A Level Physics - Materials
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Hooke's Law
the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied up until the elastic limit
Force constant units
Nm-1
Hooke's Law equation
F = kx
What is k called for springs?
spring constant
Tensile deformation
extension
Compressive deformation
compression
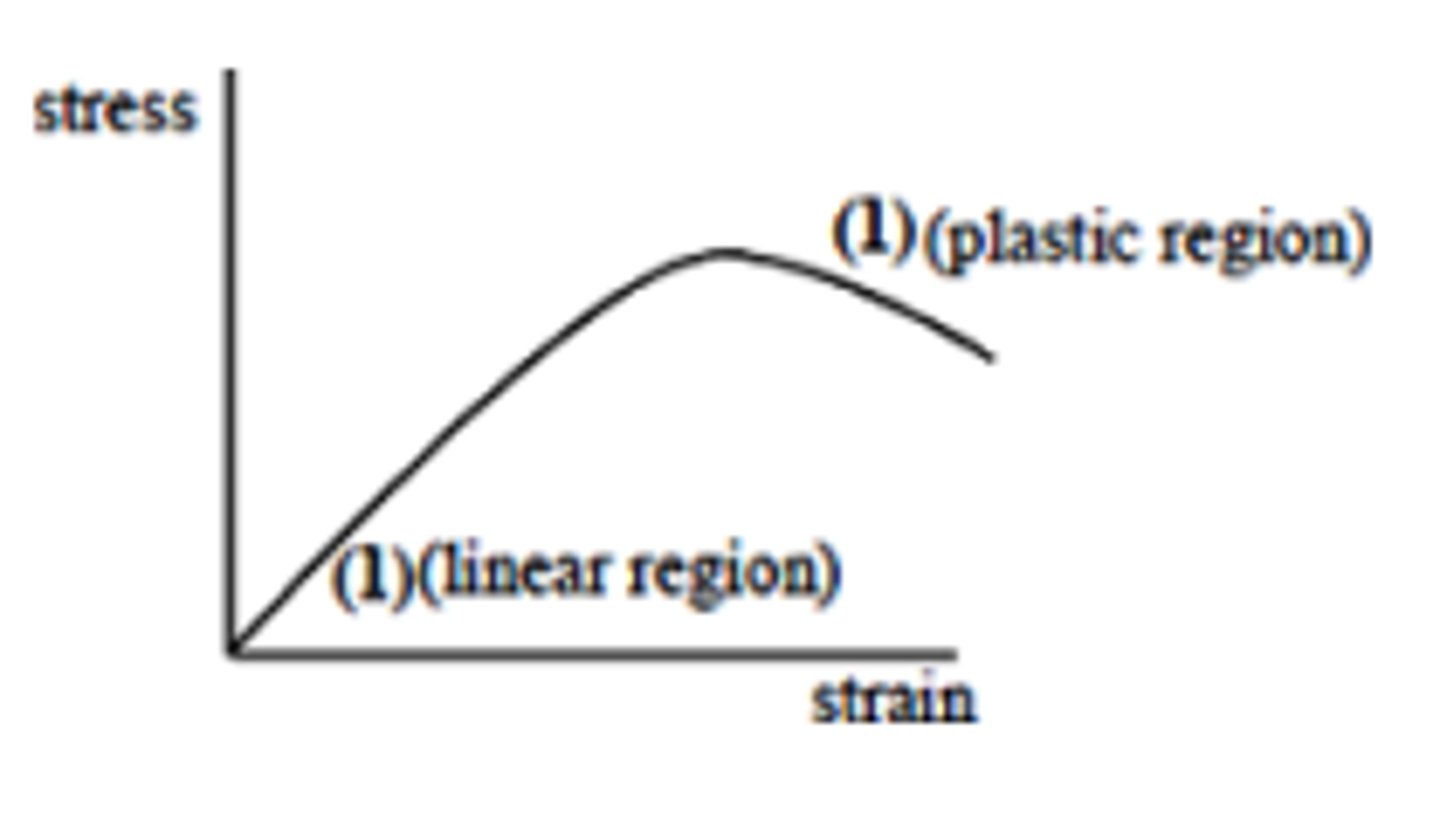
Limit of proportionality
obeys Hooke's law, but undergoes elastic deformation
What happens after the elastic limit is reached?
