IB Biology: Proteins
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Proteins
Biomolecules composed of amino acid chains.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins with variable side chains.
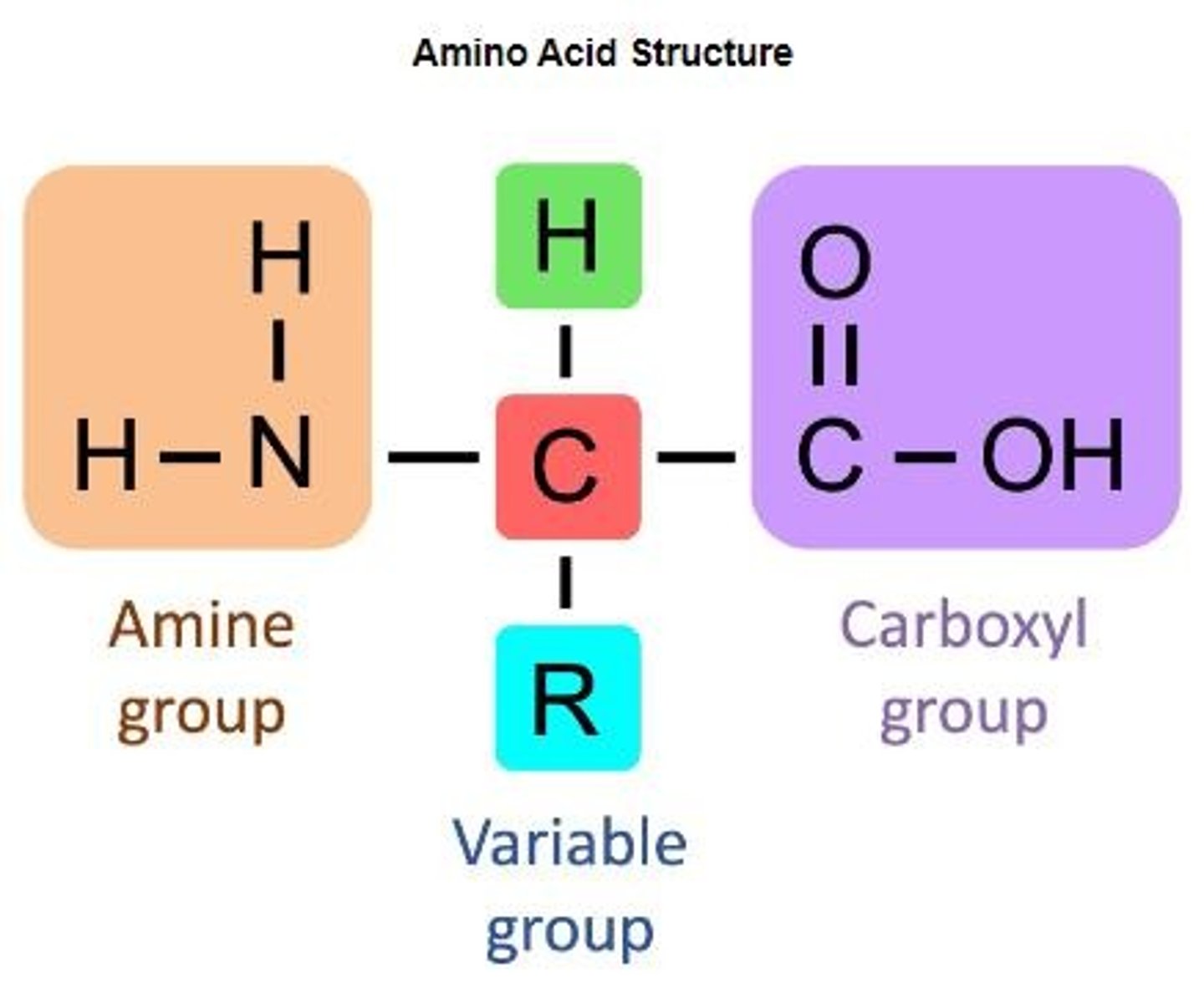
Alpha Carbon
Central carbon atom in amino acids.
