Year 2 sem 2 anatomy week 6
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
how much oxygen and cardiac output does the brain require?
⅕ of all CO
⅙ of all oxygen supply
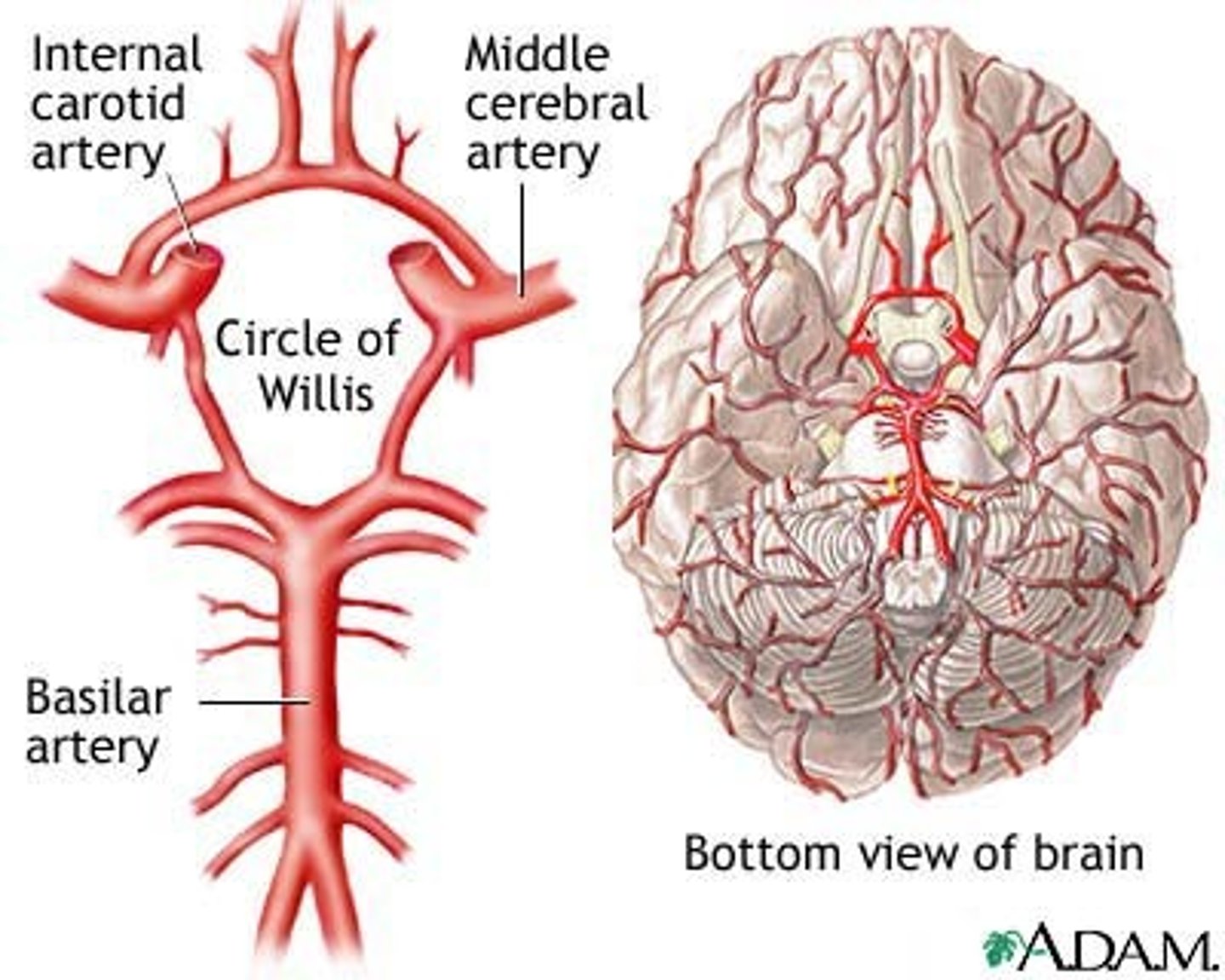
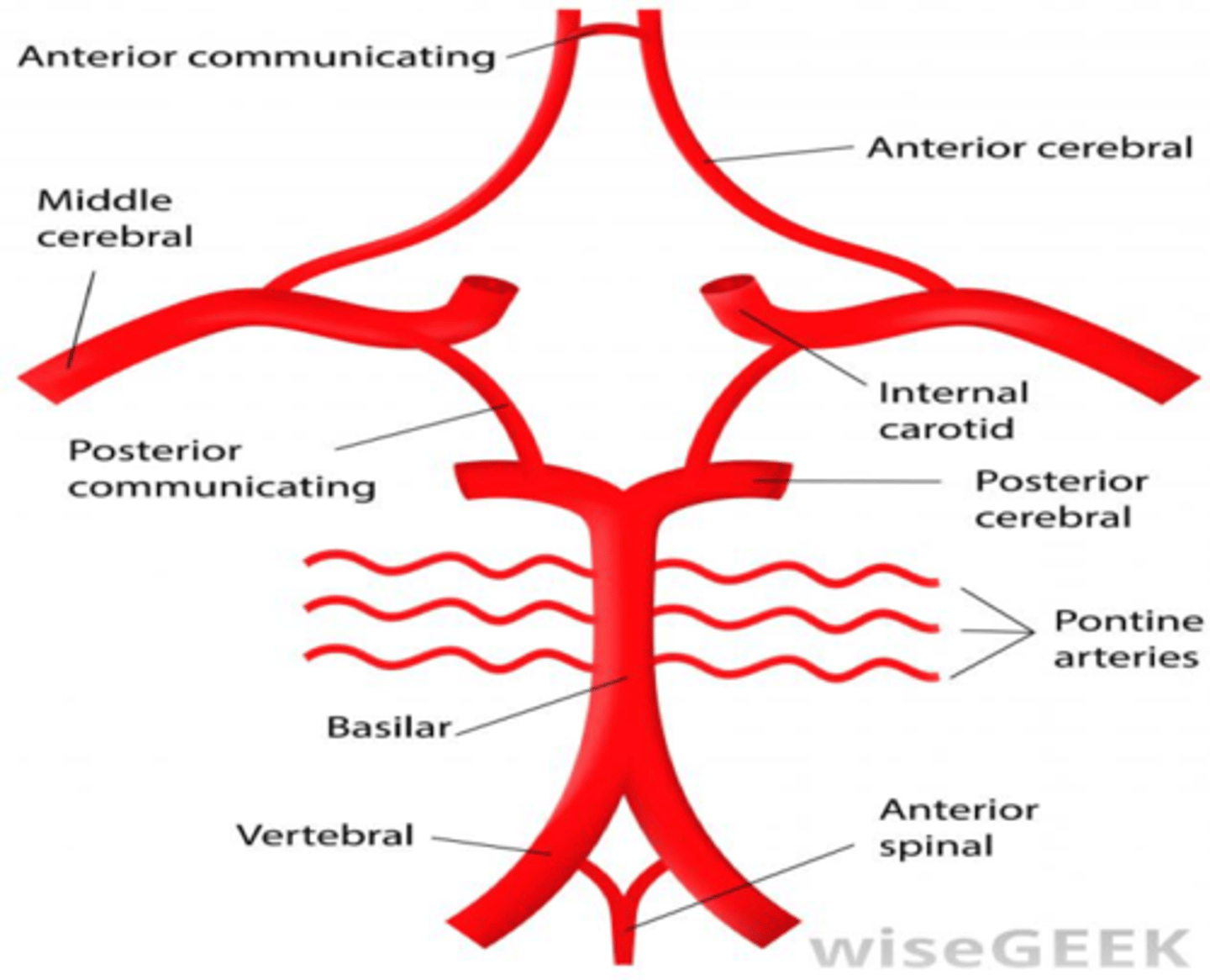
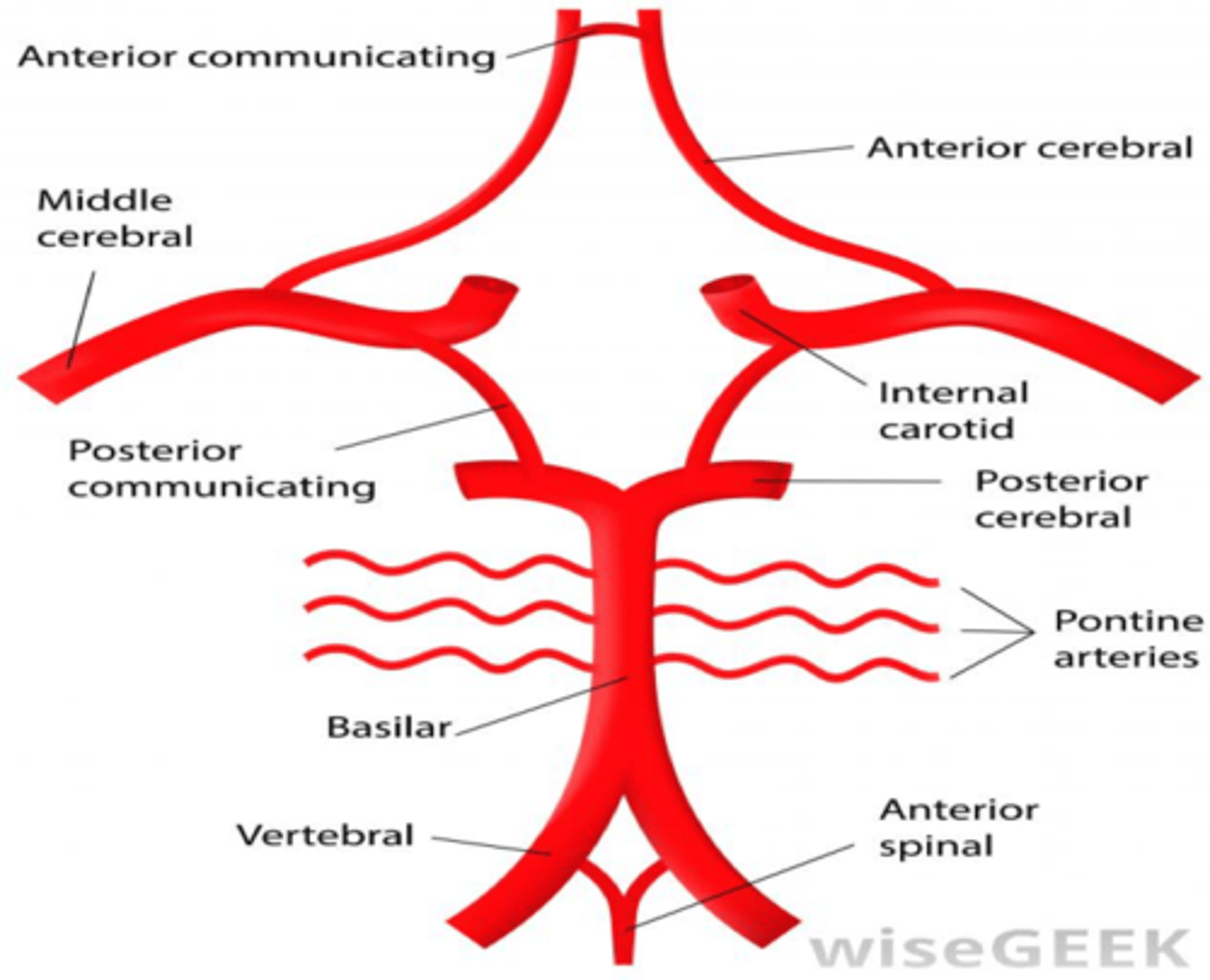
what is the circle of willis?
a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures
where is the circle of willis located?
sits neatly into the interpeduncular fossa
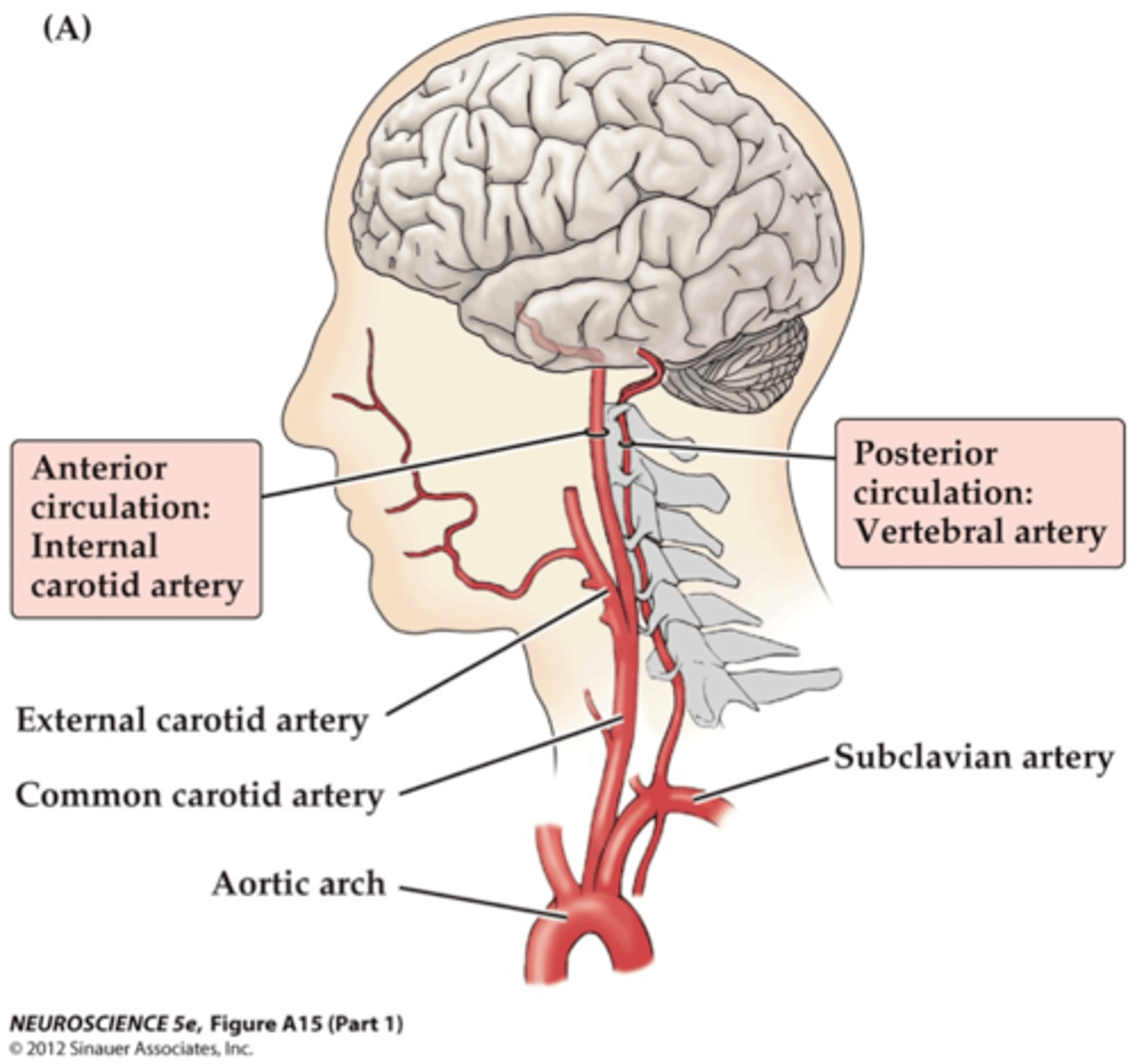
describe how the internal carotid arteries arise from the aorta
Arch of Aorta (L) or brachiocephalic trunk (R)- common carotid artery- internal carotid artery
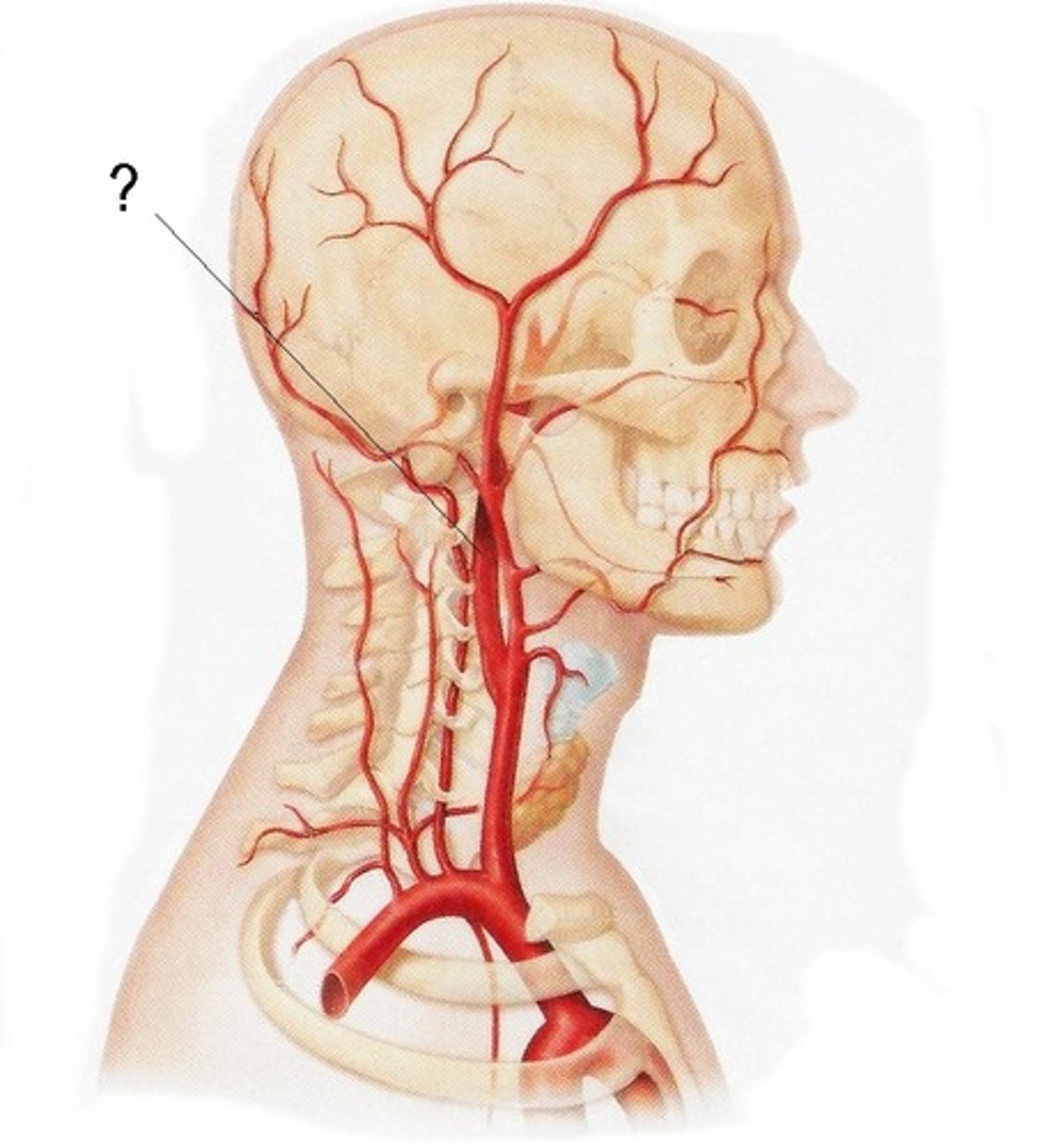
describe the path of the internal carotid arteries
Enters base of cranium via carotid canal just in front of styloid process
Goes through petrous temporal bone
Arches over foramen lacerum
Grooves either side of sella turcica
Curves upwards towards the brain on anterior clinoid process
Carotid system contributes to the anterior circulation of the brain
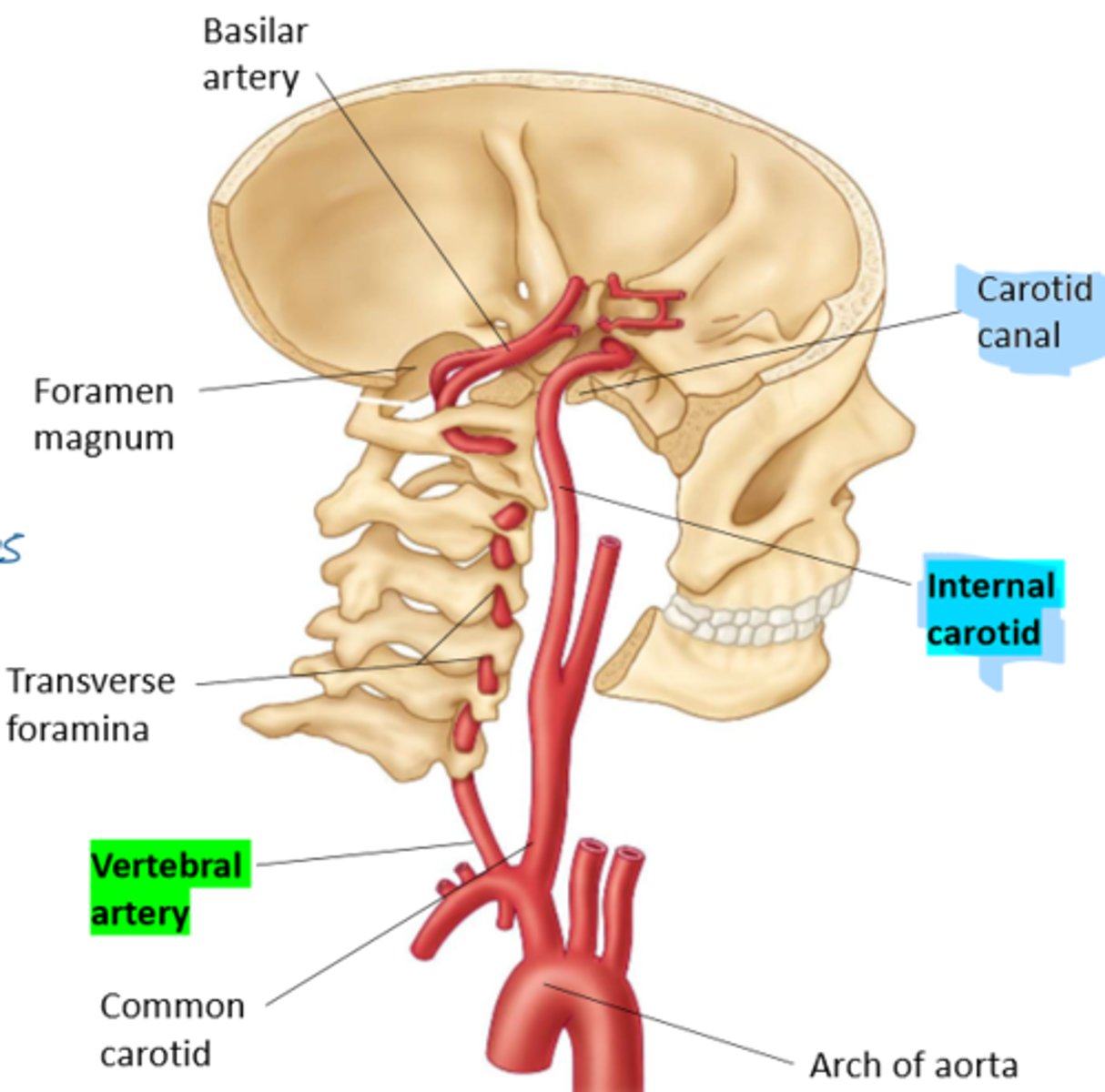
describe the path of the vertebral arteries
Arises from the subclavian artery
Courses through the transverse foramina of C6 - C1
Arches over posterior arch of atlas
Enters the foramen magnum
Immediately unit to form the basilar artery
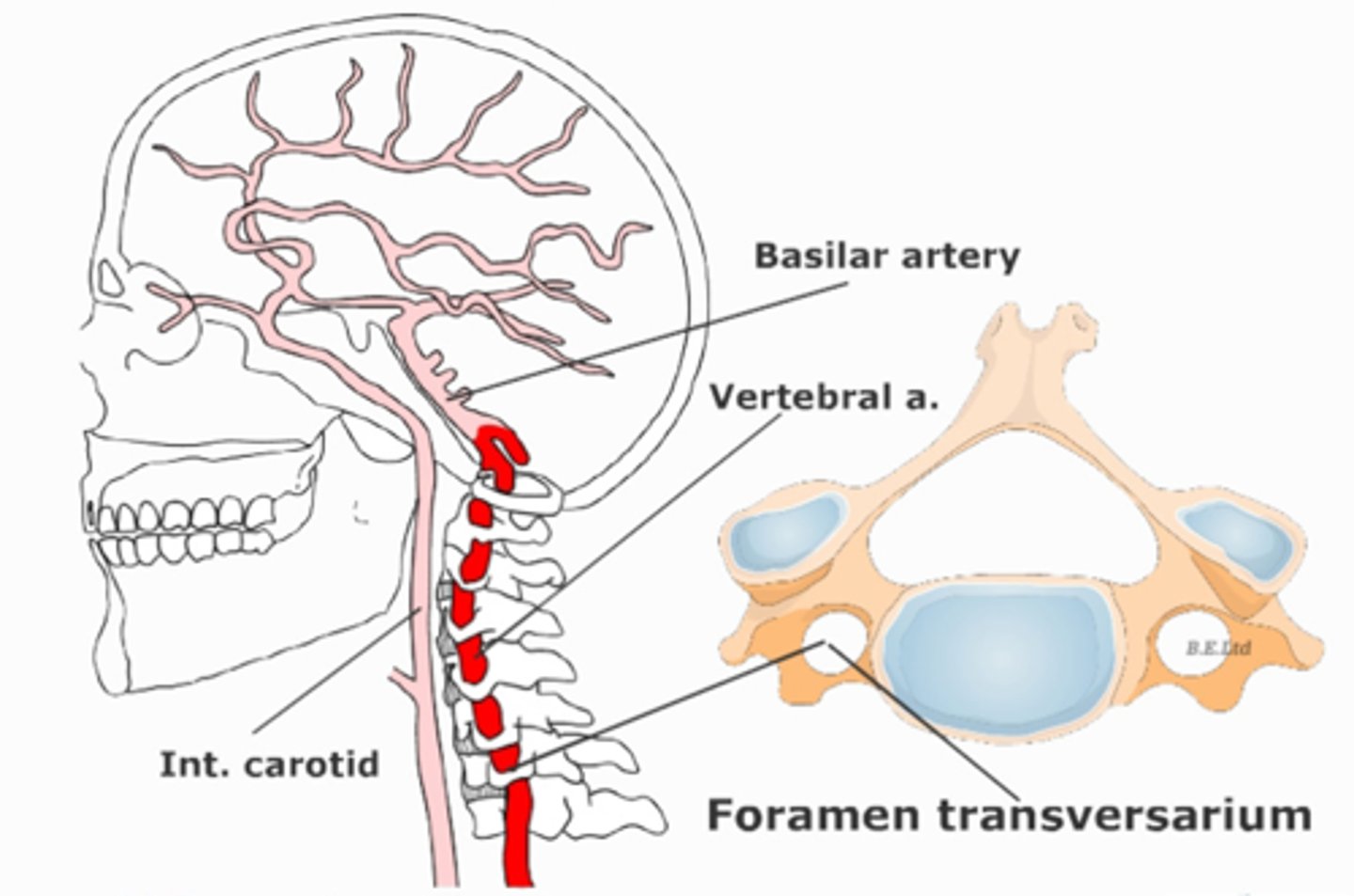
where is the basilar artery located?
