02 - Cell Chemistry and Macromolecules
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Unity of Biochemistry
Organisms are quite uniform at the molecular level
Jacques Monod (1954) – Anything found to be true in E.Coli must also be true in Elephants.
Atoms
Basic Unit of Matter
Protons and neutrons in “nucleus”, electrons in outer “shells”.
what determines chemical properties of atom
Number of outer shell electrons determine chemical properties.
__ elements make up ~99% of atoms in a human.
4
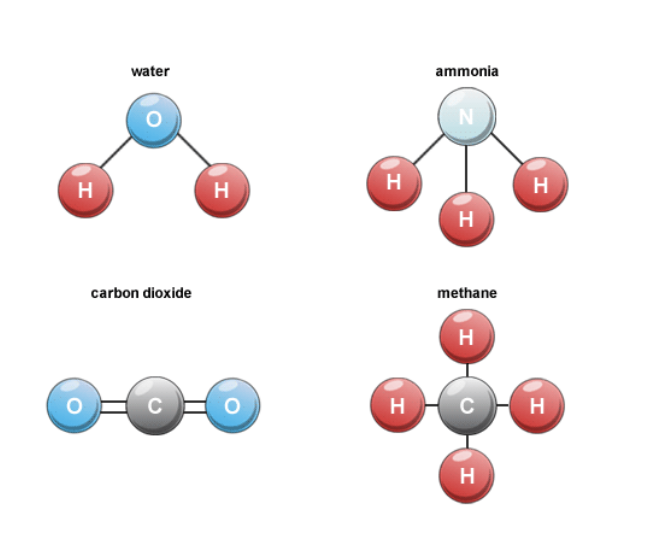
C,H,N,O
__ elements make up 0.9%
7,
na, mg, k, ca, p, s, cl
Molecules
2 or more atoms in a definite arrangement held together by chemical bonds
biomolecules
Molecules made by living organism
structure of biomolecules
centred around Carbon
• Carbon binds up to 4 other atoms
• Size and electronic structure is suited to generate large biological molecules
Covalent Bonds
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N) and Oxygen (O) can be linked together by covalent bonds to form molecules.
Can share electrons to creating stable bond
Atoms are most stable when
their outermost electron shells are full
Polar Covalent Bonds
• Unequal sharing of electrons
• Asymmetric charge distribution
• Electronegative atom
Asymmetric charge distribution
One atom has a partial negative charge and the other atom has a partial positive charge
Electronegative atom
atom with the greater attractive force is called the electronegative atom
Non-polar Covalent Bonds
Equal sharing of electrons
• lack electronegative atoms
Non-Covalent Interactions
Interactions between molecules or different parts of a large biomolecule
Depend on shared attractive forces between atoms of opposite charge
Types of noncovalent interactions important in cells:
• Ionic bonds
• Hydrogen bonds
• Van der waals attractions
• Hydrophobic interactions
Ionic bond
result of electrical attraction because of opposing charges. Involves transfer of electron(s) from one atom to the other.
eg of ionic bond in the cell
e.g. holds macromolecules together (DNA & protein) between positively charged nitrogen (protein) and negatively charged oxygen (DNA)
Hydrogen Bonds
weak bond, result of electrical attraction.
Keeps important biomolecular structures like DNA together
Polar molecules interact with other polar molecules, like water
Van der Waals Forces
weak and nonspecific interaction between two atoms in close proximity.
Temporary charges in nonpolar molecules = ‘dipoles’
Form because electrons are constantly in motion
Hydrophobic Interactions
uncharged non-polar molecules do not interact with polar molecules (e.g. water)
Form clumps or aggregates to minimize exposure
Not an actual bond
What term refers to a noncovalent bond in which an electropositive hydrogen atom is partially shared by two electronegative atoms?
