Introduction to Comparative Anatomy
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Morphology
the study of anatomy and its significance
Functional morphology
discipline that relates a structure to its function
Primitive Traits
Trait that develops for the first time

Derived Trait
newly evolved features that developed from primitive
Archetype
Model of Organism
Vertebrate Morphology
Explains vertebrate design by clarifying the reasons for and processes that produce the structural plan of a vertebrate animal
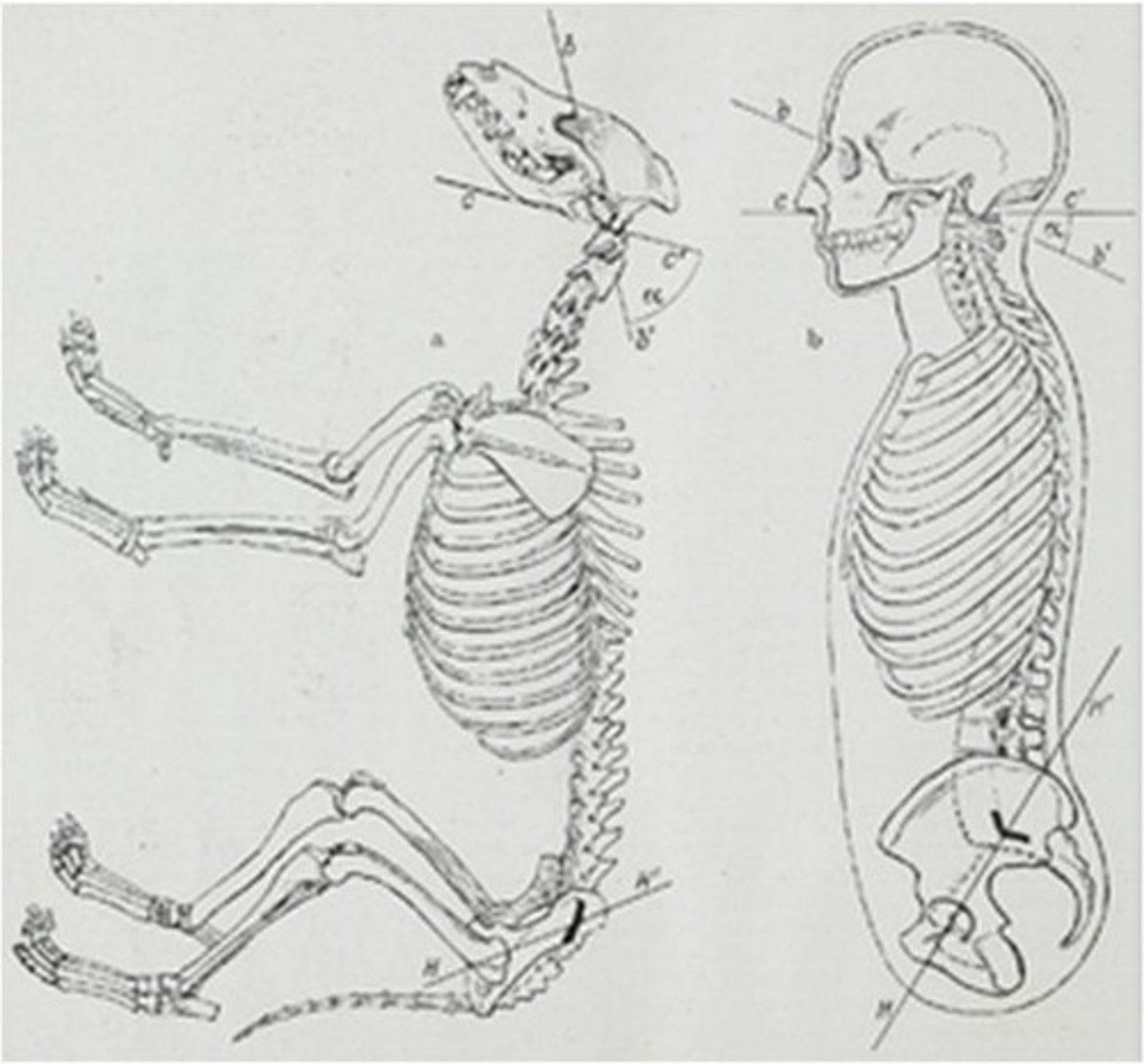
Ontogeny
The development of an organism.
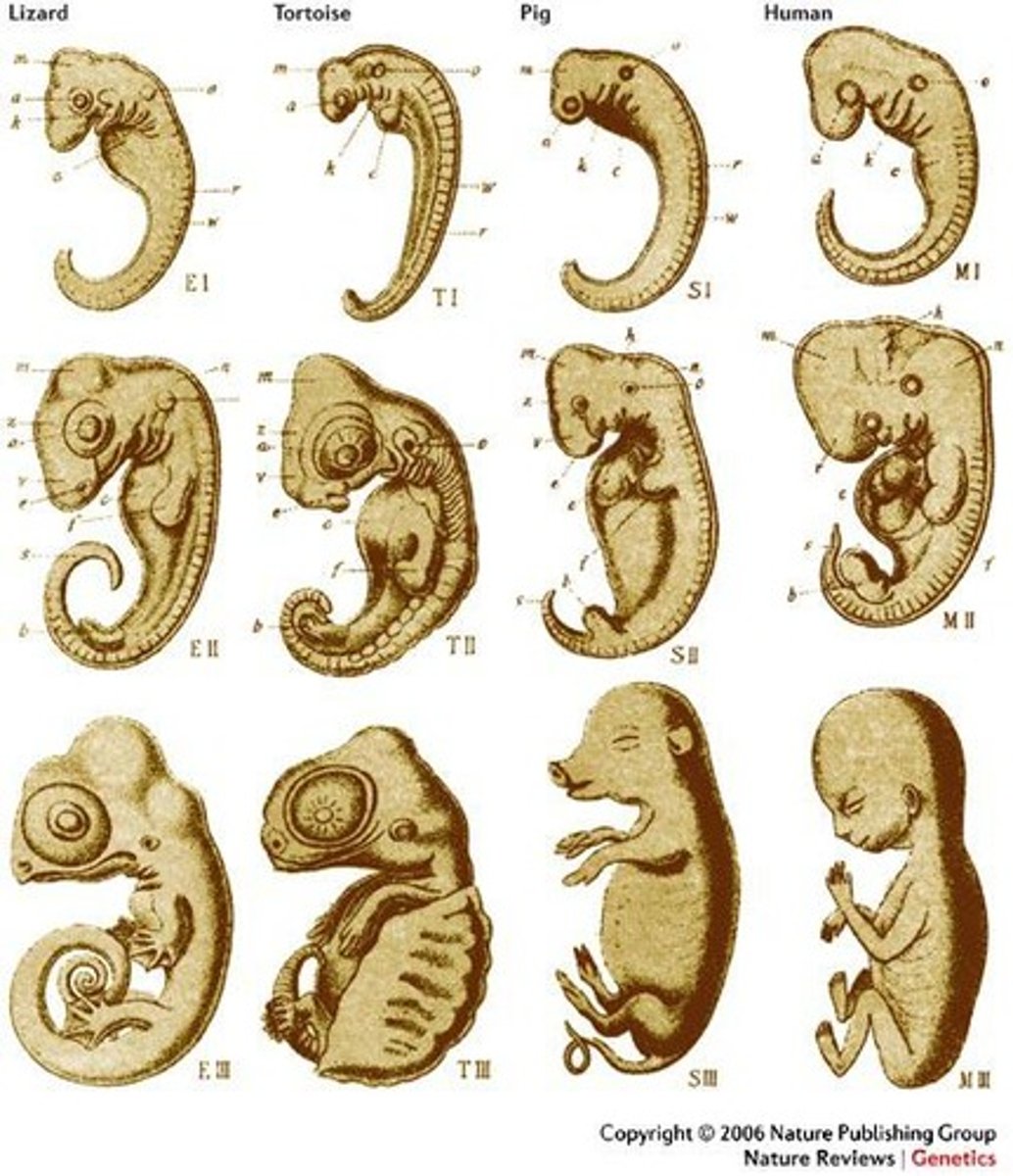
Homology
Similarity in characteristics resulting from a shared ancestry.
