FI Unit 1: Biochemistry
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Properties of water
adhesion, cohesion, surface tension, specific heat
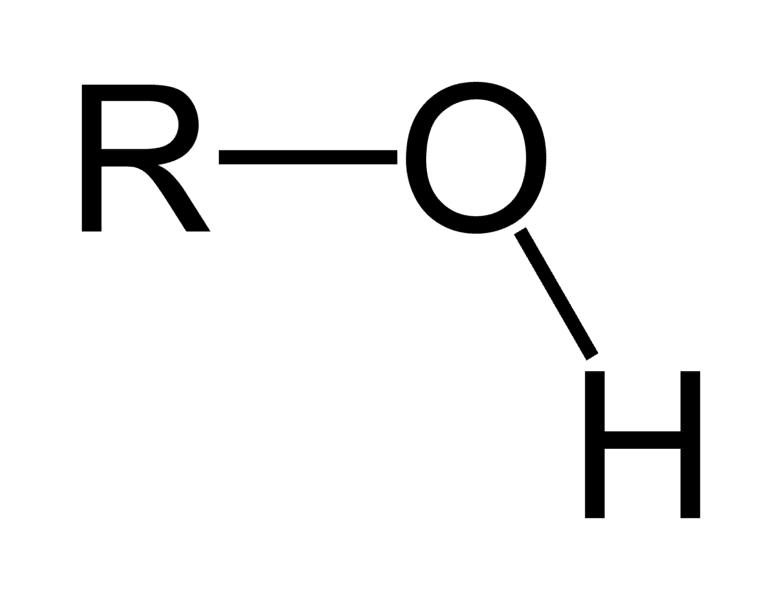
polar
Hydroxyl group
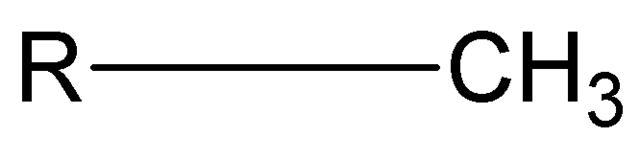
nonpolar
Methyl group
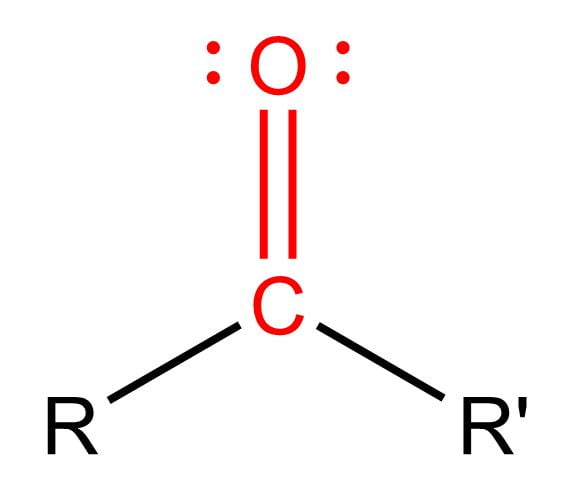
polar
carbonyl group
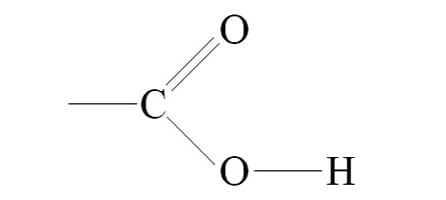
charged and acidic
carboxyl group
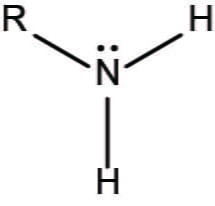
charged and basic
amino group
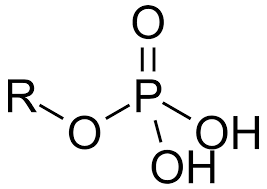
charged and acidic
Phosphate group
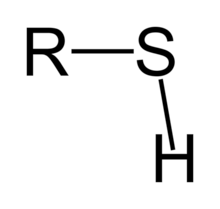
polar
sulfhydryl group
Proteins structure
amino acid sequences + environment determine shape, diverse chemical identities due to R-group
Carbohydrates structure
made of sugars, long chains, hydrophilic
Nucleic Acids structure
made of nucleotides, mostly hydrophilic, helical in shape
Lipid structure
made of fatty acids (1. fats 2. phospholipids 3. steroids), mostly hydrophobic
Protein Function
“workers” of life, enzymes, hormones, receptors, transporters, antibodies
Forward reactions
Endergonic (requires energy), Dehydration synthesis (removal of water), Anabolic (builds larger molecule)
Peptide bonds
bond amino acids together, polar covalent, nitrogen and carbon bond together
N-terminus
Side of polypeptide chain with amine group
C-terminus
Side of polypeptide with carbonyl group
Primary proteins
sequence of amino acids
Secondary structure
interactions of nearby amino acids
Tertiary structure
3-D shape of protein
Quaternary structure
interactions of protein subunits
Alpha helix
secondary structure, carbonyl group forms hydrogen bonds with amine group 4 units away
Beta sheets
secondary structure, carbonyl groups form hydrogen bonds with amide groups in different parts of polypeptide
Steric hindrance
determined by R-groups, molecules repel if take up same space, if R-groups too big, stabilization via hydrogen bonds cannot occur
Tertiary structure
Determined by R-groups that interact during backbone folding
Disulfide bonds
between 2 cysteines, very strong and cannot be broken by heat
Ionic bonds
Between acidic and basic R-groups
How proteins interact with oil
Fold in on themselves to interact with each other and not nonpolar oil
How proteins interact with salt/acid
Ions get in the way of R-group bonding and disrupt protein folding
Sugars function
energy, structure, biological specificity
Backwards reactions
