3.1.2: Business Growth
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what is internal/organic growth?
where firm increases sales and total revenue of its existing businesses by:
ploughing profits back into firm to increase capacity
borrowing money from banks (con → debt)
issuing shares (equity)
development and launch of new products
finding new markets (e.g. by exporting into emerging countries like India and South Africa)
growing a customer base through effective marketing
what are examples of organic businesses?
under armour
generates turnover around $2bn/yr
consistently growing over 20%/yr
doing this by expanding product range, extending into retail operations + pushing into emerging markets
whitbread
owned costa coffee and premier inn
can potentially have a costa in premier inn → generates more revenue, gradual growth by offering bought business
lego
never made an acquisition
focuses on using new product development + innovation as driver of revenues + profits
since 2007 has tripled revenues globally
external growth is achieved through:
mergers
two firms agreeing to join together
acquisitions
aka takeovers
one firm buying another (amicable/hostile), e.g. americans have bought out british businesses
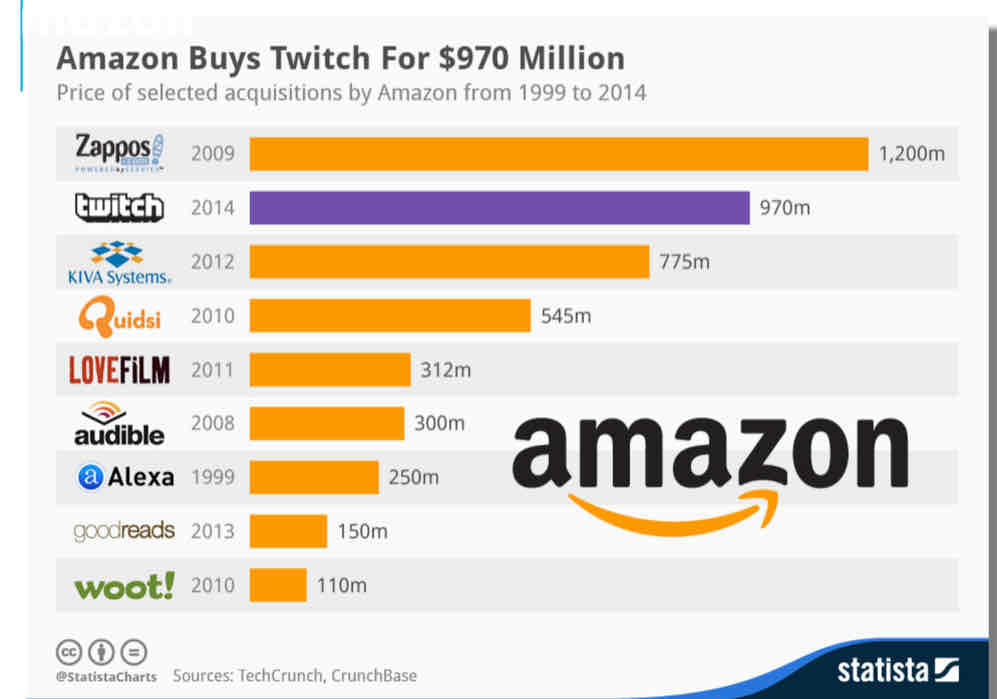
e.g. amazon bought twitch for $970m
an example of an acquisition
amazon buying twitch for $970m
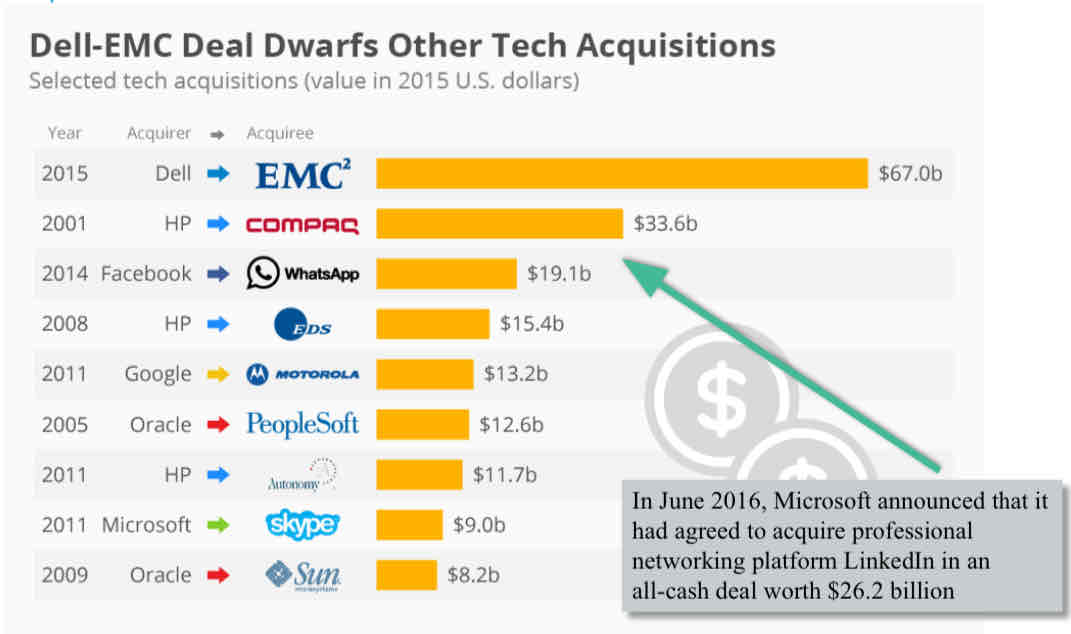
an example of a tech acquisition
in june 2016, microsoft announced it had agreed to acquire professional networking platform LinkedIn in all-cash (no loan) deal worth $26.2bn
external growth: types of mergers and acquisitions
horizontal integration
vertical integration
backward vertical integration
forward vertical integration
conglomerate integration
what is horizontal integration?
joining of two firms in same industry and at same stage of production e.g. two supermarkets Sainsbury’s and Asda
what is vertical integration?
joining of two firms in same industry but at different stages of production
what is backward vertical integration?