plastic deformation
Springs in series
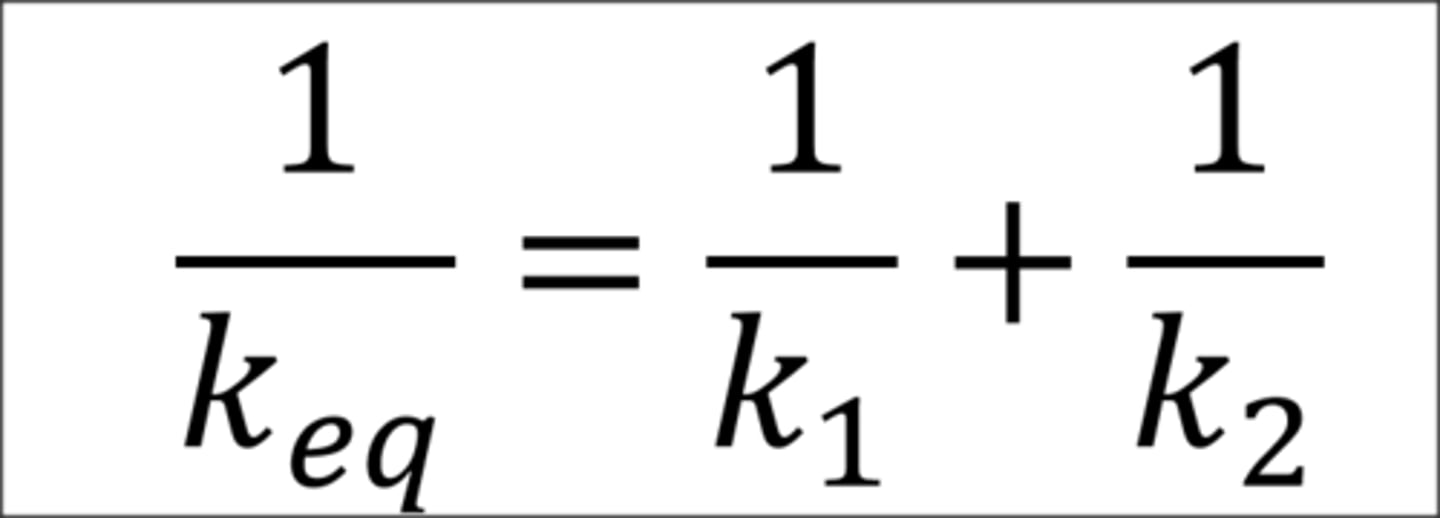
Springs in parallel
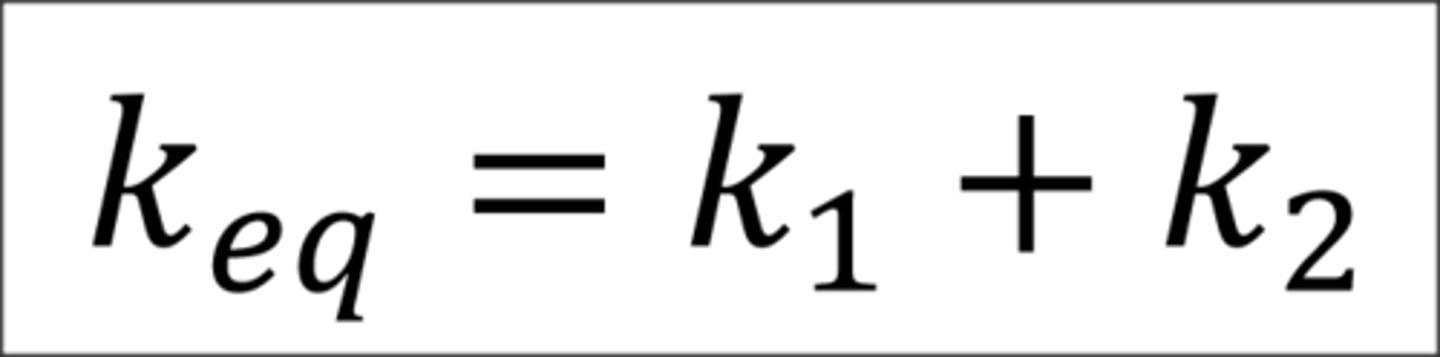
Elastic deformation
material returns to its original shape once the forces are removed
What happens to molecules in elastic deformation?
• atoms are pulled apart when force is applied
• atoms move slightly relative to their equilibrium position
• atoms return to equilibrium position when force is removed
Plastic deformation
permanent deformation
What happens to molecules in plastic deformation?
