f4 electricity and magnetism
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
describe the relationship between positive and negative charges in terms of repulsion and attraction
charges that are the same repel
but opposite attract each other
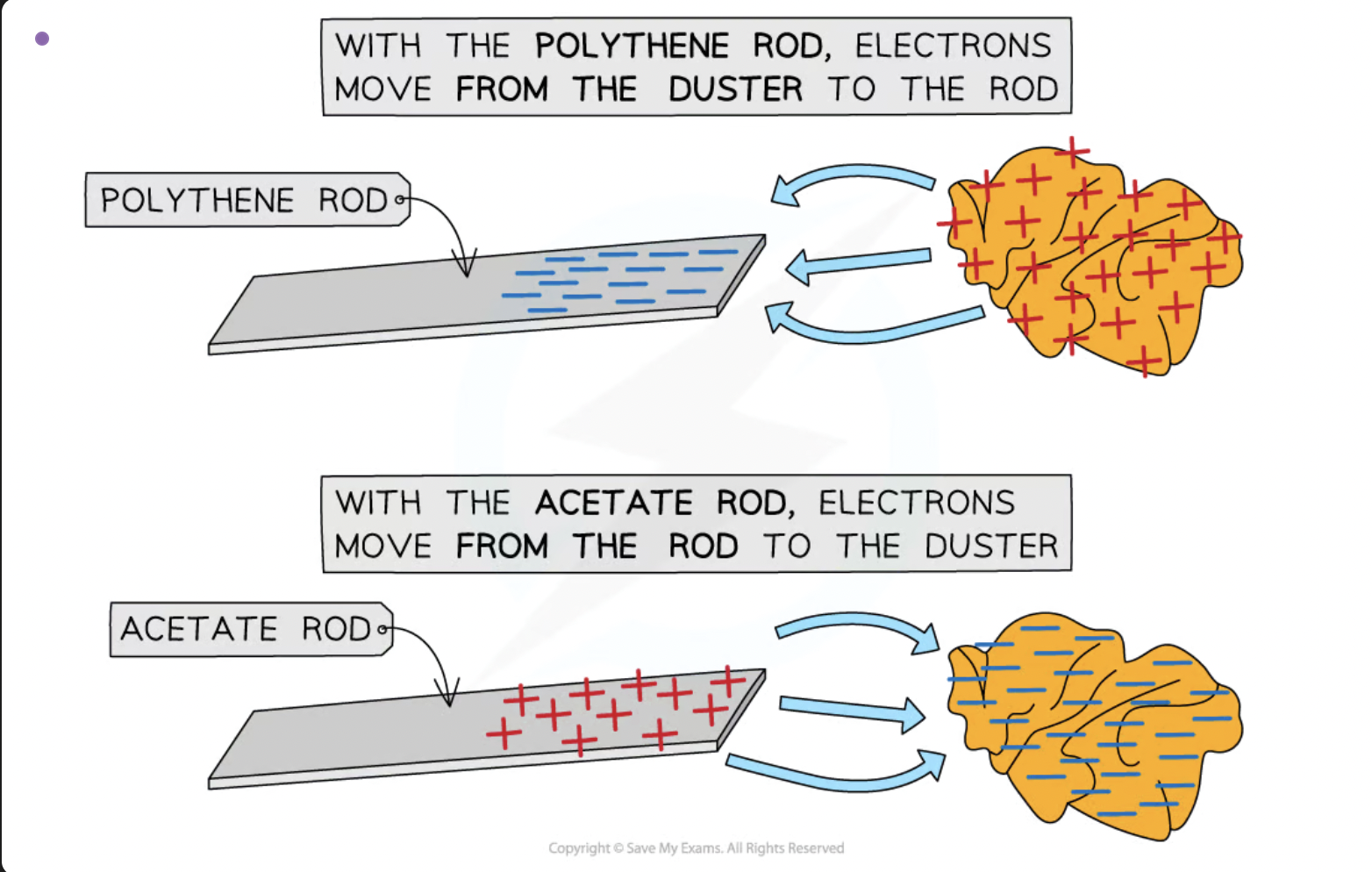
describe a simple experiment to show the product of electrostatic charges by friction and to show the detection of electrostatic charges
When certain insulating solids are rubbed against each other, they can become electrically charged
This is called charging by friction
The charges remain on the insulators and cannot immediately flow away
One gains a net positive charge and the other gains a net negative charge
An example of this is a plastic or polythene rod being charged by rubbing it with a cloth.