A) Hydrogen bond
B) van der Waals attraction
C) Ionic bond
D) Hydrophobic interaction
a
Biomolecules structure
Biomolecules centred around Carbon - Carbon binds up to 4 other atoms
Simplest group of biological molecules
hydrocarbons (C-H)
Hydrogen is often replaced by
Functional Groups
Functional Groups
particular atom groupings that behave as a unit
what do functional groups affect
Affect the properties of biomolecules (e.g. change chemical reactivity) because:
• Contain electronegative atoms (N,O,P,S)
• Can make molecules more polar or more reactive
• May confer a positive or negative charge due to ionization
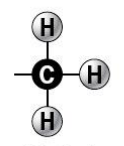
methyl
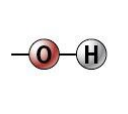
hydroxyl
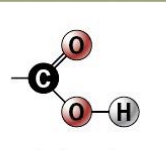
carboxyl
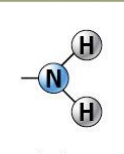
amino
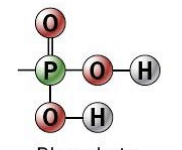
phosphate
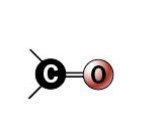
carbonyl
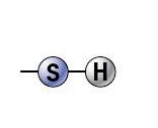
sulfhydryl
Macromolecules
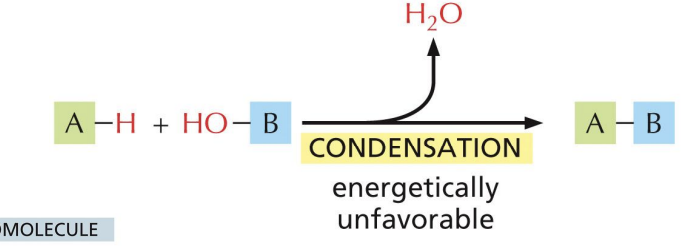
polymers of building blocks known as monomers
Polymers form by joining monomers =
condensation (water is removed)
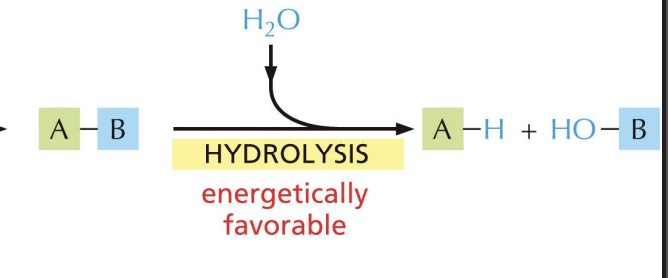
Polymers are broken down into monomers
hydrolysis (water is added)
Monomers of macromolecules are joined together by
covalent bonds.
examples of macromolecules
polysarcarides, fats, proteins, nucleic acid
Carbohydrates - general formula
(CH2O)n
• Important sugars in cell metabolism have
3-7 carbons
3 sugars = trioses; 4 sugars = tetroses; 5 sugars = pentoses; 6 sugars = hexoses
Carbonyl internal position –
forms ketone = ketose
Carbonyl at one end –
forms aldehyde = aldose
Sugars with 5 or more carbons form
a closed ring structure.
monosaccharide
is the simplest type of carbohydrate—a single sugar molecule.
