Protists: Part 2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What domain do all protists belong to?
Domain Eukarya
What type of group is Protista considered?
A paraphyletic group
What is primary endosymbiosis?
The process where a eukaryotic cell engulfs a prokaryotic cell, leading to the formation of organelles like chloroplasts.
What are examples of convergent evolution in protists?
Photosynthesis, multicellularity, sessility, and cellulose in cell walls/plates.
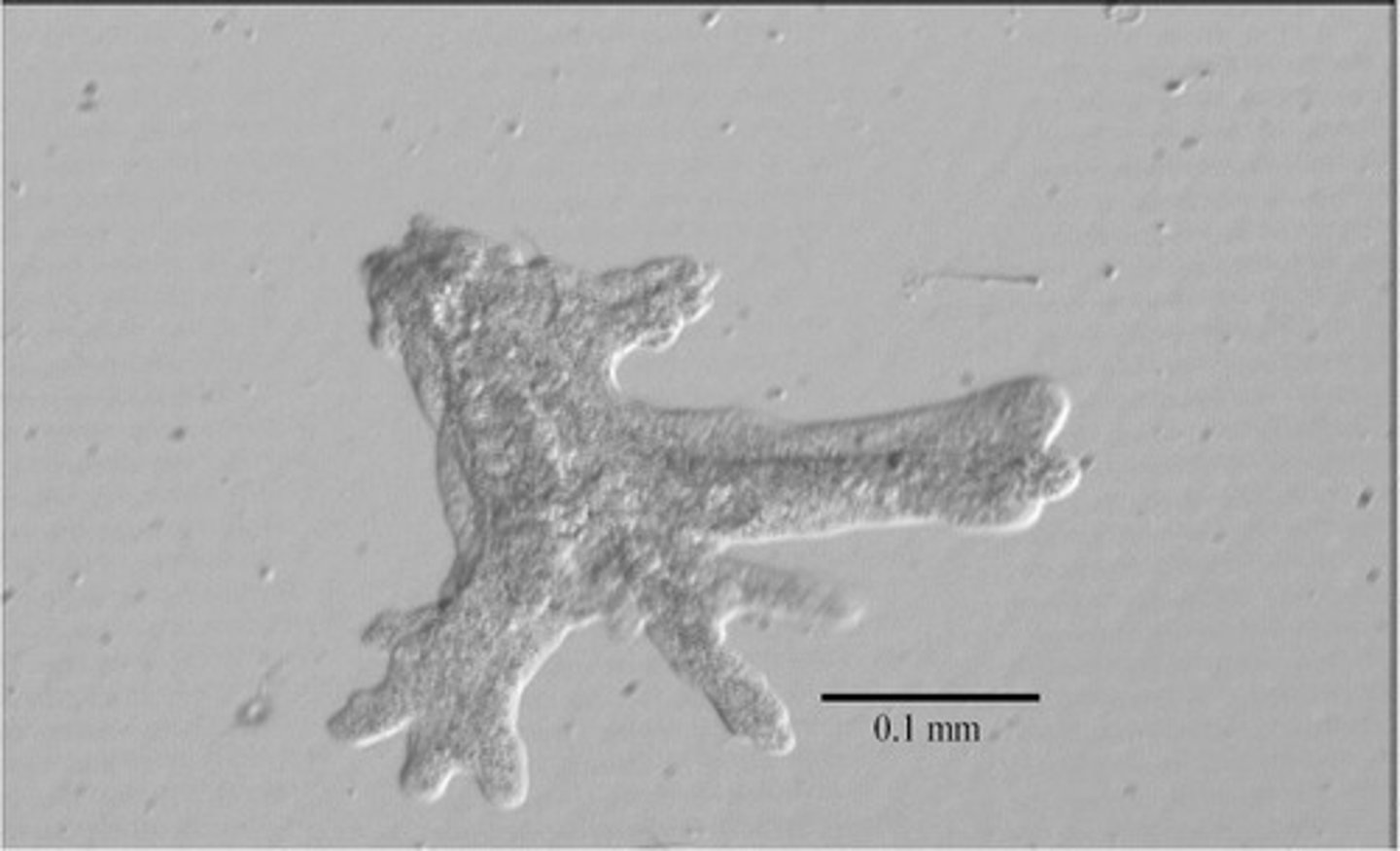
What are the defining features of Amoeba proteus?