explain how the charging of solids by friction involves only the transfer of negative charge (electrons)
the positive charges of an atom (proton) are in the nucleus and therefore cannot be transfered. the only way an object can gain a positive charge is when electrons are transfered away from it.
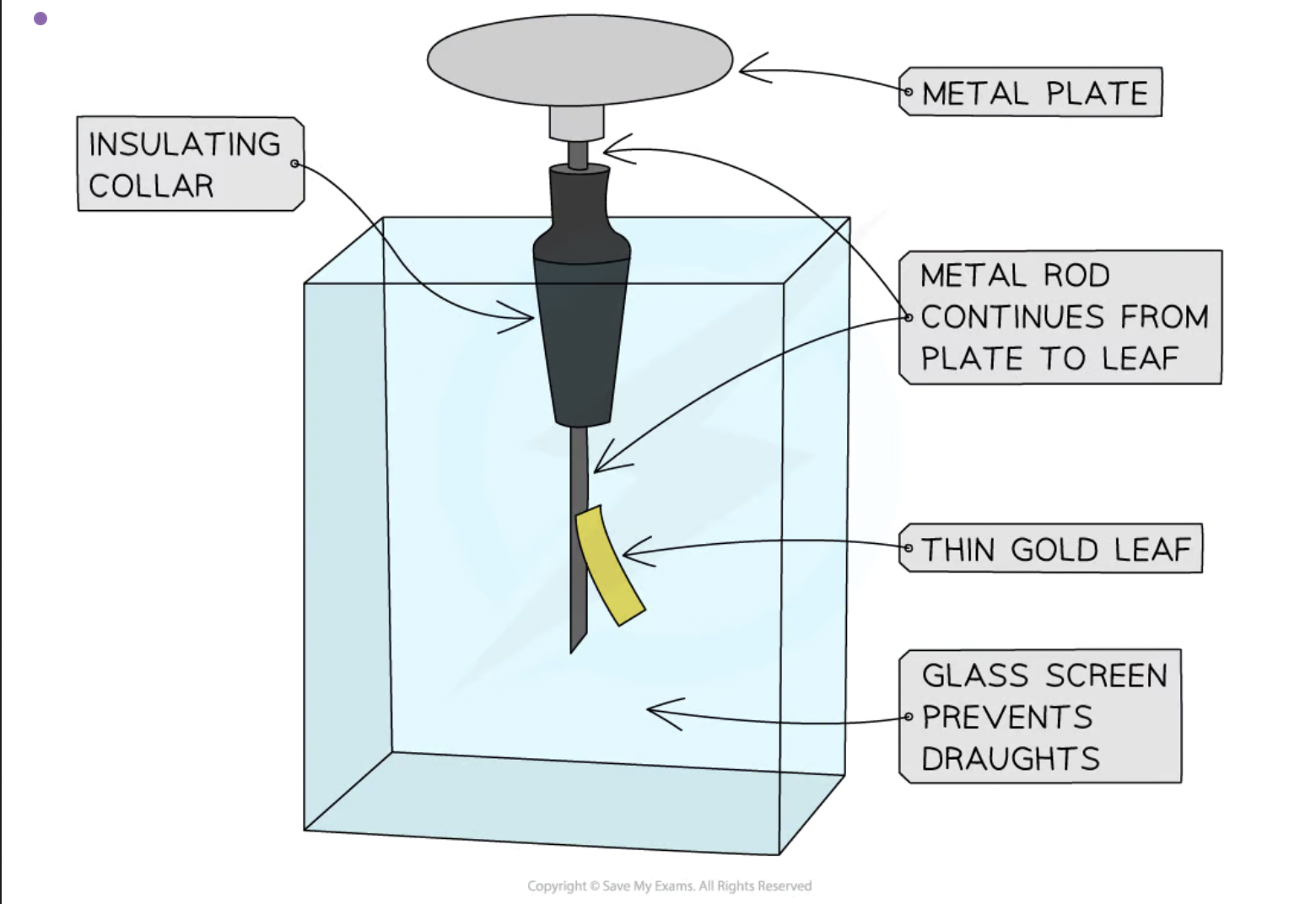
describe an experiment to distinguish between electrical conductors and insulators
Before beginning the experiment, ensure the plate of the electroscope is uncharged by touching it with your finger. The leaf should hang straight down next to the stem
Charge a polythene rod by rubbing it with a cloth
