Lecture Quiz: 10.13.25 (Photorespiration, Mitosis, Meiosis)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Photorespiration
when there is high oxygen content, plants will begin to use oxygen as a reactant than carbon dioxide
Rubisco will bind of O2 rather than CO2
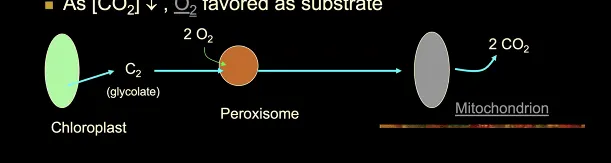
Bundle-sheath cells
underneath the mesophyll cells that help C4 plants offset the wastefulness of photorespiration
CO2 fixed in the normal Calvin Cycle by rubisco
enzymes in the Calvin cycle are only here
PEP carboxylase
enzyme in C4 and CAM plants that fixes CO2 into an organic acid
C4 pathways: CO2 → oxaloacetate
CAM pathways: CO2 → malate
Malate
a 4C molecule that can go into the bundle sheaths and gets decarboxylated into pyruvate to go back into the mesophyll cell (C4 plants & CAM (during the night))
phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP)
A 3C molecule that accepts carbon molecules from CO2, and when attached to PEP carboxylase which will be converted to oxaloacetate
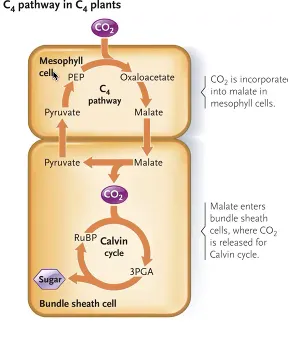
C4 Plant
type of tropical plants that has CO2 get fixed in the mesophyll cell by PEP carboxylase forming oxaloacetate
organic acid will be transported to bundle sheath cell and CO2 is released
in the bundle sheath cell → CO2 is fixed in the Calvin Cycle by rubisco
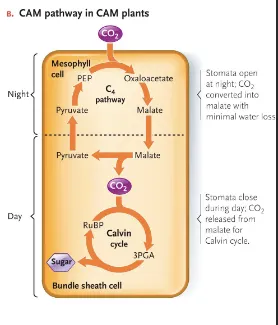
CAM Plant
type of plants that fix CO2 to oxaloacetate then produce CO2 for the Calvin cycle both occuring in the mesophyll cells
desert plants
PEP carboxylase works at night and the Calvin cycle is during the day
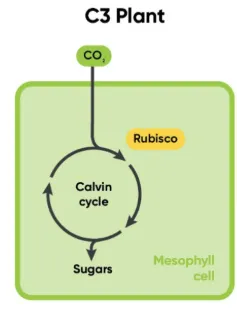
C3 Plant
most plants that use the pathway of photosynthesis where G3P is produced from the Calvin Cycle
germ cells
gametes and spores
essentially another name reproductive cells
cells that give rise to gametes (mature reproductive cells like sperm and egg)
gametes
genome
binary fission
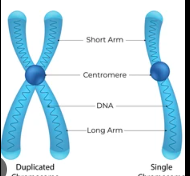
chromosome
a linear structure composed of a single DNA molecule complexed with protein
in prokaryotes → singular with few to no associated proteins
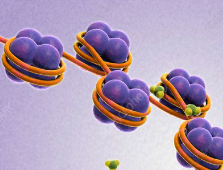
chromatin
the supercoiles of DNA and proteins (50/50)
histones
small positively charged protein that is complexed with DNA in the chromosomes of eukaryotes
help with the folding of DNA
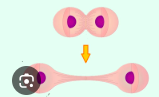
somatic cells
body cells
produced in mitosis
sister chromatids
one of two exact copies of a chromosome duplicated during replication