Peptide Bond
Covalent bond between amino acids' amine and carboxyl groups.
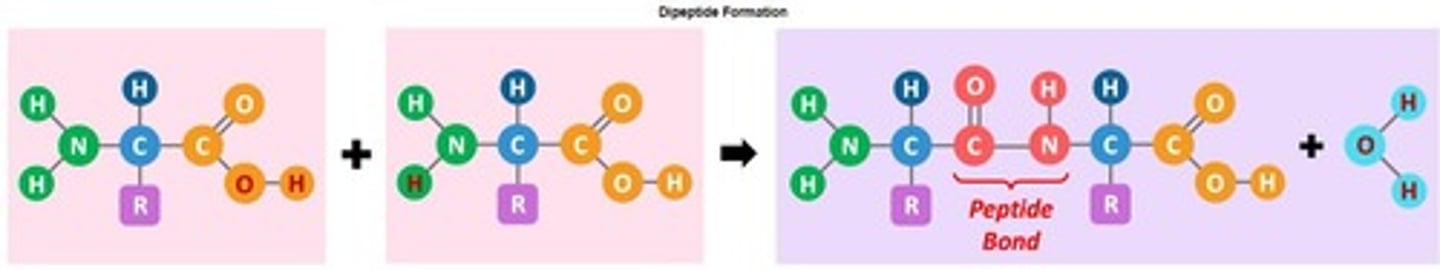
Polypeptides
Chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Essential Amino Acids
Cannot be synthesized by the body, must be ingested.
Non-Essential Amino Acids
Can be synthesized by the body from other amino acids.
Conditional Amino Acids
Required during specific conditions like illness or pregnancy.