Touch the charged rod to the plate of the electroscope. The leaf should stay risen if the electroscope has been successfully charged
Touch the plate of the charged electroscope with the first object to be tested and record any observations
Repeat for different materials
Good conductors, such as metals, allow charge to flow through them easily
Therefore, a good conductor will cause the leaf to fall quickly as it allows charge to flow to or from the plate
The faster the leaf falls, the better the conductor
Poor conductors, such as glass, do not allow charge to flow as easily
Therefore, a poor conductor will cause the leaf to fall slowly as the charge is unable to flow as well
If the leaf does not move at all, the material is a good insulator
state the units for charge
coloumbs ( c)
what is an electric field?
a region in which an electric charge experiences a force
the direction of an electric field at a point is defined as:
the direction at a force on a positive charge at that point
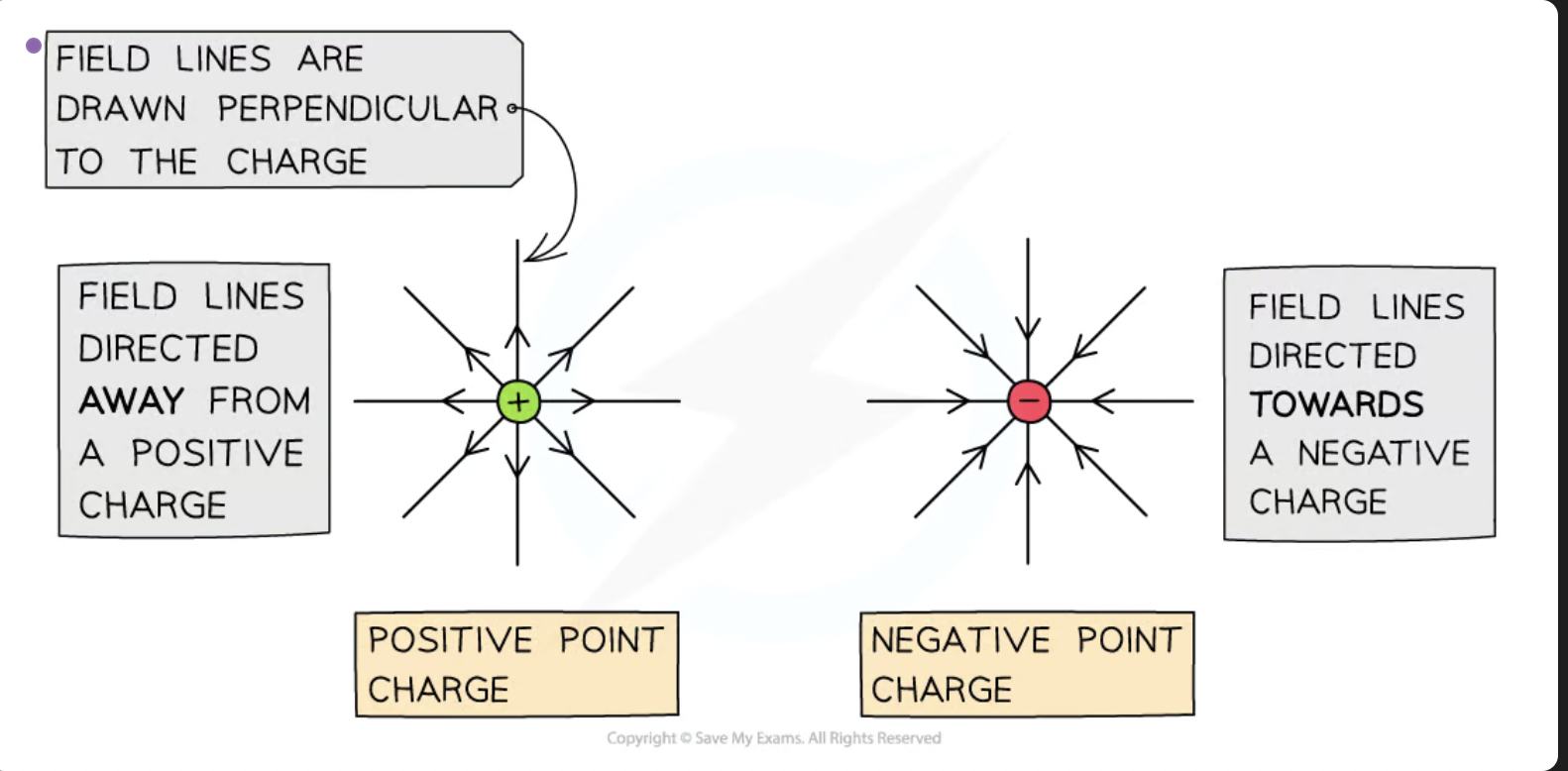
describe the simple electric field pattern around a point charge
If the charge is positive (+), the field lines are radially outwards
If the charge is negative (-), the field lines are radially inwards
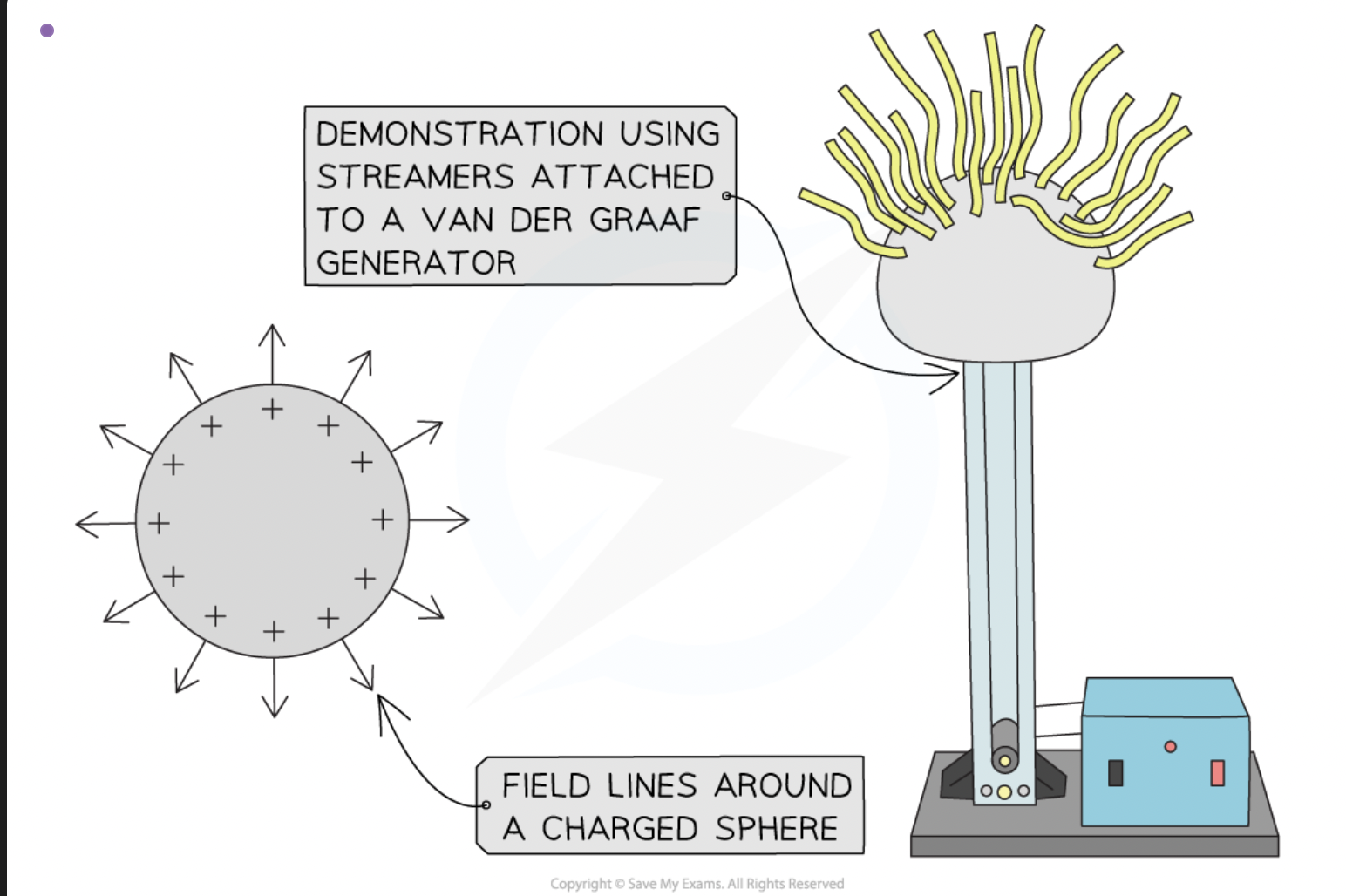
describe the simple electric field pattern around a charged conducting sphere