Freshwater, pseudopodia, cytoplasmic streaming, contractile vacuole, some are parasitic.
What is a notable fact about the 'brain-eating amoeba'?
It is actually an excavate, not an amoeba.
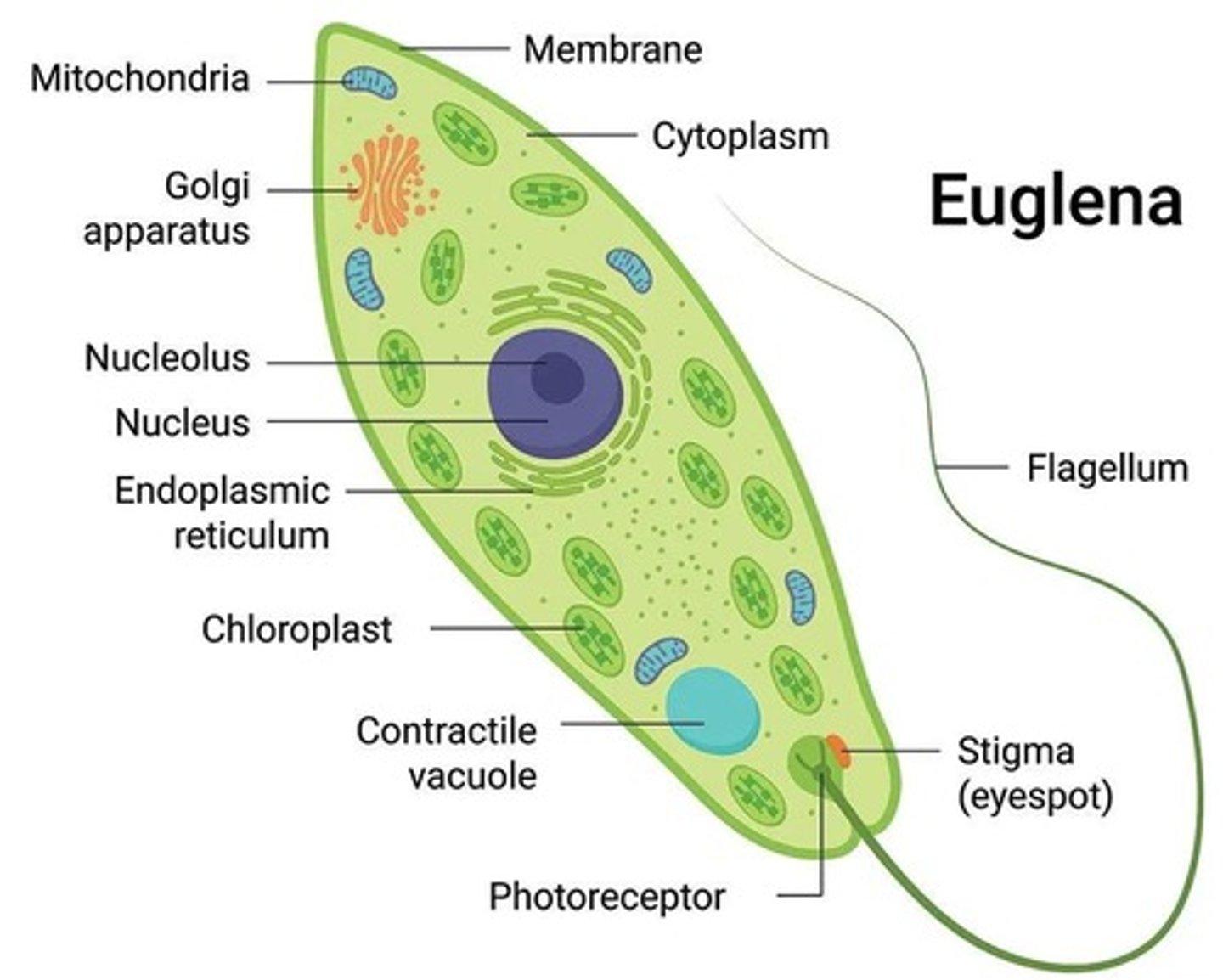
What are the defining features of Euglena?