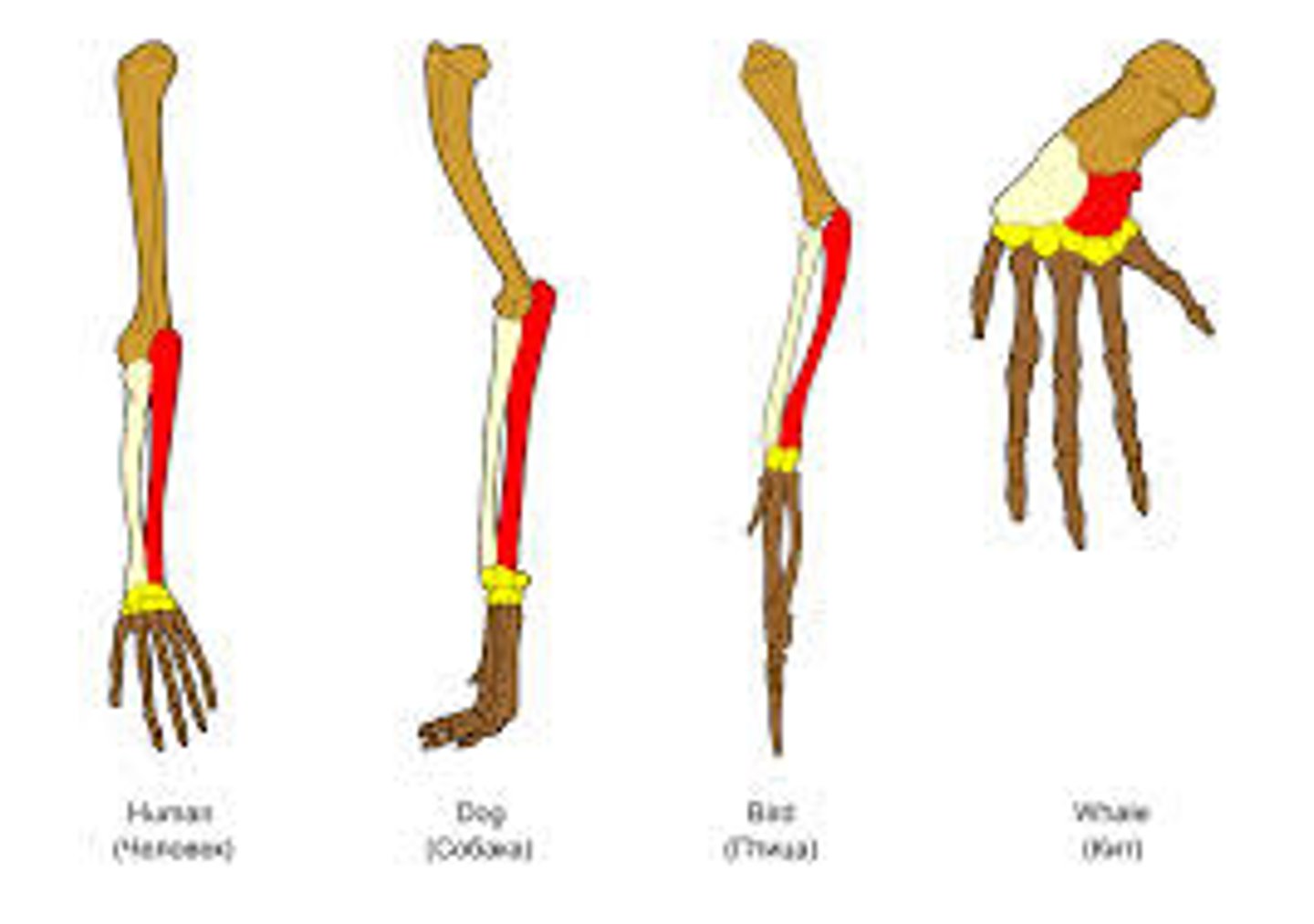
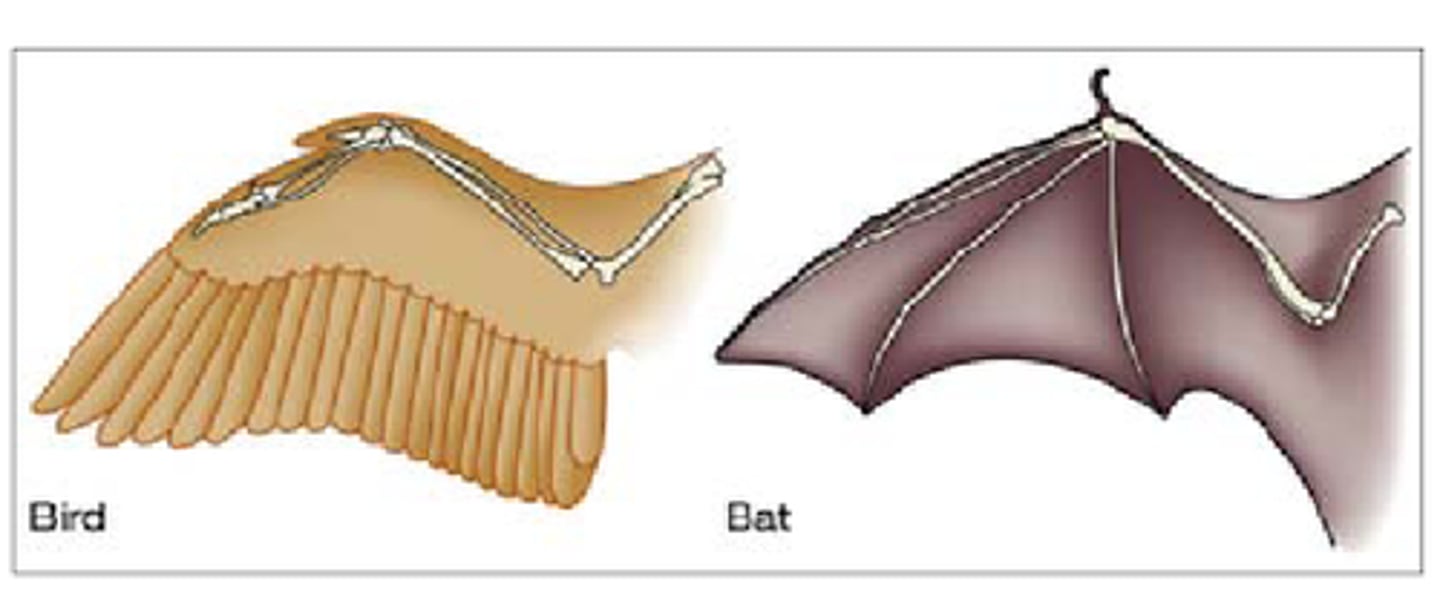
Analogy
features in different organisms that have similar function (but not necessarily due to common ancestry)
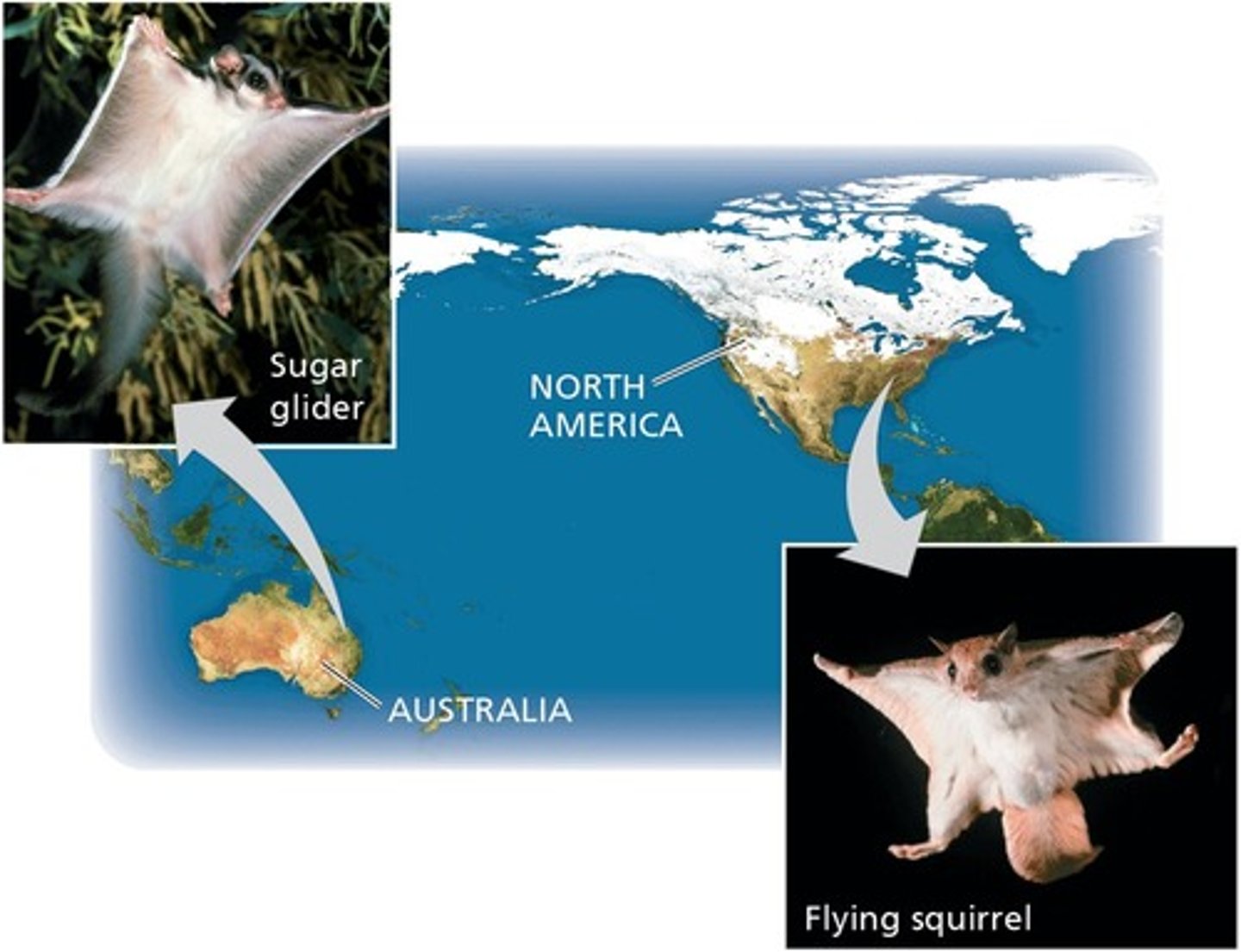
Homoplasy
Features in different organisms that look alike
Symmetry
how an animal meets its surrounding environment
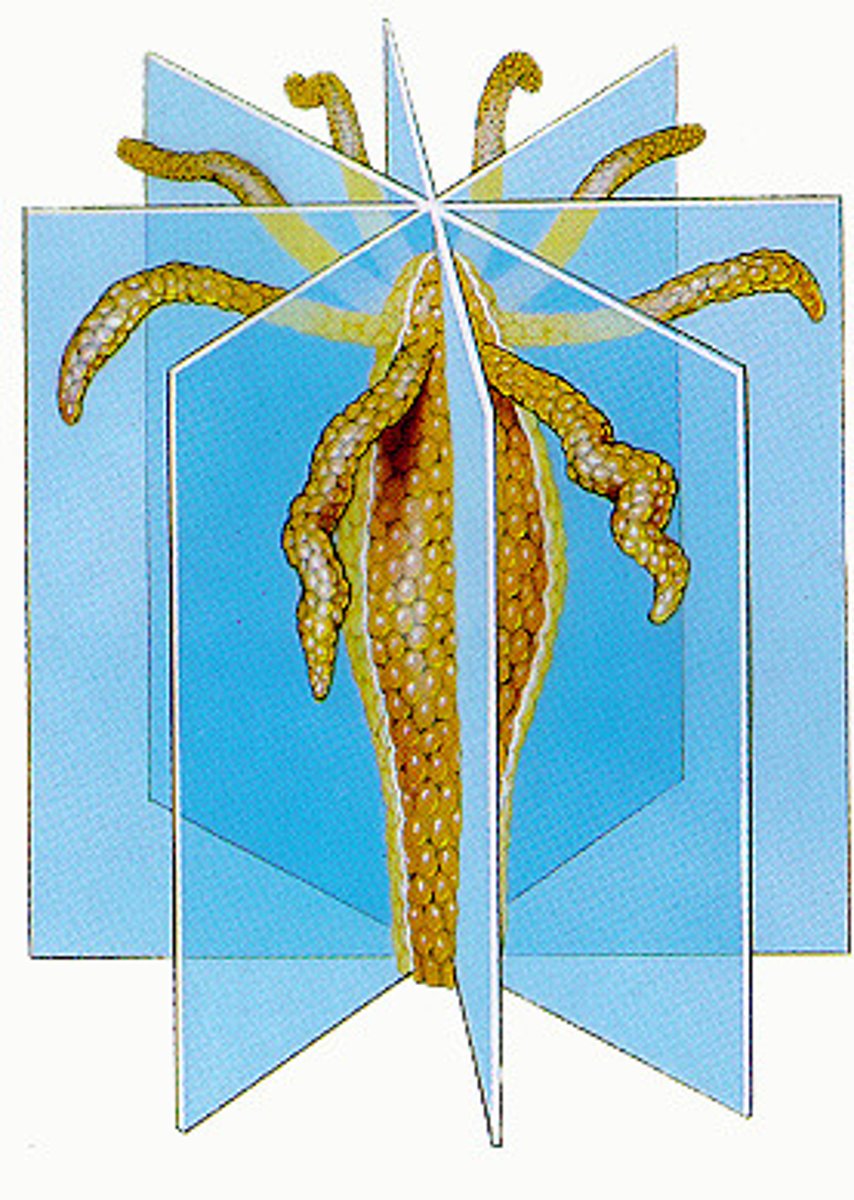
radial symmetry
body plan in which body parts repeat around the center of the body

bilateral symmetry
Body plan in which only a single, imaginary line can divide the body into two equal halves.