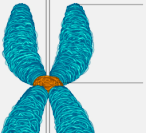
centromere
part of a chromosome where two DNA molecules are hooked together
a single chromosome will have this structure as well
cytokinesis
the division of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells following nuclear division in mitosis or meiosis
cell cycle
mitotically active
events related to DNA molecules going from one episode of cell division to the next
the series of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides into two new daughter cells
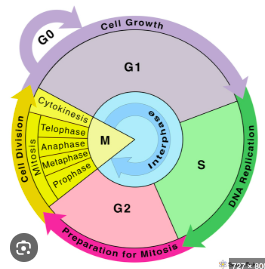
Interphase
the first stage of the mitotic cell cycle where the cell grows and replicates it DNA before undergoing mitosis and cytokinesis
when cells are accumulating Energy and matter from its surroundings → growing and increasing in size
INcreasing in size
longest period of a cell cycle
contains three phases
mitosis
series of events in the eukaryotic cell cycle that results in two nuclei being formed, each containing one complete set of genetic information
G1 Phase
the growth phase of interphase
when the two cells come out of mitotic cell division
smaller than the parent cell
actively increasing in size → taking up material from its surroundings
biosynthesis
S phase
phase of interphase where the synthesis of DNA occurs (where DNA is replicated)
DNA content doubled
contains sister chromatids
anticipates cell division
10 chromosomes (single) in G1 → 10 DNA molecules by the end (20 DNA but 10 chromosomes more like sister chromatids
G2 phase
phase in interphase where duplication of cell division occurs
mitochondria and chloroplast will replicate
end of this phase
nucleus is intact
1-2 nucleoli are present
two centrosomes adjacent to nucleus
chromosomes are not visible
very loose
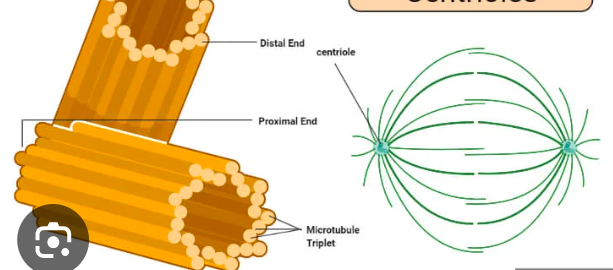
centrosome
where microtubules originate
forms the cytoskeleton and the mitotic spindle during cell division

centrioles
a cylindrical, microtubule-based cellular organelle found in animal cells that is primarily involved in cell division and the formation of cilia and flagella
forms the core of a centrosome
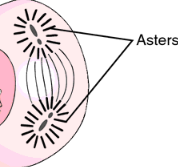
aster
radiating array produced as microtubules extending from the centrosomes of cells grow in length and extent
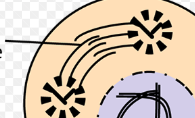
prophase
the beginning phase of mitosis where the duplicated chromosomes within the nucleus condense from a greatly extended state into compact rodlike structures
nucleoli will disappear
in order to have access to the genes they need to disappear to be at a level of relaxation
rRNA are shut down
chromatin condenses
centrosomes move apart
mitotic spindles grow

mitotic spindle
the structure that separates sister chromatids and moves them to opposite spindle poles
Prometaphase
transition period between prophase and metaphase during which the microtubules of the mitotic spindle attach to the kinetochores and the chromosomes shuffle until they align in the center of the cell
nucelar membrane breaks down
no division between condensing chromosomes and cytoplasm
the spindle poles are on opposite sides
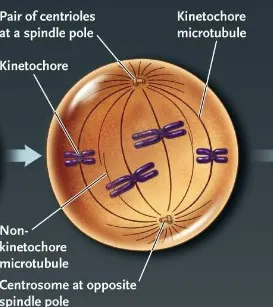
kinetochore
a structure consisting of proteins attached to a centromere that mediates the attachment and movement of the chromosomes along the mitotic spindle
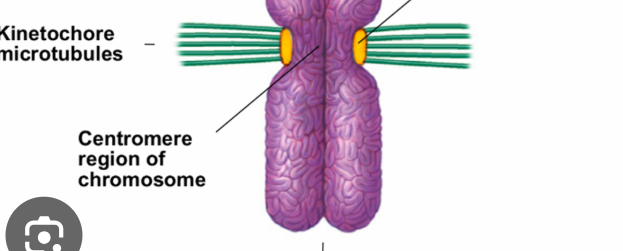
kinetochore microtubules
in mitotic and meiotic spindles, where a microtubule originating from a spindle pole and binding to a kinetochore of a chromosome
are attached to both poles north and south
one is attached to each sister chromatid