why are some sugar molecules form a ring structure
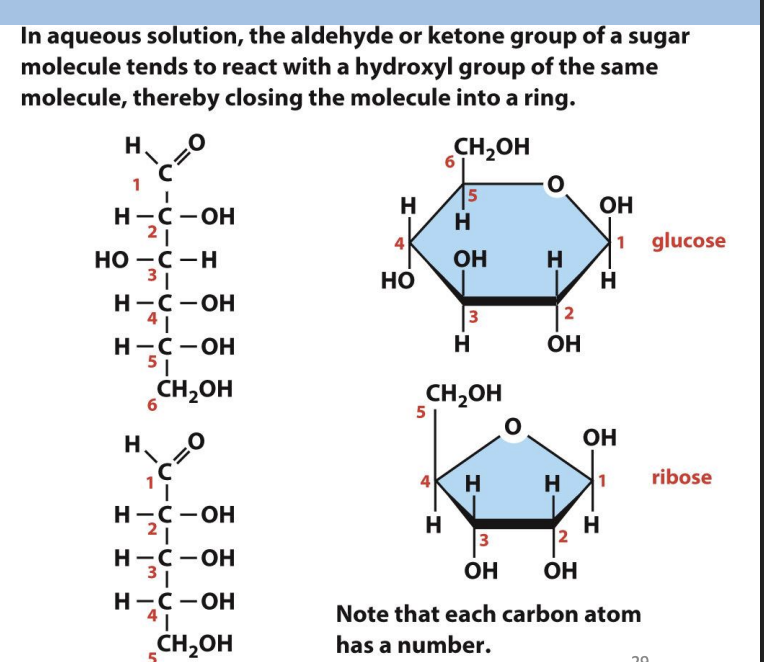
Glucose
= 6-membered ring
α-glucose
OH of C1 projects below the plane of the ring
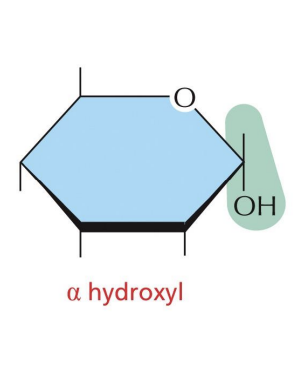
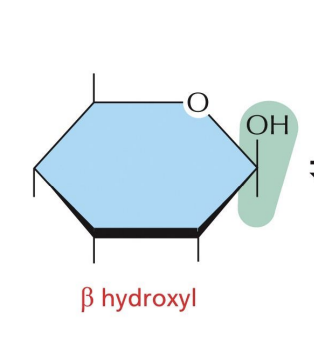
β-glucose
OH of C1 projects up from the plane of the ring
isomers
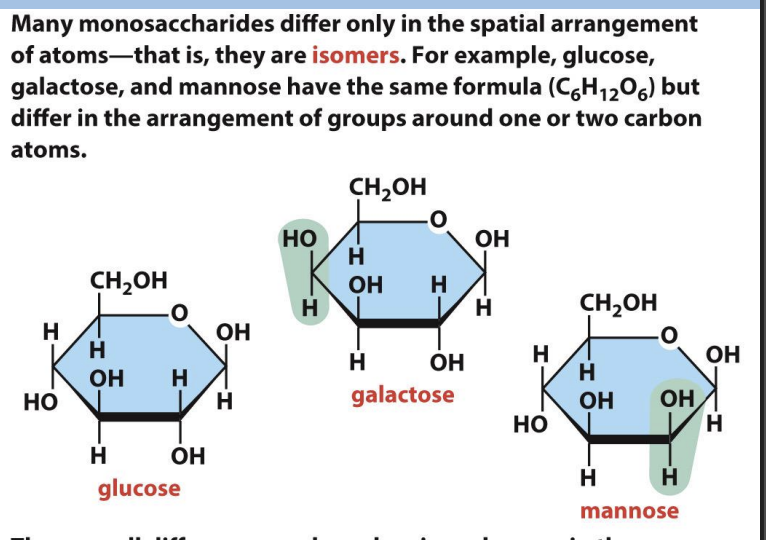
are small differences in structure that imp

Linking monosaccharides
• Covalent bond formed between C1 of one sugar and hydroxyl (OH) of another sugar
• Generates C-O-C linkage between sugars
• Alpha(1,4) linkage
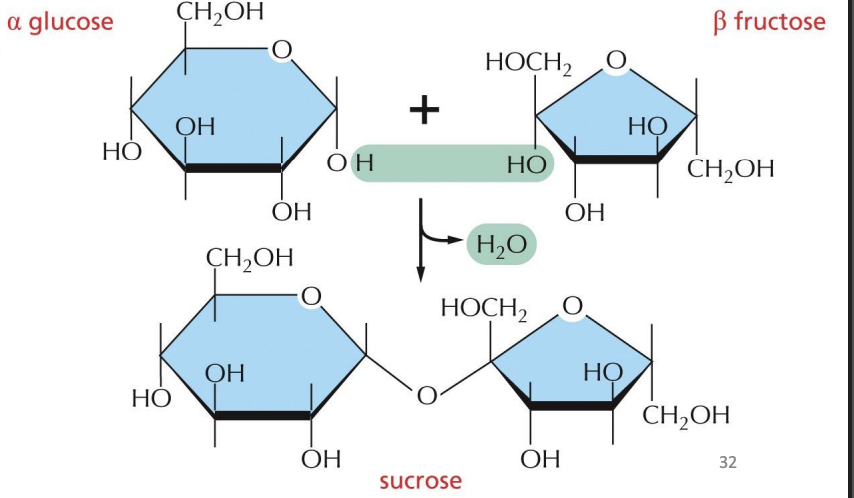
Disaccharides
2 monosaccharides covalently bonded together
• energy storage, ex. Sucrose, maltose, lactose
Oligosaccharides:
a small chain of sugars
• if attached to lipids or proteins = glycolipids or glycoproteins