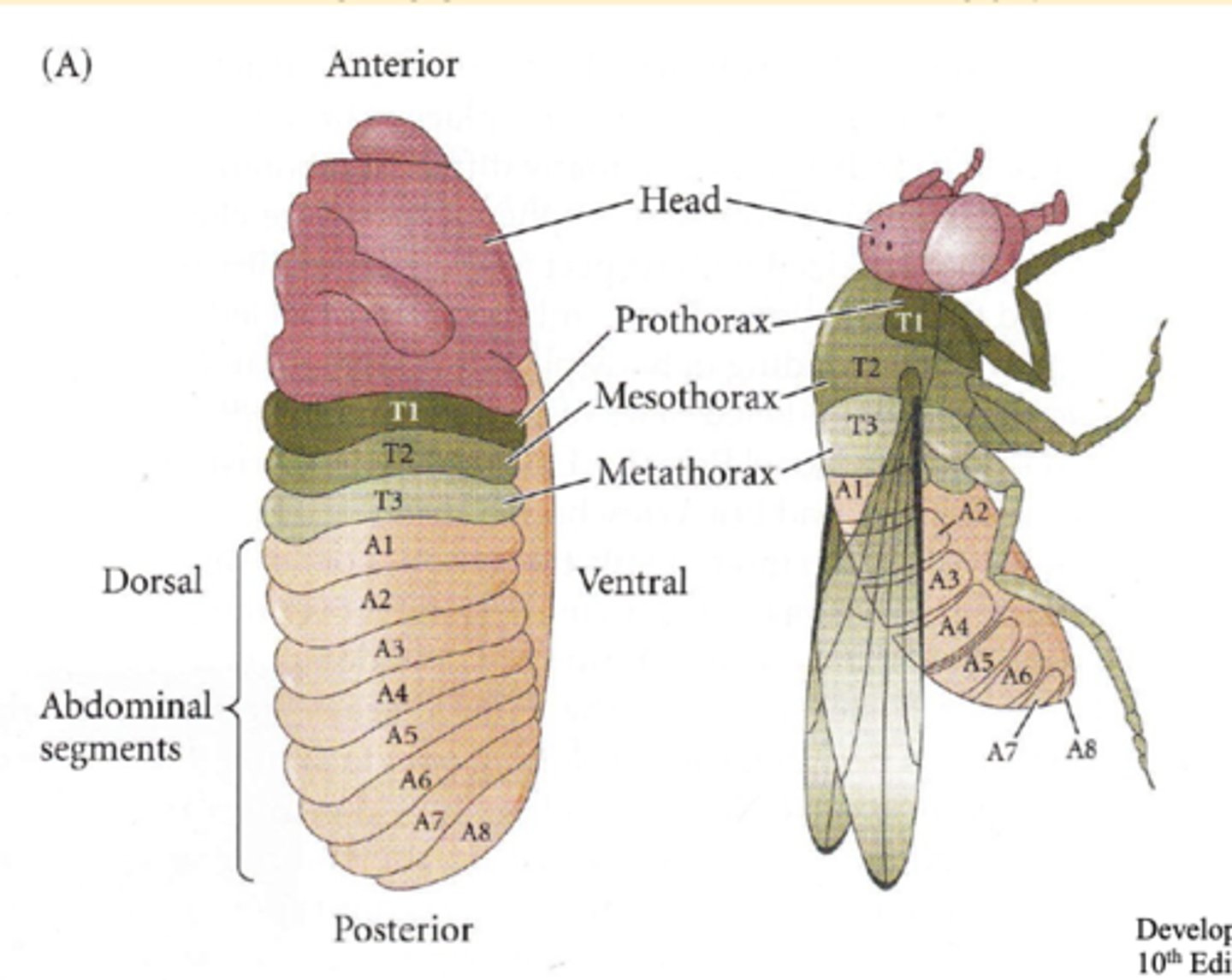
Segmentation
process that divides the body into duplicated sections; segment = metamere
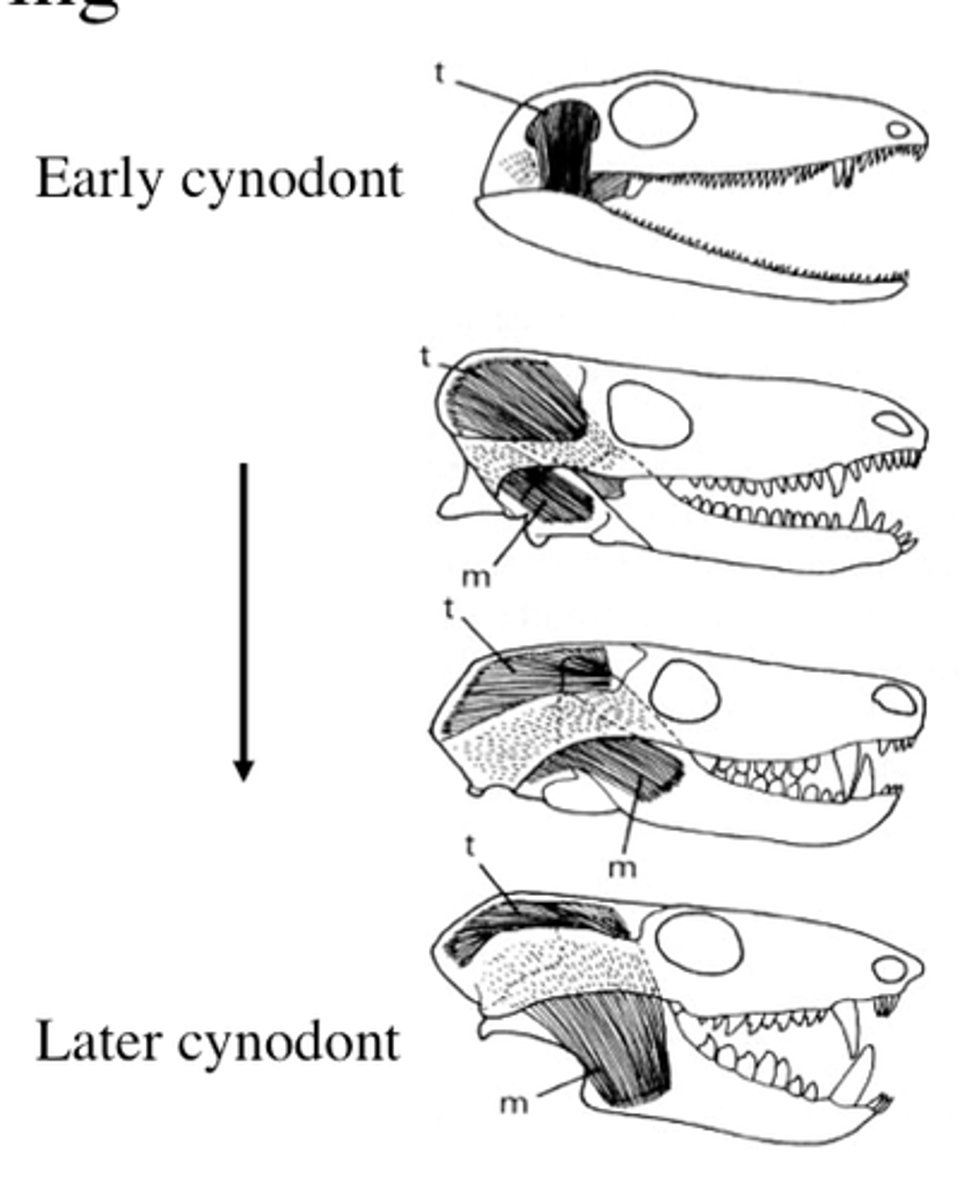
Evolutionary Morphology
The function of a structure and its role in adaptation and evolution.
Function
The action or property of a part as it works in the organism
Biological role
how the part is used in the environment during the organism’s lifetime
Phylogeny
evolutionary history of a group of organisms (species)
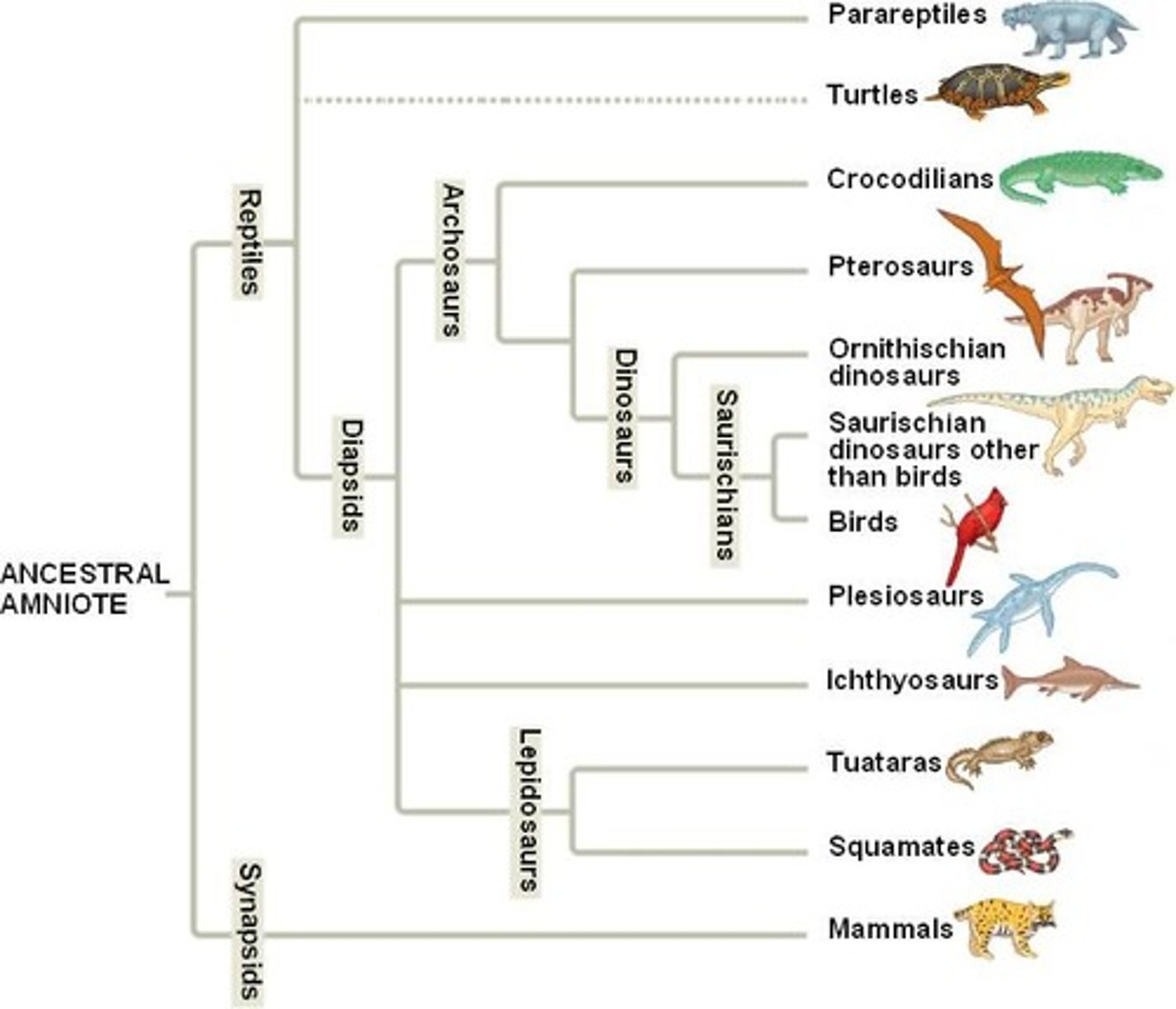
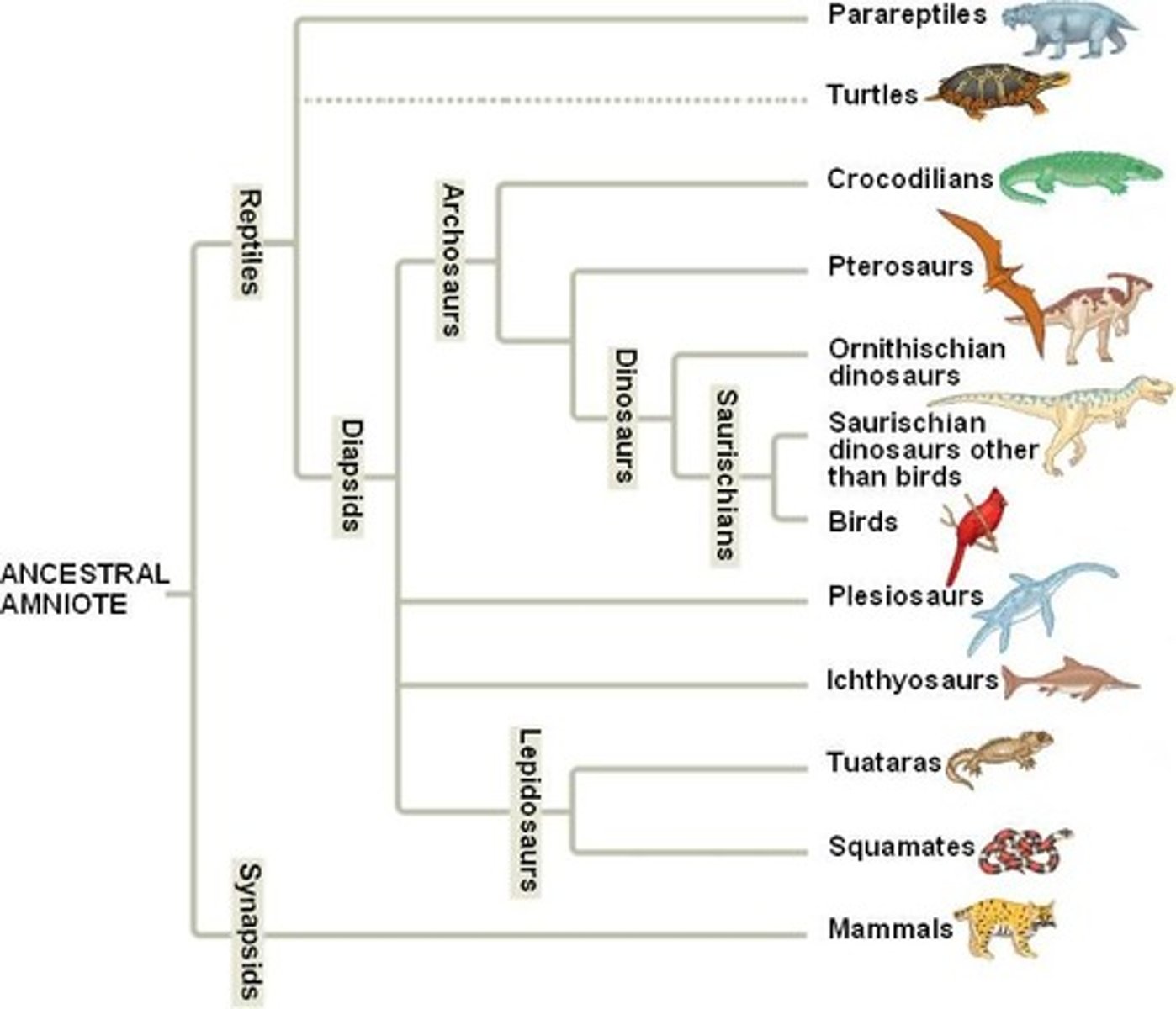