sits in front of the basilar pons
Runs on the clivus of the occ bone
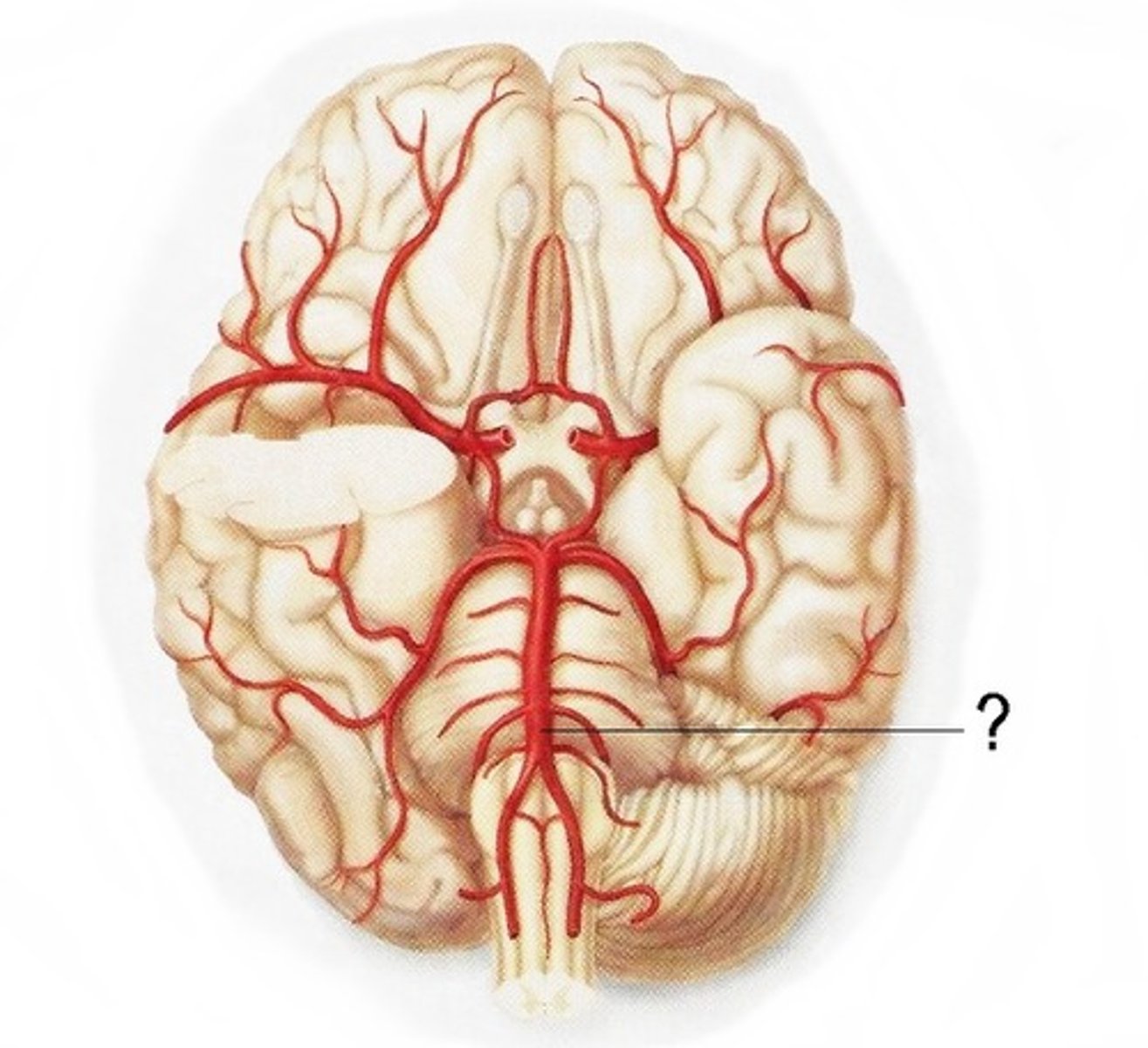
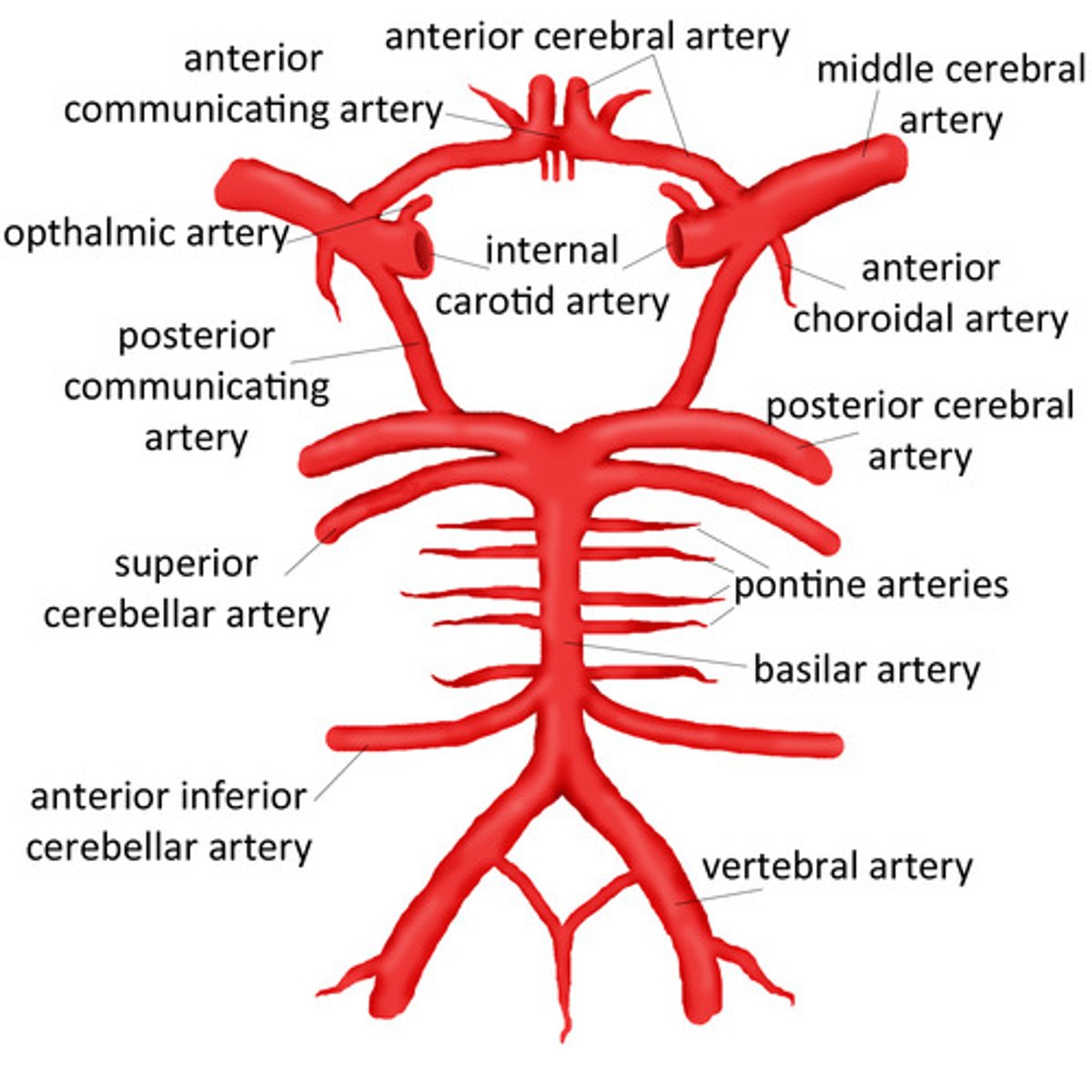
what arteries contribute to the posterior circulation of the brain?
vertebral arteries are the principle arteries of the posterior circulation
also includes the basilar artery, posterior cerebral, pontine arteries and posterior communicating arteries
(anterior spinal artery blends with vertebral arteries before they contribute to the posterior circulation)
also includes the cerebellar arteries
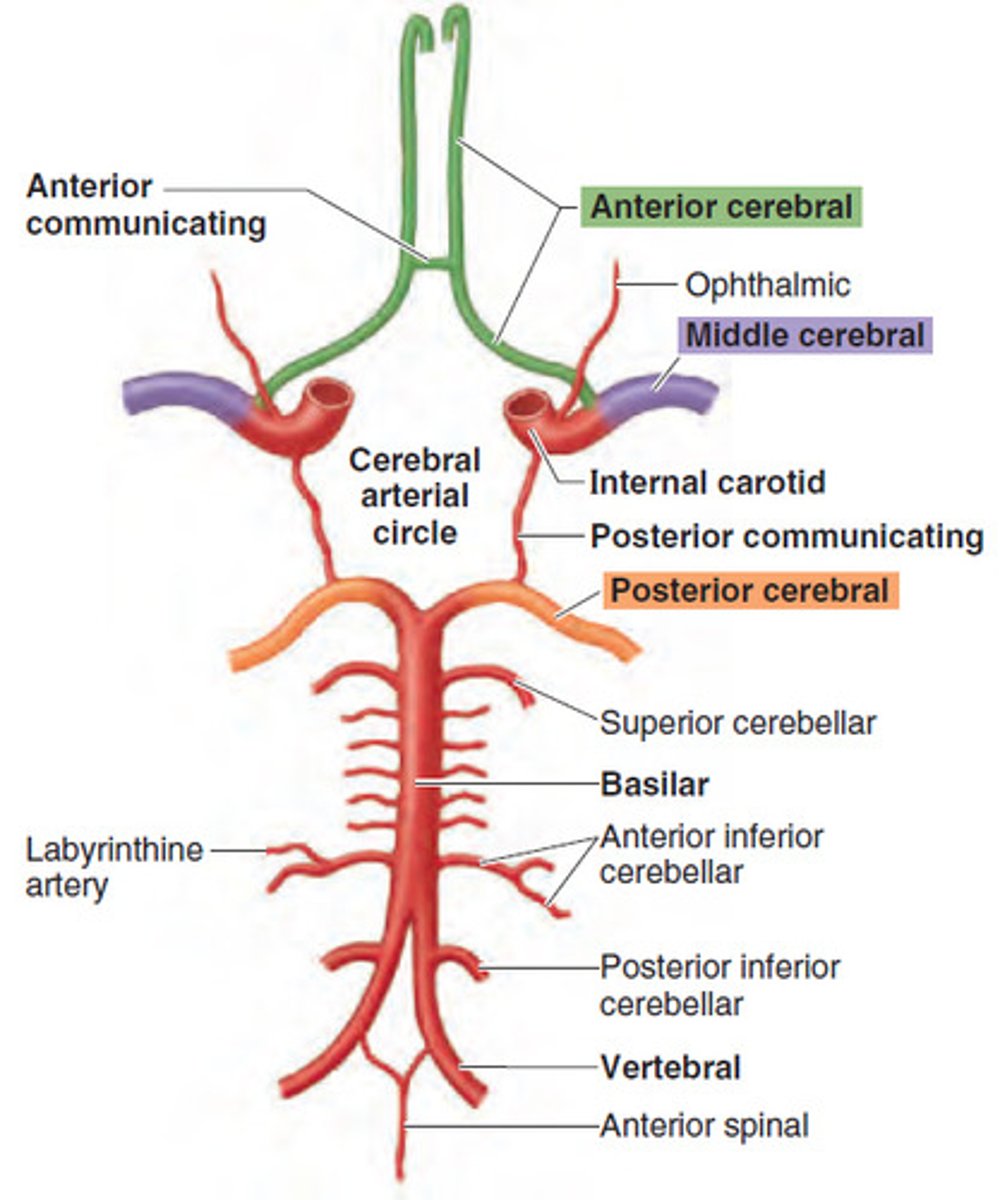
what arteries contribute to the anterior circulation of the brain?
internal carotid arteries are the principle arteries of the anterior circulation
also includes the middle, anterior cerebral arteries and anterior communicating artery
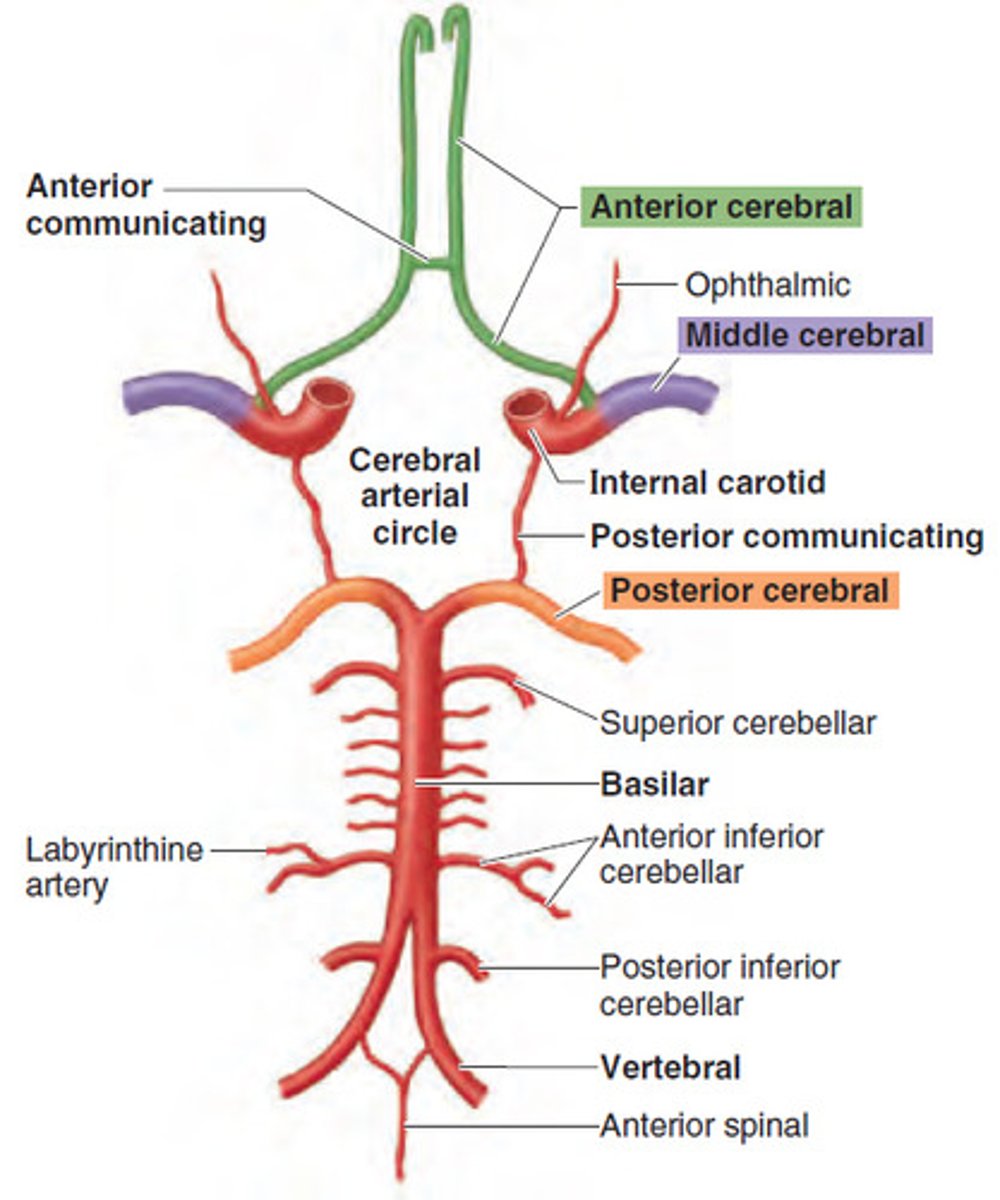
in what dural level do the cerebral arteries sit?
subarachnoid space
how do the posterior cerebral arteries arise?
Basilar artery courses across the pons and at the junction of the pons and midbrain at divides into 2 posterior cerebral arteries
how do the middle and anterior cerebral arteries arise?
internal carotid arteries divide into middle cerebral arteries that head laterally and anterior cerebral arteries that head anteriorly
middle cerebral artery is considered the direct continuation
what type of anastomoses is the circle of willis?
true anastomoses
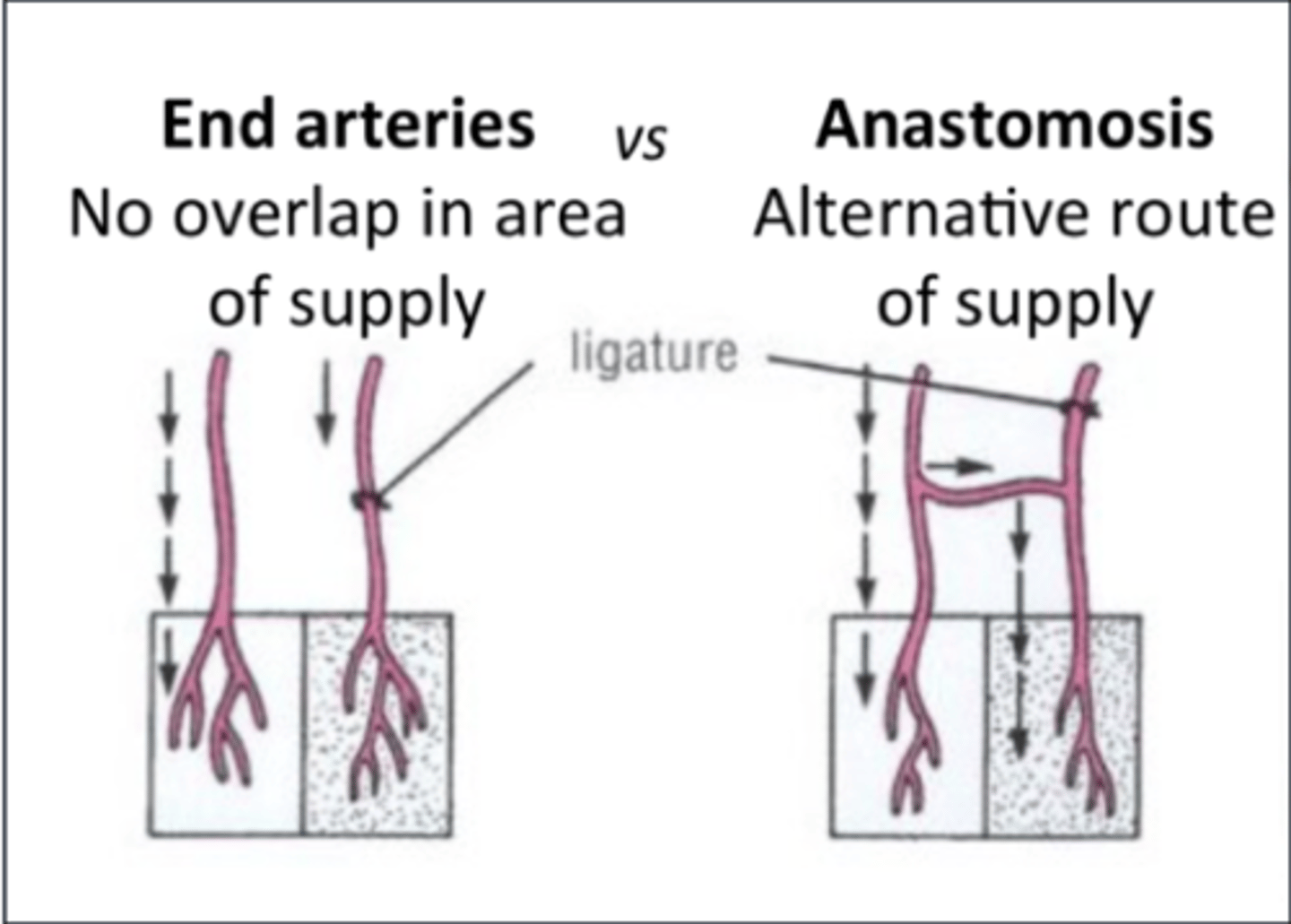
what type of arteries (anastomoses) are the 3 cerebral arteries seperate from the circle of willis?
functional end arteries
The 3 cerebral arteries supplying the forebrain have limited anastomoses (potential) between each other
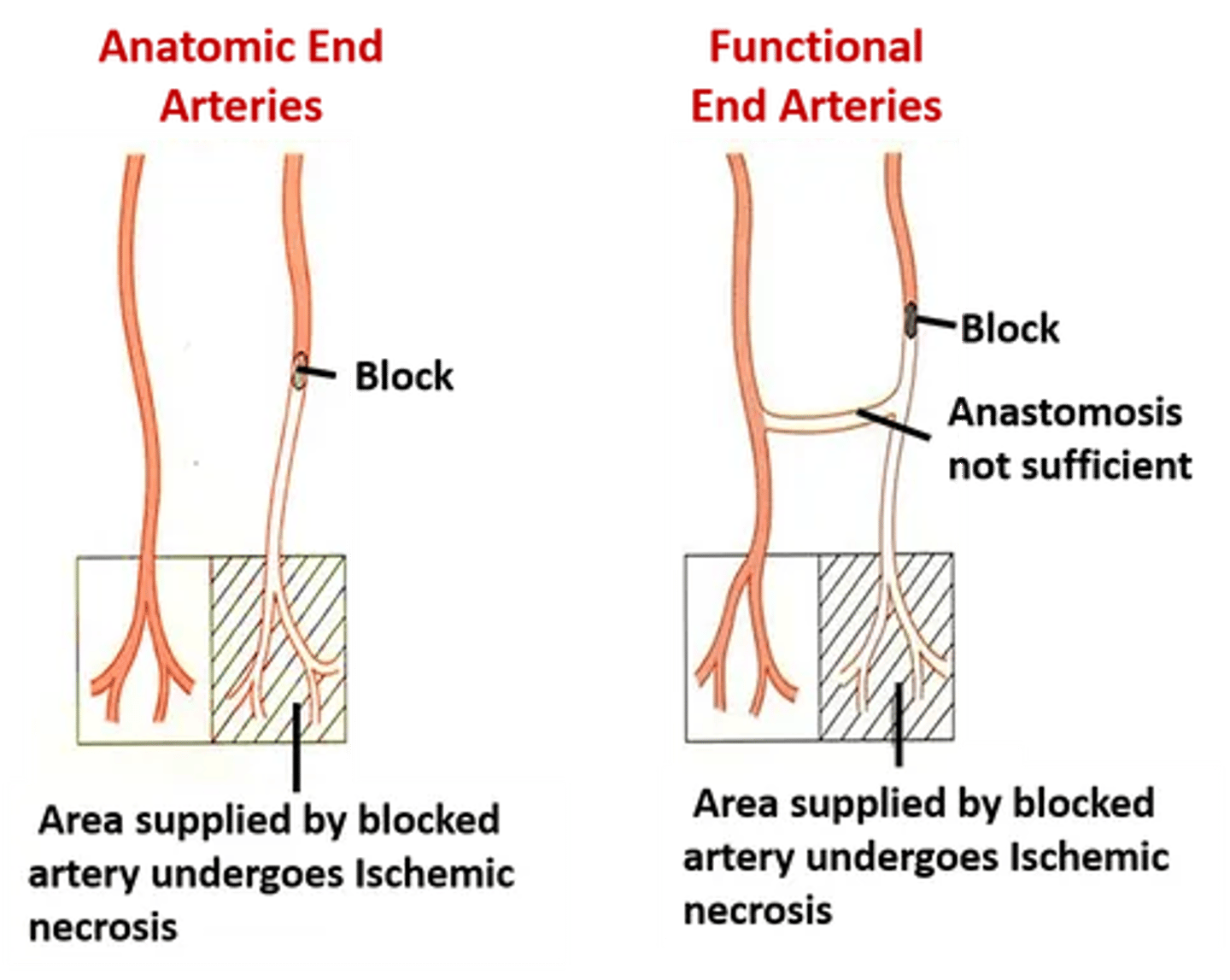
can the deep branches of the cerebral arteries anastomose?
no

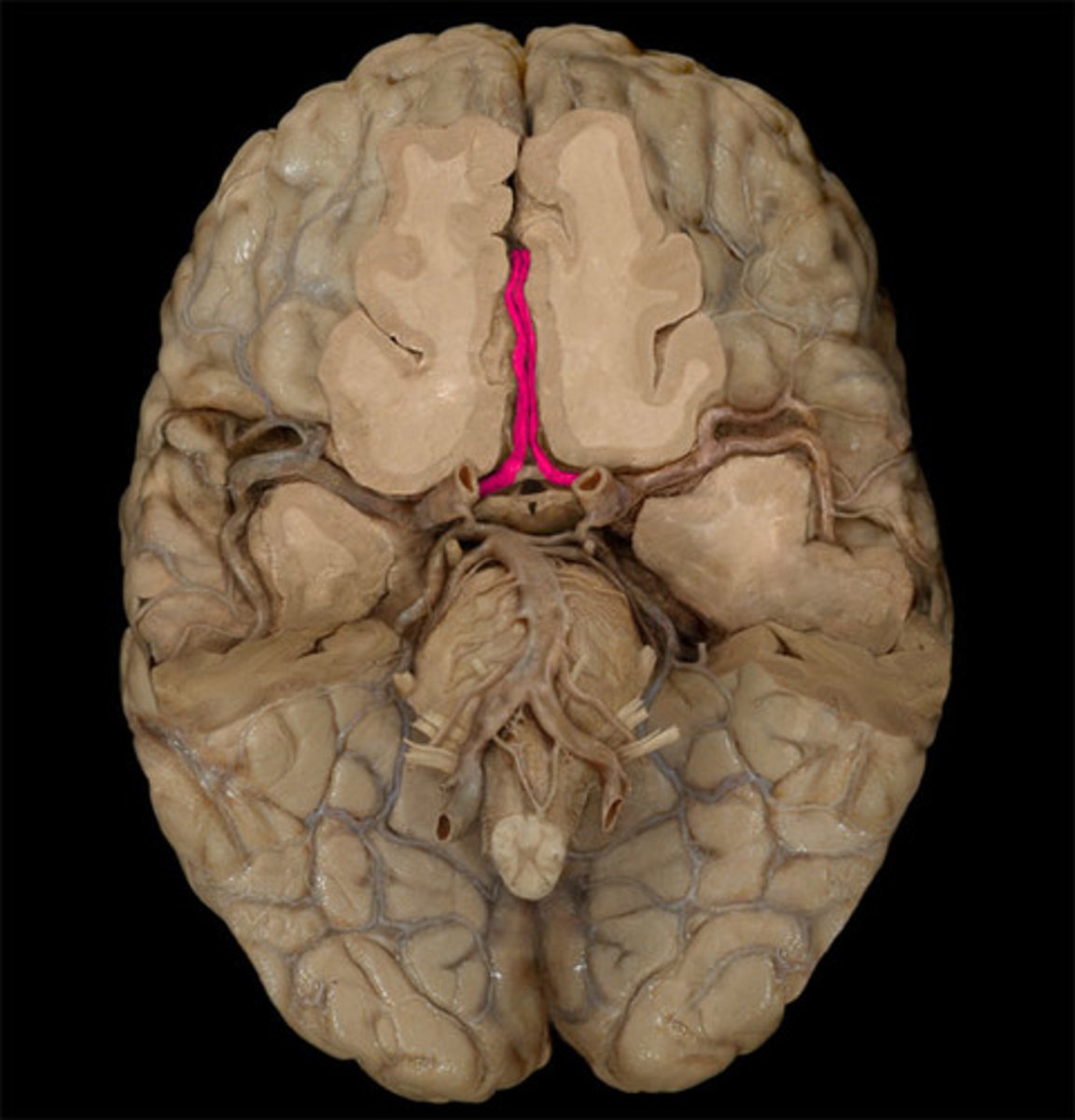
what is the course of the anterior cerebral arteries?