Protein Deficiency Malnutrition
Health issues from lack of essential amino acids.
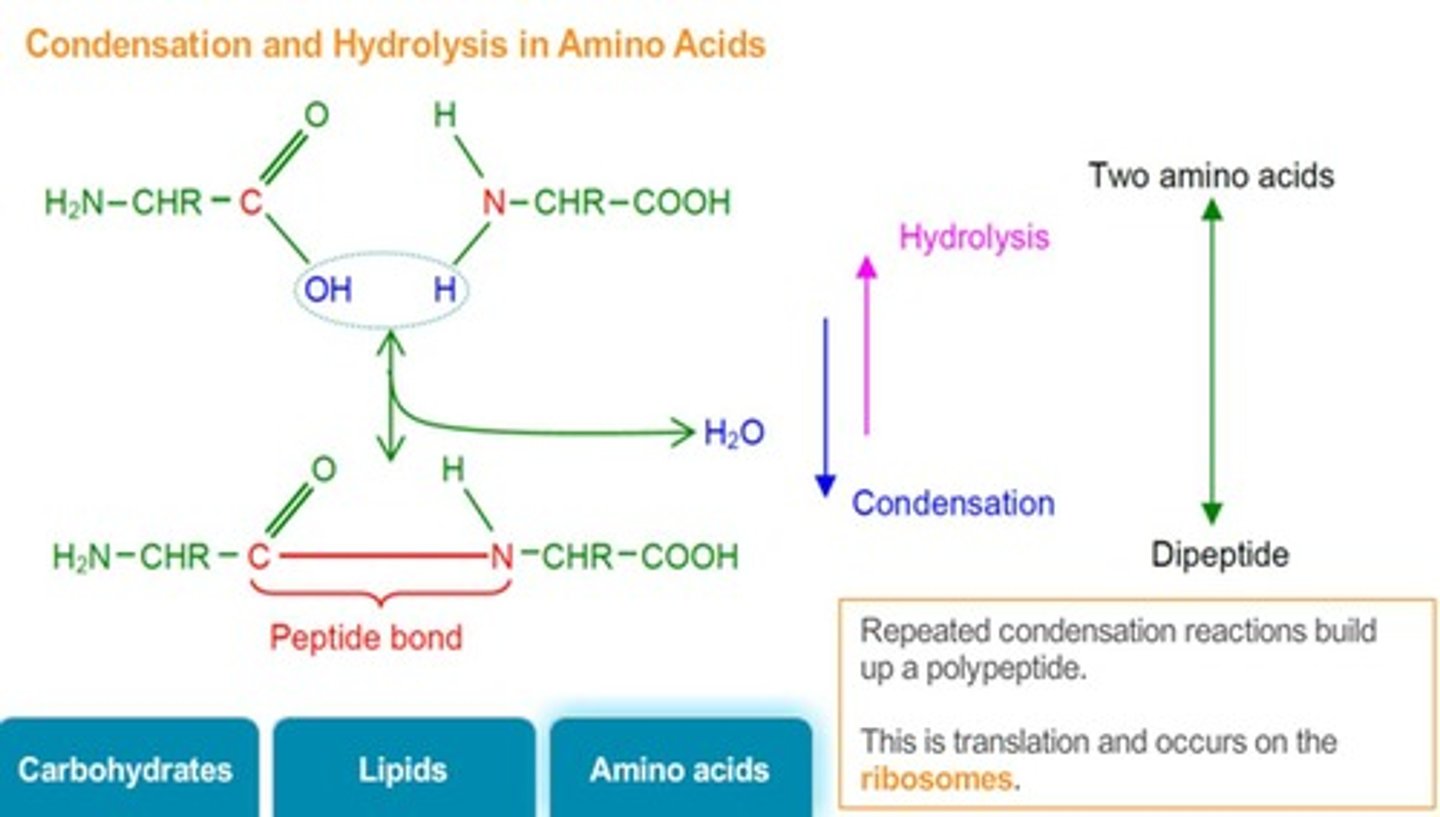
Hydrolysis Reactions
Breakdown of polypeptides into amino acids using water.
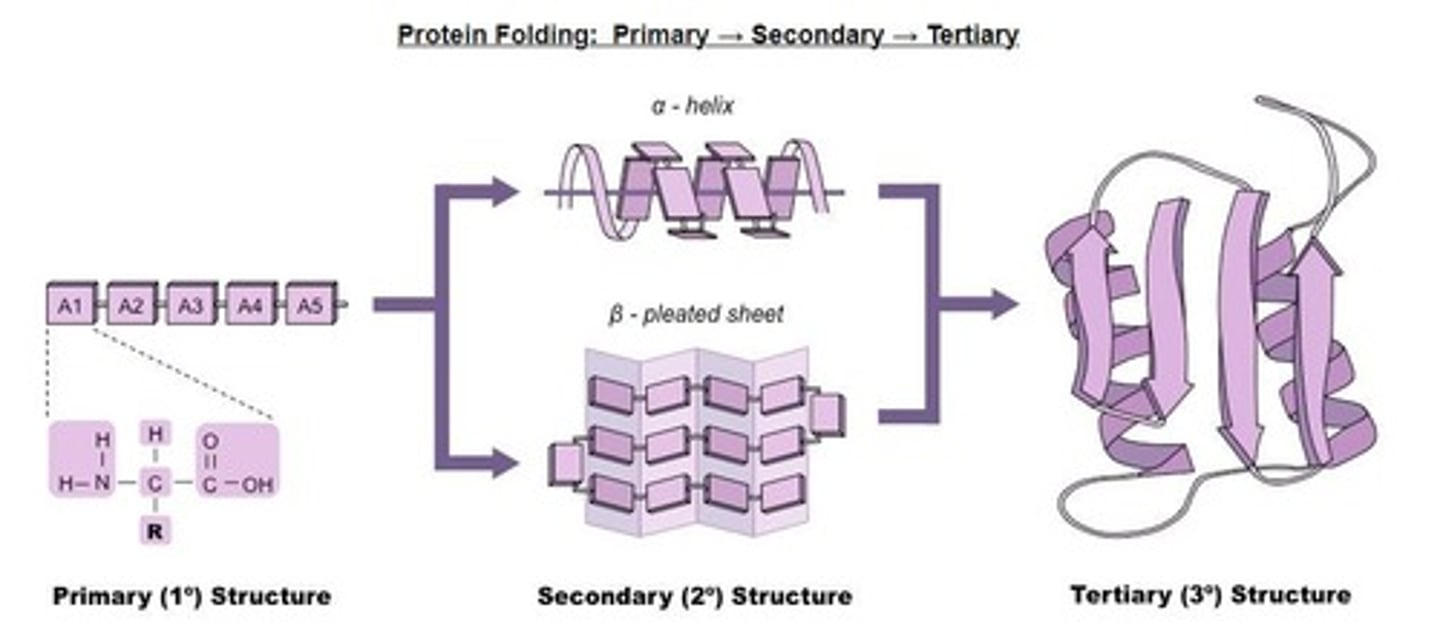
Primary Structure
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Secondary Structure
Folding patterns like alpha helices and beta sheets.