Phylogenic tree
AKA dendrogram AKA tree of life - relationships of a group in the form of a branching tree
Character
physical feature of organism
Character State
condition or type of character
Primitive Condition
an earlier (ancestral) state of a character
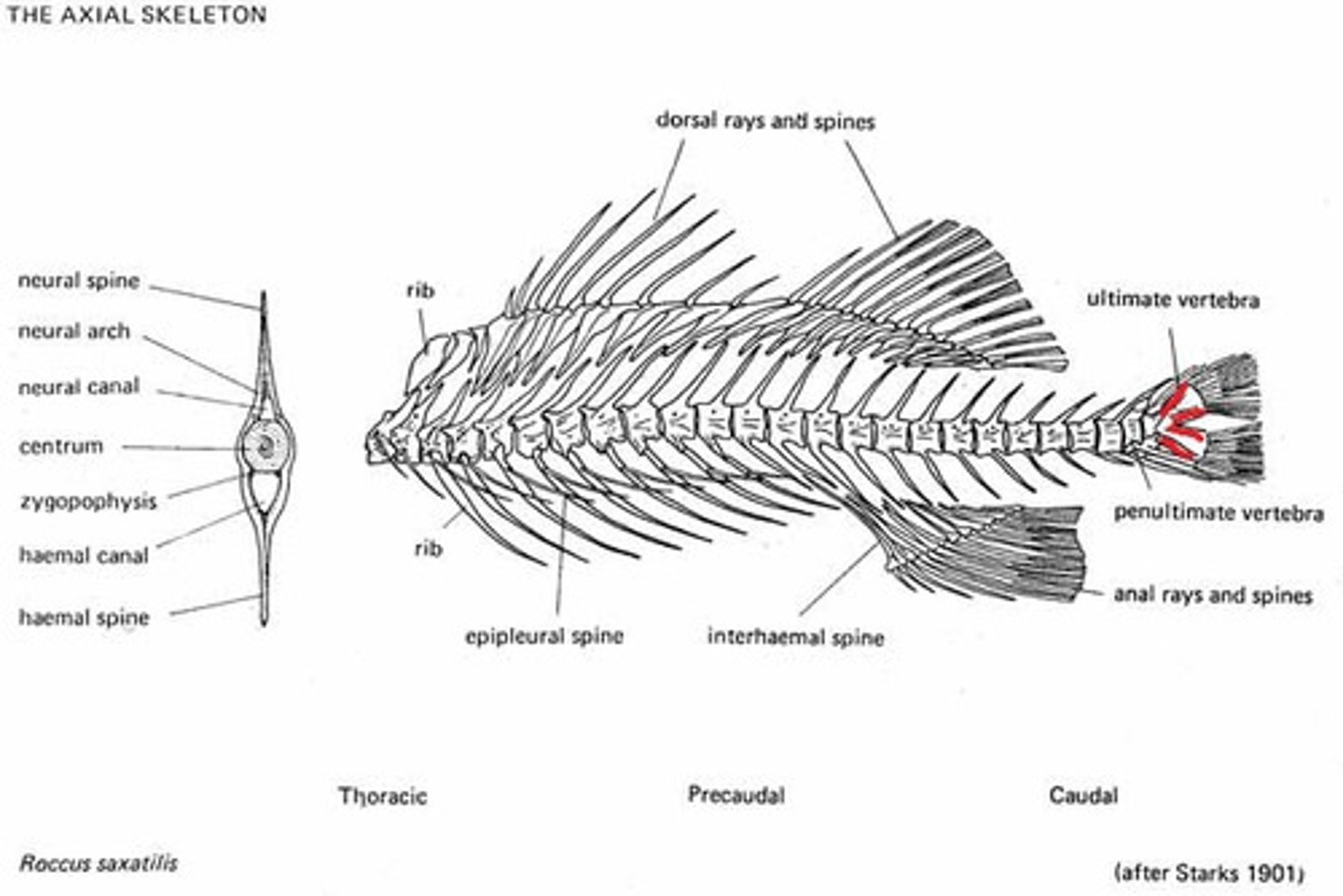
Plesiomorphic traits
ancestral traits ( come from primitive condition)
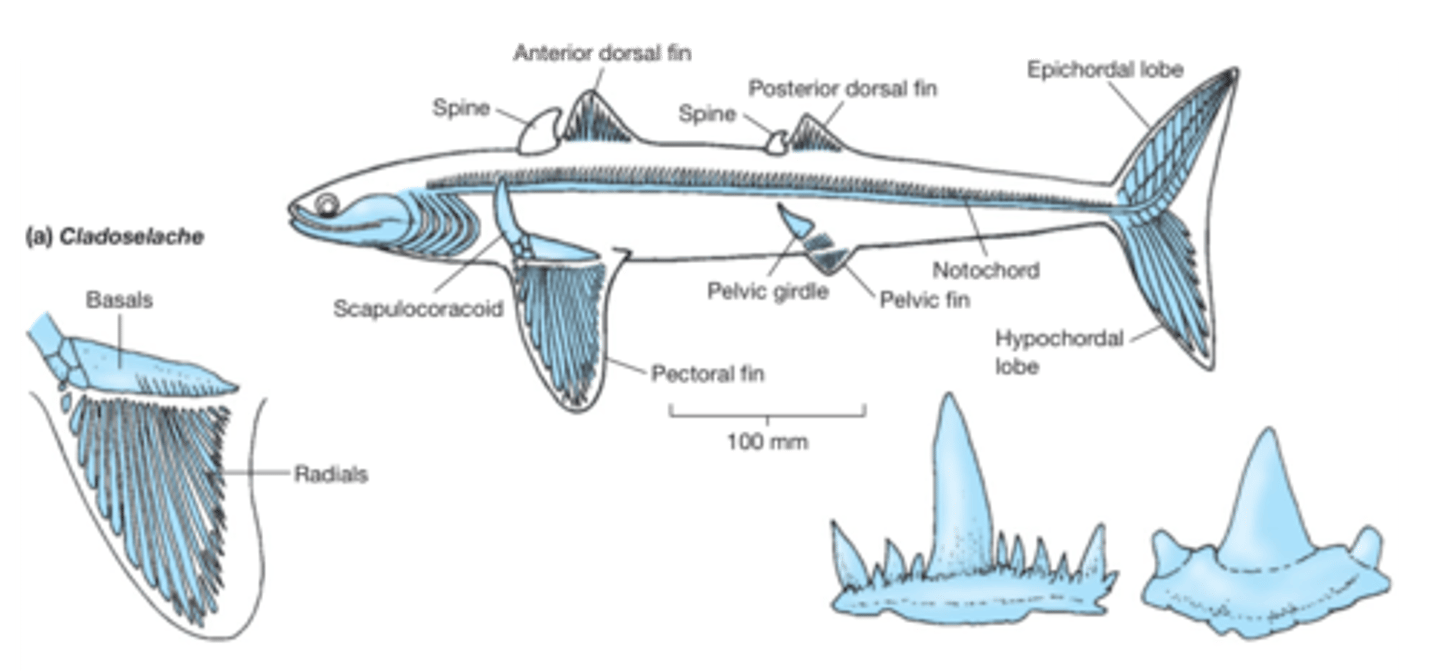
Derived condition
later or descendant state after transformation
Synaphomorphic or Apomorphic trait
Trait from a Derived condition
Taxon