One flagellum, pellicle strips, eye spot, contractile vacuole, some are heterotrophic.
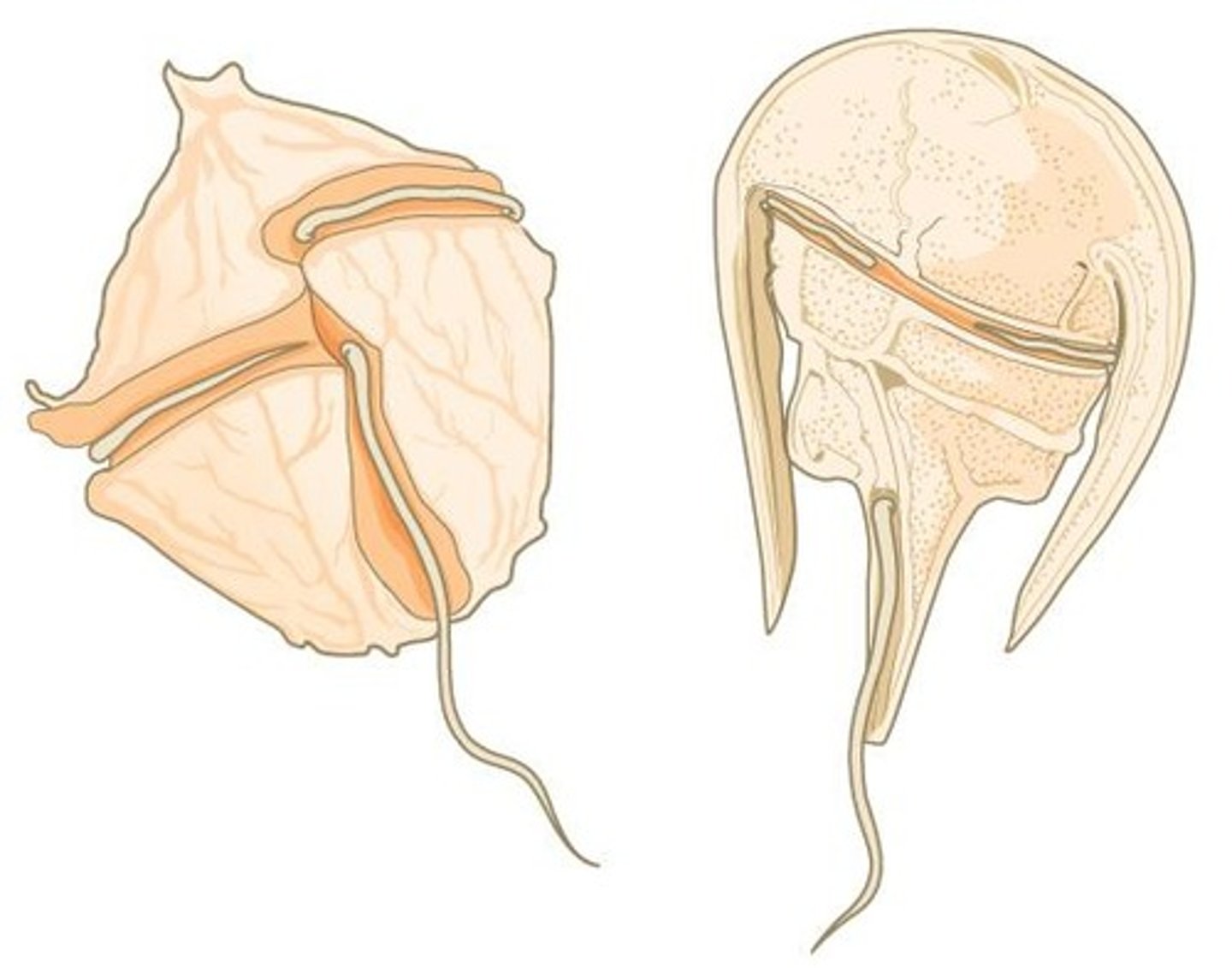
What structures do dinoflagellates possess?
Cellulose plates (armor) and some are bioluminescent.
What is the role of dinoflagellates in coral reefs?
They live in mutualism with coral, providing nutrition through a symbiotic relationship.