Exergonic (lose energy), hydrolysis (break up water), catabolic (break down molecules)
How carbs used for structure
cell walls, exoskeleton, backbone of nucleic acid
Carbohydrates biological specificity
glycoproteins, glycolipids, on outside of molecules
Types of polysaccharides
starch + glycogen (alpha-helices), cellulose and chitin (beta-linkages)
Starting amino acid
Methionine
How do enzymes accelerate reactions
bonding to substrate + holding them in proper conformation + making different exchanges of electrons possible
Creating intermediate steps
Stabilize transition state allowing more reactions to happen over a period of time
cofactors
vitamins/divalent cations, helps substrate fold and holds it in place
coupled reactions
energy release of 1 reaction drives another reaction
Nucleic acid function
information storage (DNA/RNA) and utilization (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA), metabolism (ribozymes)
Nucleotide function
cell energetics (ATP) and cell signaling (cAMP)
DNA structure
3 phosphate groups (acidic), ribose sugar (polar), nitrogenous base
DNA vs RNA
RNA has OH on 2’C DNA has H on 2’C making RNA more polar and prone to interactions/reactions
pyrimidines
1 ring, Thymine (DNA), cytosine (both), uracil (RNA)
Purines
2 rings, adenine (both), guanine (both)
Bond holding nucleotides together
phosphodiester bond, between phosphate group and 3’ C
mRNA
carries info from DNA to make proteins, single-stranded
tRNA
translator between language of nucleic acids and language of proteins + builds primary structure of protein, double-stranded,
rRNA
part of ribosomes, enzyme that forms peptide bonds, double-stranded
Lipid function
cell energetics (triglycerides, fats and oils), cell membranes (phospholipids, steroids), signaling (steroids, fatty acids)
Saturated fatty acids
single bonds only, pack closely together and strong hydrophobic interactions so more energetically favorable
Unsaturated fatty acids
contain double bonds, kinked and rigid so cannot pack closely, more movement
Why do nonpolar bonds have more energy
electrons further away from nucleus have more energy —> electrons equally shared in nonpolar bonds so further from both nuclei creating more potential energy
Phospholipids
made up of unique polar phosphate heads and nonpolar fatty acid tails, spontaneously assemble in water
Steroids
Hydrocarbon rings + polar functional groups, can pass through cell membrane but polar functional groups make this process slower