named group of organisms
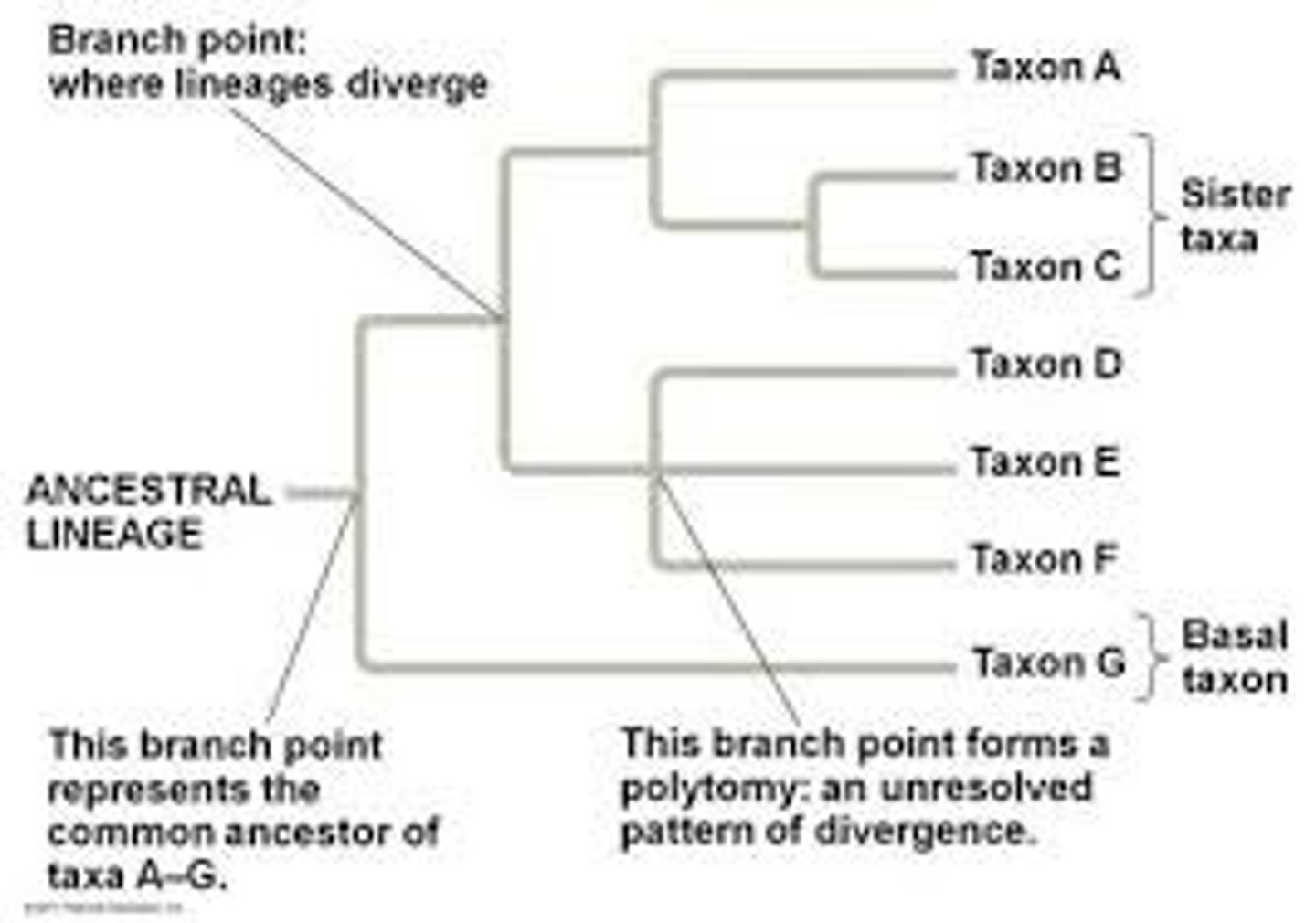
Sister group
taxon most closely related to the group we are studying
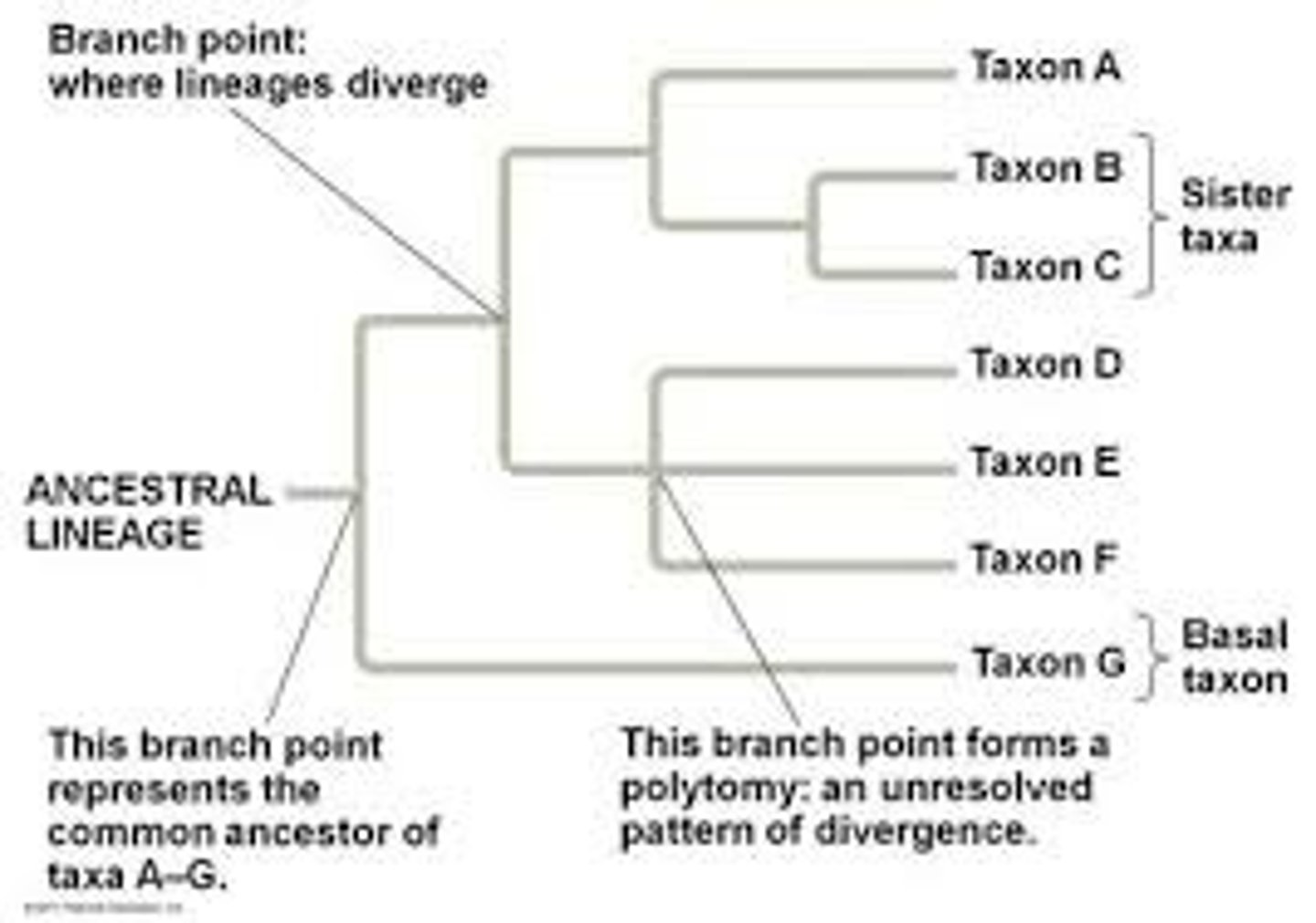
Phylogenetic systematics (cladistics)
method for determining relationships of organisms based on evolutionary history (genealogy)
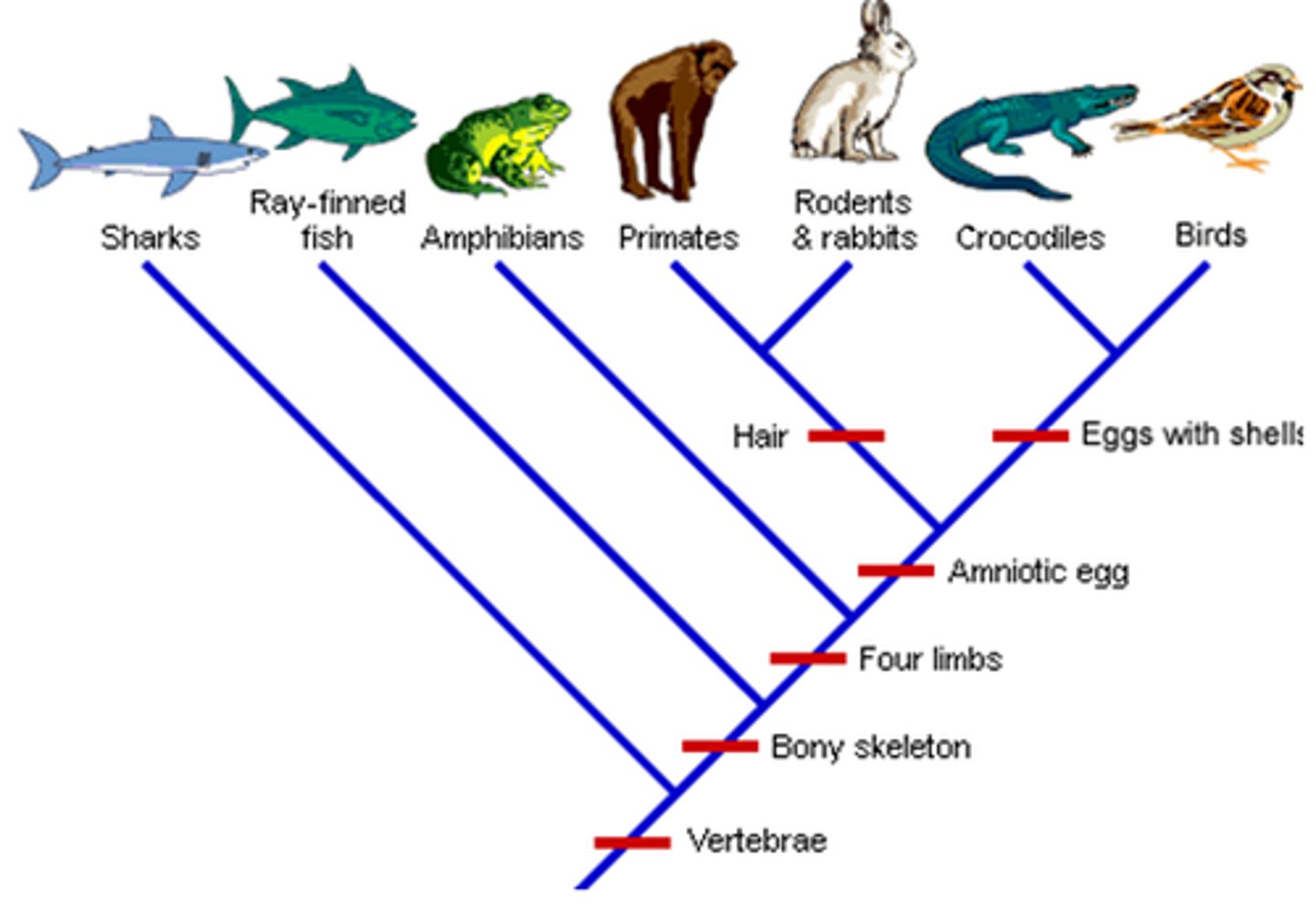
Cladogram
dendrogram (tree) depicting genealogical relationships
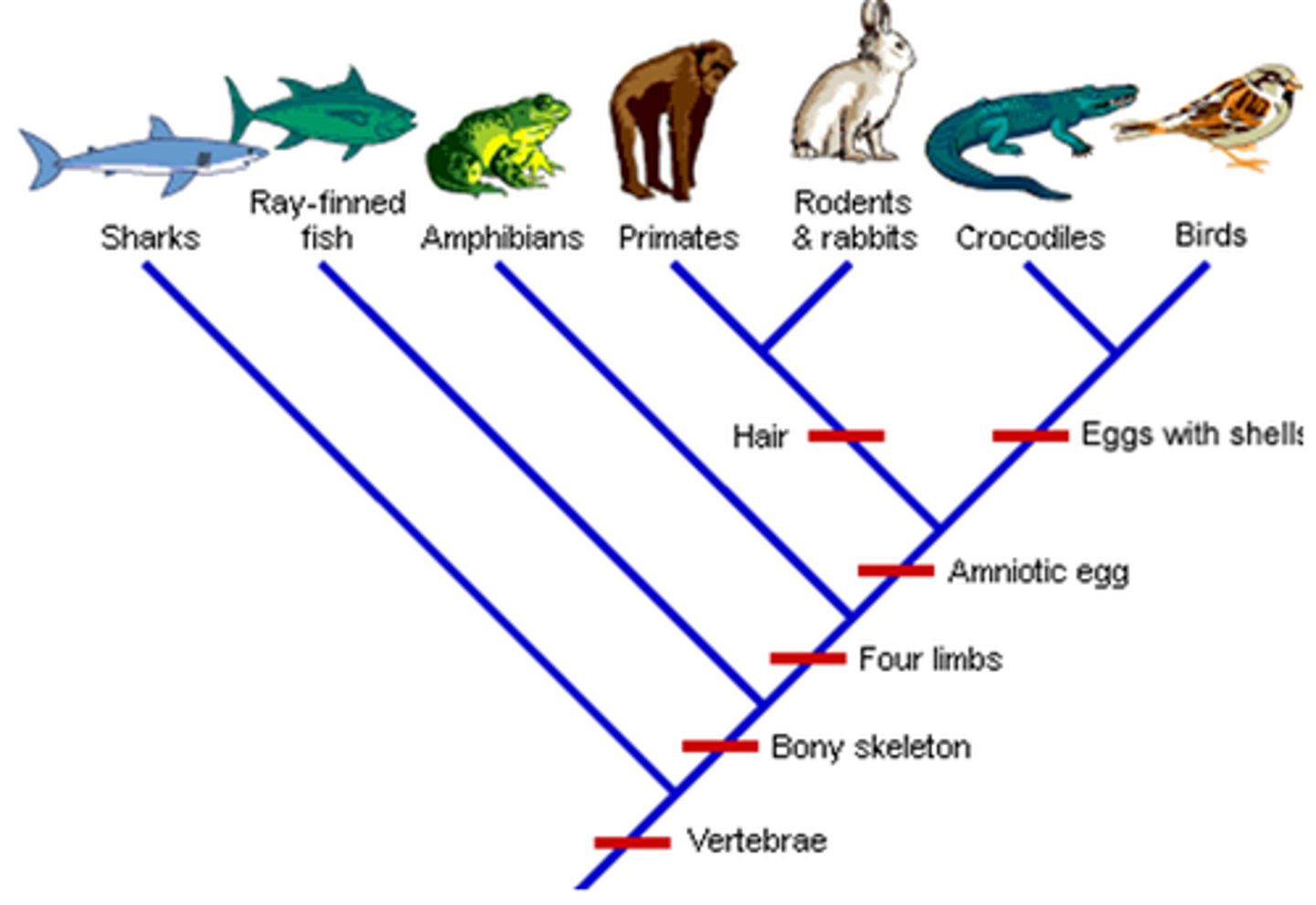
Grade
an expression of the degree of change or level of adaptation reached by an evolving group
Clade