Courses anteriorly and medially
Sits within the longitudinal fissure
Courses backwards over the corpus callosum
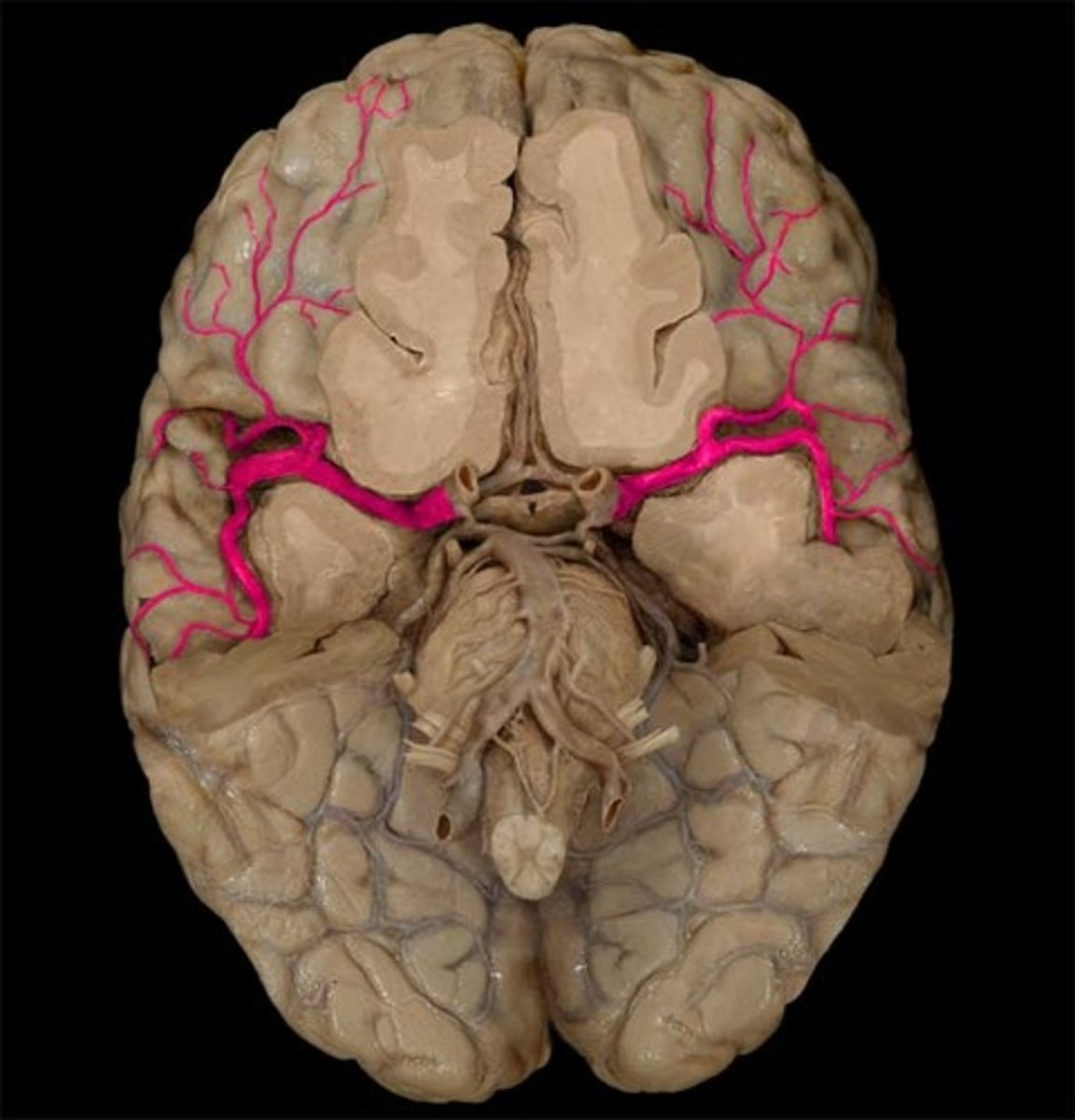
what is the course of the middle cerebral arteries?
Head out laterally
Sits within the lateral fissure
Supplies the lateral cortex
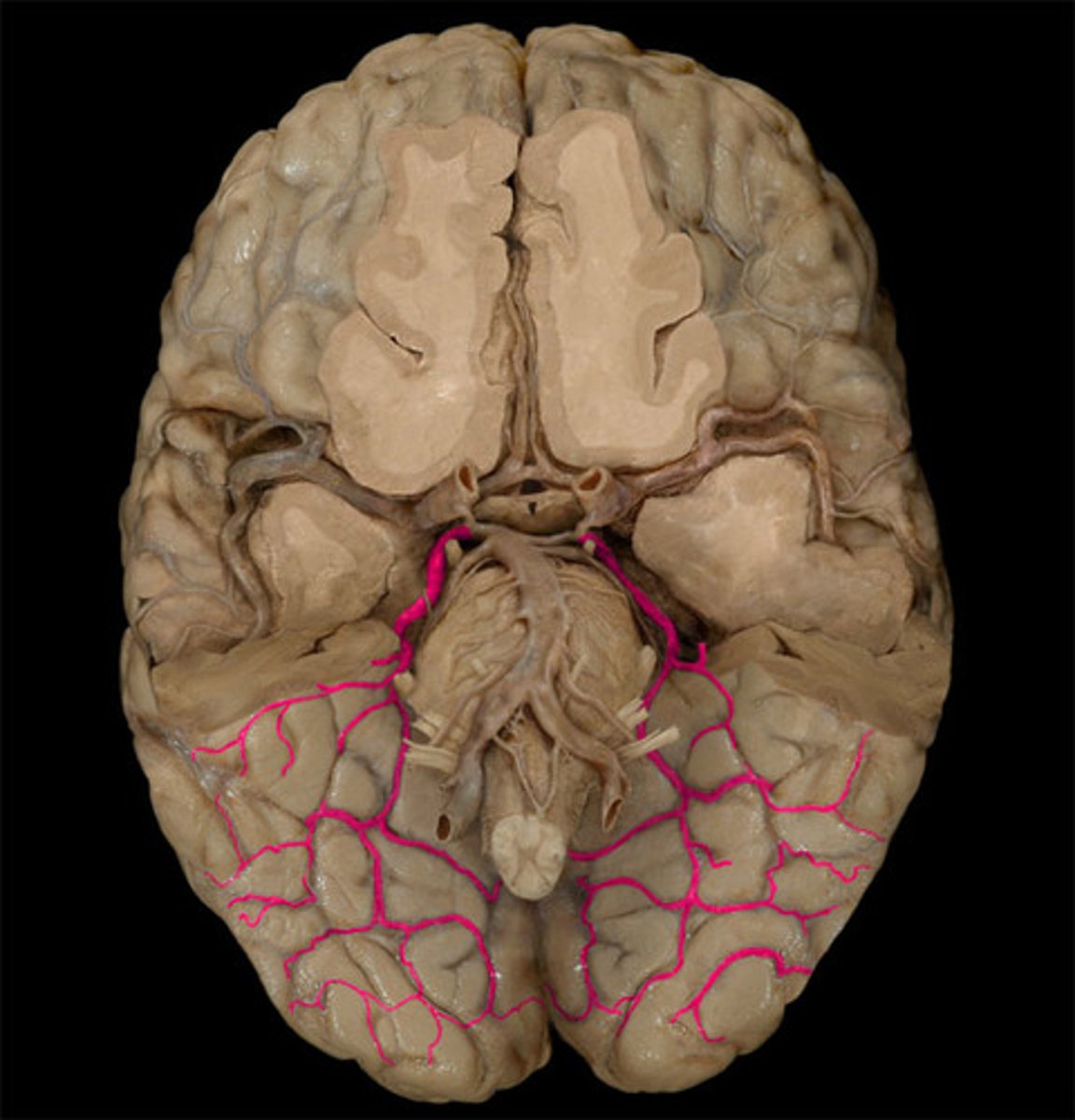
what is the course of the posterior cerebral arteries?
Wrap around the midbrain and head posterior
what does the anterior cerebral artery supply?
Medial aspect of the hemispheres to the hypothalamus
Parietal and frontal lobe
Supplies the medial aspect of primary motor and primary somatosensory cortex and optic chiasm
Thus this artery control LL motor and sensory function (and perineum)
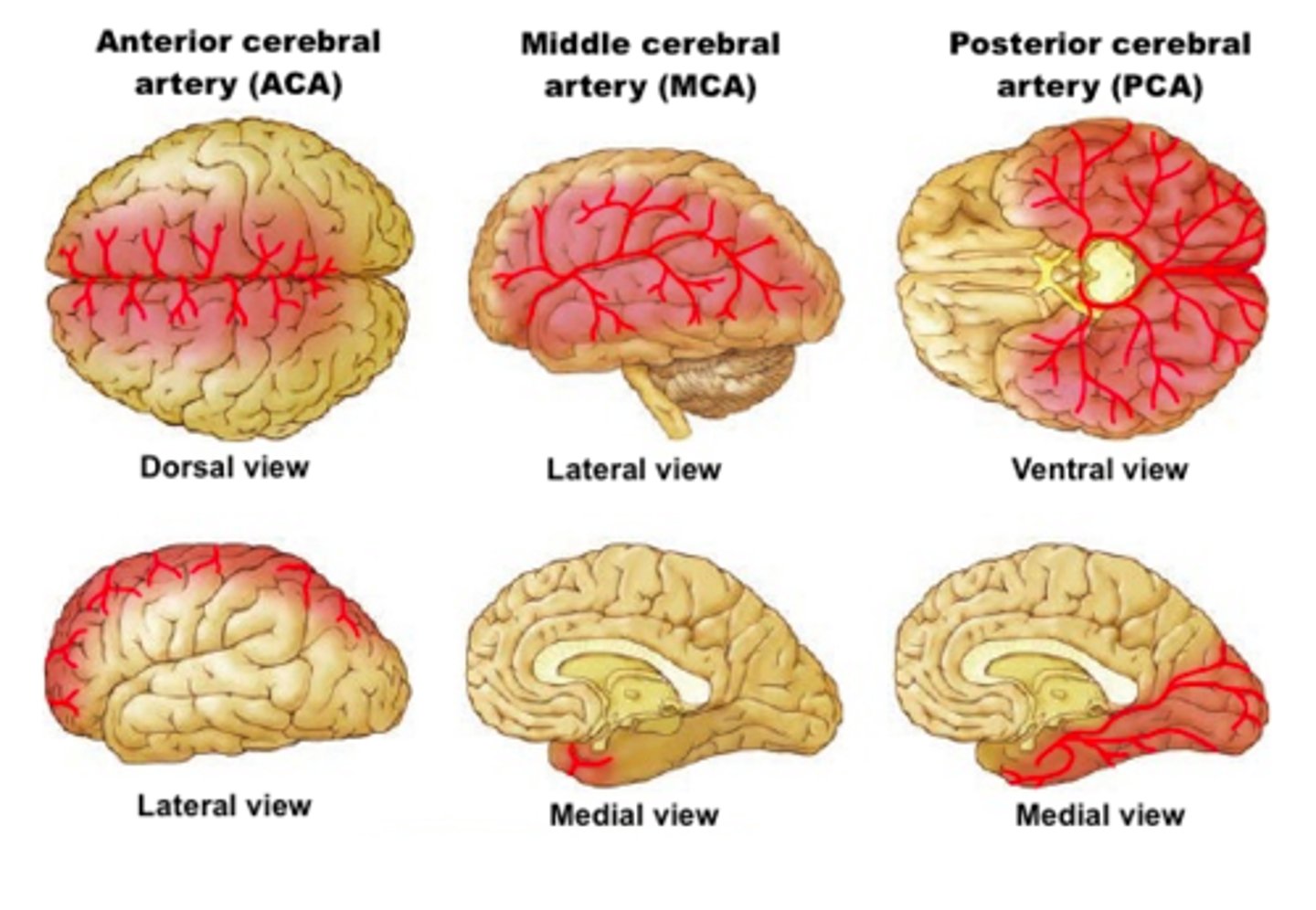
what does the middle cerebral artery supply?
Supplies the insula
Supplies the lateral aspect of frontal, parietal and temporal lobes
Lateral aspect of the primary motor and primary sensory cortexes
Thus this artery supplies the primary motor and sensory cortexes of the upper limb
Controls UL motor and sensory, as well as broca's and wernicke's area
Also supplies basal ganglia and internal capsule with its deeper branches (true anatomical end arteries)
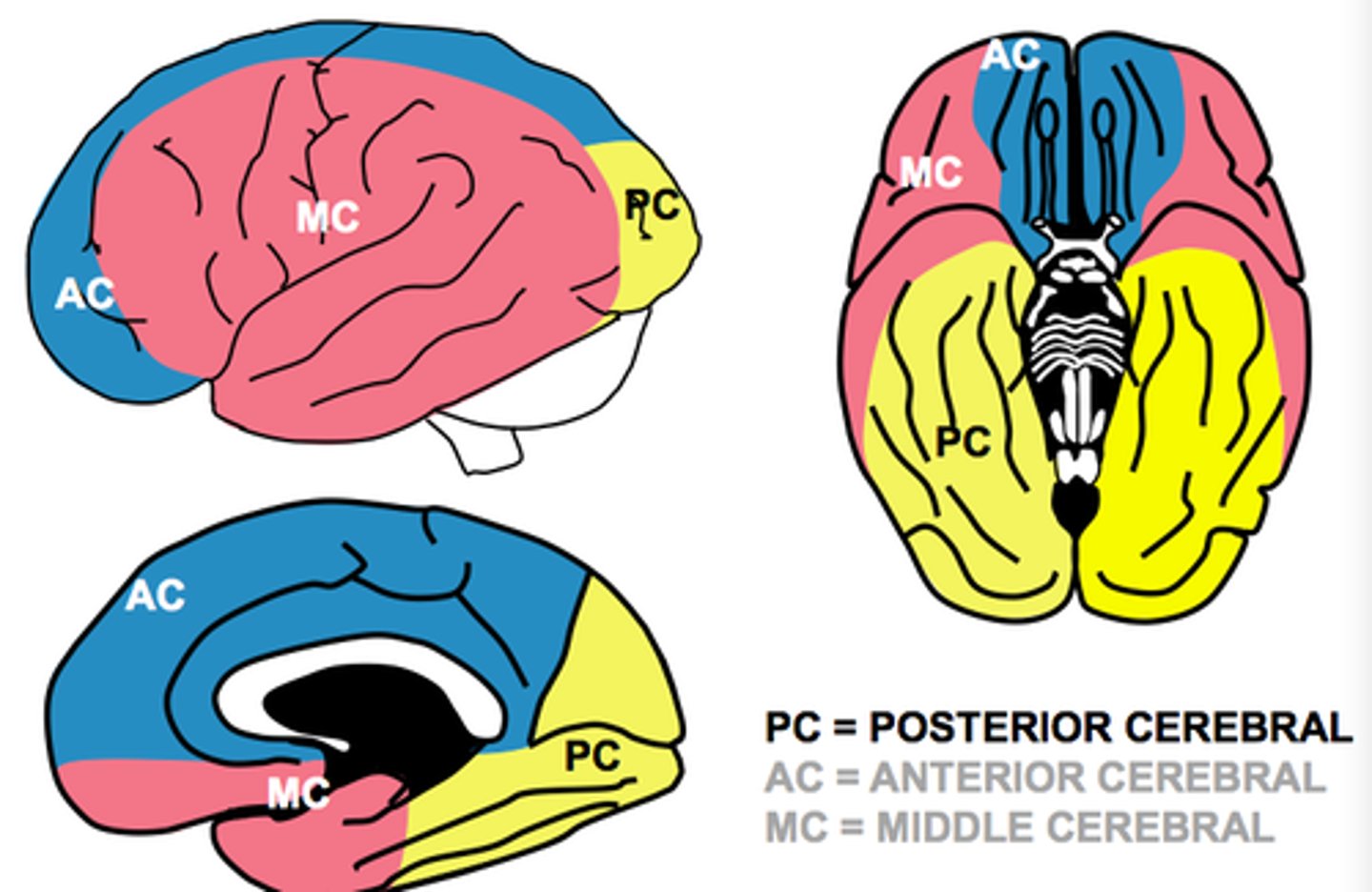
what do the posterior cerebral arteries supply?
Supply the occipital lobe and the inferior portions of the temporal lobe
Thus controls vision, optic tract
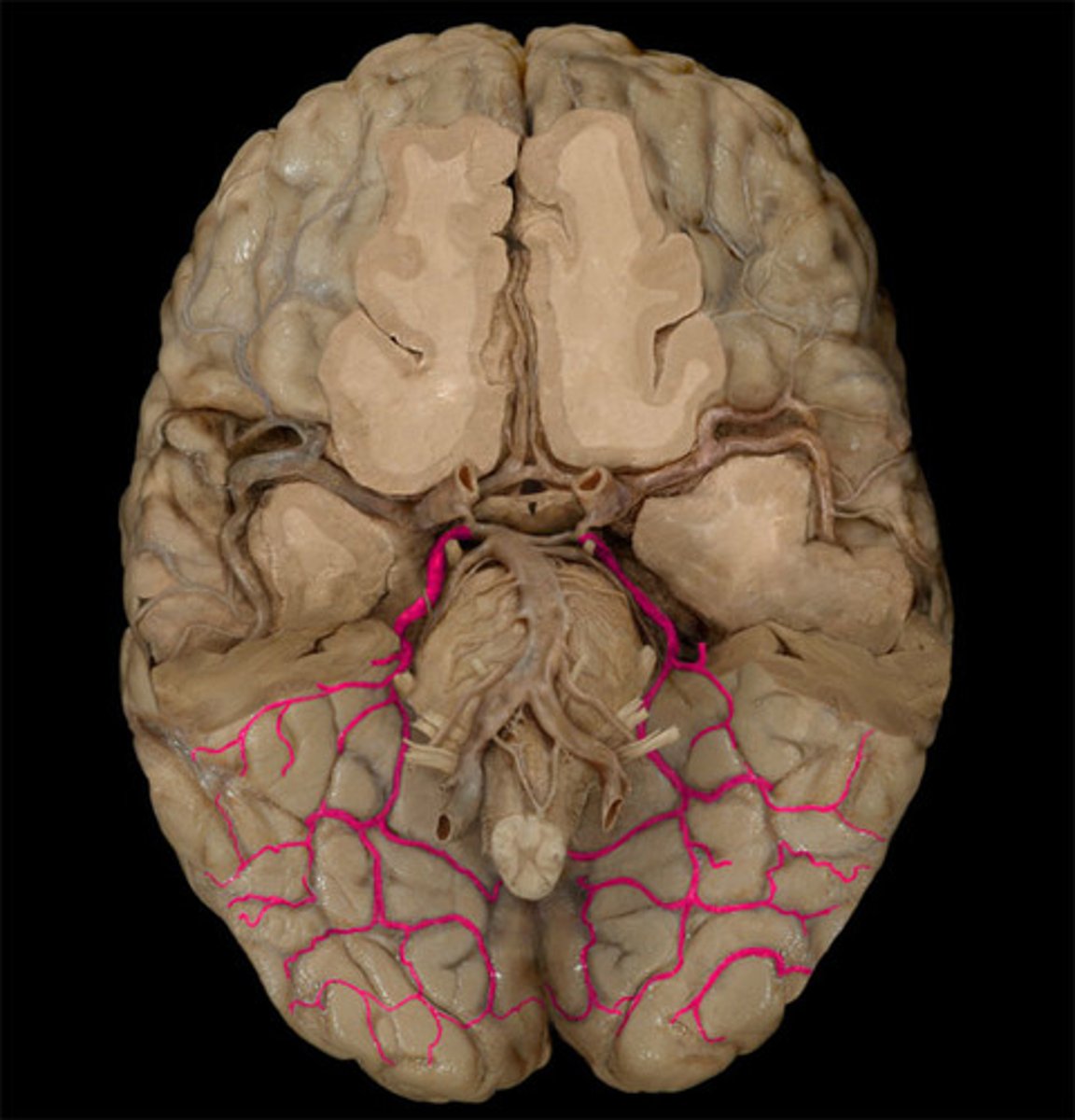
which artery is most commonly occluded?
middle cerebral artery
Largest branch
continuation of carotid artery so embolism can lodge here
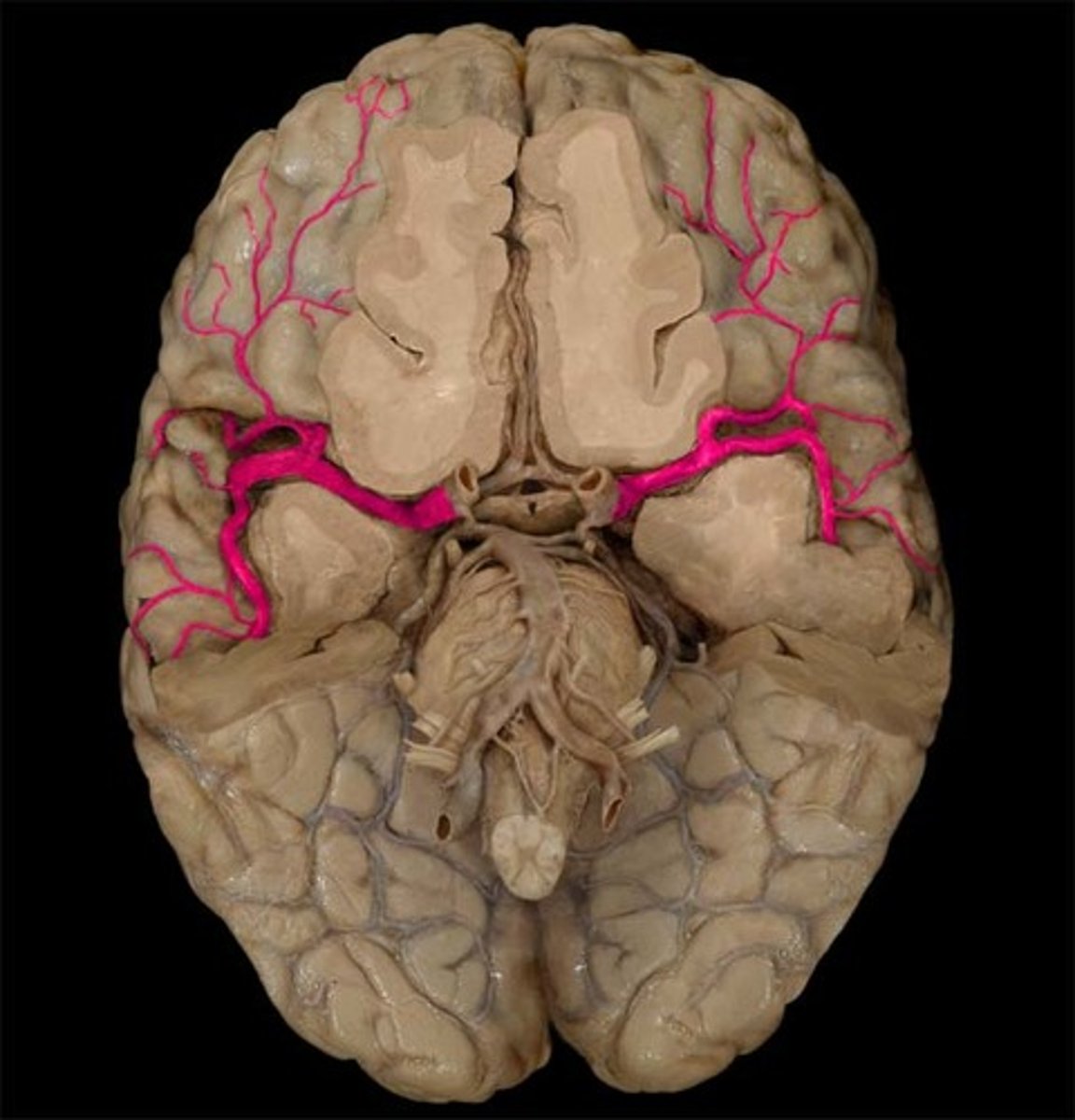
which circulation supplies the cerebellum and brainstem?