The field lines around a charged conducting sphere are similar to that of a point charge
This is because the charges on the surface of the sphere will be evenly distributed
The charges are the same, so they repel
The surface is conducting, allowing them to move
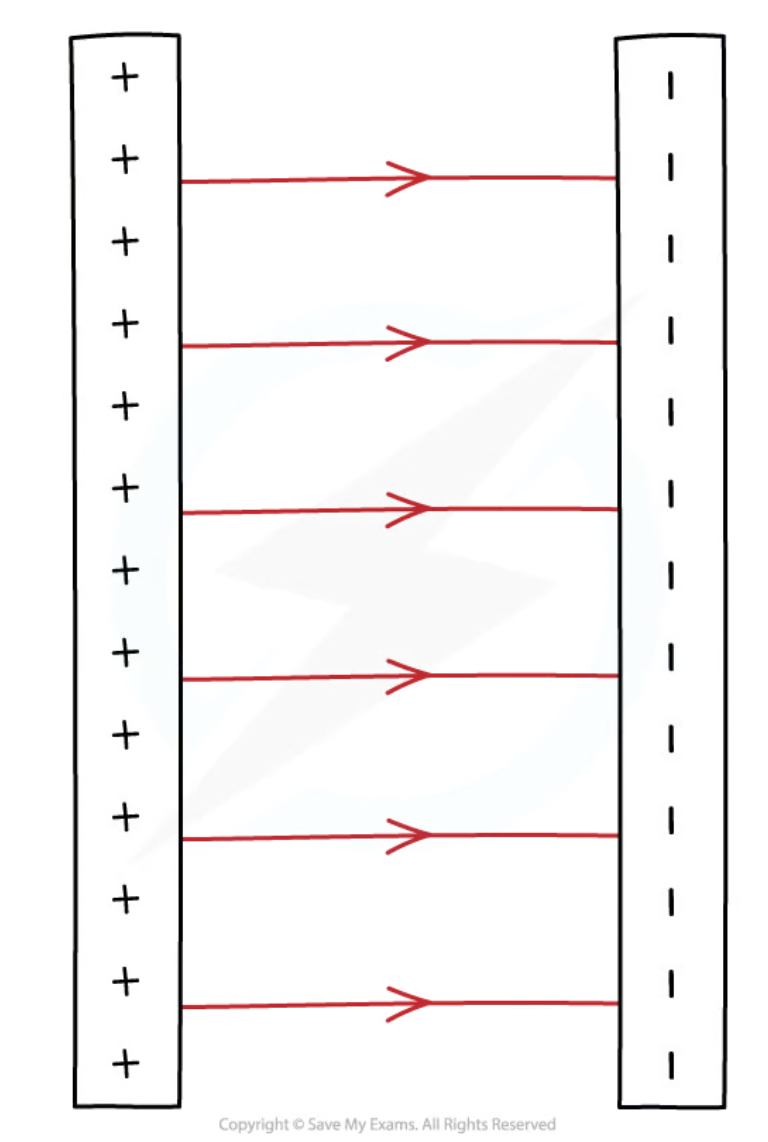
describe the simple electric field pattern between two parallell plates
The electric field between two parallel plates is a uniform electric field
The field lines are:
directed from the positive to the negative plate
parallel
straight lines
define electric current
the rate of flow of electric charge
describe the use of ammeters with different ranges