atoms have been moved permanently
Experiment to investigate extension
• hang spring from a clamp and attach meter ruler to clamp stand
• add weights to the end of the spring
• extension = new length - original length
• plot force-extension graph
• gradient = k
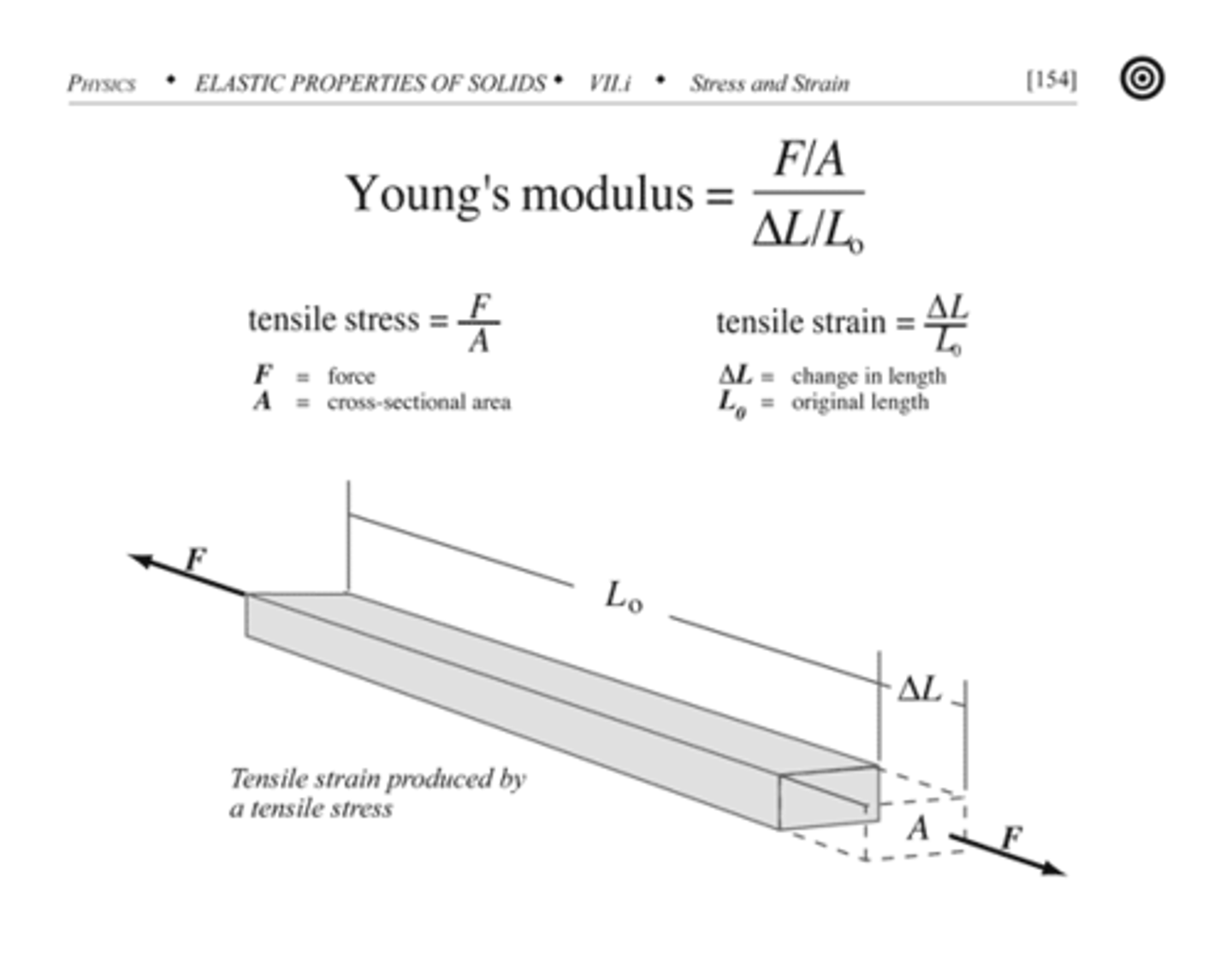
Tensile stress
σ = F/A
Units of stress
Nm-2 or Pa
Tensile strain
strain = extension/original length
ε = x/l
Units of strain
no units
Ultimate tensile strength
the maximum stress the material can withstand before breaking
Area of a force-extension graph
work done (elastic potential)
Derive E = (1/2)kx^2
work done = area of force-extension graph = 0.5Fx = 0.5kx^2
What is work done in stretching or compressing a material stored as?