taking over a firm in a preceding stage of production (closer to raw materials in supply chain)
e.g. Tesco buying wholesale Booker for £4bn in 2018
what is forward vertical integration?
taking over a firm in the next stage of production (closer to final consumers)
e.g. Live Nation merging with Ticketmaster
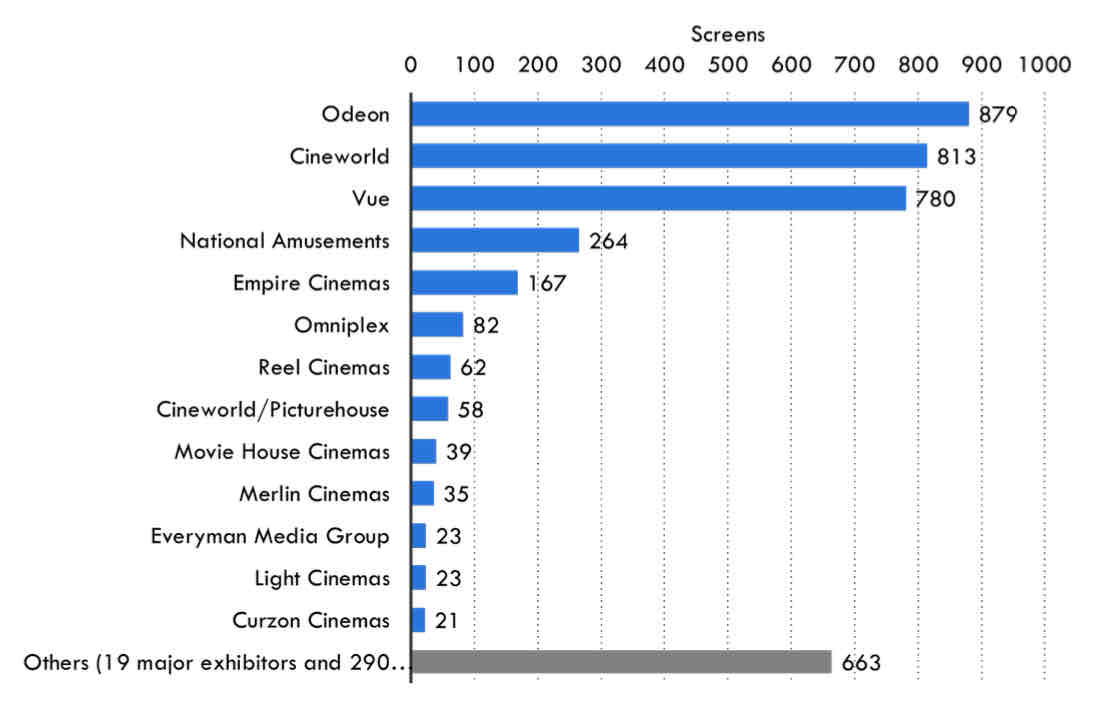
horizontal integration → UK cinemas
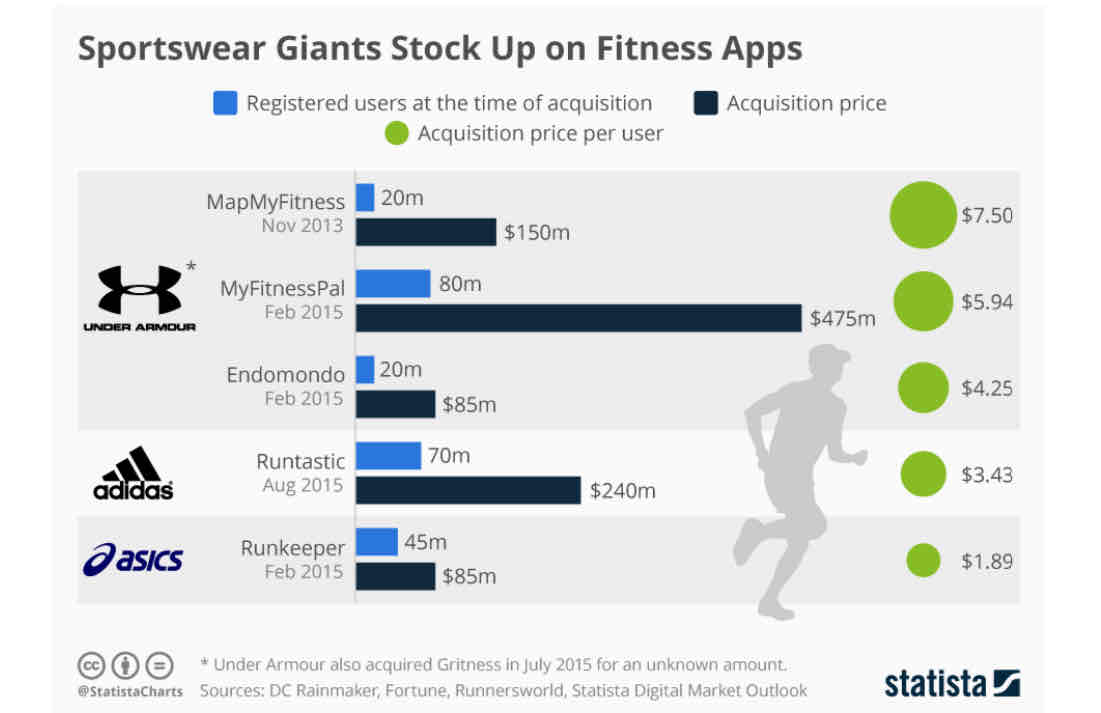
vertical integration → fitness app acquisitions
what are examples of vertical integration?
film distributors owning cinemas + digital streaming platforms
brewers owning/operating pubs (forward vertical) or buying hop farms (backward vertical)
record labels and radio / online music stations
drinks manufacturers such as Coca Cola integrating with bottling plants
pig processing business buying a pig farm
technology companies growing vertically through hardware, software and services
PayPal, acquired by eBay for $1.5bn in 2002
Google buying Motorola, a phone maker
what is conglomerate integration?
