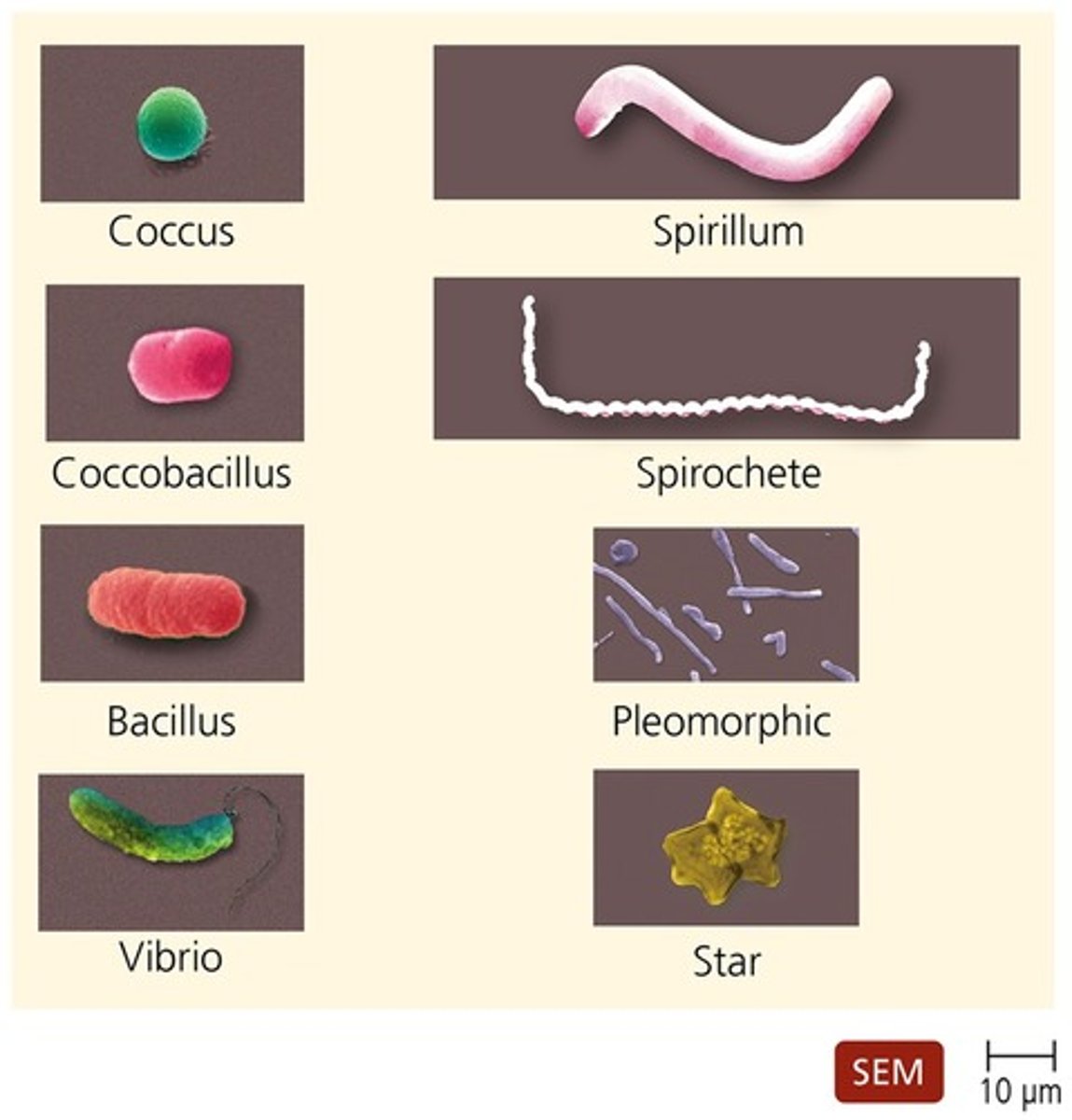
Prokaryotic morphologies
coccus-roughly spherical
Bacillus-rod shaped
vibrio- curved rods
coccobacillus-intermediate shape of cocci and bacilli
pleomorphic- many shapes
spiral-(two forms)
spirillum-stiff spiral(worm)
spirochetes-flexible spiral
binary fission steps
1.DNA replicate
2.cytoplasmic membrane elongates
3.cross wall forms when cytoplasmic membrane invaginates
4.daughter cell separates
_________lives in temperature above 45C
thermophiles
_______live in 9% or greater NaCI concentration
Halophiles
what does it mean that bacterium is low G +C?
Looks at organism to look at genomes that have less than 50%
what is the difference between spores and endospores ?
Spores are reproductive structure in plants; endospores are stable resting structure in bacteria
_________form when planes of cell division are random not at 90-degree angles.
Staphylococci
If organism X has a G +C content of 60% and organism Y has a G +C content of 35% ?
They are not closely related
What molecule is most used to determine phylogeny of a bacterium?
rRNA molecule
Meiosis
process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell
Budding
Asexual reproduction in which a part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism
Schizogony
asexual reproduction by multiple fission
Chemoheterotrophic
an organism that uses organic molecules as a source of carbon and energy
Characteristics of a Protist
Unicellular
lack a cell wall
eukaryotic
lives in ponds ,lakes (moist places)
Mold
composed of long filaments called hyphae
Yeast
small, globular and composed of a single cell
Single-celled eukaryotes lacking a cell wall are_____
protozoa
The _______ have shells composed of calcium carbonate and thin pseudopods.
Foraminifera
plasmodium (protists) causes
Malaria
Trypanosoma (protist) causes
African sleeping skickness
Entamoeba(protist) causes
amoebic dysentery
Plasmodium species reproduce asexually via a process called
Schizogony
what do you call the free living ,motile feeding stage or protozoa?
Trophozite
Characteristic of the fungi
- chemoheterotrophic eukaryotes
- do not photosynthesize
- can be unicellular, filamentous, or multicellular
- have chitin in their cell walls
- classified by spores
-decomposed dead organism, absorpt nutrients
septate hyphae
there is a septum that forms in between into each single cell
aseptate hyphae
no septum its a continuous cell that contain multiple nuclei
Mycelium
entire interwoven mass of one multicellular fungal organism
unicellular fungus is called a
yeast
Fungal spores produced asexually within a sac-like chamber at the tip of a hypha are called
sporangiospores
sexual reproduction in Basidiomycota results in the production of
basidiospores
asexual reproduction in multicellular Ascomycota leads to the production of ____
asci
Hyphae are associated with which of the following?
molds
Fungi called Deuteromycetes are not known to reproduce sexually. Nonetheless, most of them are considered members of the ________ on the basis of genetic sequences.
ascomycota
what is a vector?
living organism that transmit an infectious agent from a infected animals to human
which of the following is transmitted by mosquitoes?
malaria
which statement regarding mosquitoes is TRUE?
Mosquitoes are a type of mite
mechanical vector
insects touch your food even though is been everywhere
biological vector
transmit pathogens and serve as hosts for the multiplication of a pathogen during stages of its life(penetrating your skin)