Polysaccharides:
a long chain of sugars
• very large molecules with a structural or storage function, ex: Chitin, cellulose, starch, glycogen
All carbohydrates have the following:
A. Ketone group.
B. Aldehyde group.
C. Hydroxyl group.
D. All of the above.
c
Lipids
A large group of nonpolar biological molecules
• Composed mainly of C,H and O
• Dissolve in organic solvents but not in water (lack polar groups)
Lipids with important cell functions:
• Fats
• Steroids
• Phospholipids
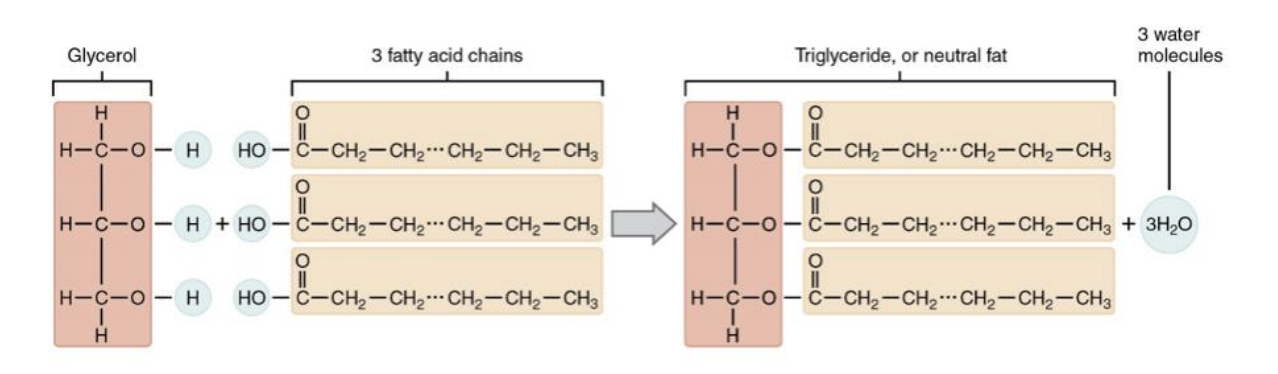
Fats
triacylglycerol
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
Fatty acids
long hydrocarbon chains with a single carboxyl at one end
they vary in length
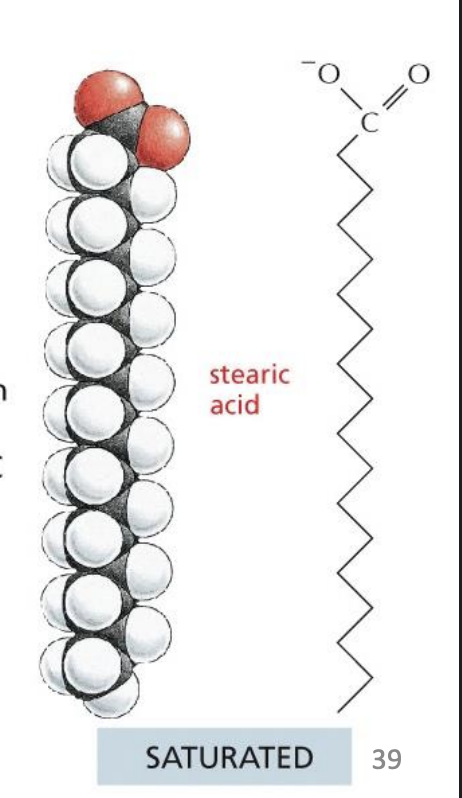
saturated fatty acids
No double bonds
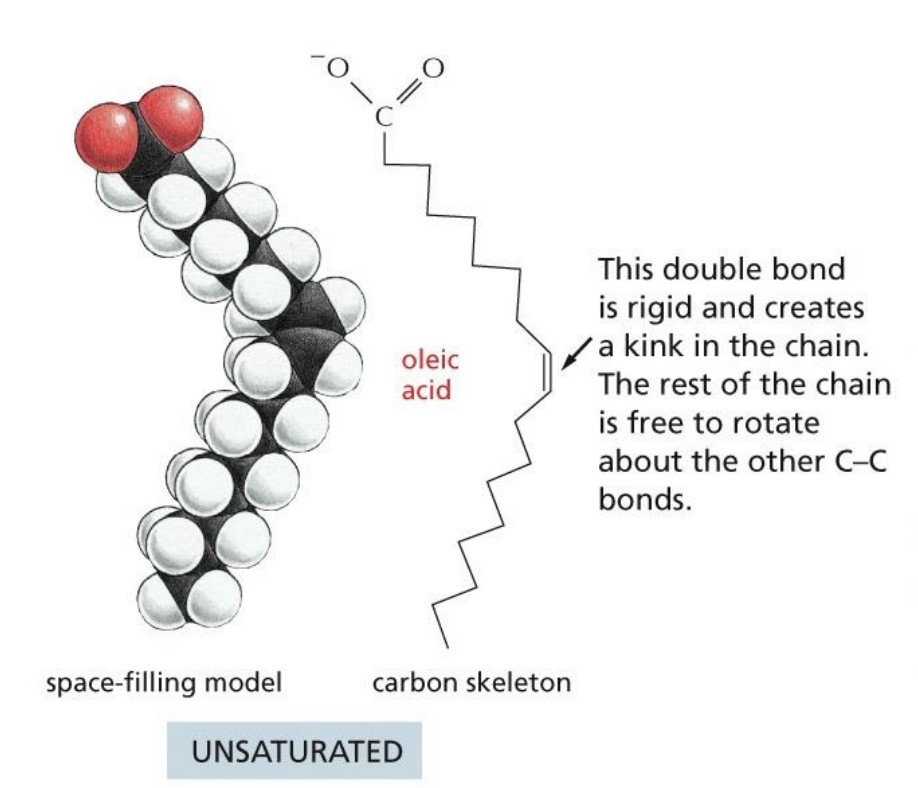
unsaturated Fatty acids
Double bonds
Linking Fatty Acids
Ester bonding links fatty acids to glycerol
Steroids
Complex ring structures = 4 hydrocarbon rings
example of Steroids
Cholesterol = important animal plasma membrane component
estrogen
testosterone
Cholesterol are the Building blocks of
many steroid hormones
is cholesterol in plant cells
• Not present in plant cells, “cholesterol-free”
Phospholipids
Composed of glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group
Major component of plasma and organelle membranes
Hydrophilic end on Phospholipid
phosphate head
hydrophobic end on Phospholipid
fatty acid tail
amphipathic
Hydrophilic on one end and hydrophobic on the other
phosphatidyl choline
Positively charged choline group attached to the phosphate
what do phospholipids form
Lipid bilayers are formed by phospholipids.