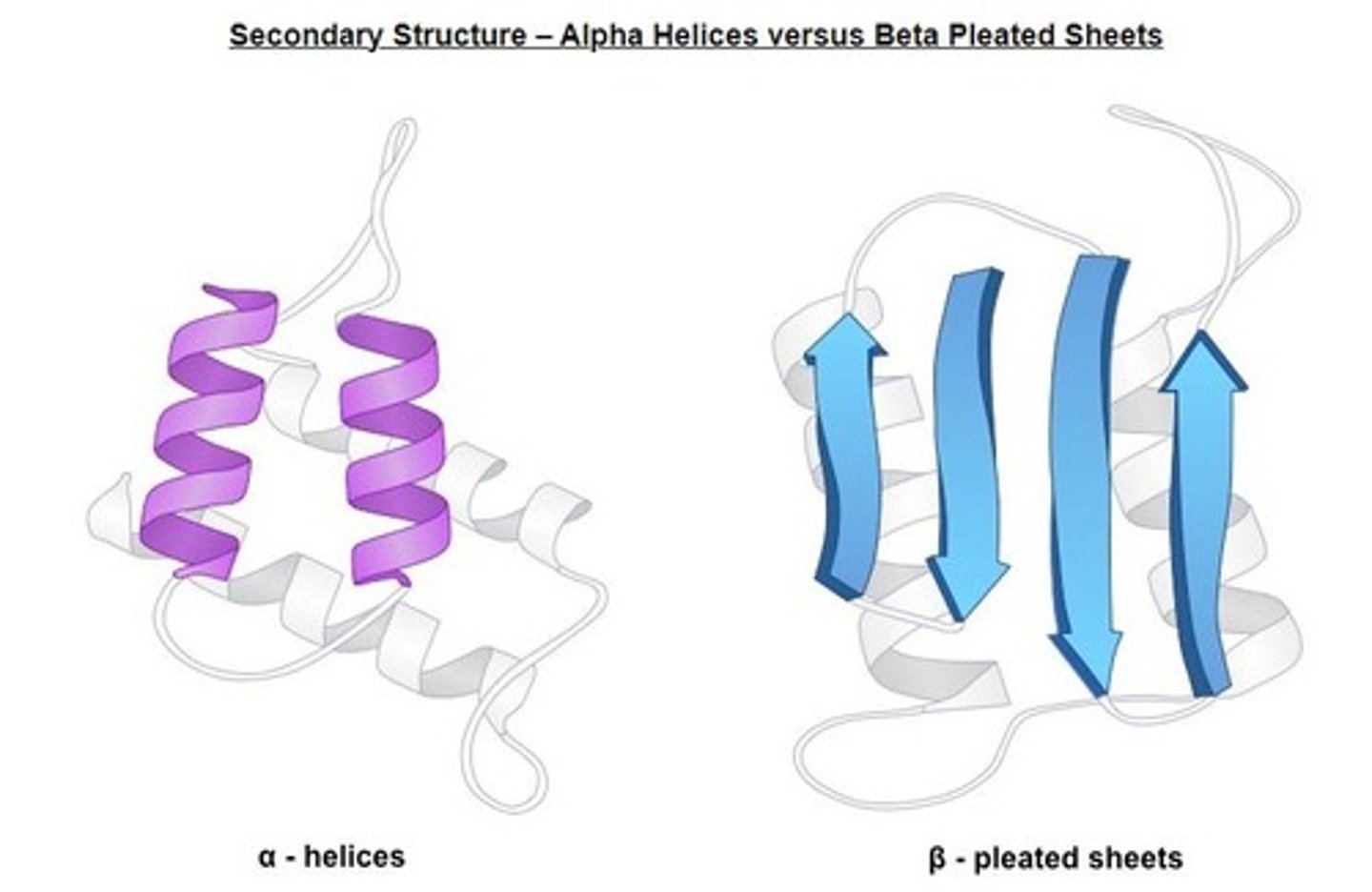
Alpha Helices
Coiled structure formed by hydrogen bonds in proteins.