nonkinetochore microtubules
a microtubules originating from a spindle pole that doesn’t bind to a kinetochore of a chromosome
metaphase
a phase in mitosis where the mitotic spindle reaches its final form and the spindle microtubules move the chromosomes into alignment at the spindle midpoint
centromeres line up in the middle (on the metaphase plate)

metaphase plate
the spindle midpoint
anaphase
phase in mitosis where the centromeres divide and the sister chromatids are pulled to opposite spindle poles
no longer a chromatid → daughter chromosome which consists of 1 chromatid
kinetochore microtubules start to shorten
poles will begin to move apart and the cell elongates
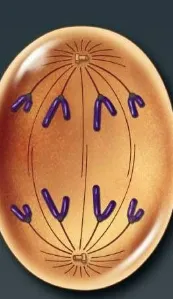
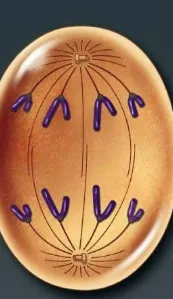
telophase
the final phase of mitosis, where the mitotic spindle disassembles and the chromosomes decondense and the nuclei form (rRNA genes can be accessed)
happens in the metaphase plate
cells continue to elongate
daughter chromosomes are at the poles
vesicles start to fuse together and the nuclear envelope redevelops around the chromosomes
2 daughter cells at the end
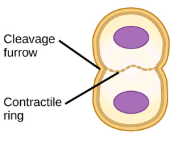
cleavage furrow
in cytokinesis where a contractile ring of microfilaments are in the plasma membrane are along with metaphase plate and tightens constricting the cell forming a groove
clone
individual that is genetically identical to an original cell from which it descended
autosome
any chromosome that isn’t a sex chromosome
sex chromosome
chromosomes that differs between sexes → males and females
homologous chromosome
chromosomes that have the same
size
centromere location (metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric)
staining pattern (light and dark banning pattern)
carrying the genes in a linear sequence
different alleles help with genetic diversity
diploid
2n
2 sets of chromosomes (one from mom other from dad)
2 copies of the genome
haploid
n
1 set of chromosomes (1 of chromosome 1, 1 of chromosome 2, 1 sex chromosome set etc)
human set → 22 autosomes + 1 sex chromosome
asexual reproduction
a mode of reproduction in which a single individual gives rise to offspring without the fusion of gametes
sexual reproduction
form of reproduction that shuffles genetic information
important for evolution as it helps organisms adapt to changing conditions
inheriting genetic information from both parents
gametes fuse together → fertilization
fertilization
where an egg and a sperm fuse together to form a zygote
zygote
a cell that is produced from the fertilization of an egg and sperm
contains 1 set from egg and another set from sperm
spore
a type of germ cell that are in plants where they can start dividing on their own without fusing together
sporophyte
an individual of the diploid generation produced through fertilization in organisms that undergo alternation of generations producing haploid spores
their gametes are a dead end unless they fuse together
gametophyte
produces gametes
in organism where alternation of generations occur in plants in green algae mainly
Meiosis
the division of diploid cells to haploids
consisting of 2 rounds of nucelar and cellular division
meiosis I
the first division of the meiotic cell cycle in which homologous chromosomes pair and undergo an echange of chromosome segments and then the homologous chromosomes separate resulting in two cells