Lipid Bilayers Form Cell Membranes
Polymers of nucleotides
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Nucleotides
5-carbon sugar + nitrogenous base + phosphate
dna vs rna sugar
DNA has deoxyribose sugar, RNA has ribose sugar
Linking Nucleotides
Nucleotides are joined by sugar-phosphate linkages
• 3’ hydroxyl attached to 5’phosphate of the adjoining nucleotide
• Phosphodiester bond
bases are paired with which type of bond
hydrogen
purine
2 rings
a, g
pyramidines
1 ring
t, c
Which statement is true?
A. Thymine is only found in RNA.
B. In RNA, the pentose is ribose.
C. Uracil is only found in DNA
D. Adenine and Guanine form a complementary base pair
b
functions of a nucleotide
As nucleoside di- and triphosphates, they carry chemical energy in their easily hydrolyzed phosphoanhydride bonds
They combine with other groups to form coenzymes.
They are used as small intracellular signaling molecules in the cell.
function of protein
Carry out almost all cellular functions. Examples:
• Enzymes - accelerate chemical reactions in the cell
• Signaling - kinases, phosphatases are involved
• Hormones - long range messenger molecules
• Growth factors
• Membrane receptors - communication between cells
• Cell movement - cytoskeleton
what are amino acids composed of
Composed of H, C, O, N and also S or P
how many types of amino acids are there
20
structure of a amino acid
• Amino (NH2) and Carboxyl (COOH) groups
• -These groups are separated by a single carbon (α-carbon)
• R groups (side chains) give amino acids their variability
4 categories of R groups:
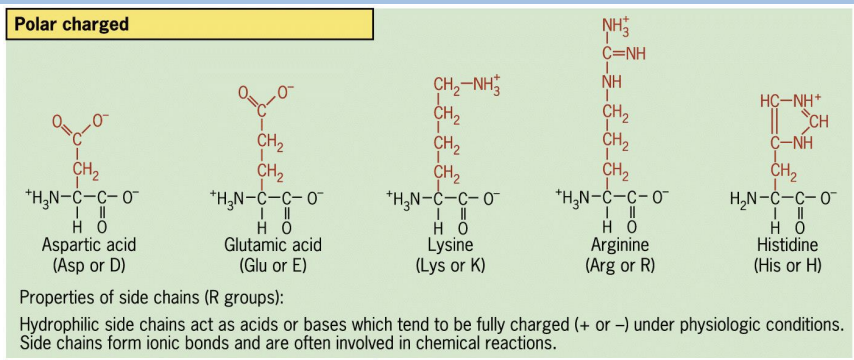
• Polar charged
• Polar uncharged
• Nonpolar
• Other
Polar charged
form ionic bonds
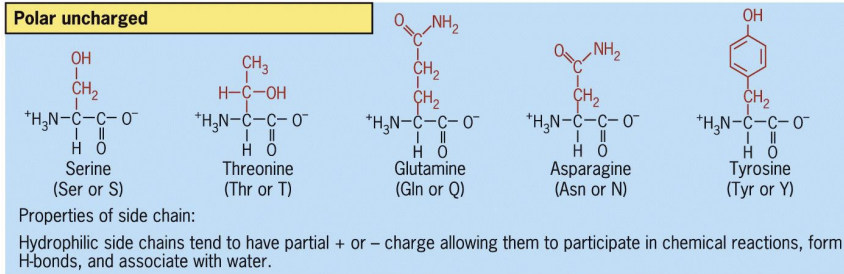
Polar uncharged
form H bonds