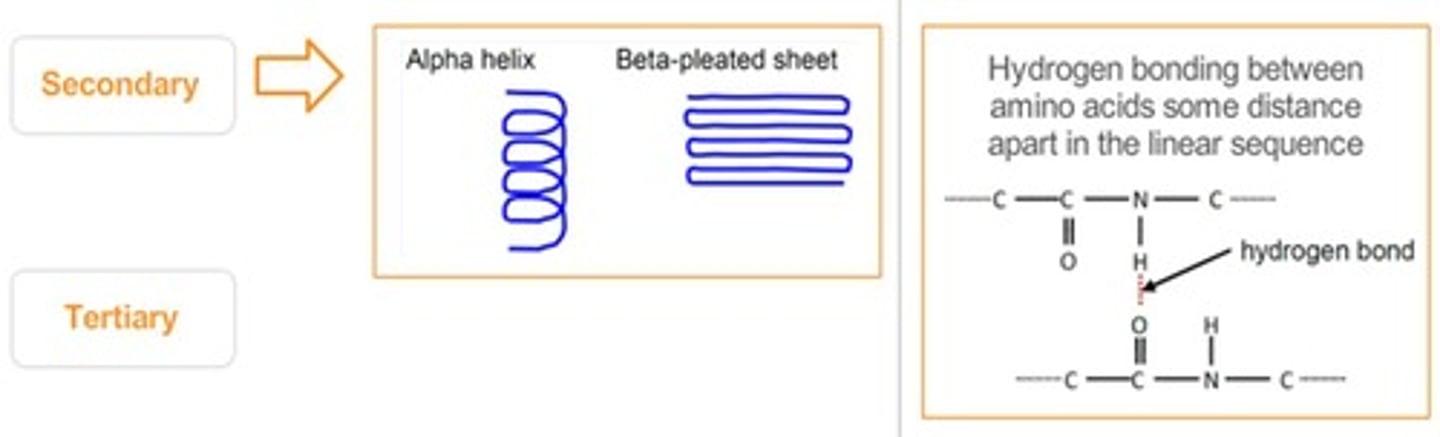
Beta-Pleated Sheets
Staggered strand conformation in protein folding.