describe electrical conduction in metals in terms of free electrons
what are the two types of current
direct
alternating
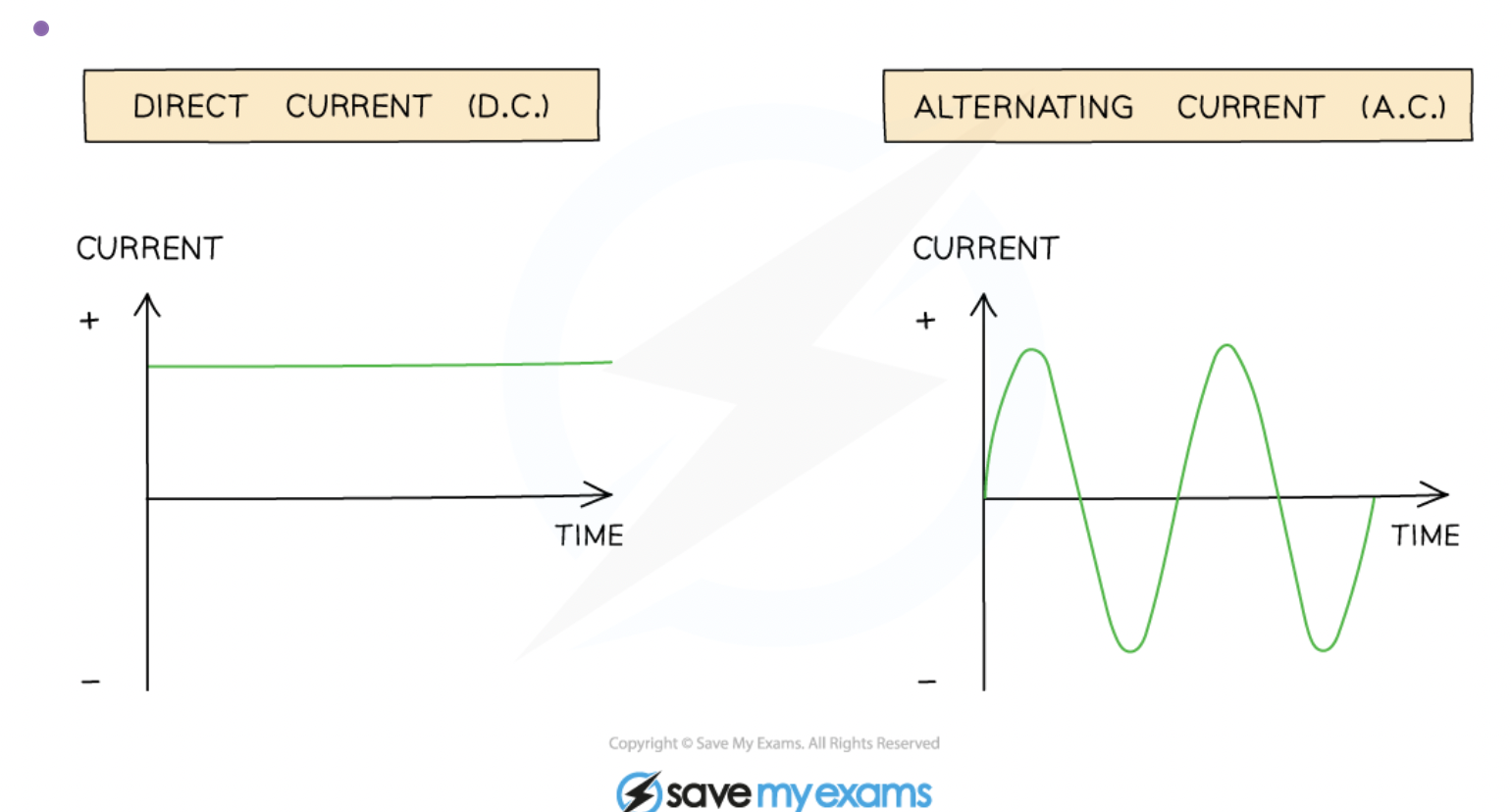
what is the difference between direct and alternating current
A direct current (d.c.) is defined as
A steady current, constantly flowing in the same direction in a circuit, from positive to negative
An alternating current power supply has two identical terminals that change from positive to negative and back again
The alternating current always travels from the positive terminal to the negative terminal
Therefore, the current changes direction as the polarity of the terminals changes
define electrical current with the use of its equation
the charge passing a point per unit of time
I= Q/t
Q = charge, measured in coulombs (C)
I = current, measured in amps (A)
t = time, measured in seconds (s)
state what is a conventional current
a conventional current is from positive to negative and the flow of free electrons is from negative to positive
define what is meant by electromotive force (e.m.f)
the electrical work done by a source in moving a unit charge around a complete circuit.
what is e.m.f measured in
volts (v)
define what is meant by poteintial difference
pd. is defined as the work done by a unit charge passing through a component
what is p.d between 2 points measured in?