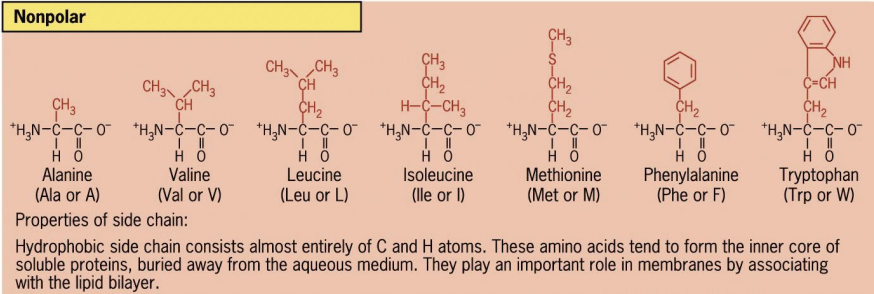
Nonpolar
hydrophobic interactions
Other
e.g. sulfhydrl or cysteine
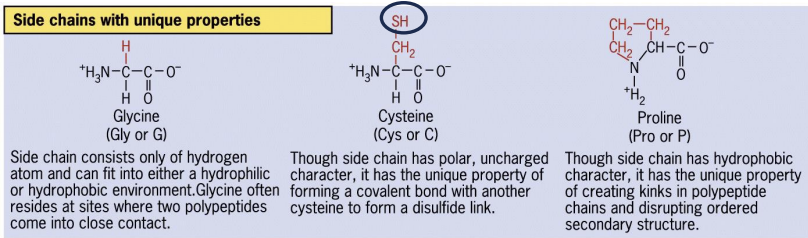
Cysteine amino acids
can form disulfide bonds in oxidizing conditions.
Peptide bonds
Carboxyl group of one amino acid becomes attached to the amino group of another
polypeptide chains
proteins
How many water molecules would be produced in making a
polypeptide that is 14 amino acids long?
A. 13
B. 14
C. 27
D. 28
a
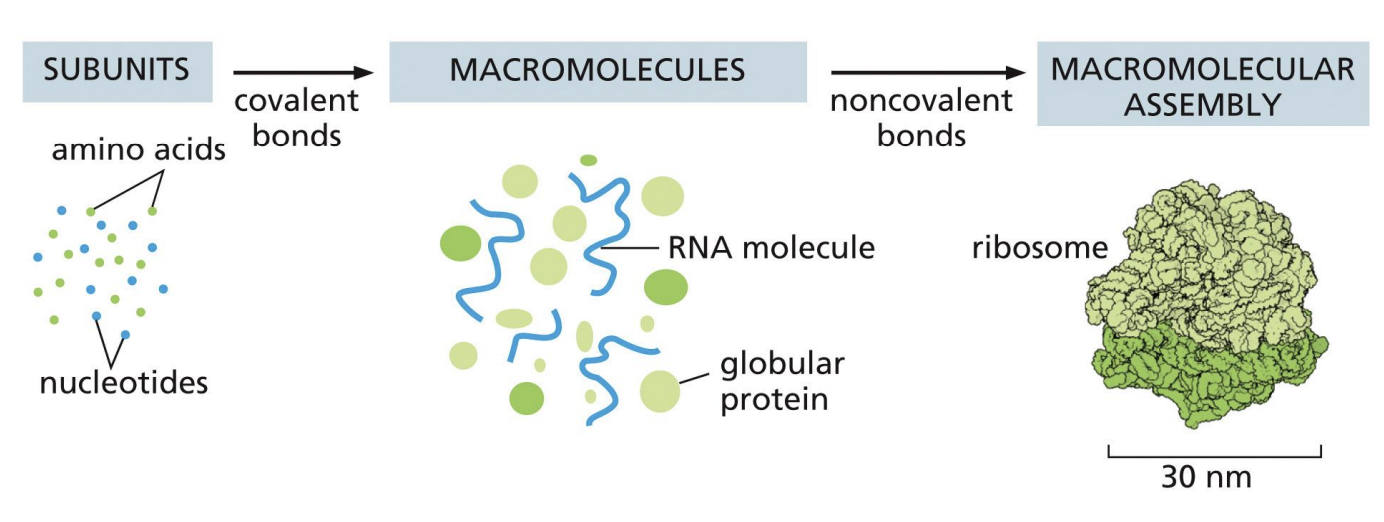
how can macromolecules assemble in complexes
is reversing disorder spontaneous or not
not spontaneous
Second law of thermodynamics
cannot reverse the state of a system without increasing entropy of surroundings
Need release of heat (energy conversion)
Catabolic
lose heat
breakdown
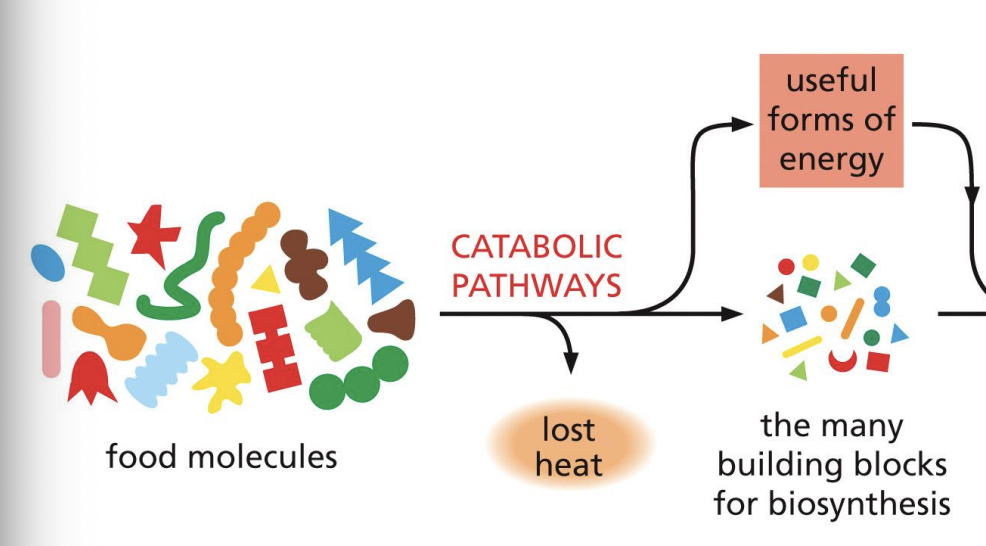
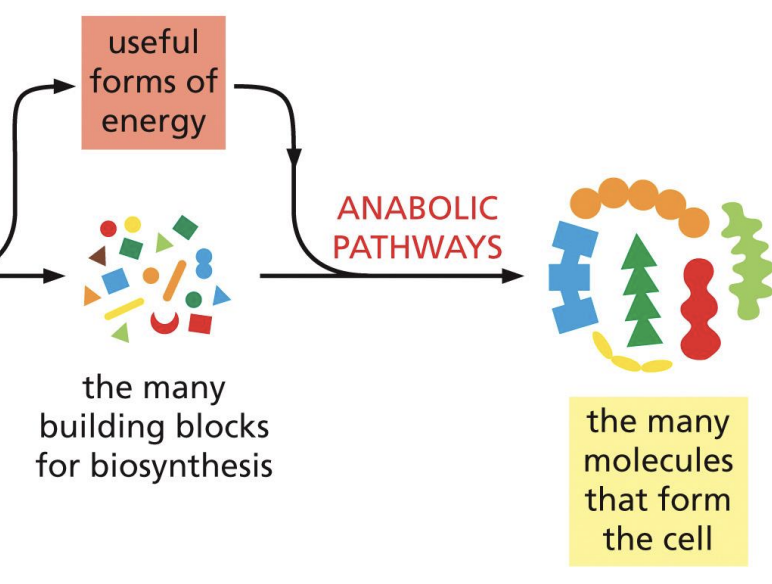
Anabolic
build up