lineage, which is all organisms in a lineage plus the ancestor they have in common; it is also considered a monophyletic group because it includes an ancestor and its descendants (but only its descendants)
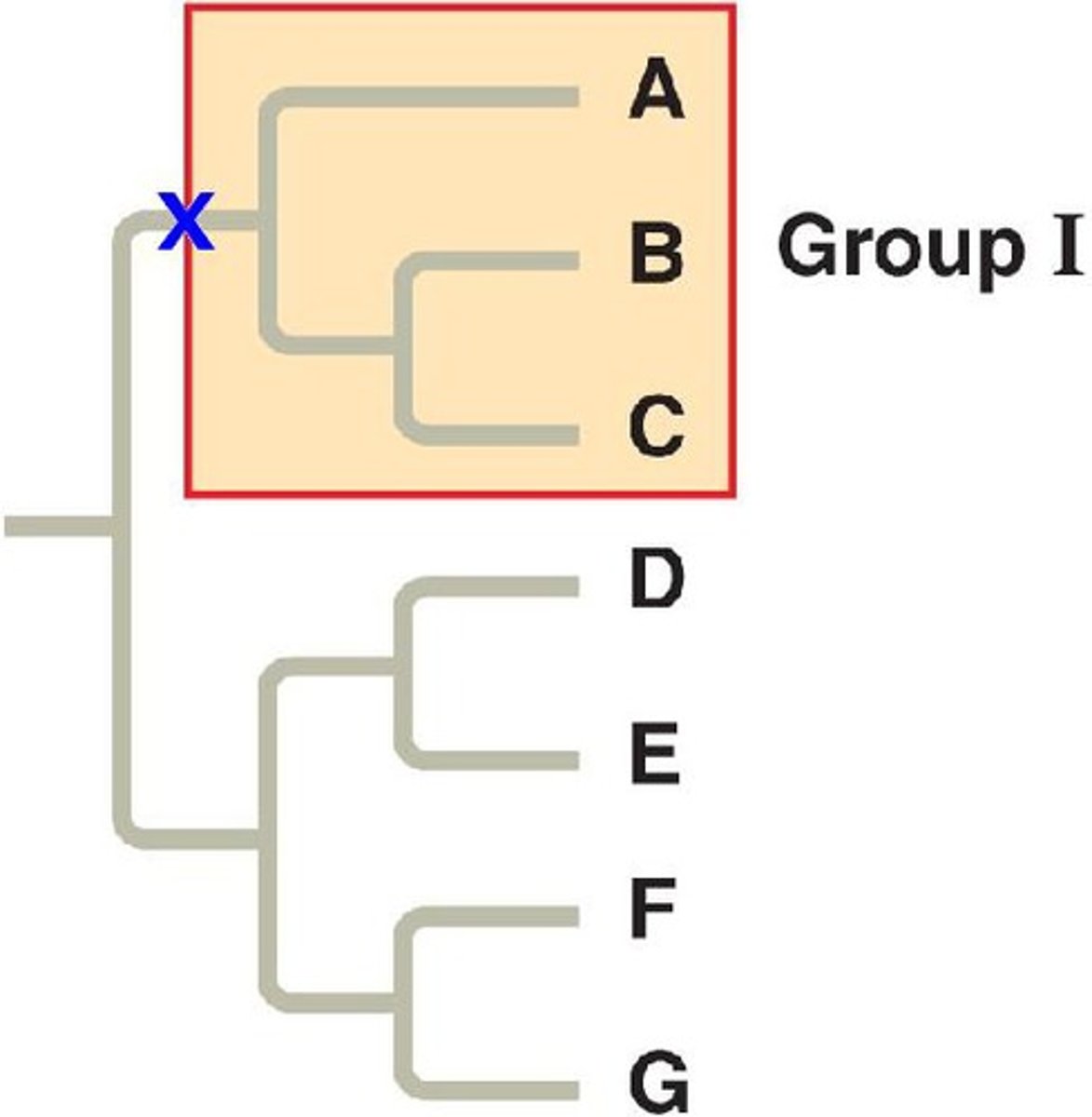
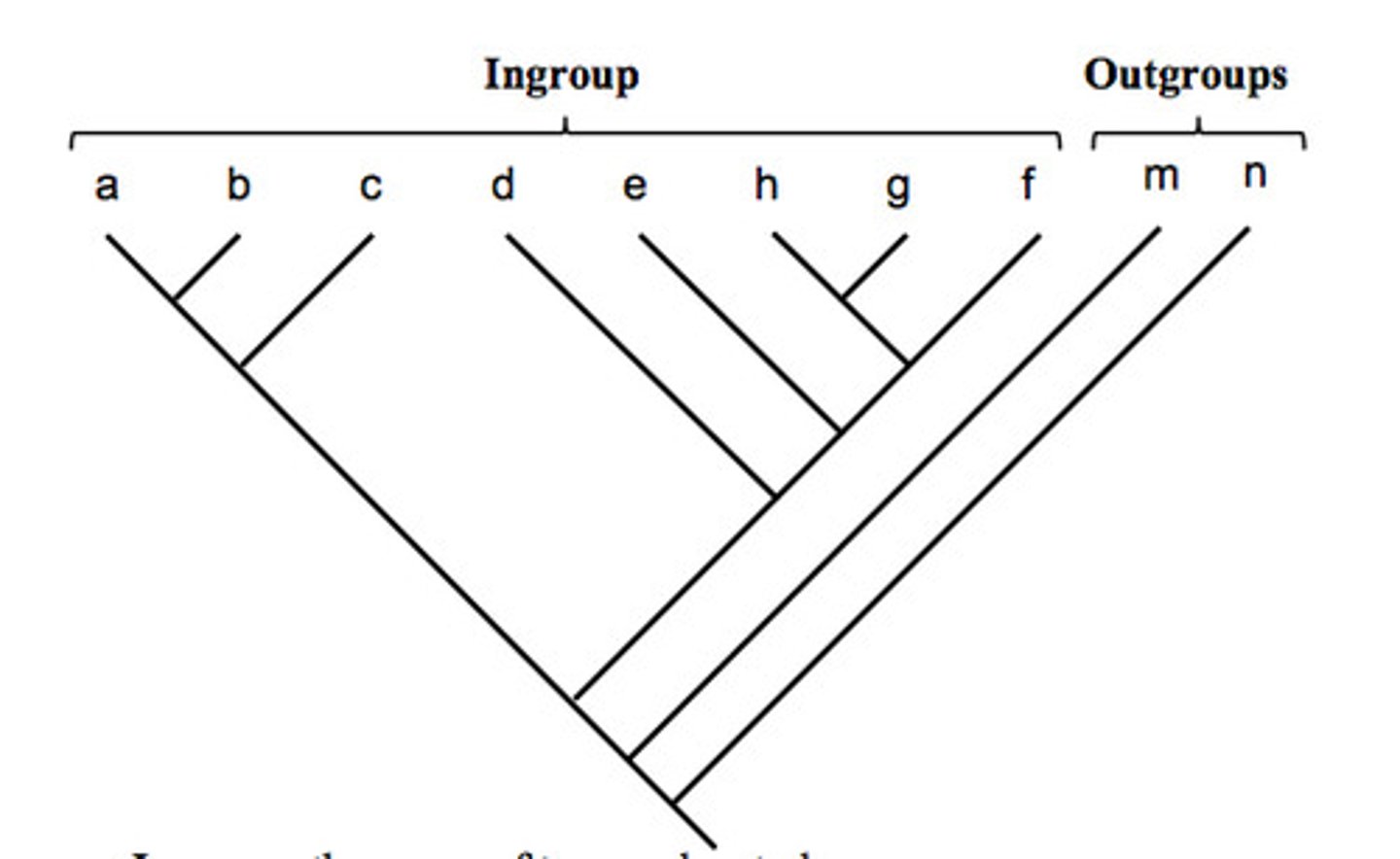
Ingroup
assortment of species (taxa) of interest in examining
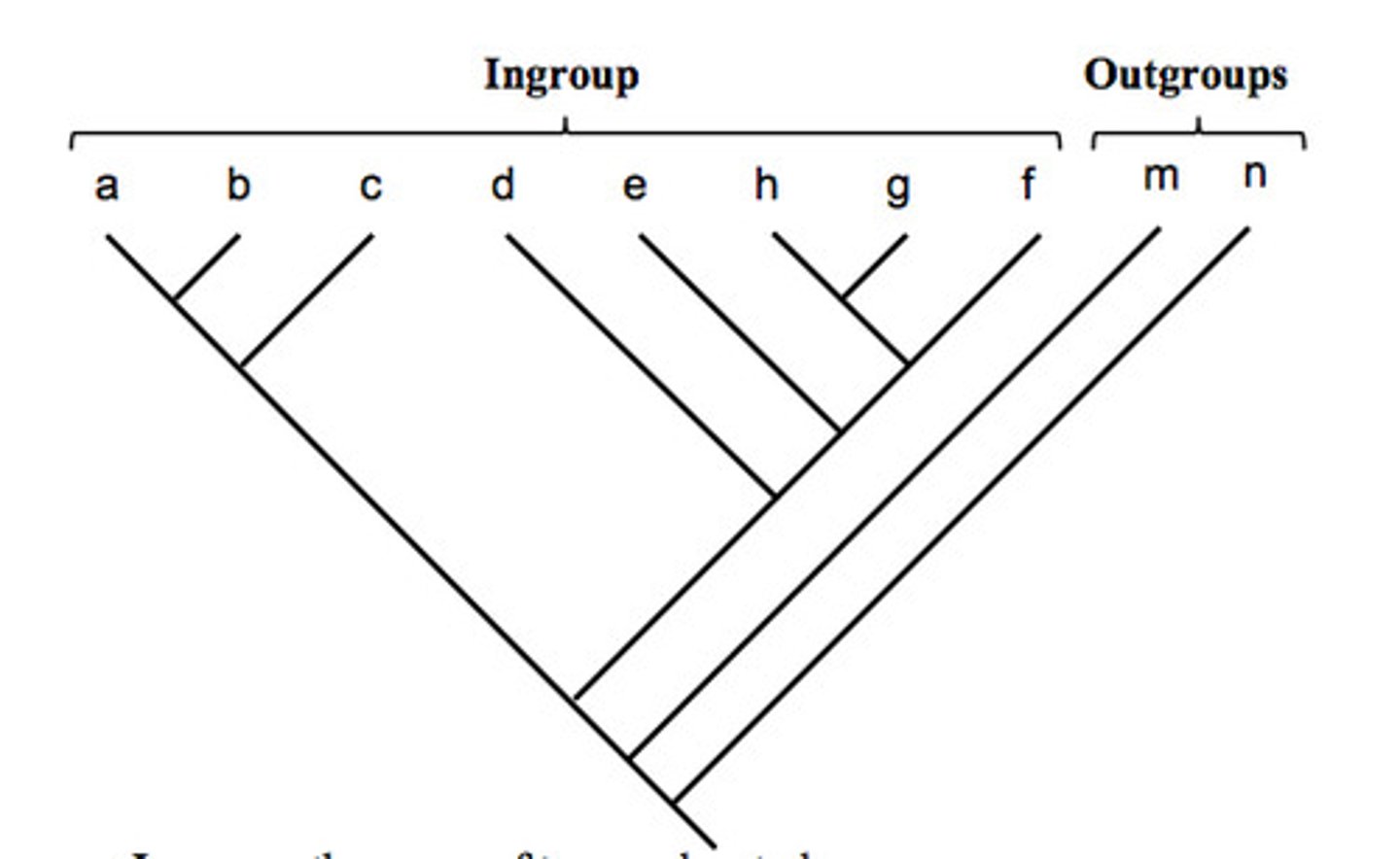
Outgroup
close relative to but not party of this assortment; used for reference to determine the character state that is derived (it could be a sister group or a less related group)