posterior circulation
which cerebellar artery is a direct branch off the vertebral artery
posterior inferior cerebellar artery
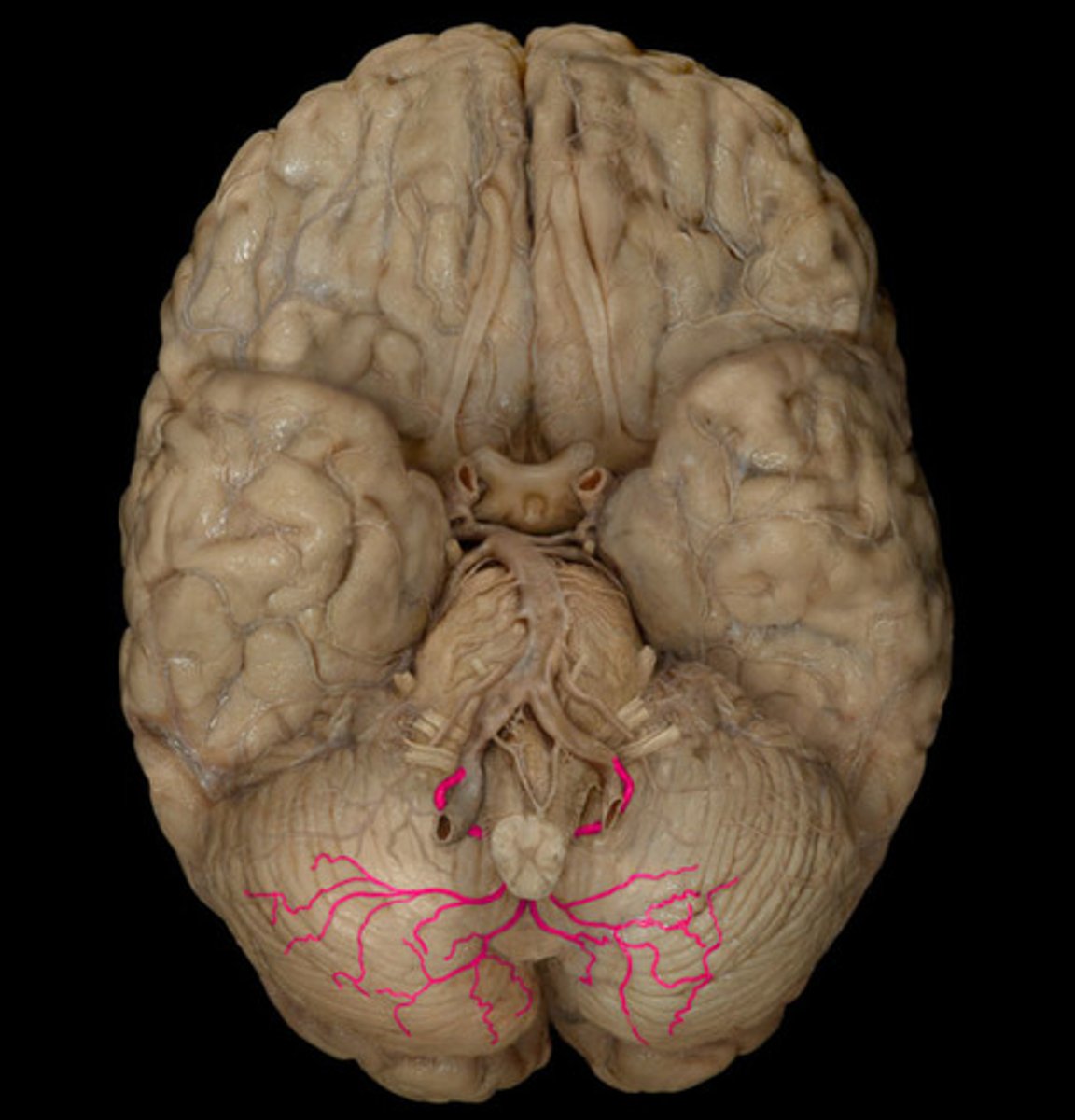
what are the symptoms of PICA infarction?
5 D's
dizziness, diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, drop attacks

which cerebellar artery is the first cerebellar branch of the basilar artery?
anterior inferior cerebellar artery
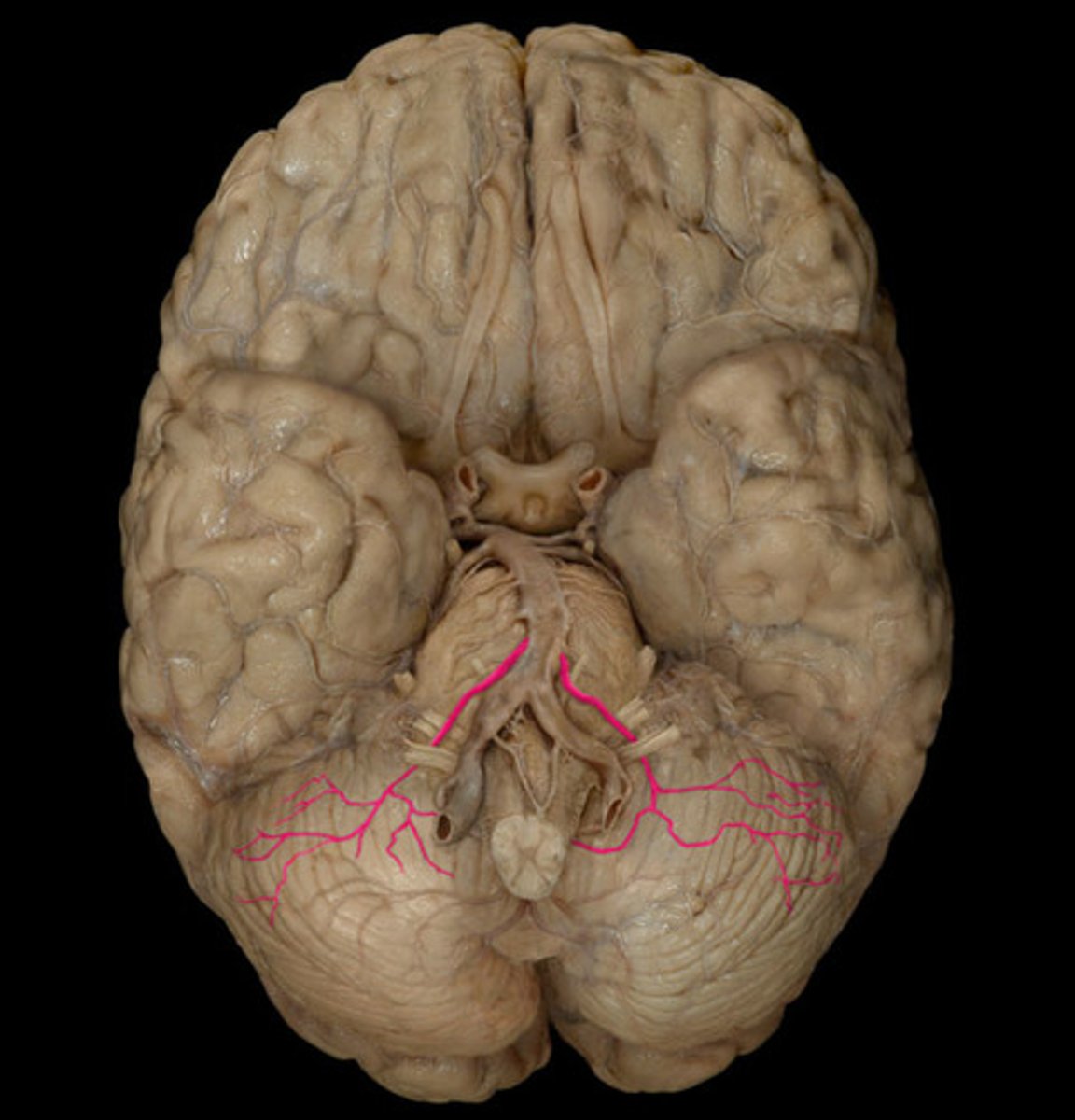
which cerebellar artery is a branch of the basilar artery that arises right before the basilar artery divides?
superior cerebellar artery
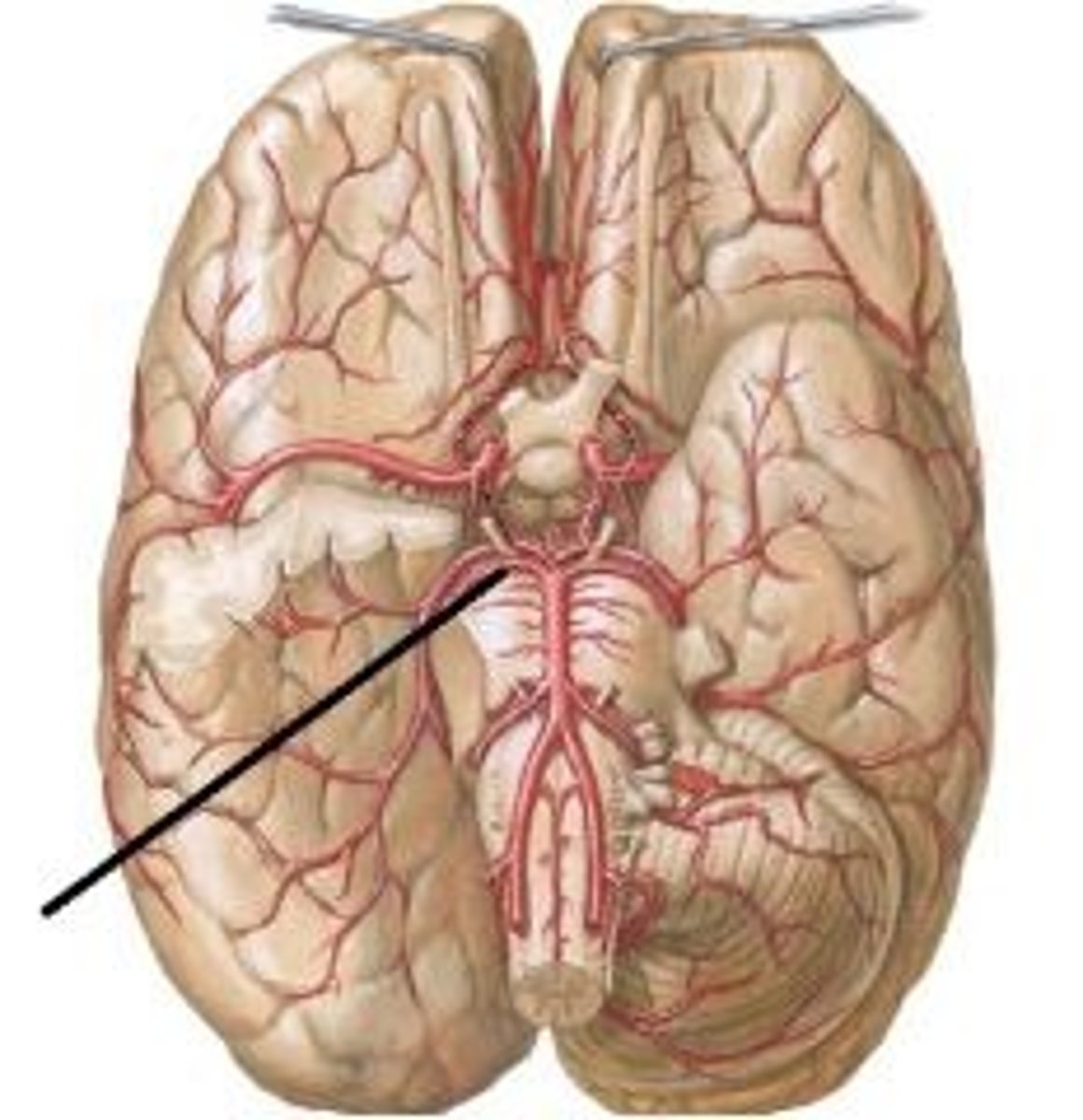
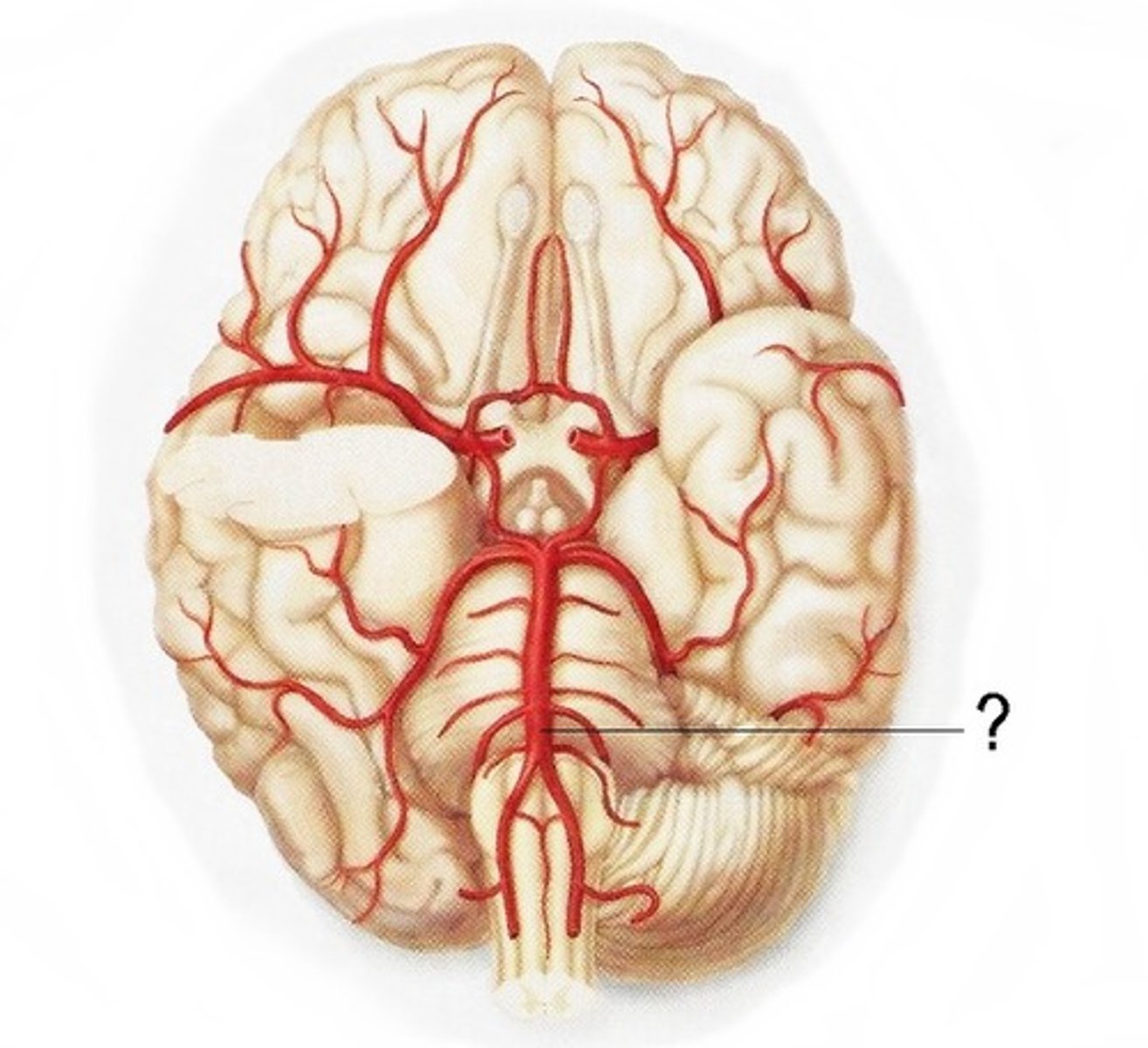
what are the pontine arteries?
Branches of the basilar artery
Supply the pons
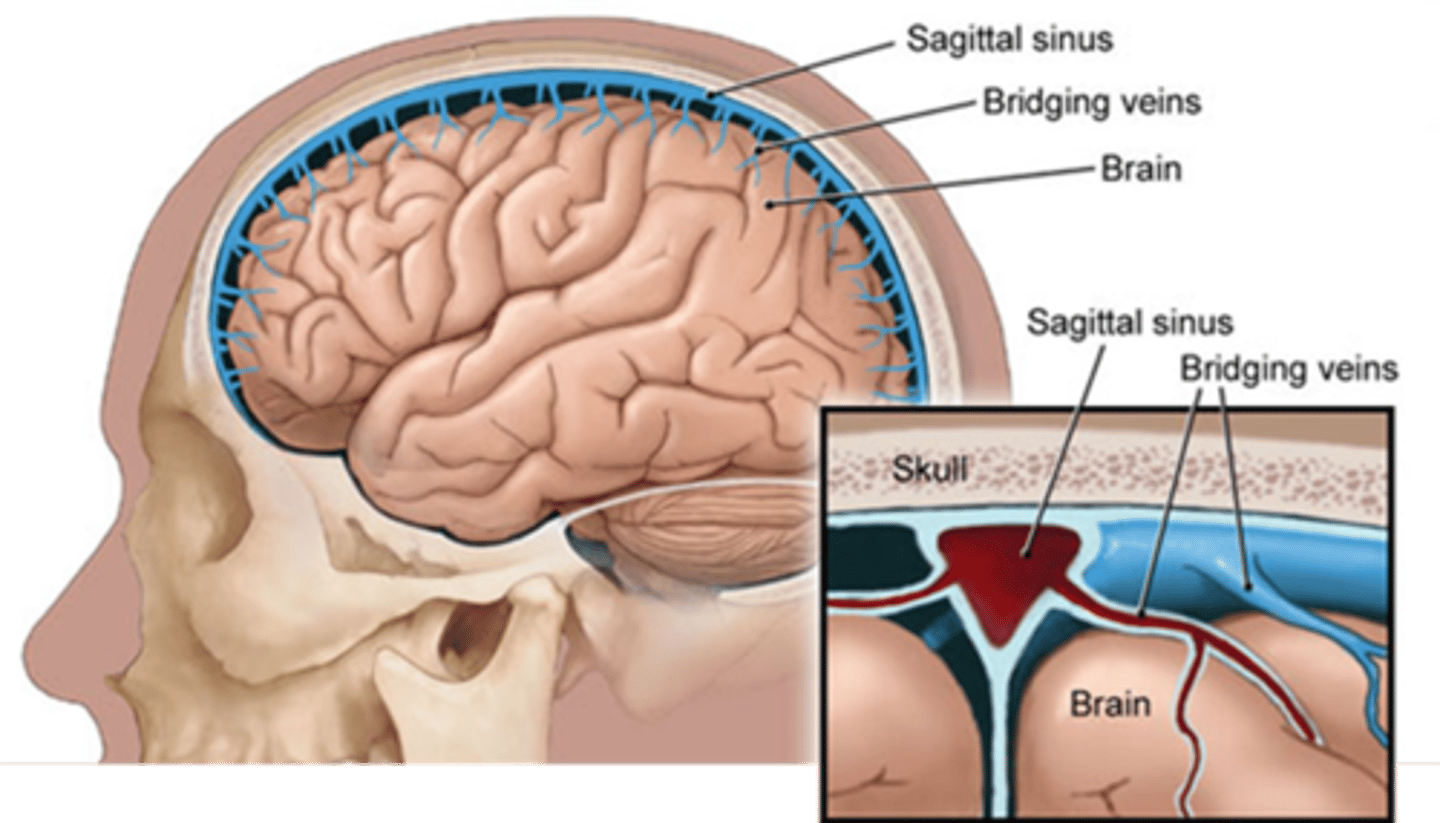
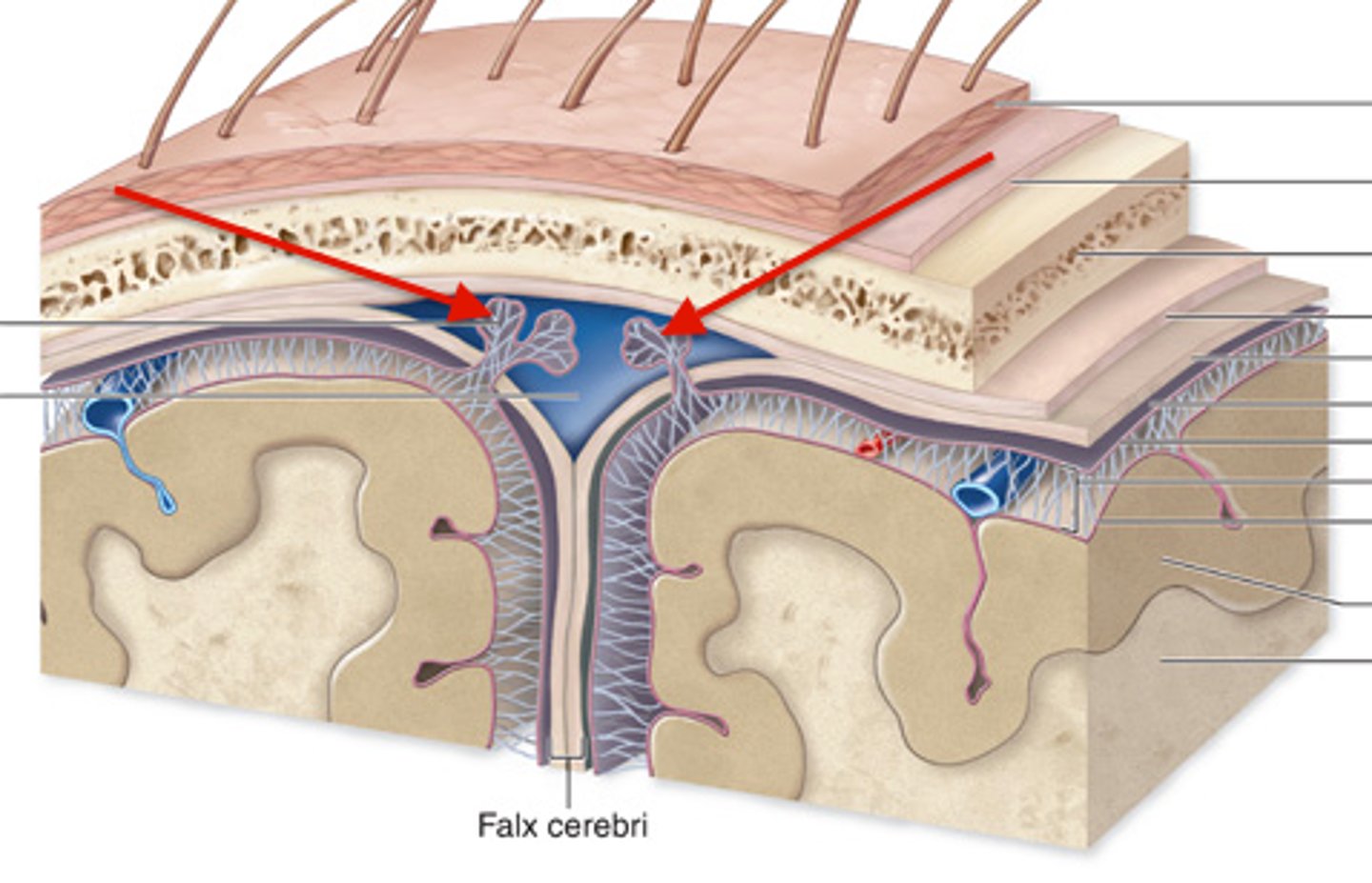
what are bridging veins?
Veins that connect arachnoid layer to sinuses by puncturing the dural mater
drain into the dural venous sinuses
what are dural venous sinuses?