volts (v)
describe the use of a voltmeter (analague and digital) with different ranges
recall the use of the equation to calculate e.m.f
E= W/Q
E = electromotive force (e.m.f.), measured in volts (V)
W = energy transferred to the charges from the power source, measured in joules (J)
Q = charge moved, measured in coulombs (C)
recall the use of the equation to calculate p.d
v= W/Q
V = potential difference, measured in volts (V)
W = energy transferred to the charges from the power source, measured in joules (J)
Q = charge moved, measured in coulombs (C)
recall the use of the equation to calculate resistance
R= V/I
where:
R= resistance, meausured in ohms Ω
V= potential difference measured in volts(v)
I= current, measured in amps (A)
describe an experiment to determine resistance using both an ammeter and a voltmeter
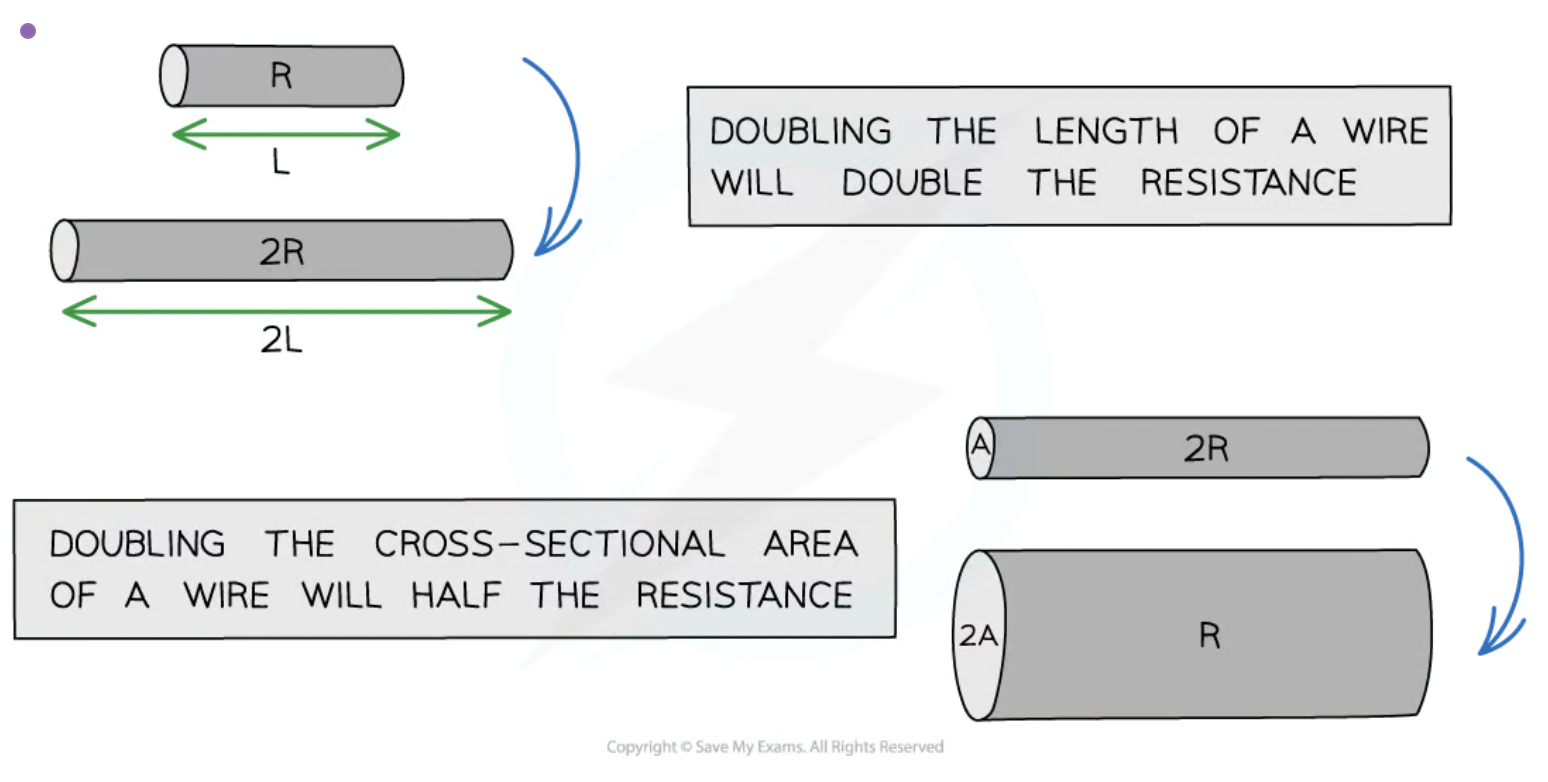
describe qualitatively the relationship of the resistance of a metal wire to its length and to its cross section area
Resistance is directly proportional to length
Resistance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area (width, or thickness)
sketch and explain the current- voltage graphs for a resistor of constant resistance, a filament, lamp and a diode