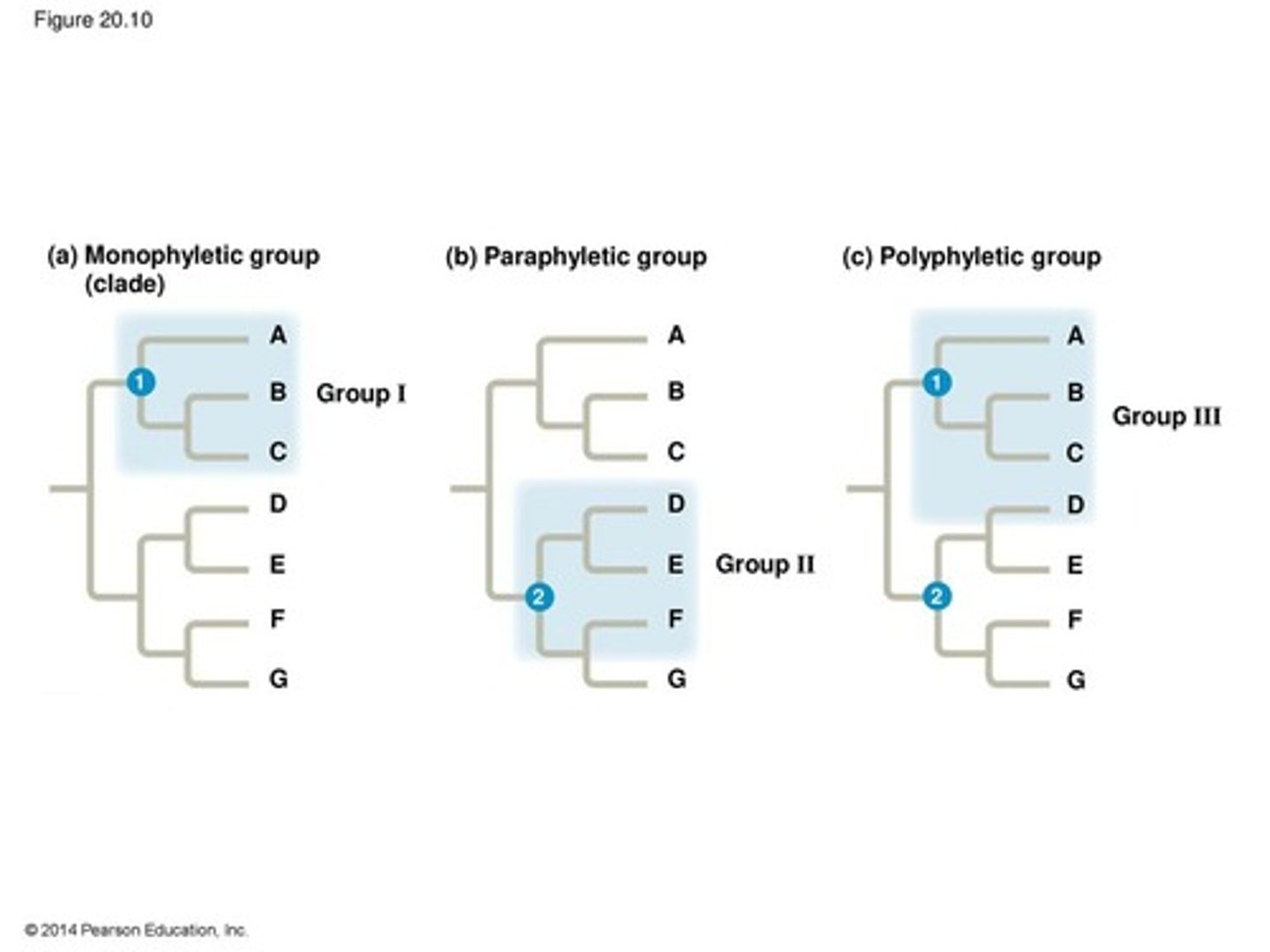
Monophyletic group
taxon that includes the common ancestor and all descendant species
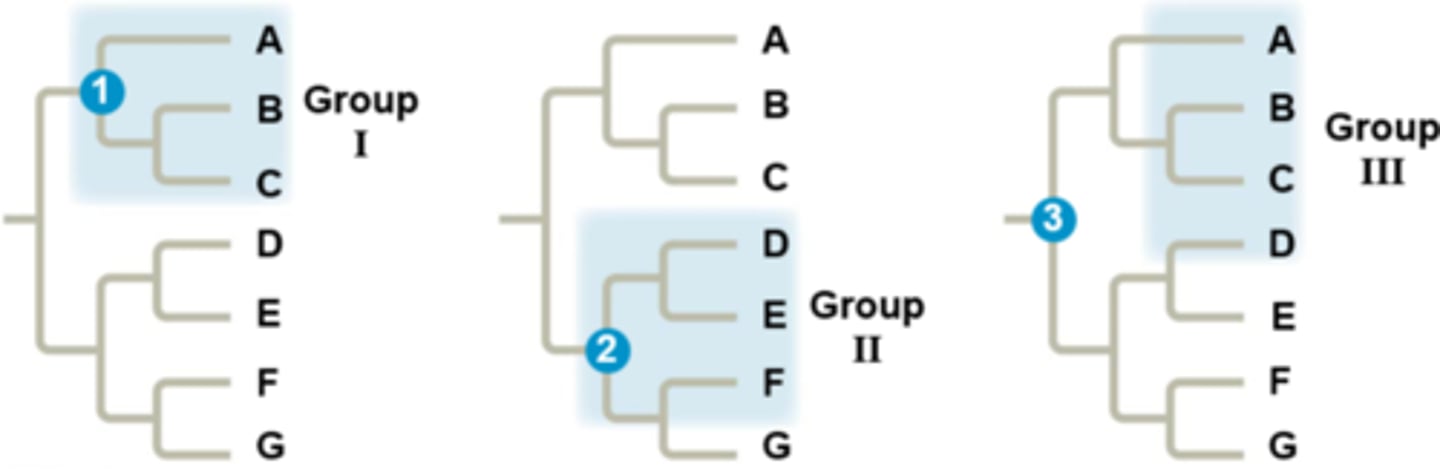
Paraphyletic group
taxon that includes the ancestor and some of the descendants (part of a monophyletic group)
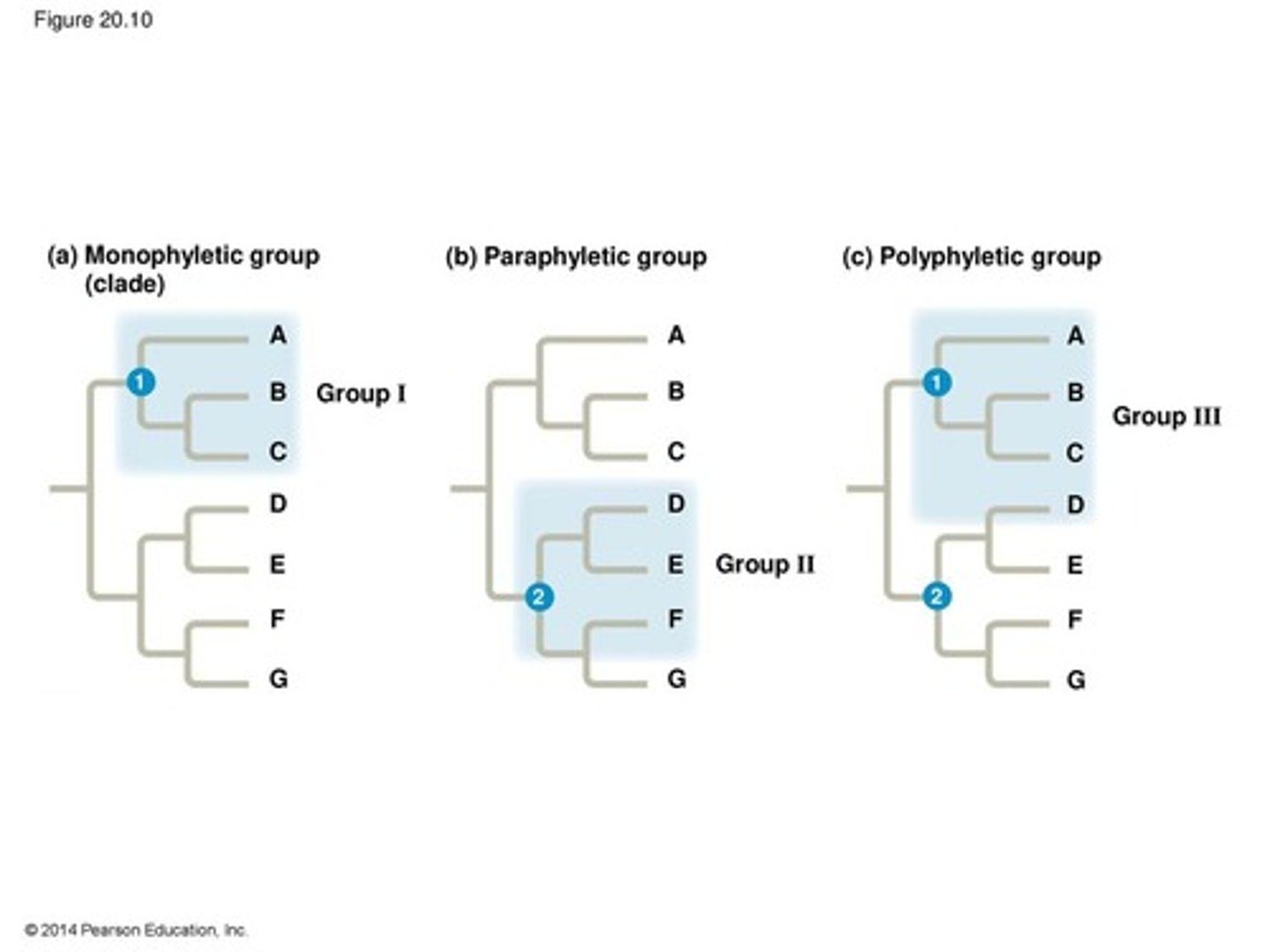
Polyphyletic group
taxon that is formed on the basis of nonhomologous characters (ex. from convergent evolution)
Binomial
The two-part scientific name of a species

Genus
The first part of the name

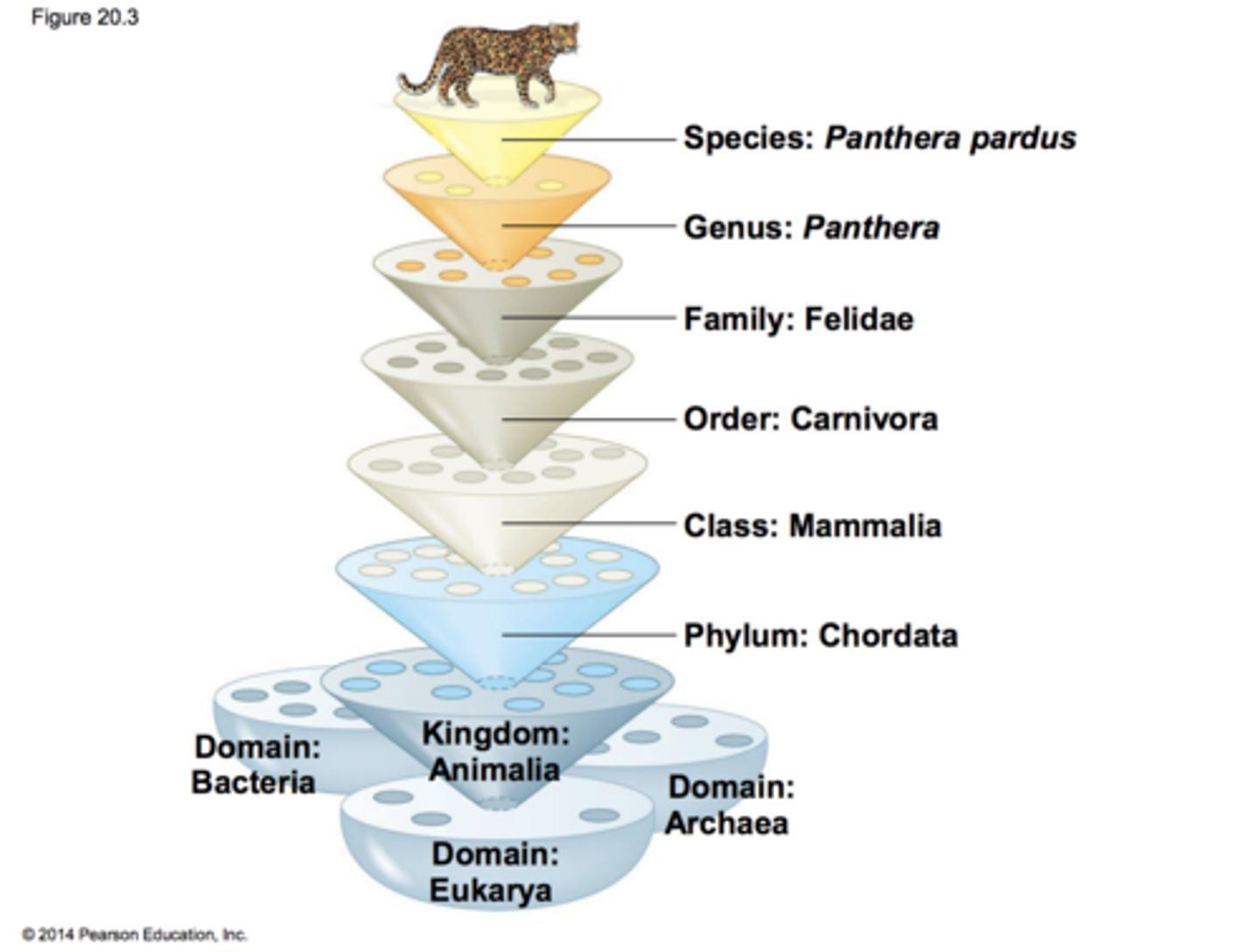