Gaps within perisoteal and meningeal layers of dura mater where venous (deoxygenated) blood can collect
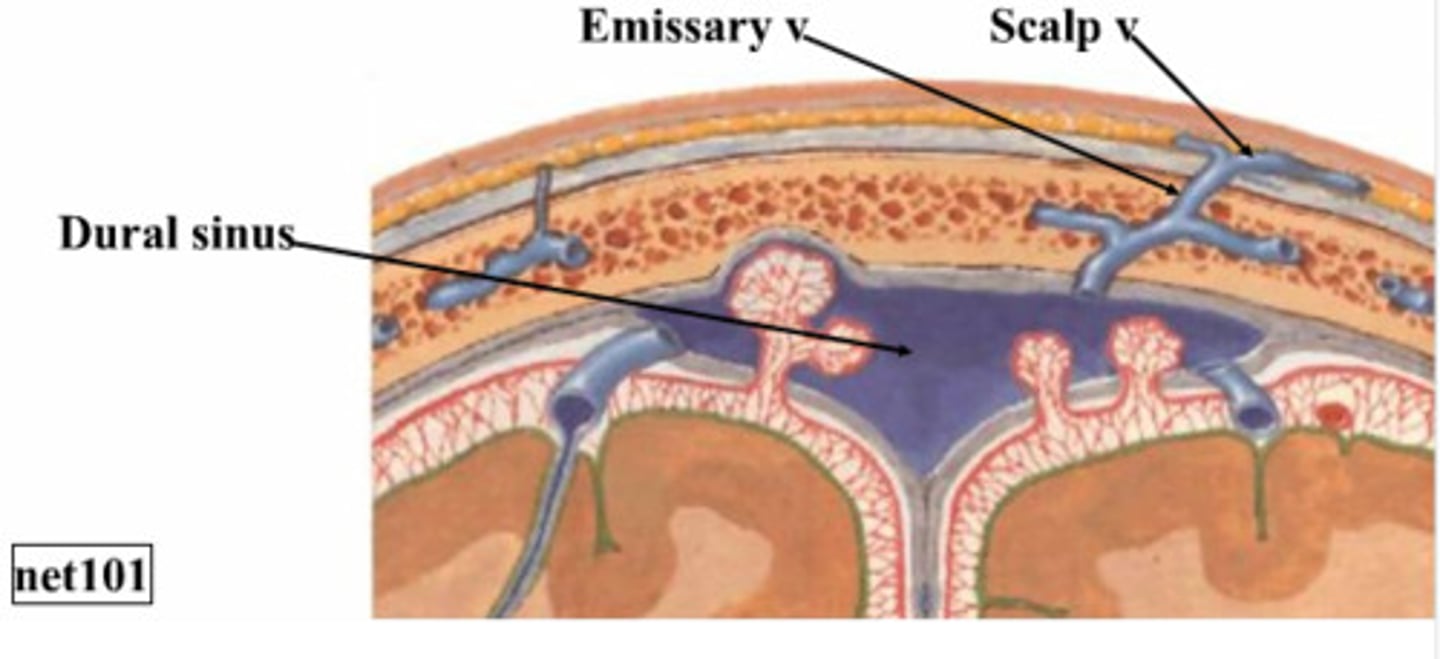
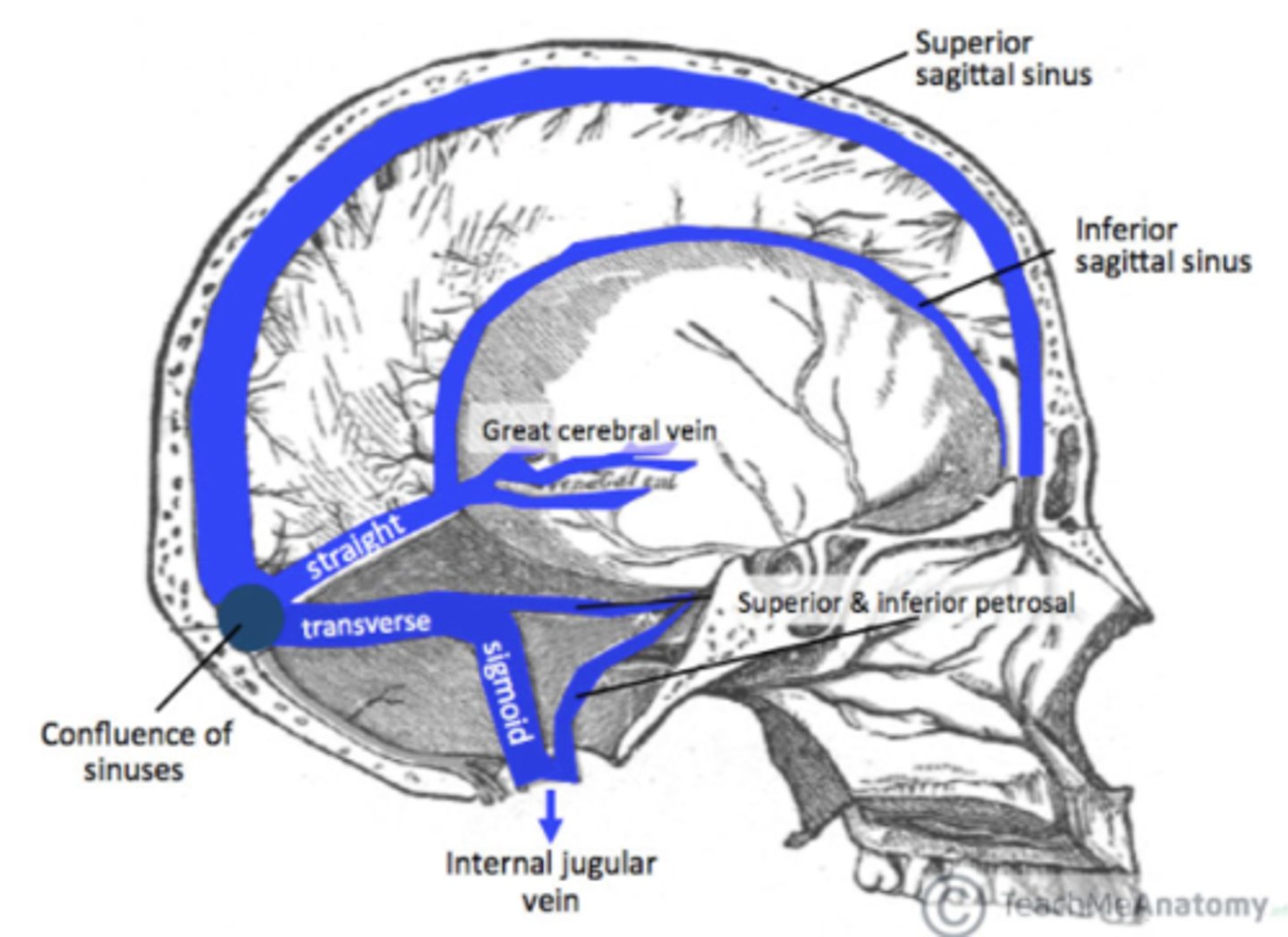
what are the names of the dural venous sinuses?
superior sagittal sinus
inferior sagittal sinus
straight sinus
confluence of the sinuses
transverse sinus
sigmoid sinus
cavernous sinus
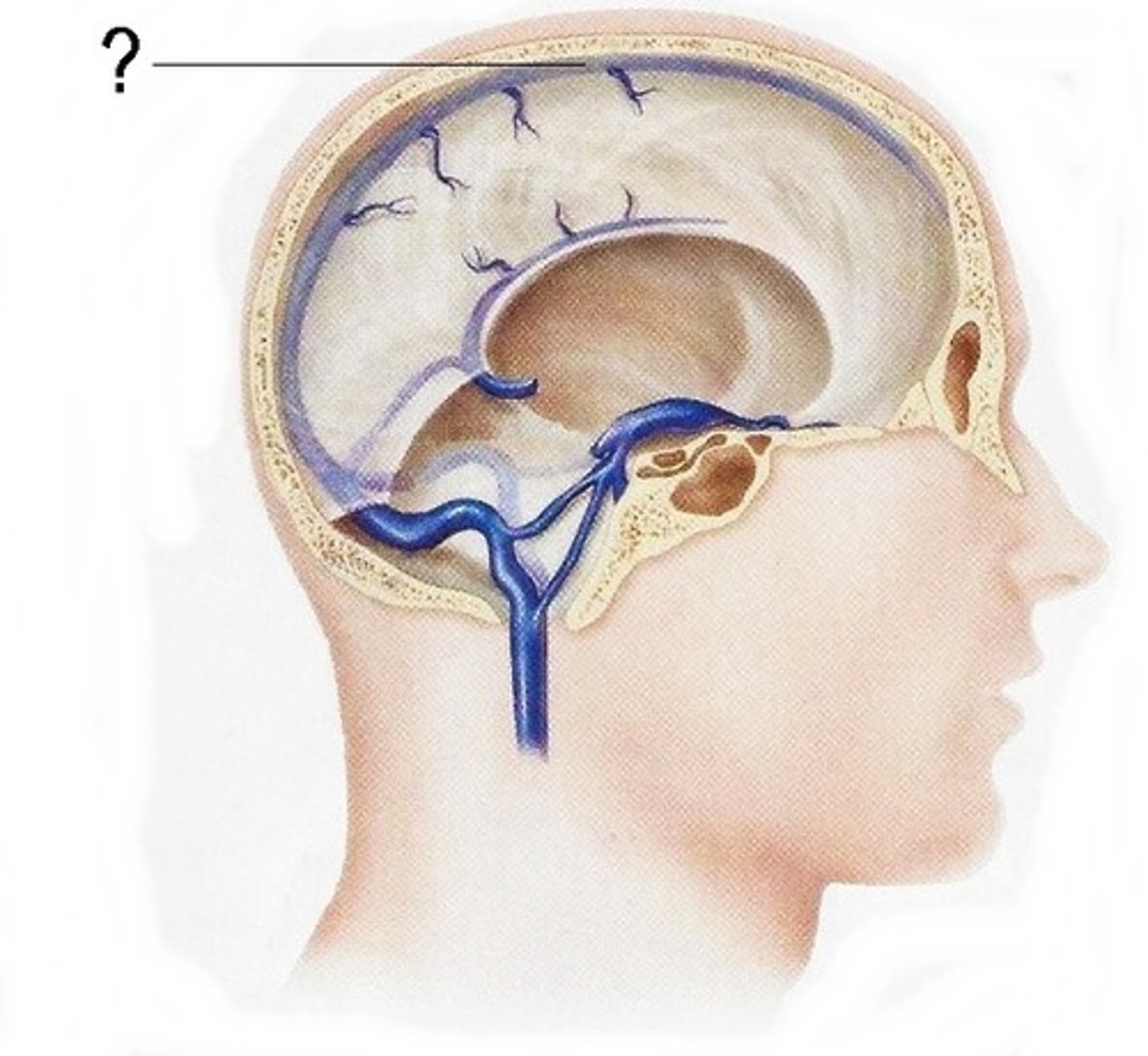
where is the superior sagittal sinus?
Sits in the superior edge of the falx cerebri
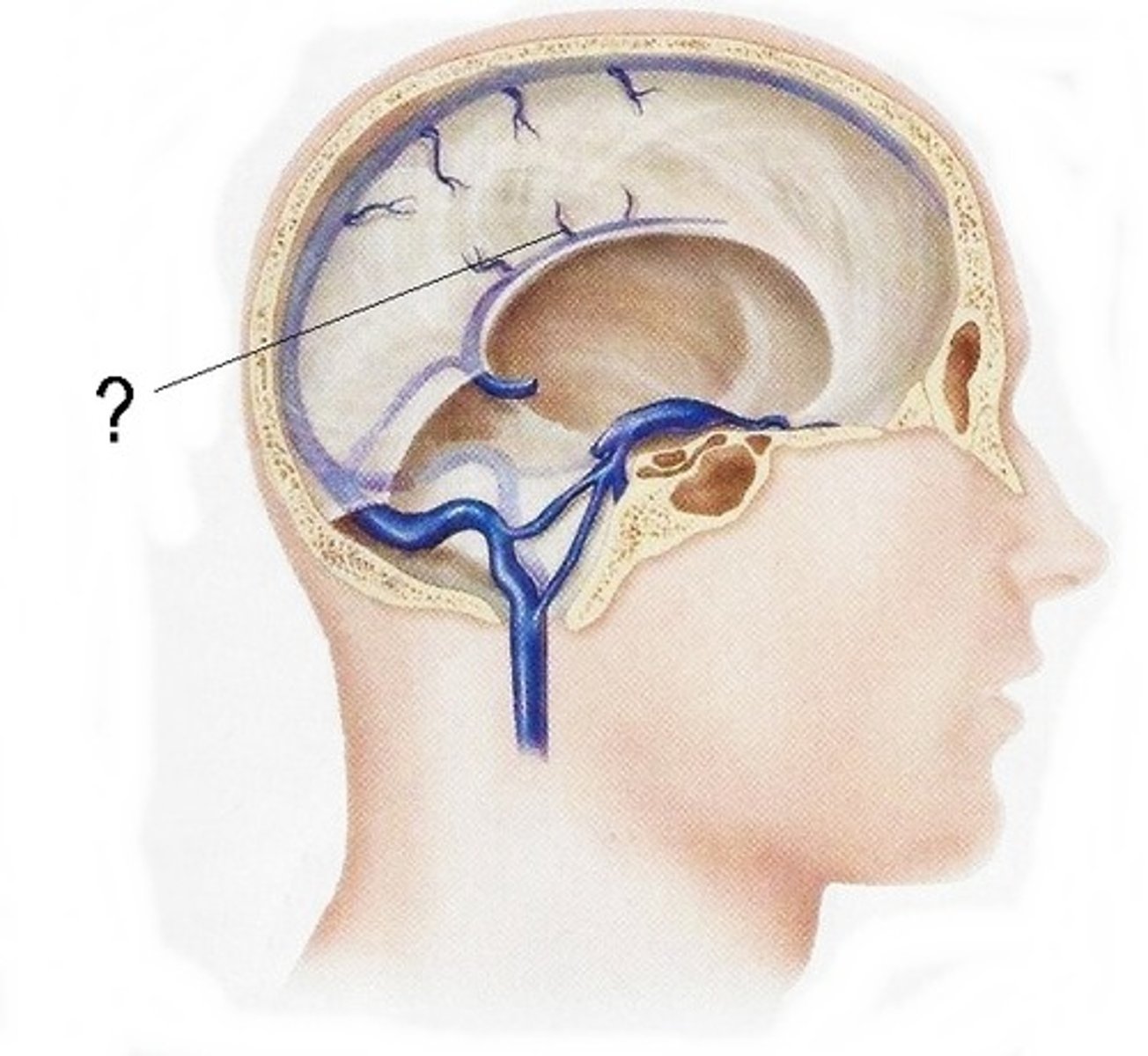
where is the inferior sagittal sinus?
Sits in the inferior edge of the falx cerebri
where is the confluence of the sinuses?
Junction point where the straight sinus meets the inferior sagittal sinus and transverse sinus posteriorly
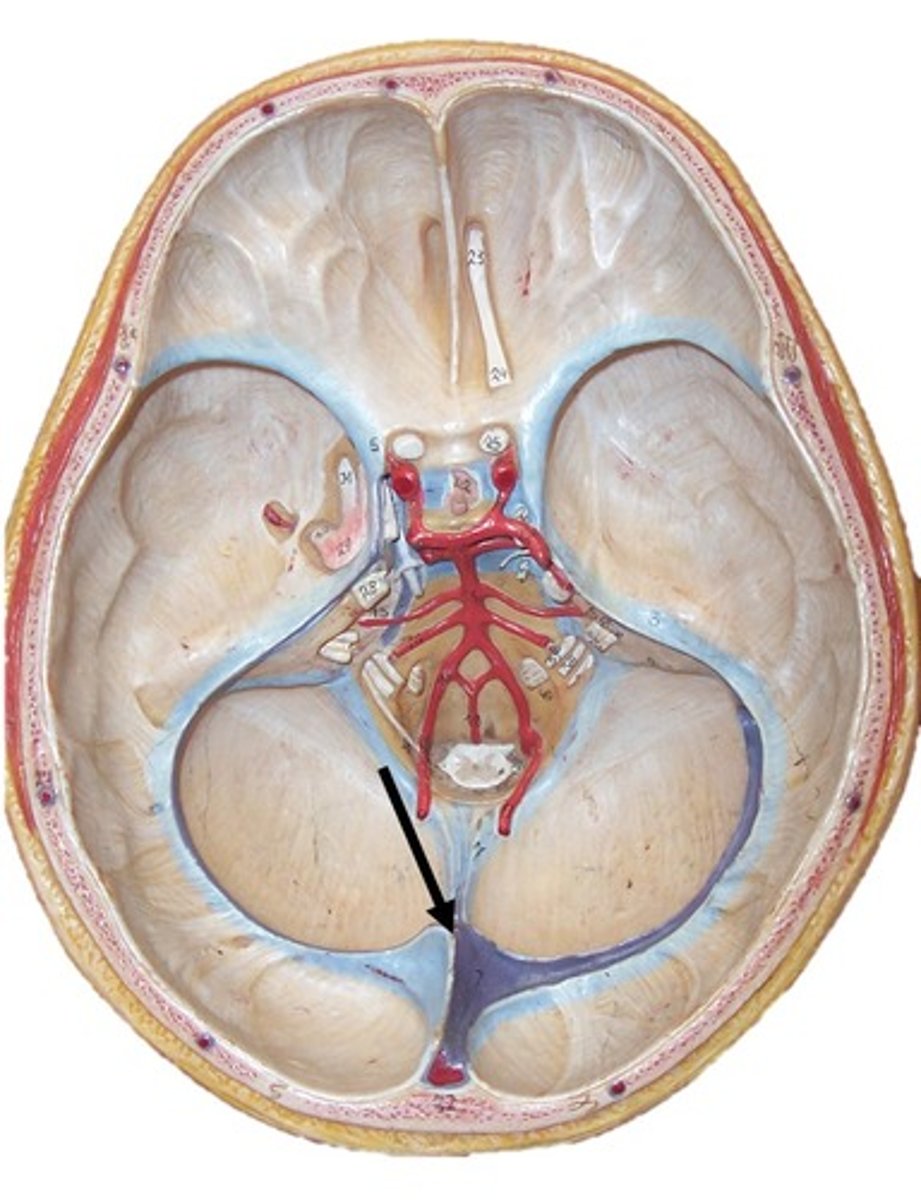
where is the straight sinus?
Connects to 2 sagittal sinuses posteriorly
Sits on top of the tentorium cerebelli
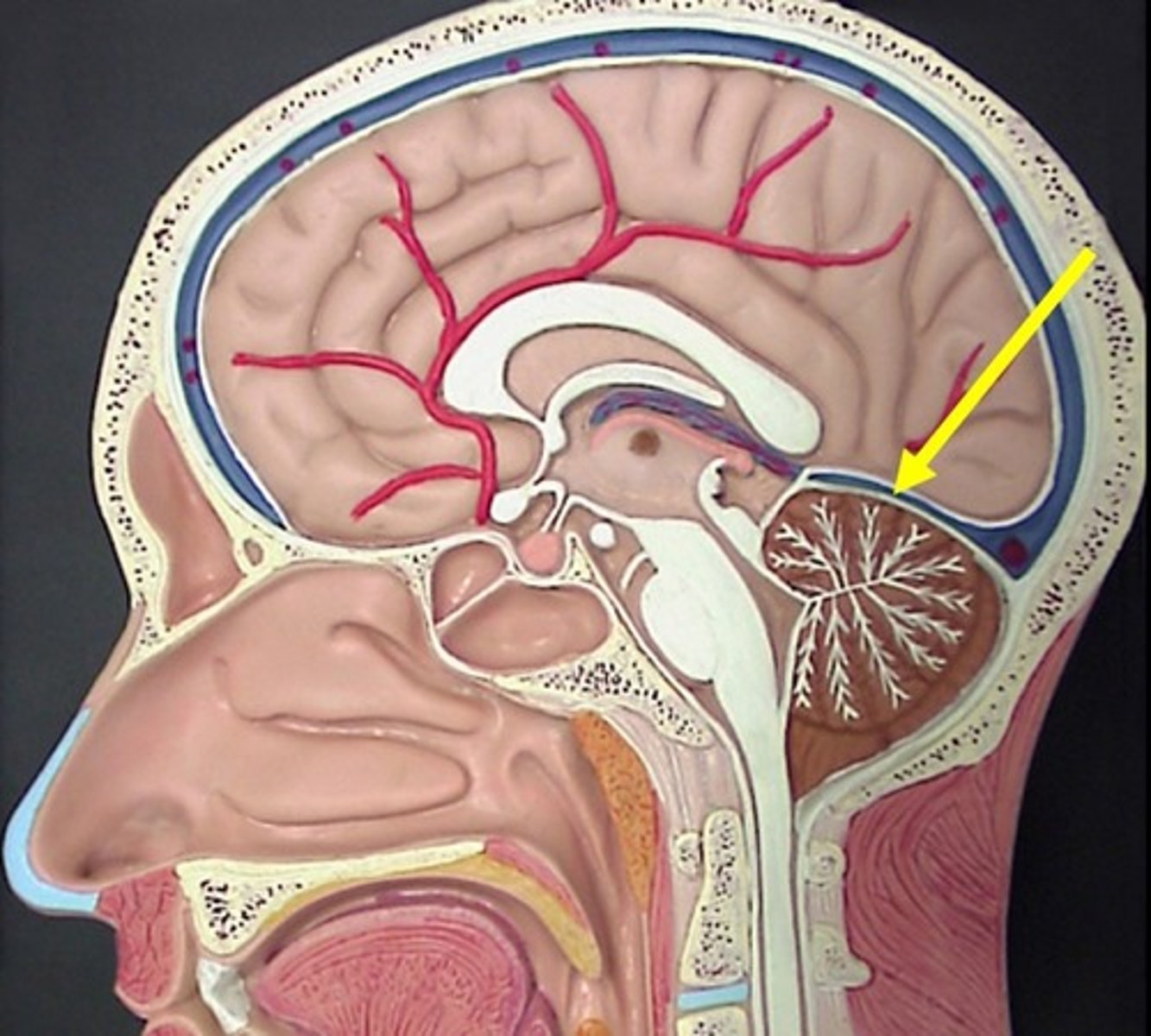
where is the transverse sinus?
Heads out horizontally around posterior cranium
Drains into the floor of the posterior cranial fossa into the sigmoid sinus
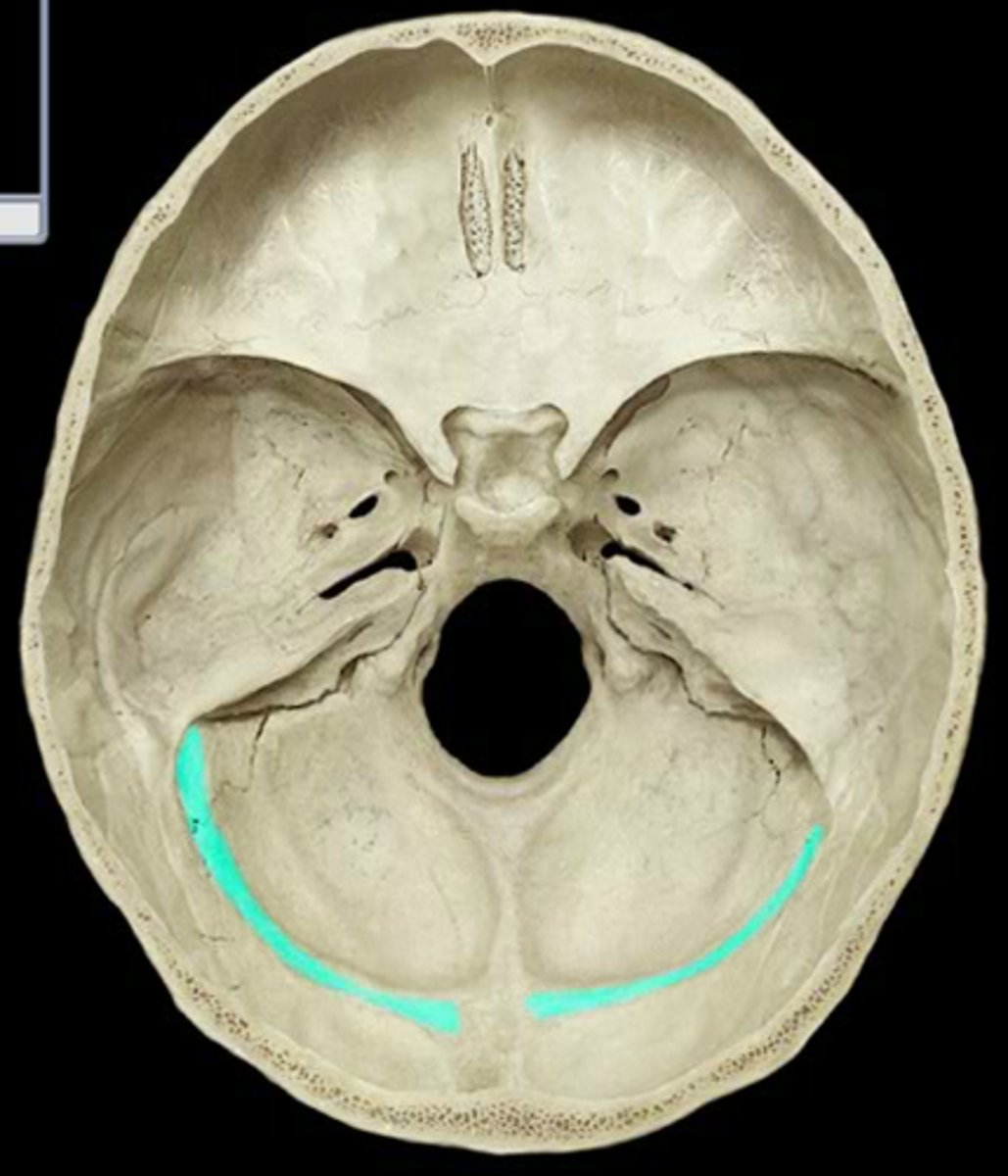
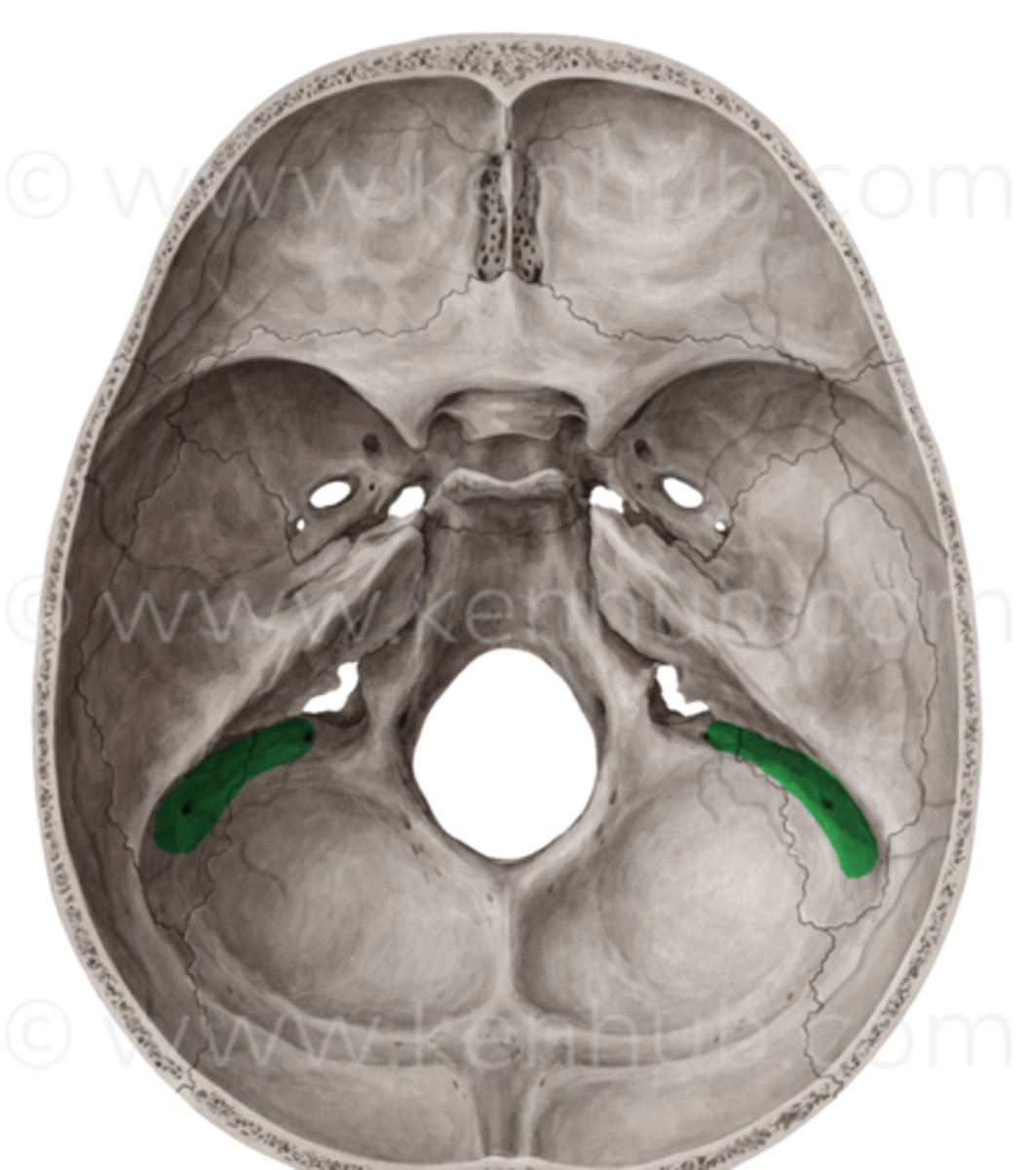
where is the sigmoid sinus?