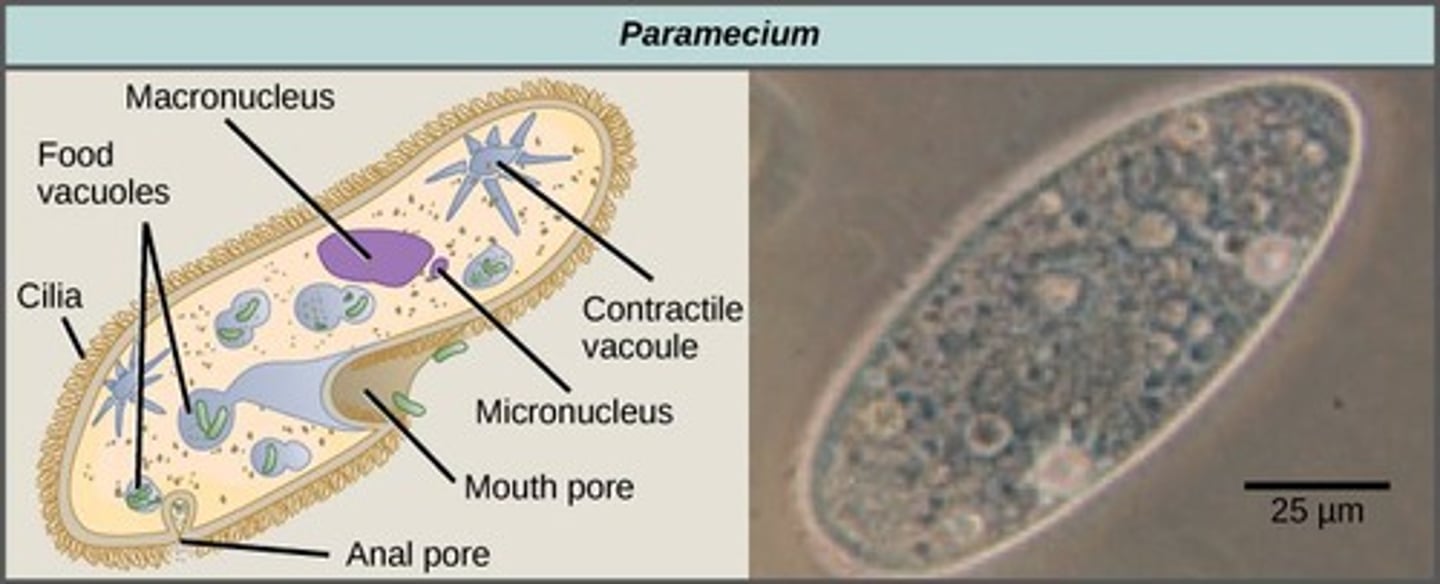
What are the defining features of ciliates?
Found in fresh and salt water, propel through water using cilia, possess a contractile vacuole and an oral groove.
What are the characteristics of brown algae?
All multicellular, mostly marine, photosynthetic, and contain the brown pigment fucoxanthin.