taxonomic groups from broad to narrow
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
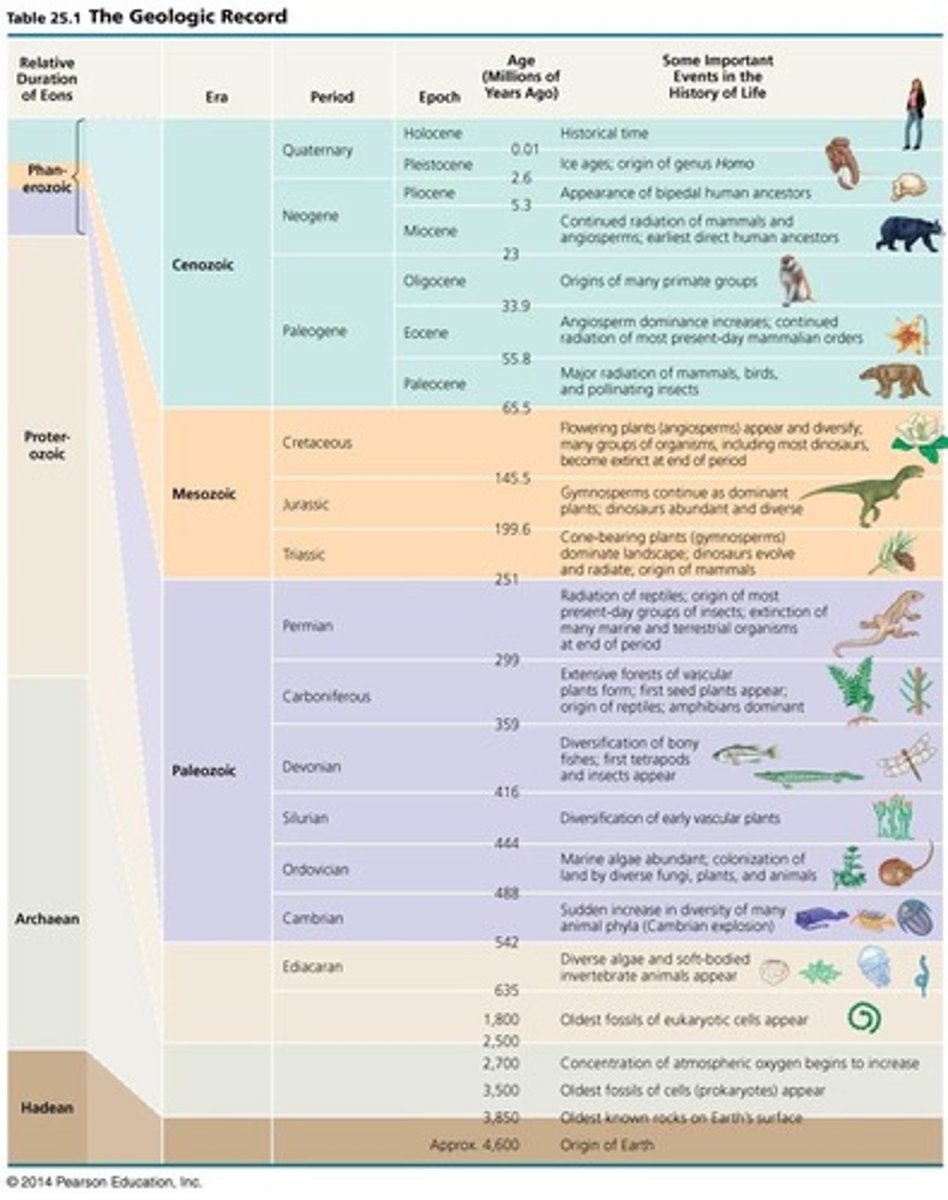
Paleozoic Era
the oldest era - immediately after Precambrian; organisms developed hard parts

Mesozoic Era
middle life (245-144 million years ago); rise of mammals and dinosaurs; the rise of birds; extinction of dinosaurs, rise of flowering plants

Cenozoic Era
era that began about 66 million years ago, known as the "Age of Mammals"
Geologic record
a standard time scale that divides Earth's history into four eons and further subdivisions