Sits in the posterior cranial fossa
Heads down into the jugular foramen
Drains venous blood into the internal jugular vein
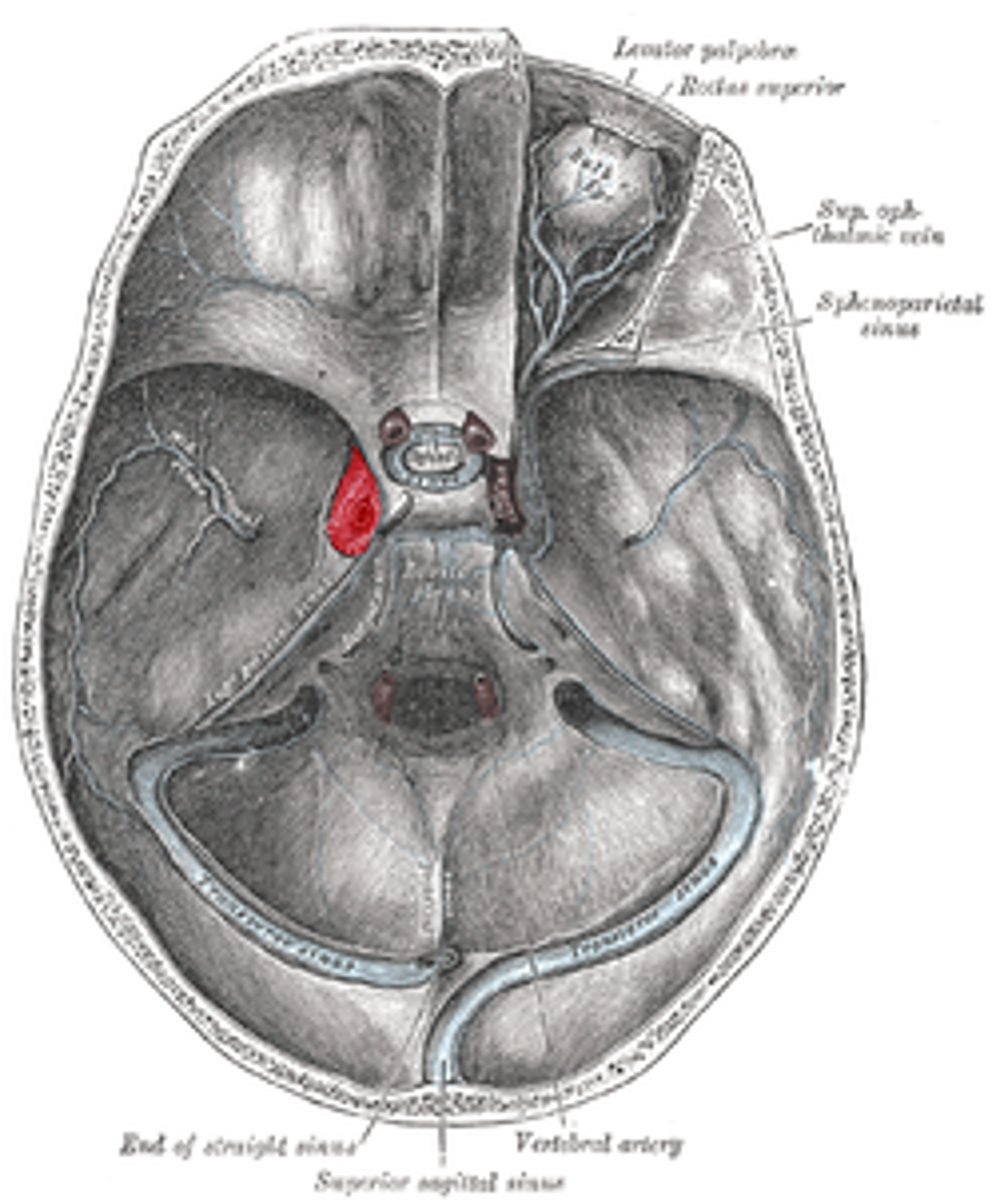
what is the significance of the cavernous venous sinus?
Holds the internal carotid artery within it
Drains into the sigmoid sinus via 2 smaller sinuses
what is an extradural hemorrhage?
Trauma to the head- perhaps in the pterion
Leads to a rupture of the underlying vessel (commonly the middle meningeal artery as this sits in the periosteal layer of the dura)
Pressure from the bleed peels the periosteal dura away from the bone
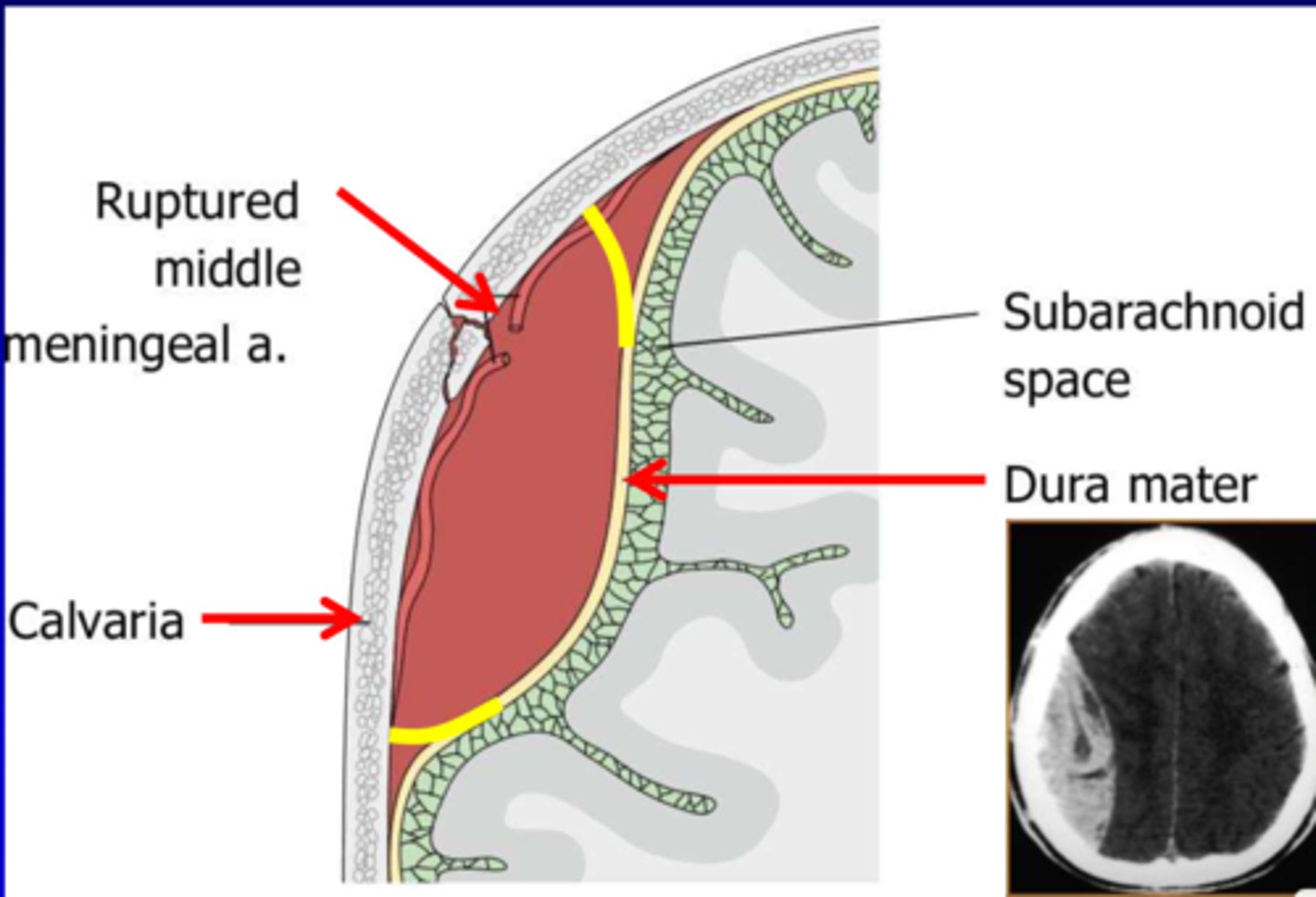
what is the shape of an EDH on CT?
lens shape
what is a subdural hemorrhage?
Fall or knock to the head (accel-decel)
Shearing force damages a bridging vein as it heads into a dural sinus
Venous bleed between dura mater and arachnoid mater (potential space)
Raised ICP and mass develops more slowly
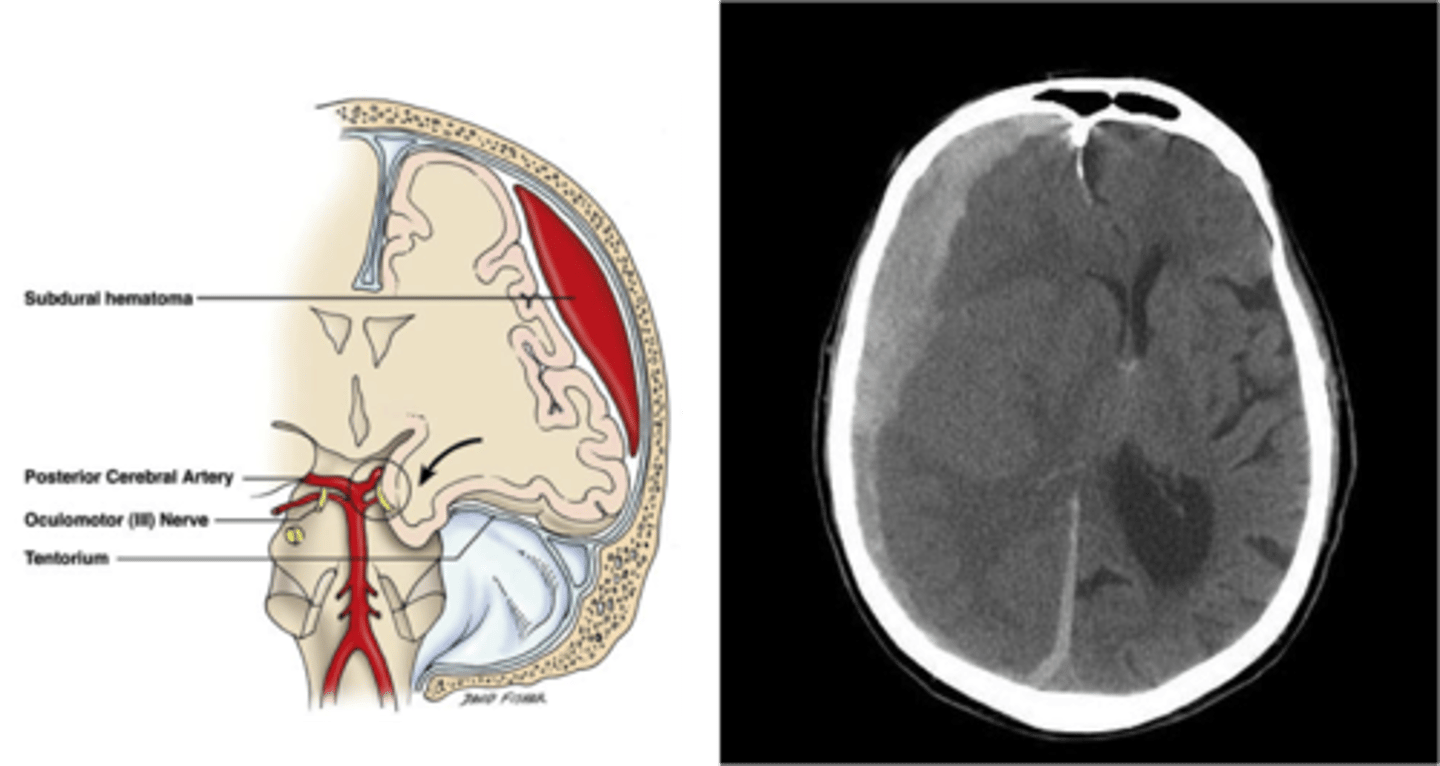
what is the shape of an SDH on CT?
crescent shape
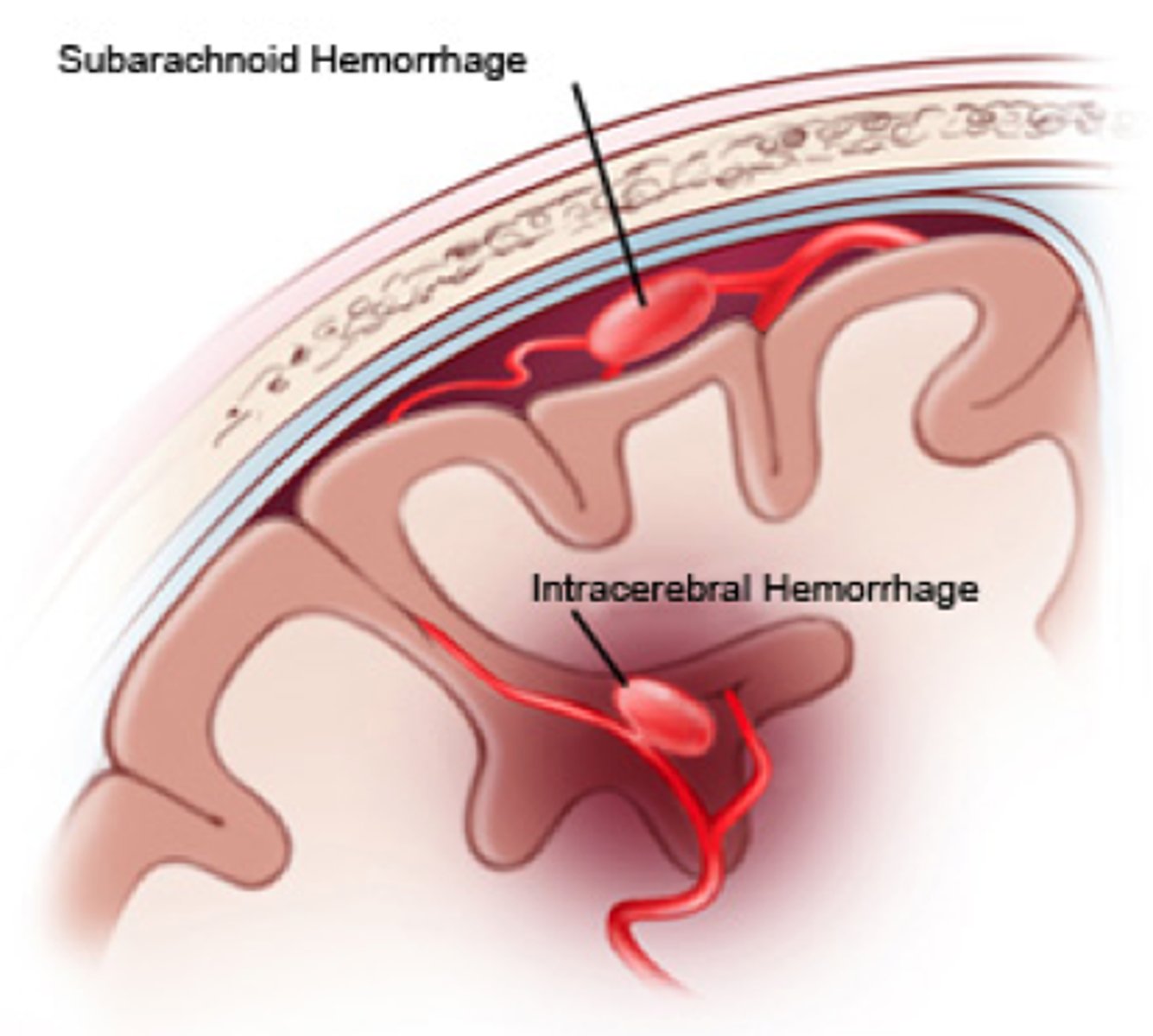
what is an intracerebral hemorrhage
Bleeding into the substance of the brain tissue
Smaller arteries that supply deeper structure can haemorrhage
Most commonly occur due to vascular disease (hypertension)
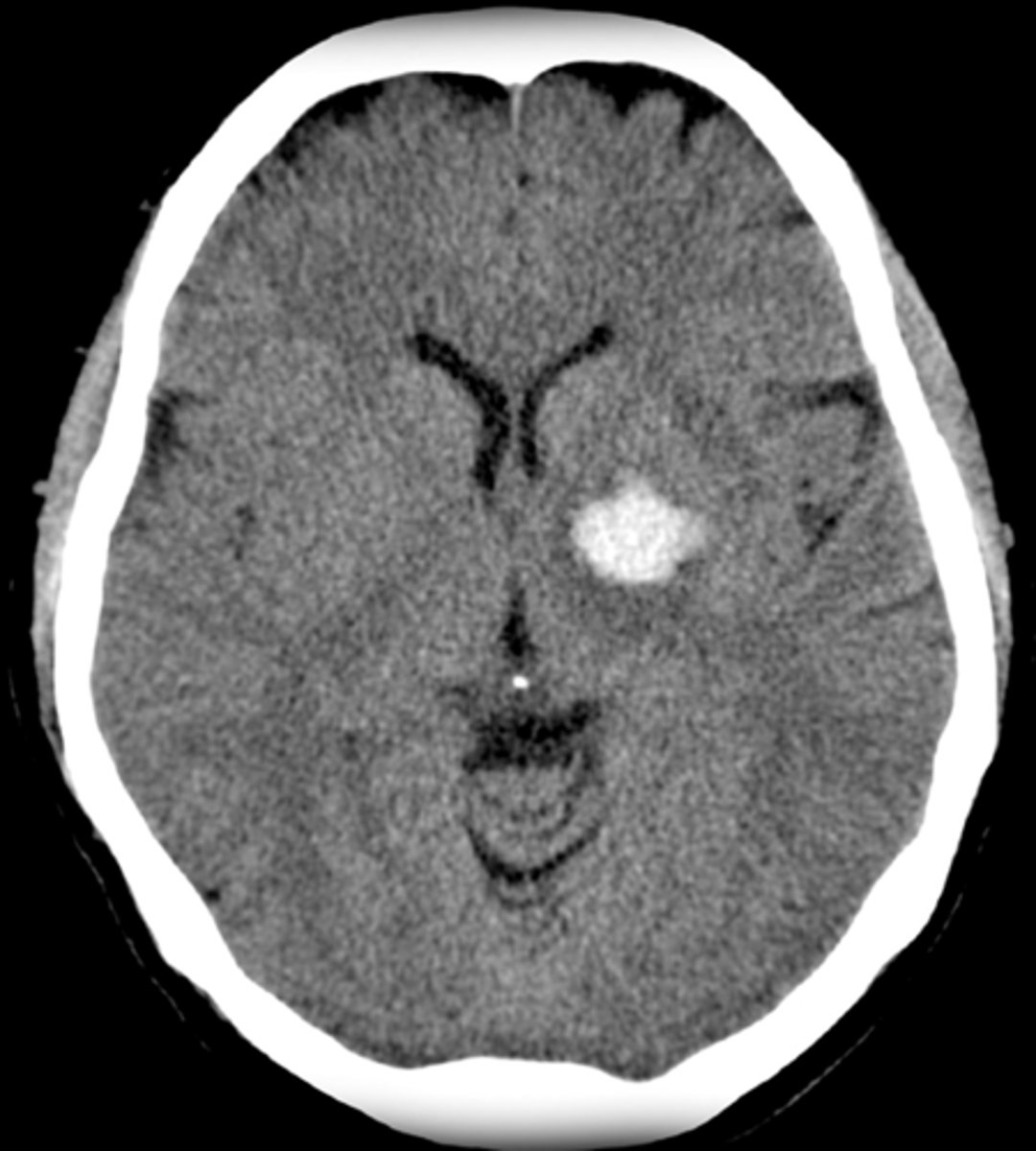
how does an ICH present on CT?
white blot in the middle of the brain
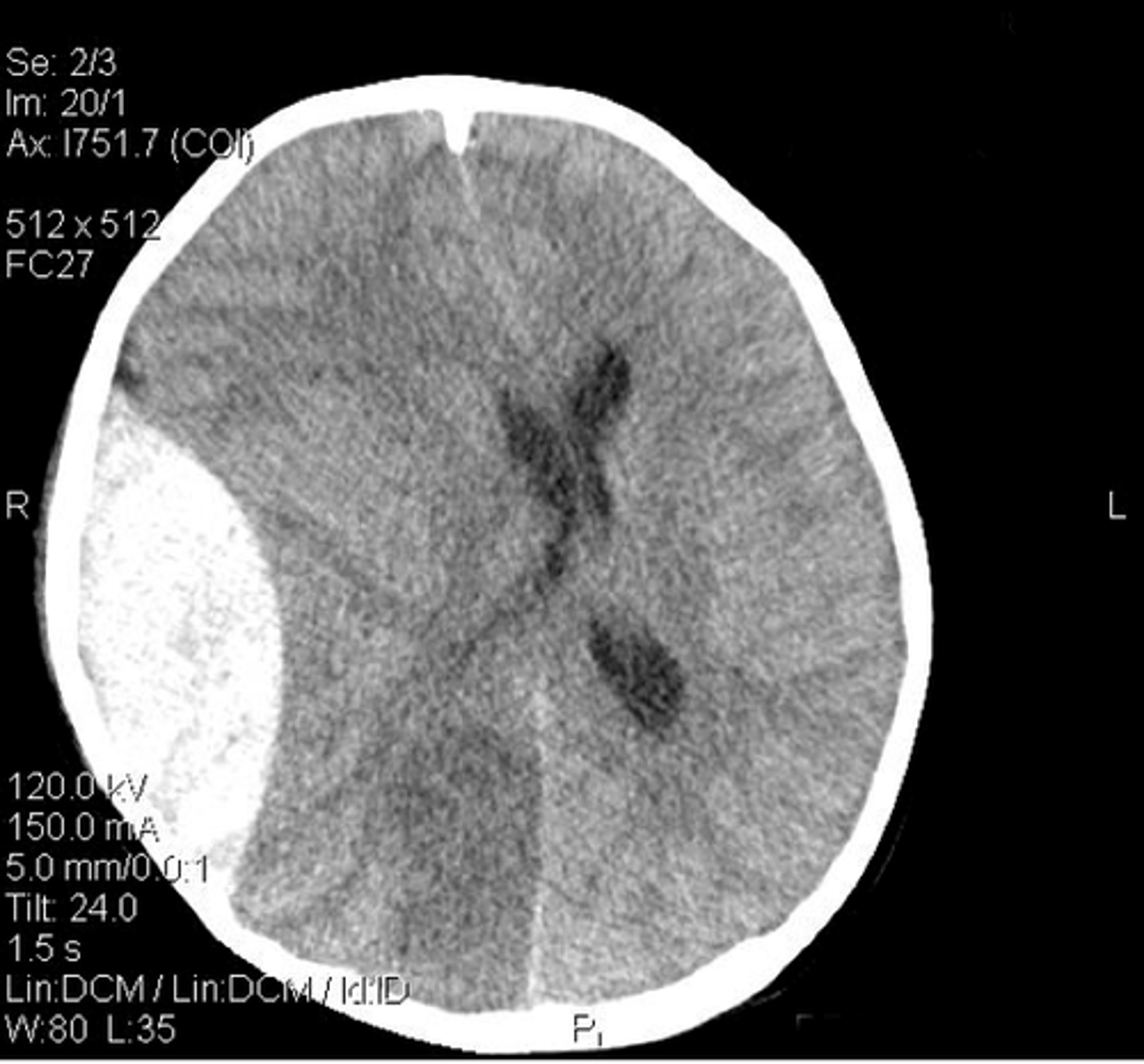
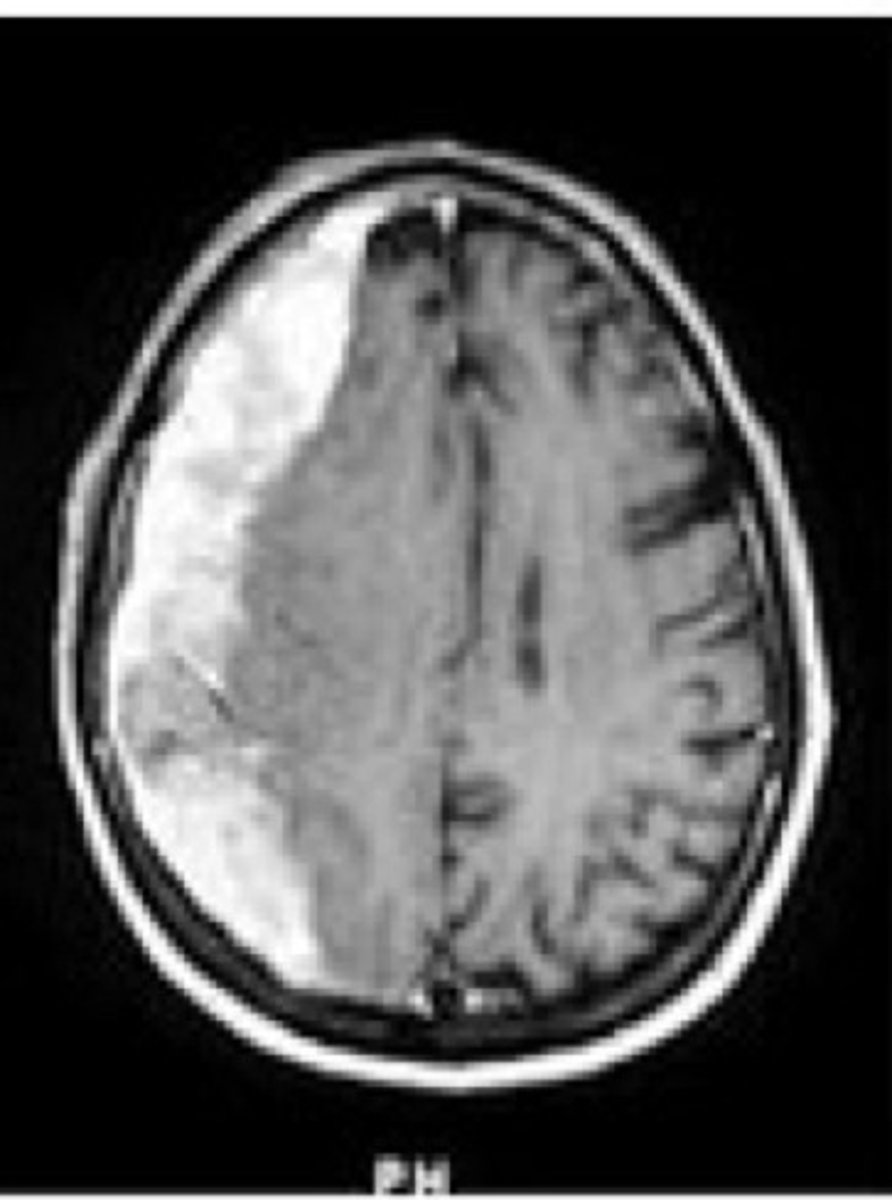
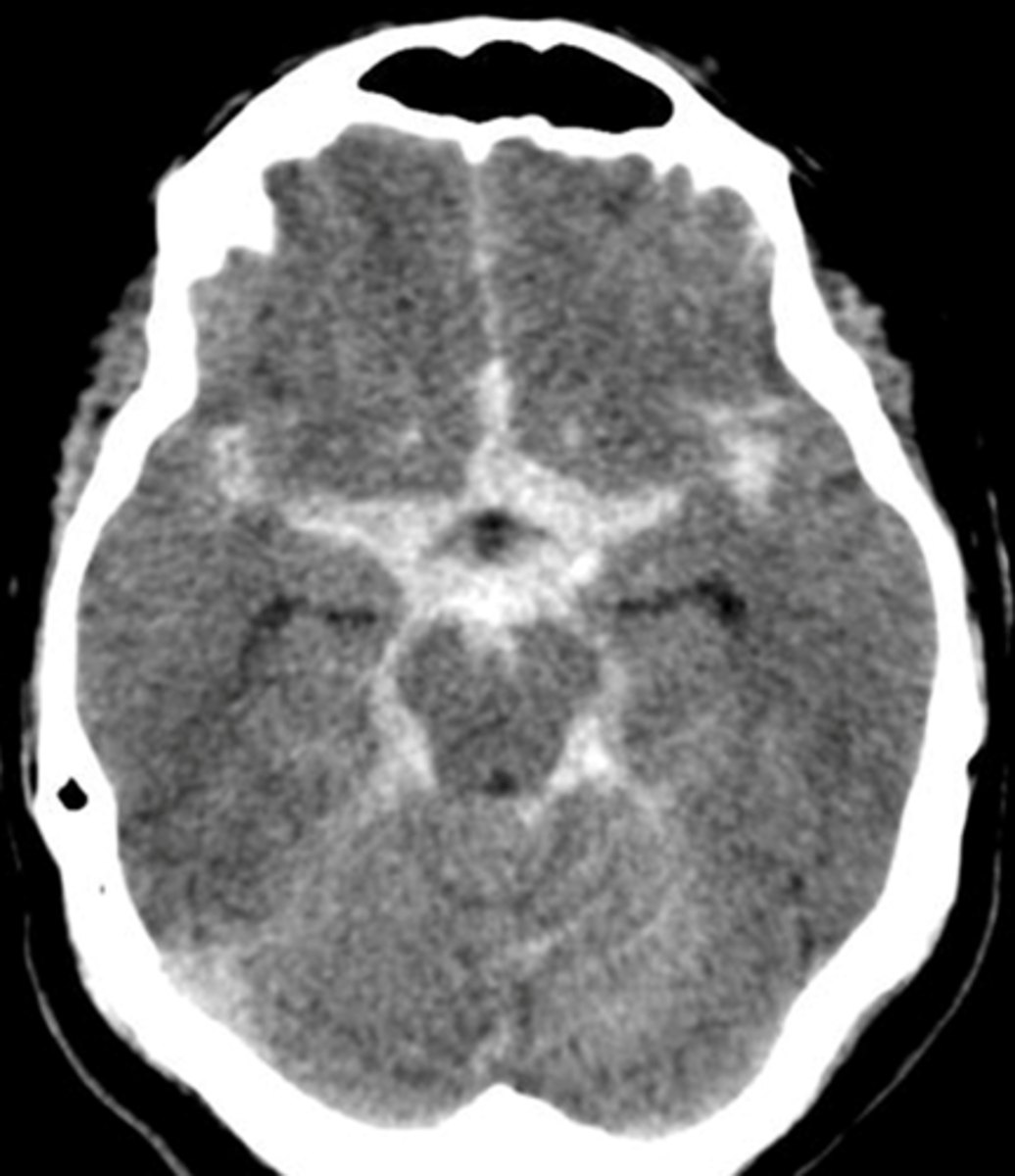
what is a subarachnoid haemorrhage?