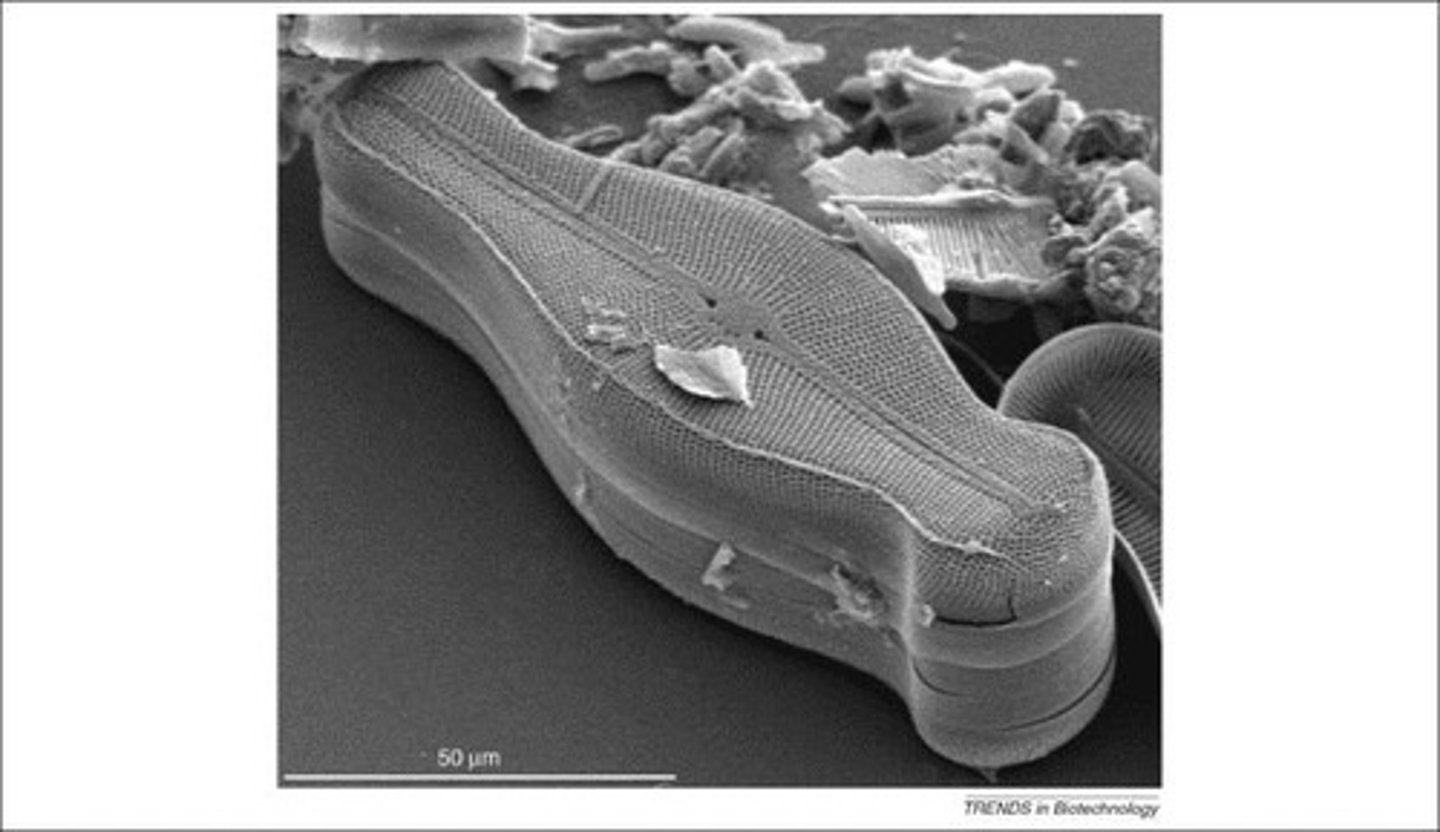
What defines diatoms?
Unicellular, photosynthetic phytoplankton with silica cell walls; they are mined for diatomaceous earth.

What are the defining features of red algae?
Many are multicellular, common in deep tropical waters, and contain red pigments (phycoerythrin).
What distinguishes green algae?
Diverse forms and life cycles, found in both freshwater and marine environments, includes chlorophytes and charophytes.
What is the zygotic meiosis life cycle?
The only diploid stage is the zygote; haploid cells undergo mitosis to form gametes.
What defines a haploid dominant life cycle?
The organism spends most of its life cycle in the haploid stage.
What is the gametic meiosis life cycle?
The only haploid stages are the gametes; diploid organisms undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes.
What is the sporic meiosis life cycle?
Involves alternation of generations where meiosis produces haploid spores and mitosis produces gametes.
What are the ecological roles of protists?
They serve as primary producers, contribute to food chains, and provide nutrition.
What was the cause of the Irish potato famine?
It was caused by the oomycete Phytophthora infestans, leading to massive crop failure.
What is Giardia intestinalis known for?
It causes giardiasis, also known as 'backpacker's disease' or 'beaver fever.'
What is the life cycle of Plasmodium?
It causes malaria and is characterized by nonphotosynthetic plastids and infectious spores.
What disease does Trypanosoma cause?
It causes sleeping sickness, affecting the nervous system.
What are red tides?
Blooms of dinoflagellates that can lead to massive fish kills and shellfish poisoning.