the joining of two firms in completely unrelated markets
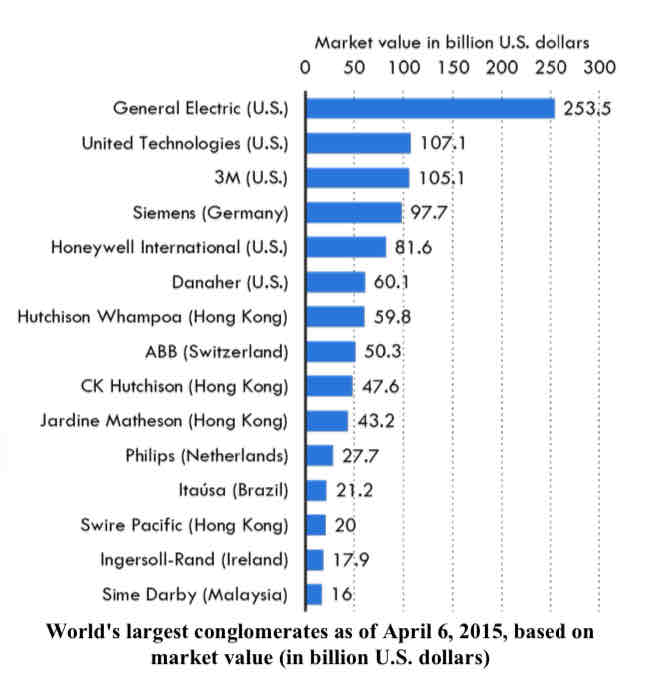
what are examples of conglomerate integration?
the world’ s biggest conglomerates include businesses such as General Electric and 3M in the United States and Siemens from Germany
another is Samsung – the electronics giant also makes military hardware, apartments, ships and Samsung also operates a Korean amusement park!
what is a joint venture?
when two or more businesses join together to pursue a common project, e.g. uber and volvo teaming up for self-driving ubers
advantages of vertical integration
control of the supply chain - this helps to reduce unit costs and also improve the quality of inputs into the production (supply) process
improved access to key raw materials perhaps at the expense of rivals who must then pay more for them
better control over retail distribution channels + adding new channels to sales platforms to build business revenues
removing suppliers and taking market intelligence away from competitors which then helps to make a market less contestable (le. it increases a firm's market
drawbacks of vertical integration
mergers can often create new problems of communication and coordination within a bigger and more disparate firm; can lead to diseconomies of scale where the new bigger firm is more inefficient
real world examples of businesses that have grown through vertical integration
Amazon: Amazon has expanded its operations through vertical integration by acquiring companies involved in different stages of the e-commerce supply chain. For instance, Amazon has acquired Whole Foods to enter the grocery business, and it has also acquired logistics companies like Kiva Systems and Colis Prive to improve its delivery capabilities.
Ford Motor Company: Ford has practiced vertical integration by owning its own iron mines, steel mills, and rubber plantations. By owning these suppliers, Ford could control the quality and cost of the materials used in its vehicles and improve efficiency in its manufacturing process.
Walt Disney Company: Disney has grown through vertical integration by acquiring companies that create content for its various entertainment platforms. For instance, Disney acquired Pixar, Marvel, and Lucasfilm to bolster its movie and TV offerings, and it has also acquired companies involved in theme park operations and merchandise production.
Apple: Apple has used vertical integration to create a seamless user experience for its products. For instance, Apple designs its own processors and software, which are then used in its iPhones, iPads, and other devices.
Apple also operates its own retail stores, which allow it to control the customer experience and increase brand loyalty.Tesla: Tesla has grown through vertical integration by producing many of the components used in its electric vehicles in-house, including batteries, motors, and drivetrains. This allows Tesla to maintain control over the quality of its products and to innovate more quickly than if it relied on external suppliers.
potential benefits of horizontal integration
exploit internal economies of scale (lower LRAC)
cost savings from the rationalisation of the business - this often this involves job losses in a bid to increase productivity
create a wider range of products - (i.e. diversification) - this then creates opportunities for economies of scope
reduces competition by removing one or more key rivals - this increases market share and long-run pricing power
buying an existing and well-known business can be cheaper in the long run than organically growing a brand - this then makes entry barriers into a market higher for potential rivals
potential drawbacks of horizontal integration
risk of diseconomies of scale from the enlarged businesses
reduced flexibility - the addition of more personnel and processes means the need for more transparency and therefore, more legal accountability and red tape
mergers risk destroying shareholder value rather than creating it: This often happens because synergies never materialize despite the potential benefits
risk of attracting scrutiny from competition authorities who might be worried that a horizontal merger might lead to a substantial lessening of competition in a market which could then lead to a decline in consumer welfare. e.g. A merger between Sainsbury and Asda was blocked on competition grounds in 2019.