Arterial bleed between arachnoid and pia mater
Most arteries that supply the brain sit in the subarachnoid space
often caused by a berry aneurysm (ballooning of vessel wall)
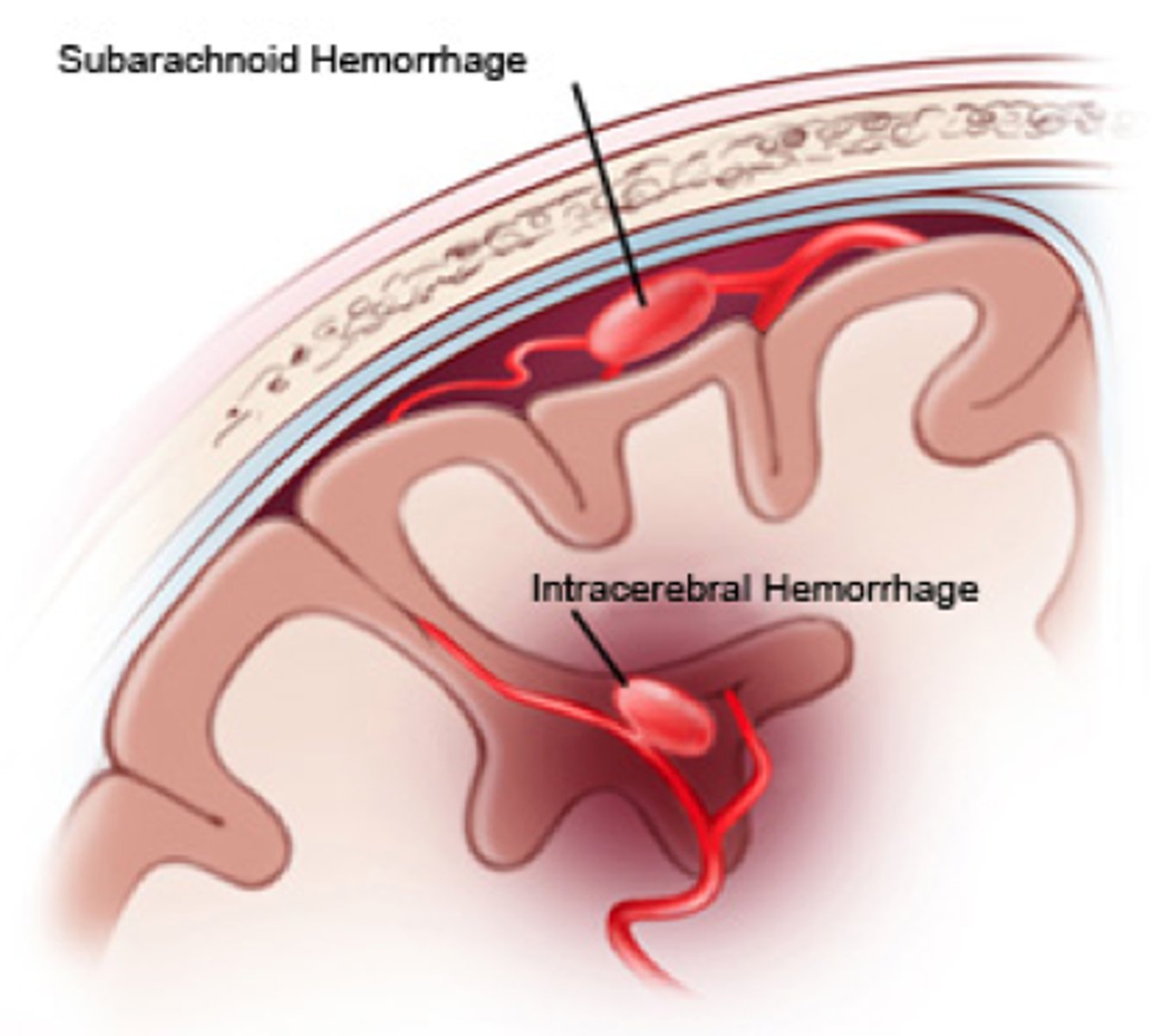
how does a subarachnoid hemorrhage present on CT?
bleeding appears to follow the sulci of the brain
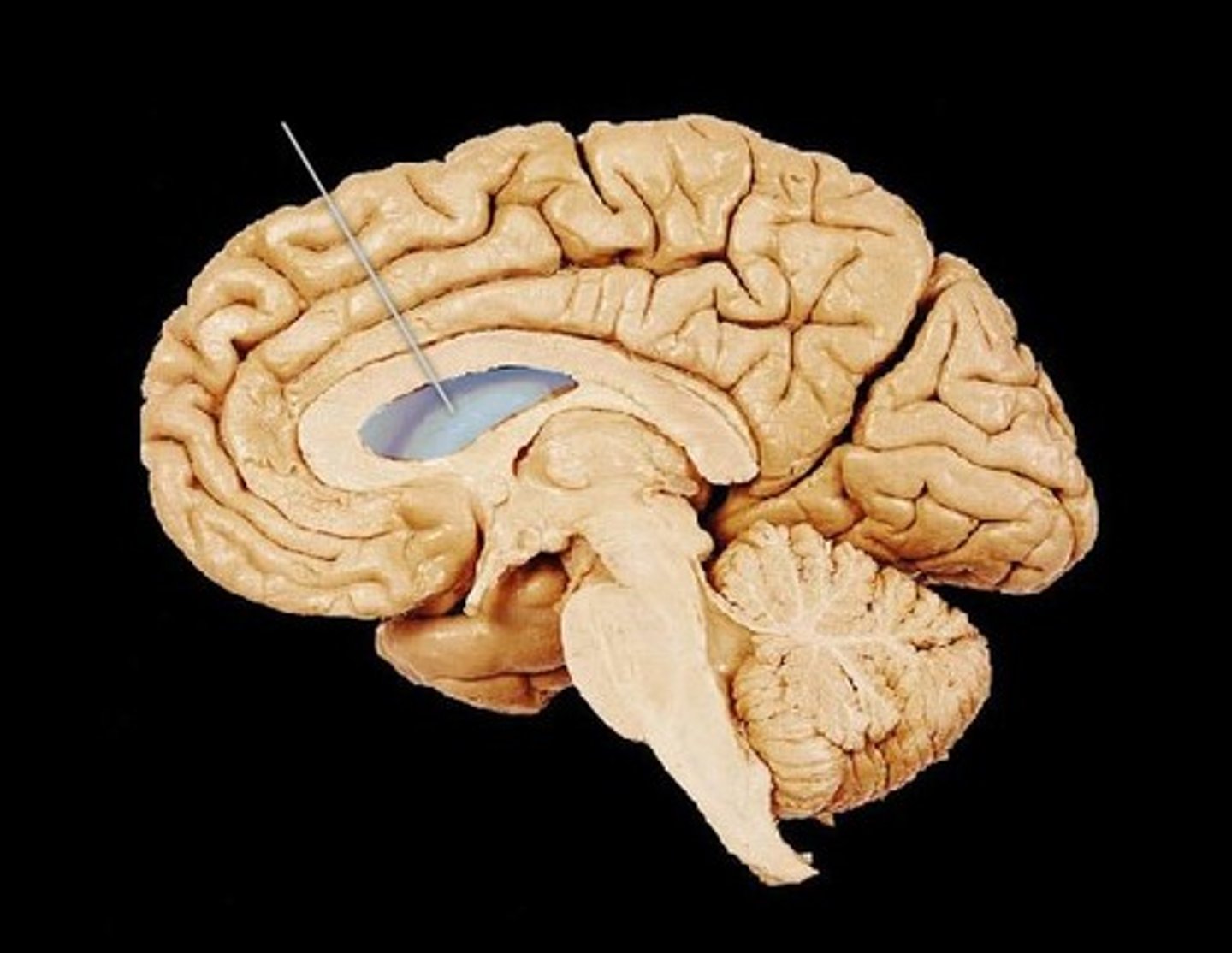
what are the structures that surround the lateral ventricles?
Corpus callosum is the roof the lateral ventricles
Thalamus makes up the floor of the lateral ventricle
Caudate nucleus is part of the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles (roof of inferior horn)
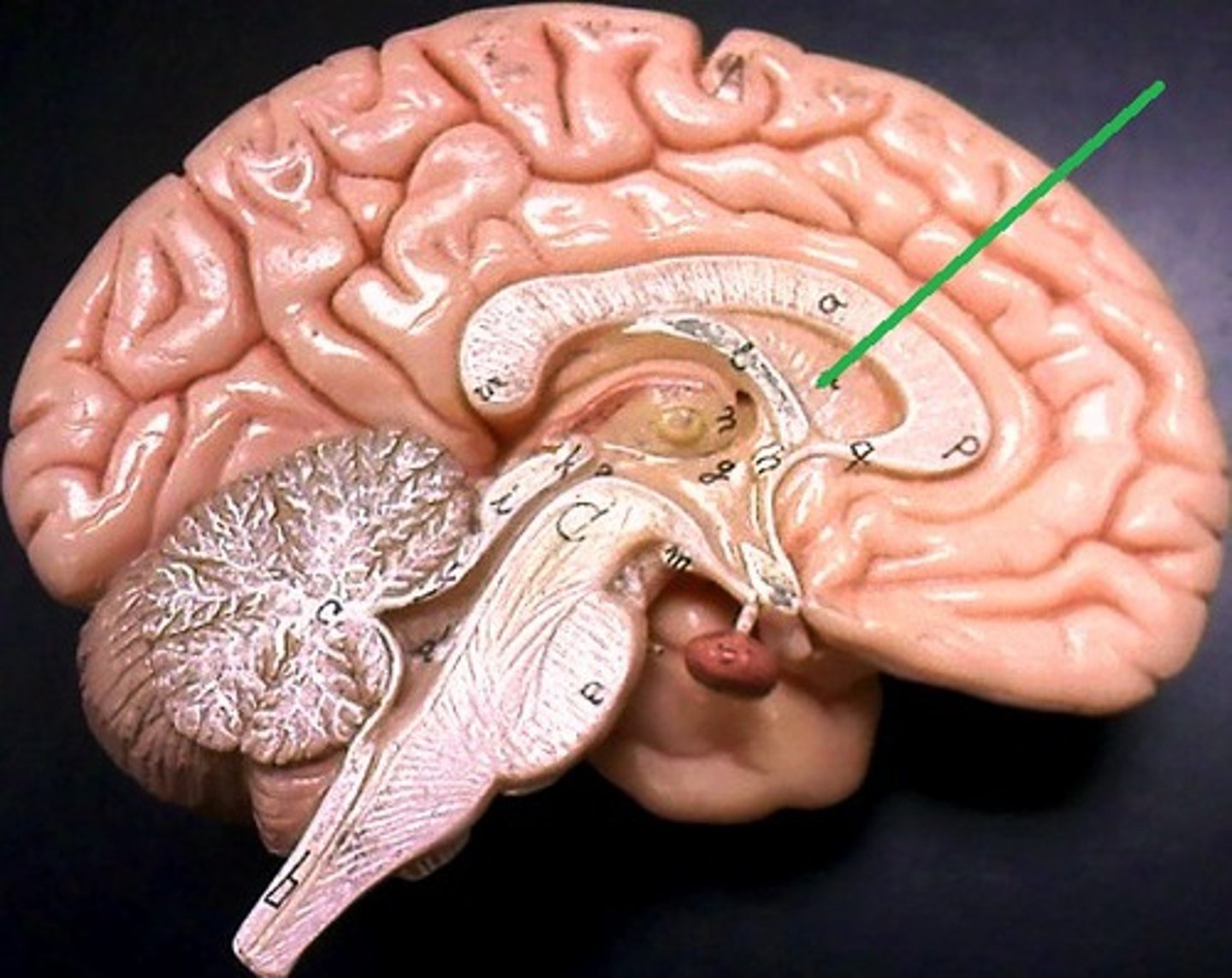
What is the septum pellucidum?
thin membrane that separates lateral ventricles
runs from the corpus callosum to the fornix
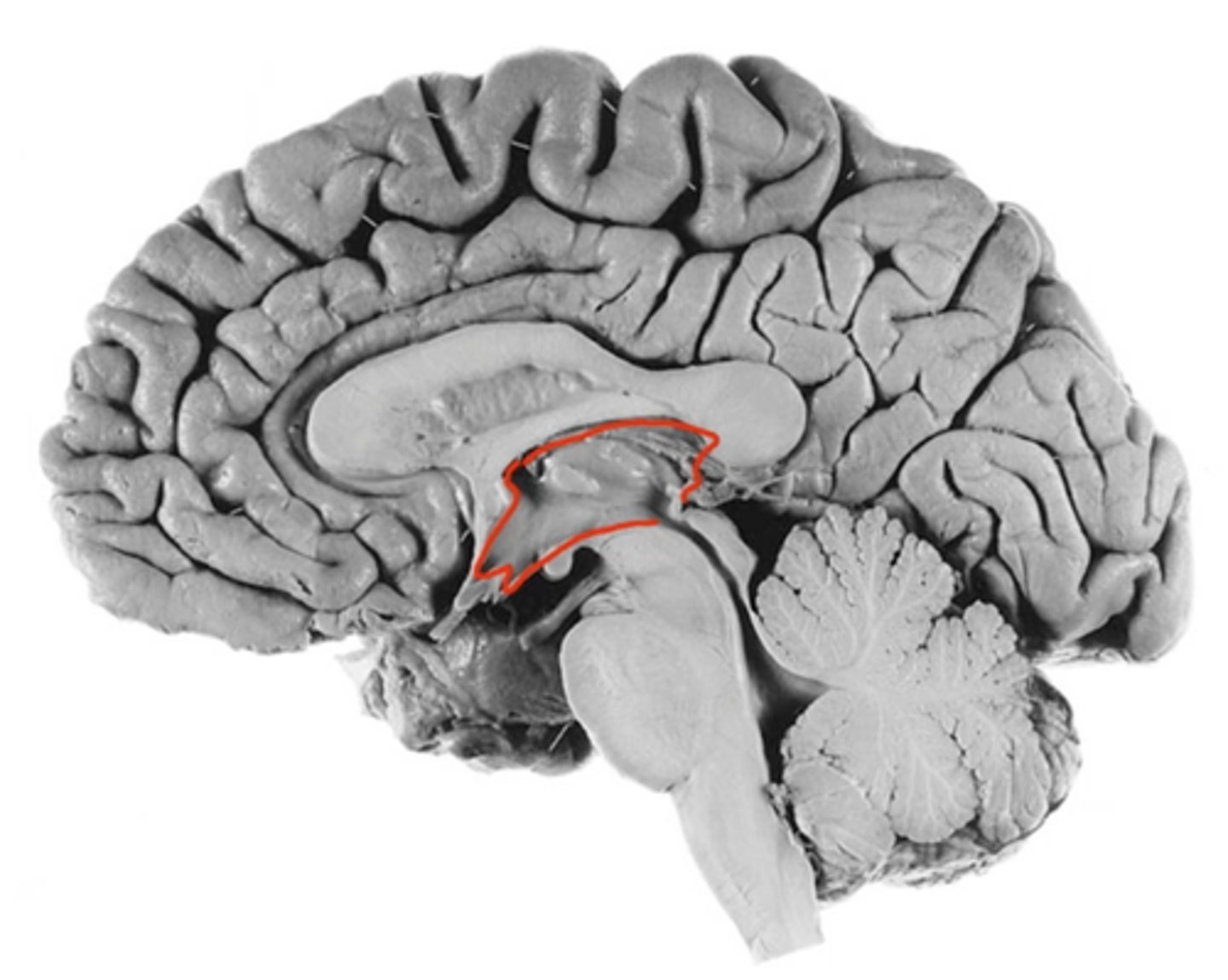
what structure surrounds the third ventricle?
Thalamus in each side creates the lateral walls of the 3rd ventricle
what structure does the cerebral aqueduct run through?
midbrain
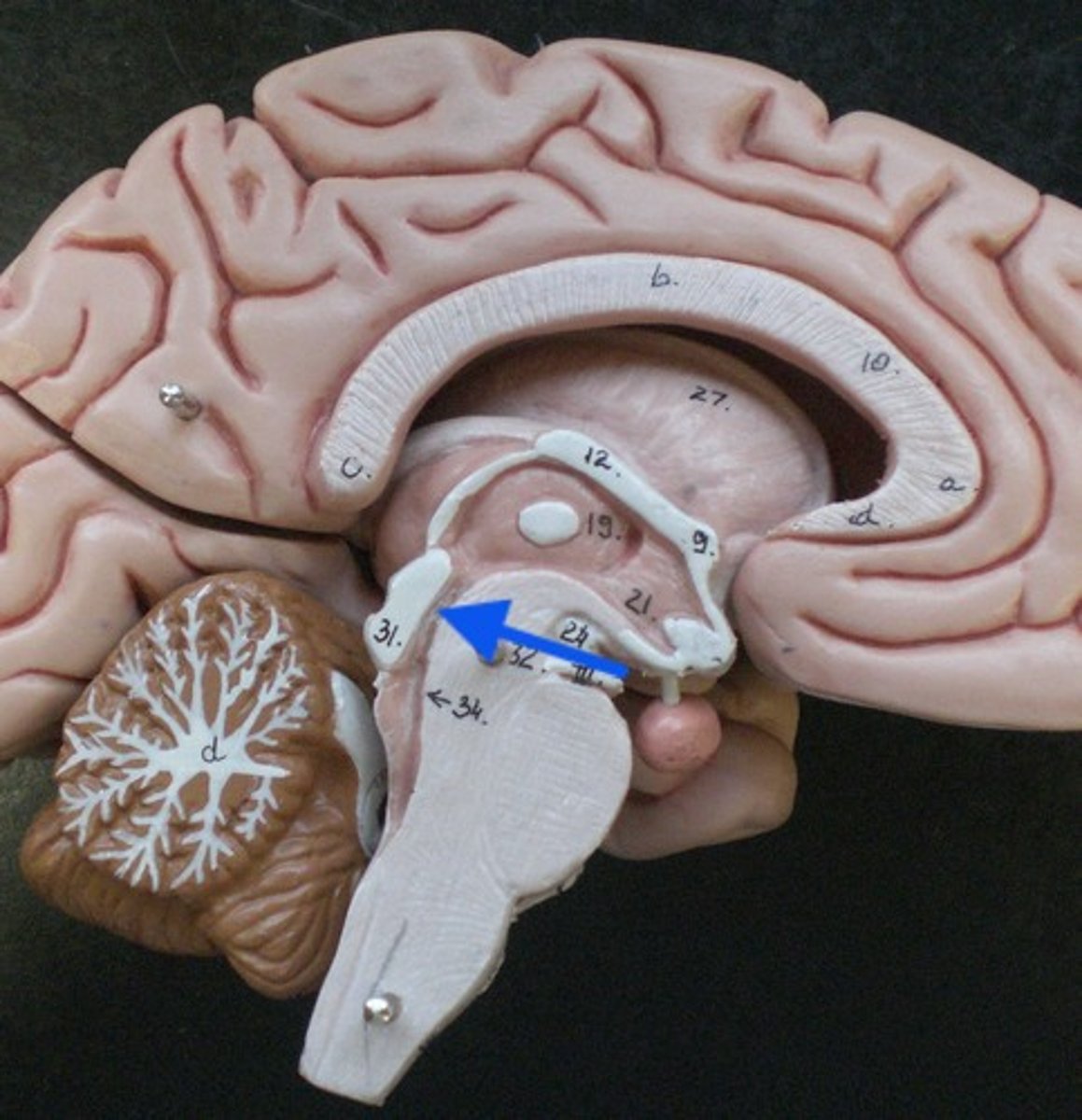
what structures surround the 4th ventricle?