elastic potential
Young modulus
stress/strain
units of Young modulus
Nm-2 or Pa
Experiment to find Young Modulus
• measure diameter of wire using micrometer to find cross sectional area
• start attach small weight to end to straighten the wire
• measure initial length
• increase weight in steps and record extension (stretched - unstretched)
• calculate stress and strain
• plot stress-strain graph and find gradient
Area under a stress-strain graph
elastic potential energy stored per unit volume
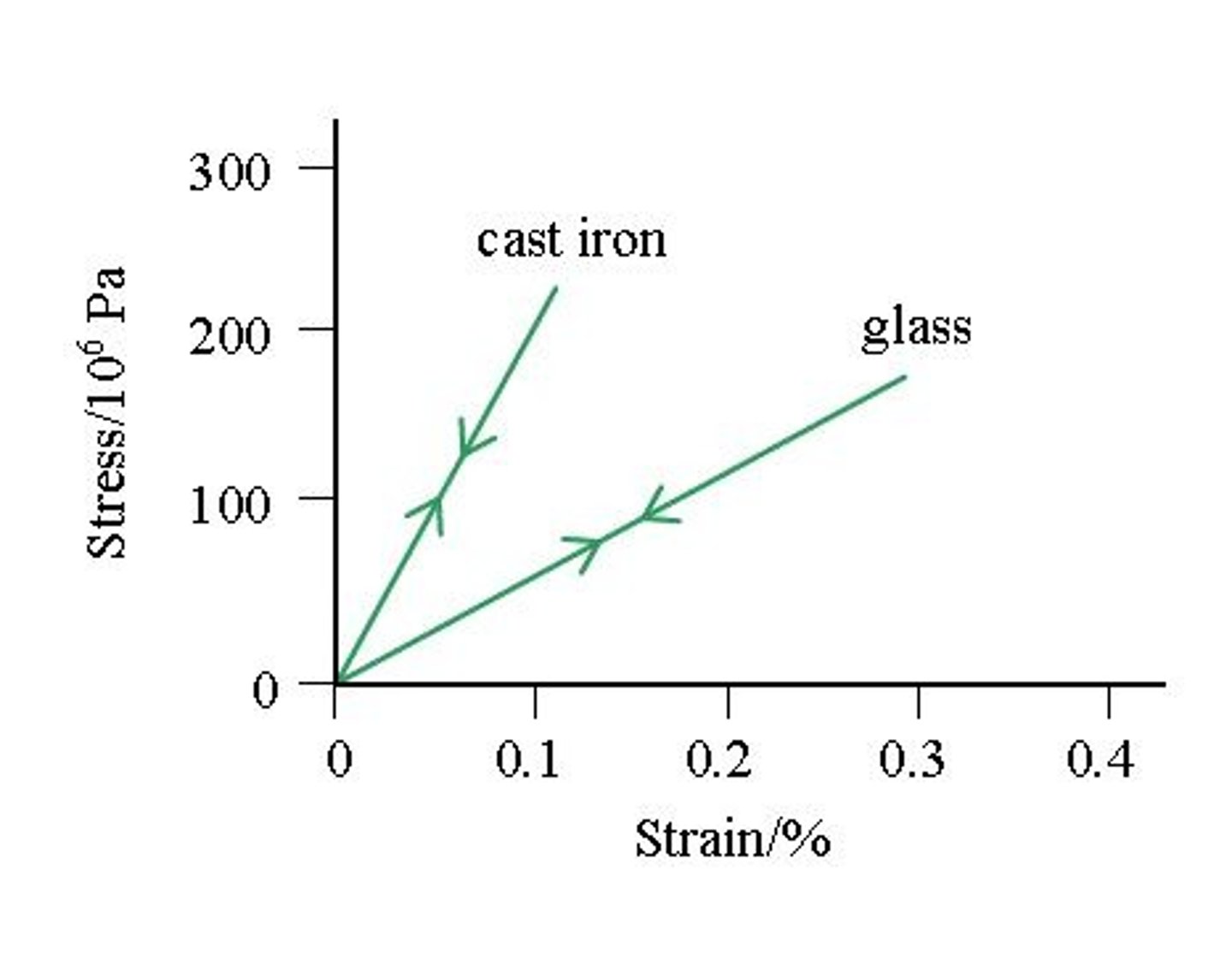
Ductile material
Brittle material
Yield point
stress at which a large amount of plastic deformation takes place with a constant/reduced load
Polymeric materials
molecules are arranged in long chains
Area between loading and unloading curves
amount of energy converted to heat per unit volume
Crack propagation
Existing microscopic cracks in a material, grows because of stress and leads to fracture
Crystalline
Ordered Structure making a crystal lattice, Ductile and tough. E.g metals
Amorphous
Non- ordered structure, rigid structure directional covalent bonds E.G ceramics/glass
Polymeric
Long- chain, Strong and flexible. Cross links can be added to make them stronger.
Foreign atoms
Fills gaps → less movement and more grain boundaries.
Grain boundaries
regions between individual crystals (grains) in a polycrystalline material where the atomic arrangement is irregular or misaligned
Necking
Cross-sectional area of a metal that reduces as it plastically deforms
How does Crack propagation cause brittle fracture?
Small imperfections lead to cracks on the surface of materials. →brittle fracture- hardly extends then breaks
Rubber
Low Young Modulus
Hysteresis
Stress-Strain graph is different for loading and unloading.