Behind the brain stem (pons and medulla)
In front of cerebellum
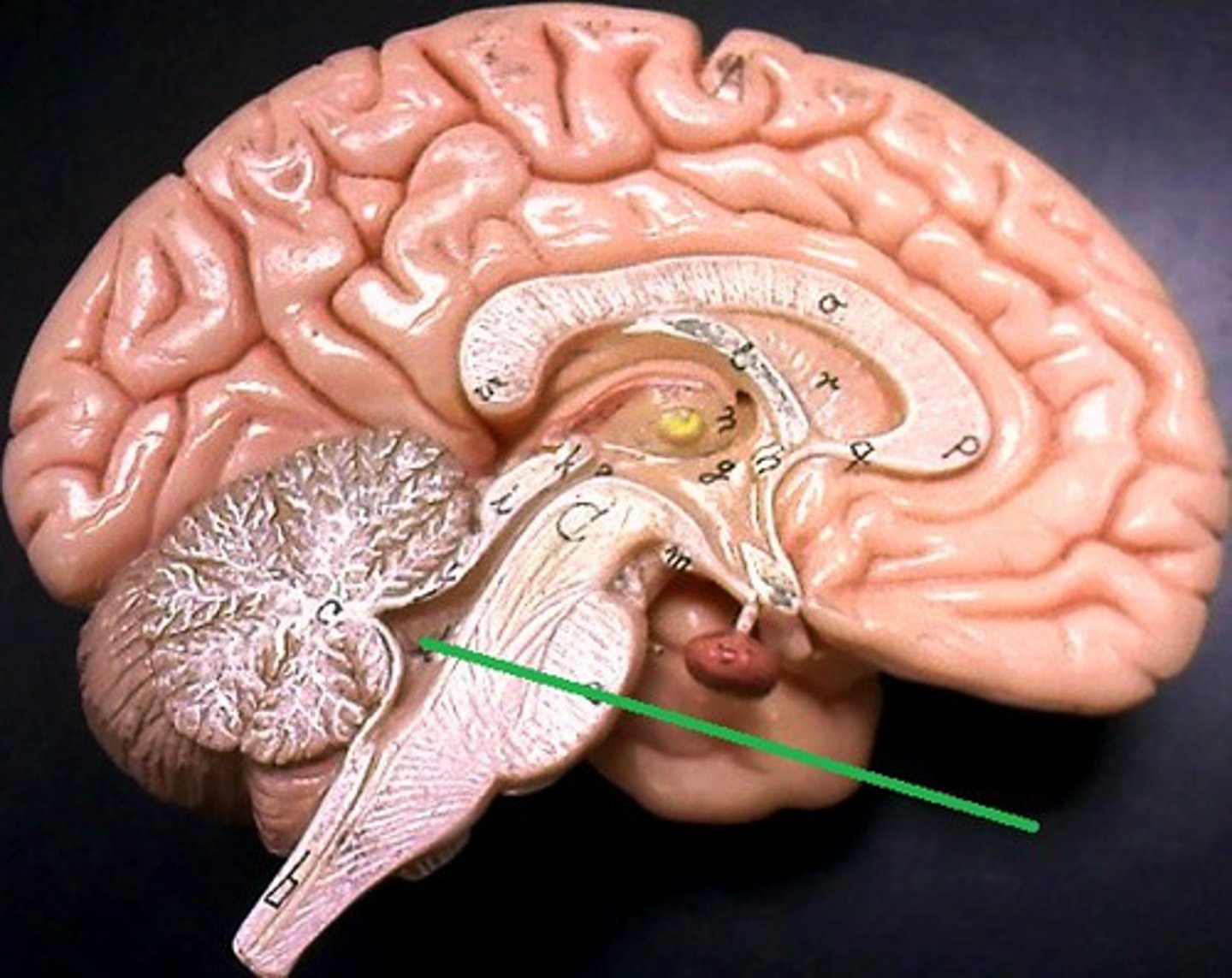
what are the apertures of the 4th ventricle?
where the 4th ventricle drains its CSF
2 lateral recesses with lateral apertures drain into the subarachnoid space
Inferior angle leads to the median aperture drains into the subarachnoid space
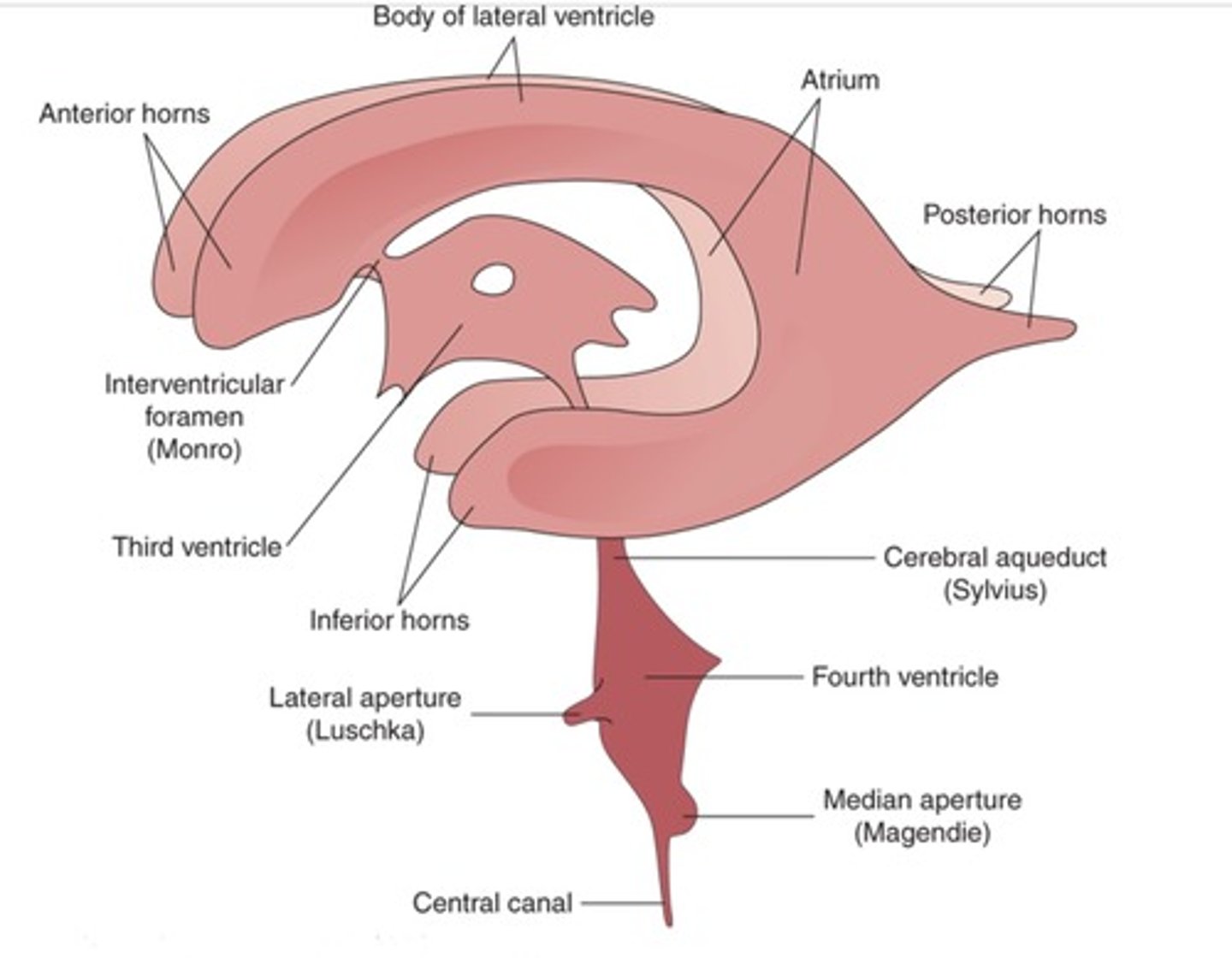
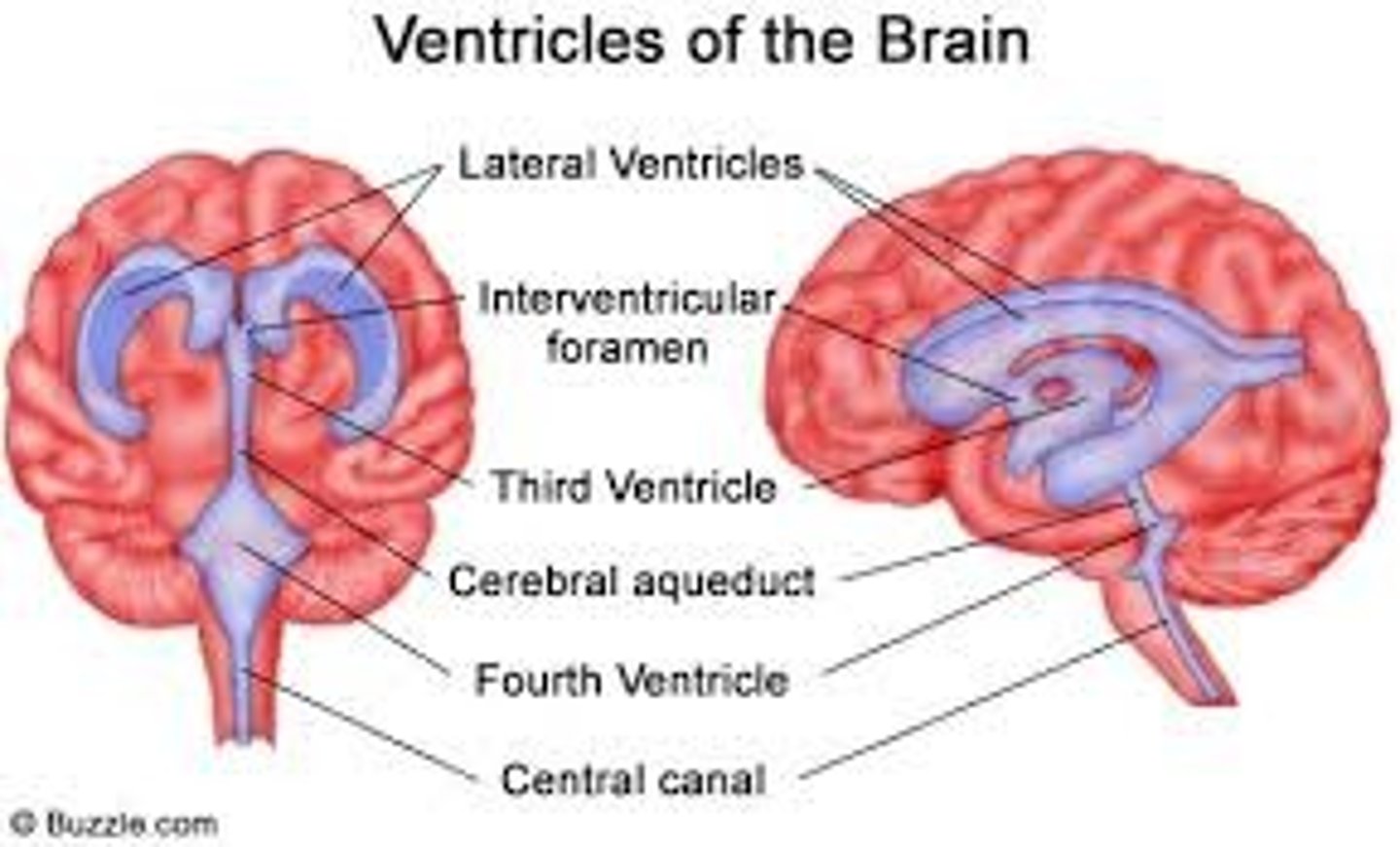
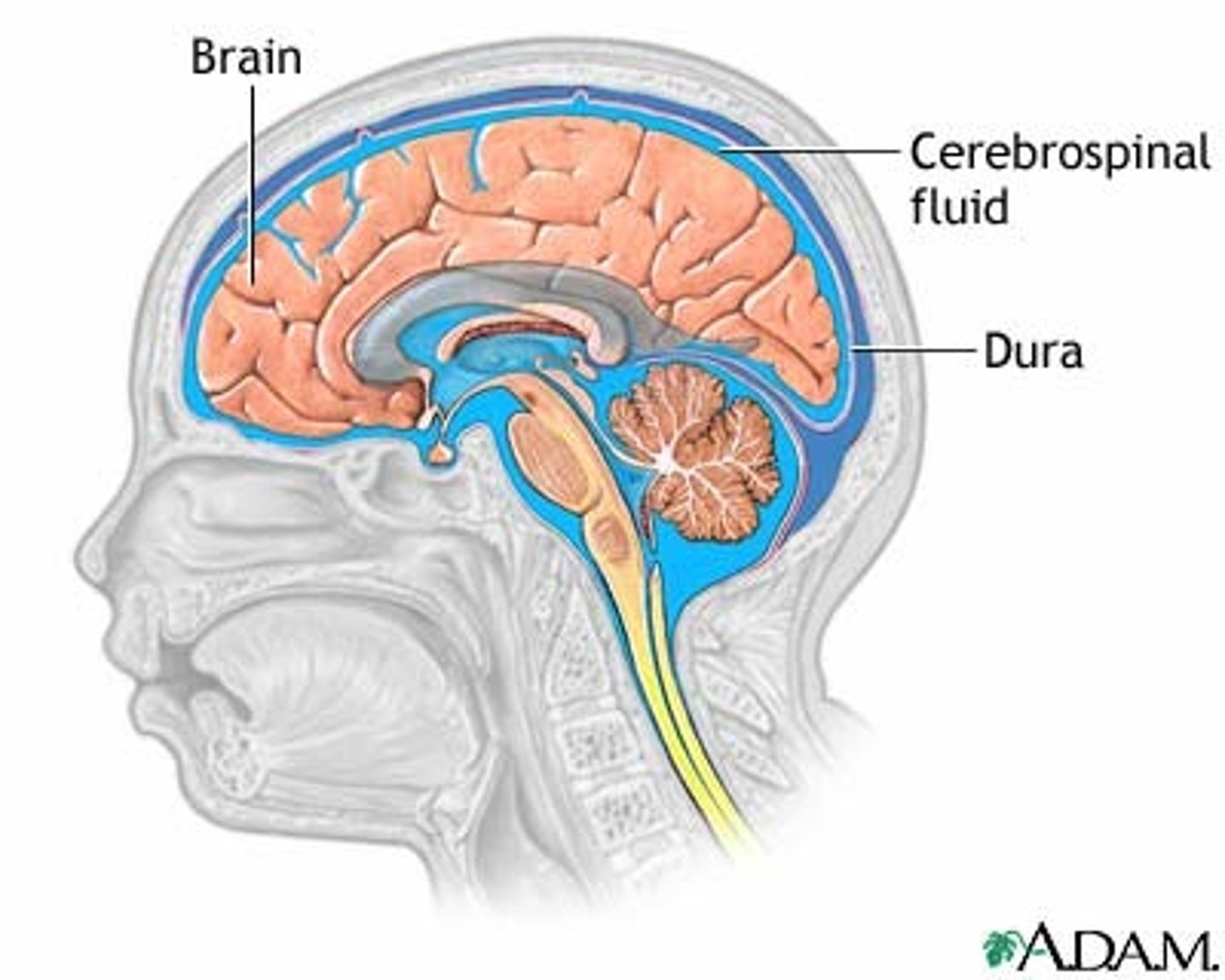
where is CSF found?
Subarachnoid spaces
Vertebral canal
Central canal
Cranial cavity
ventricles
what is CSF?
clear colourless fluid that contains cells and protein
how often is CSF reabsorbed?
Produced and reabsorbed continuously, thus all CSF is replaced 2-4 times a day
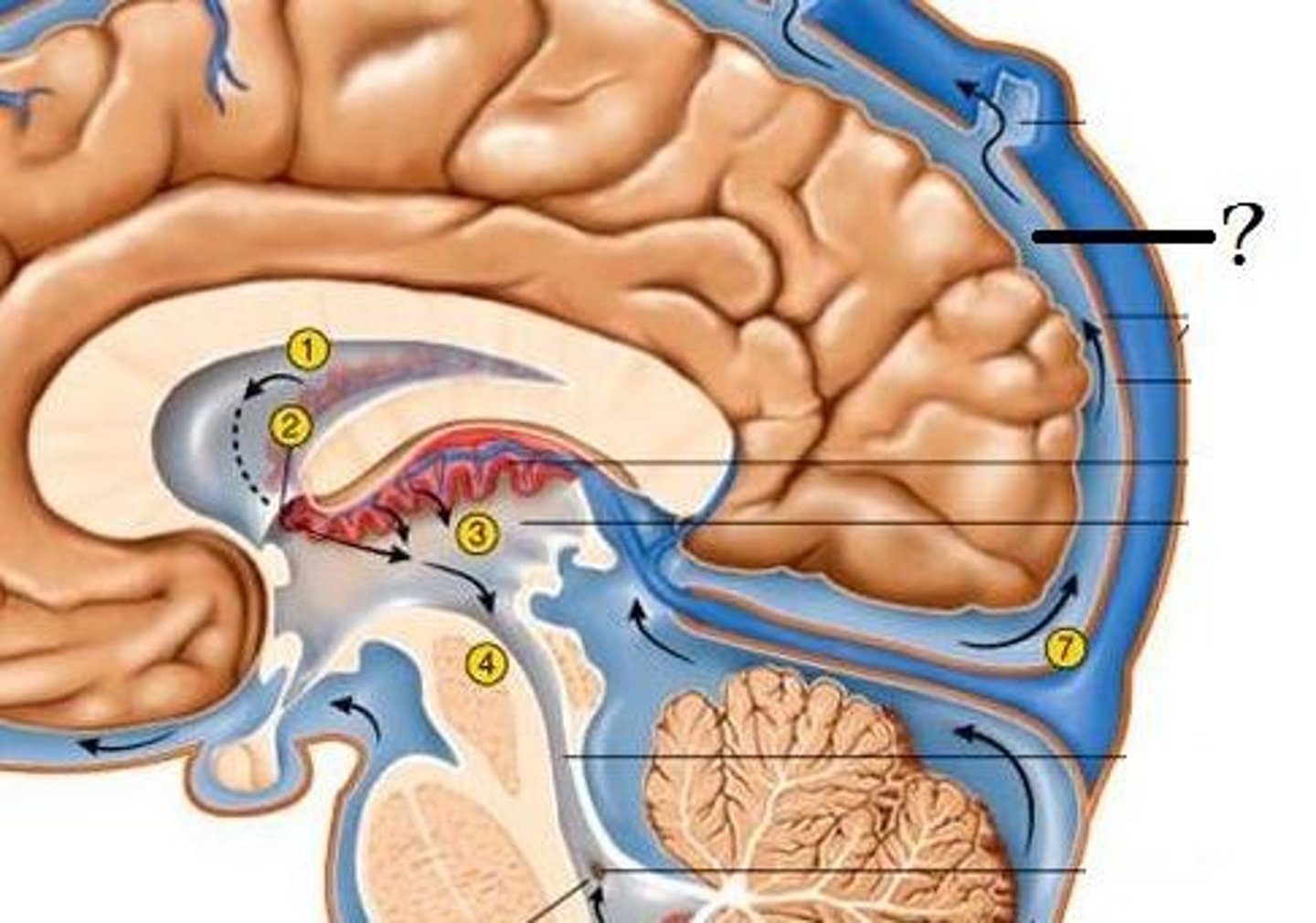
where is CSF produced?
choroid plexus, this is formed by an invagination of the pia mater into the lumen of the lateral ventricles, inside this lumen it becomes highly folded
Thus most CSF is produced in the lateral ventricles, that then flows through the cerebral aqueduct and into the 4th ventricle
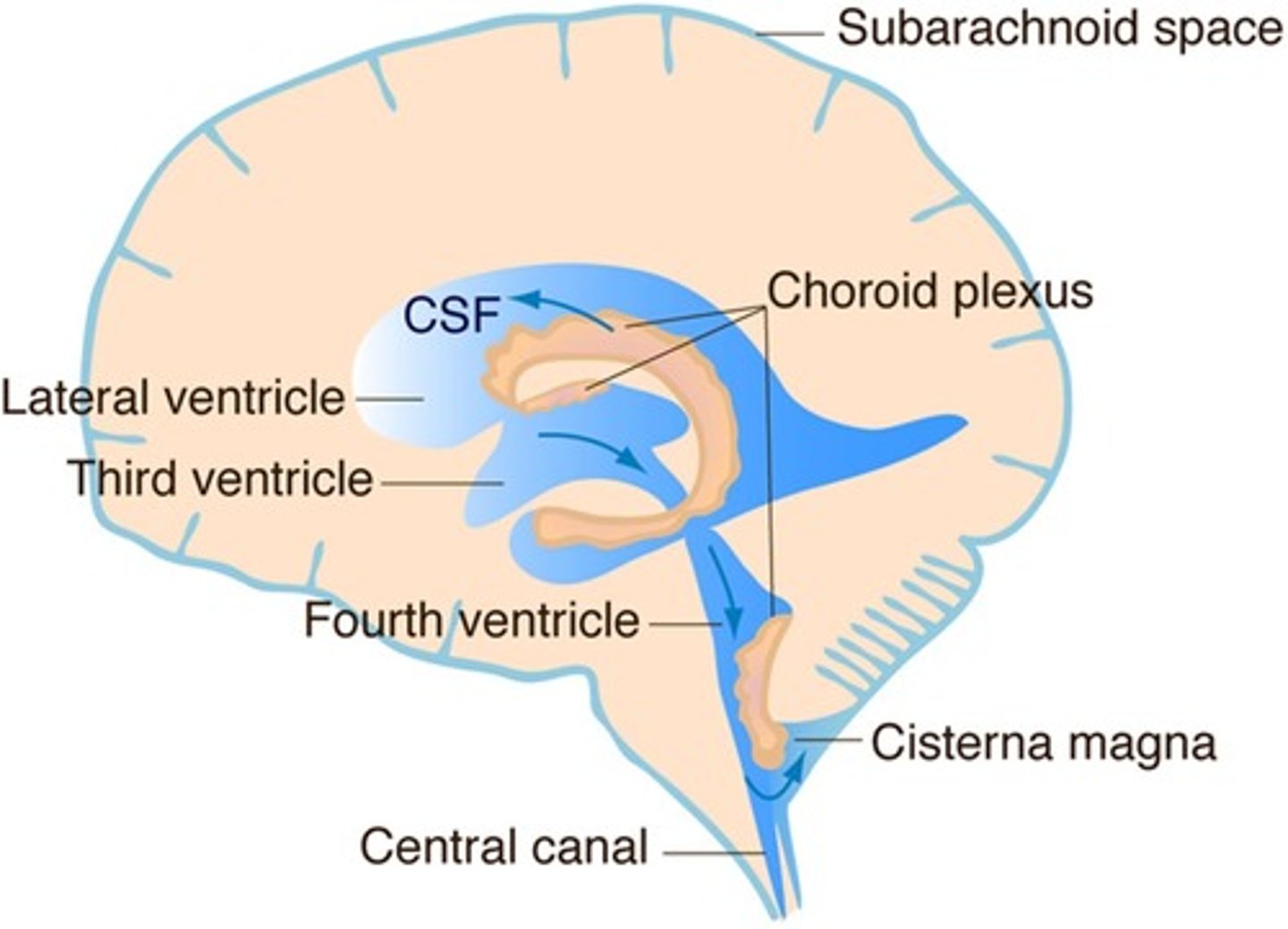
how is CSF reabsorbed?
CSF then flows within the subarachnoid space, back into the dural venous sinus via the arachnoid villi
Site of reabsorption- arachnoid villi within dural sinus
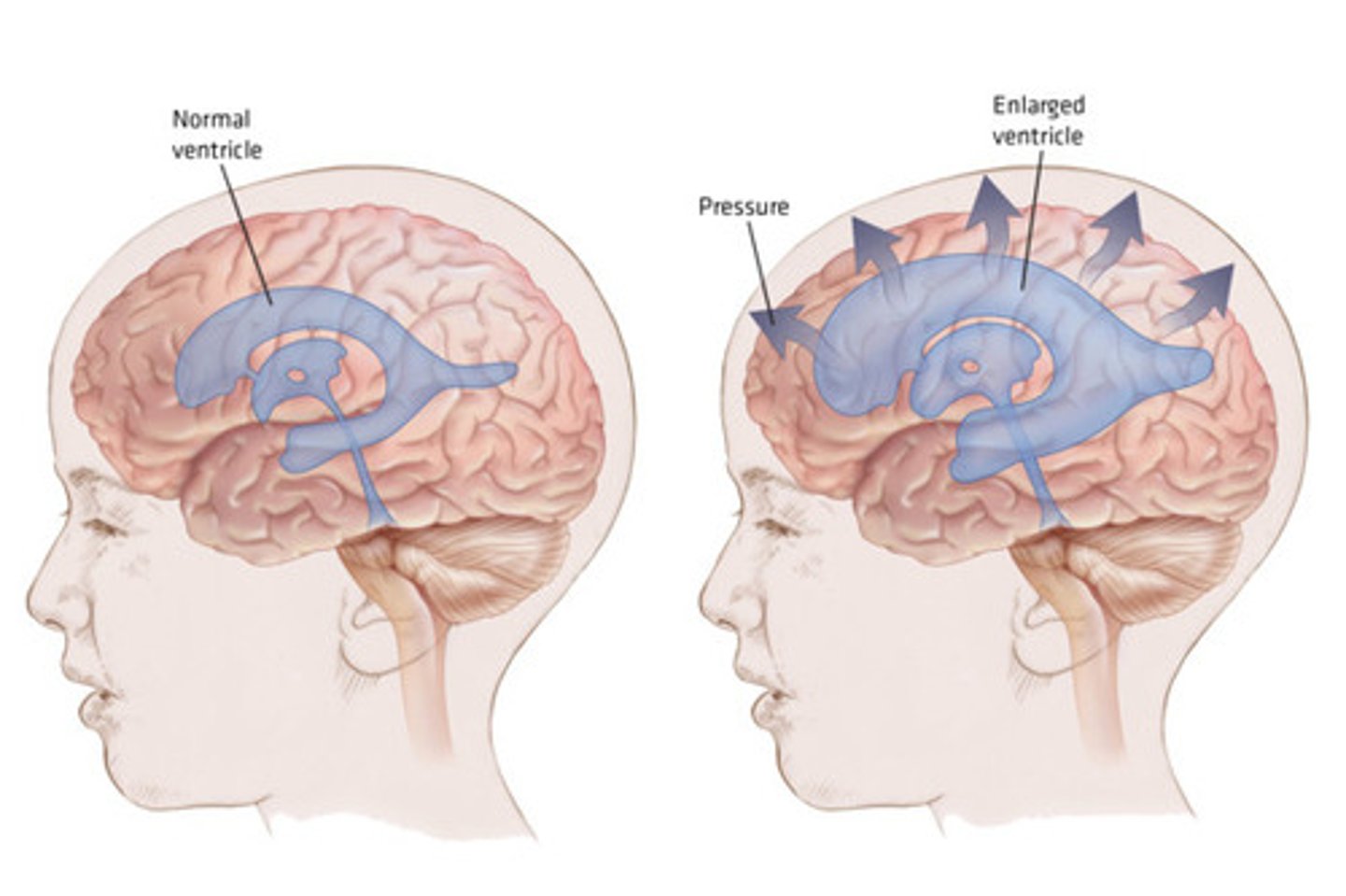
what is hydrocephalus?
Obstruction of CSF flow
excessive accumulation of CSF
Widens the ventricles and puts pressure on surrounding neurological tissue
Managed with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt- redirect fluid to peritoneal or pleural cavity