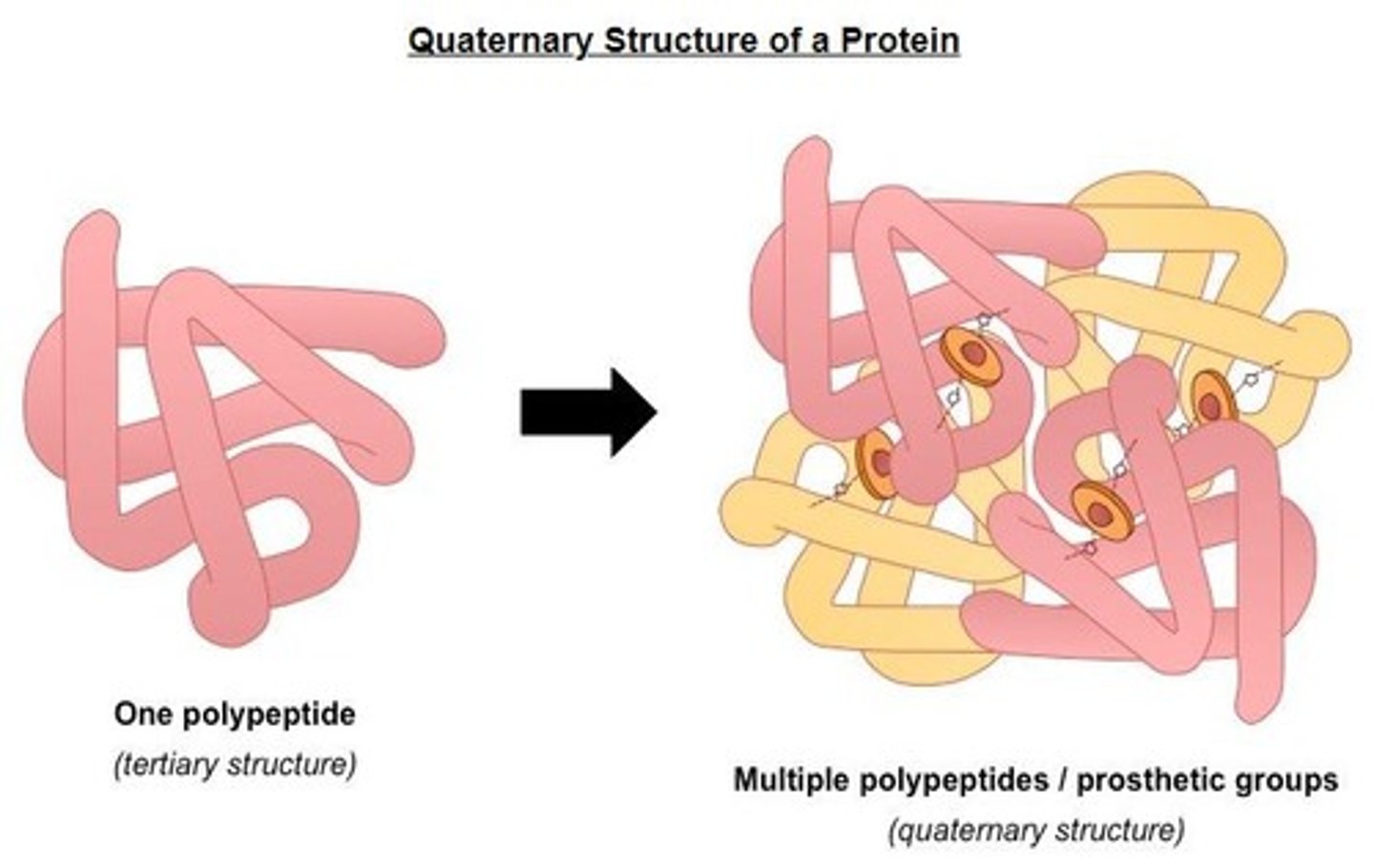
Tertiary Structure
Three-dimensional shape of a protein determined by side chains.
Quaternary Structure
Complex of multiple polypeptide chains or prosthetic groups.
Denaturation
Loss of protein structure and function due to stress.
Hydrophobic Properties
Non-polar amino acids cluster inside globular proteins.
Hydrophilic Properties
Polar amino acids interact with water, influencing protein function.
Integral Proteins
Proteins embedded in cell membranes with hydrophobic regions.
Chemical Diversity
Variety in amino acid side chains affects protein function.
Protein Functions
Roles include structure, hormones, immunity, transport, and enzymes.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds stabilizing protein structures like secondary and tertiary.
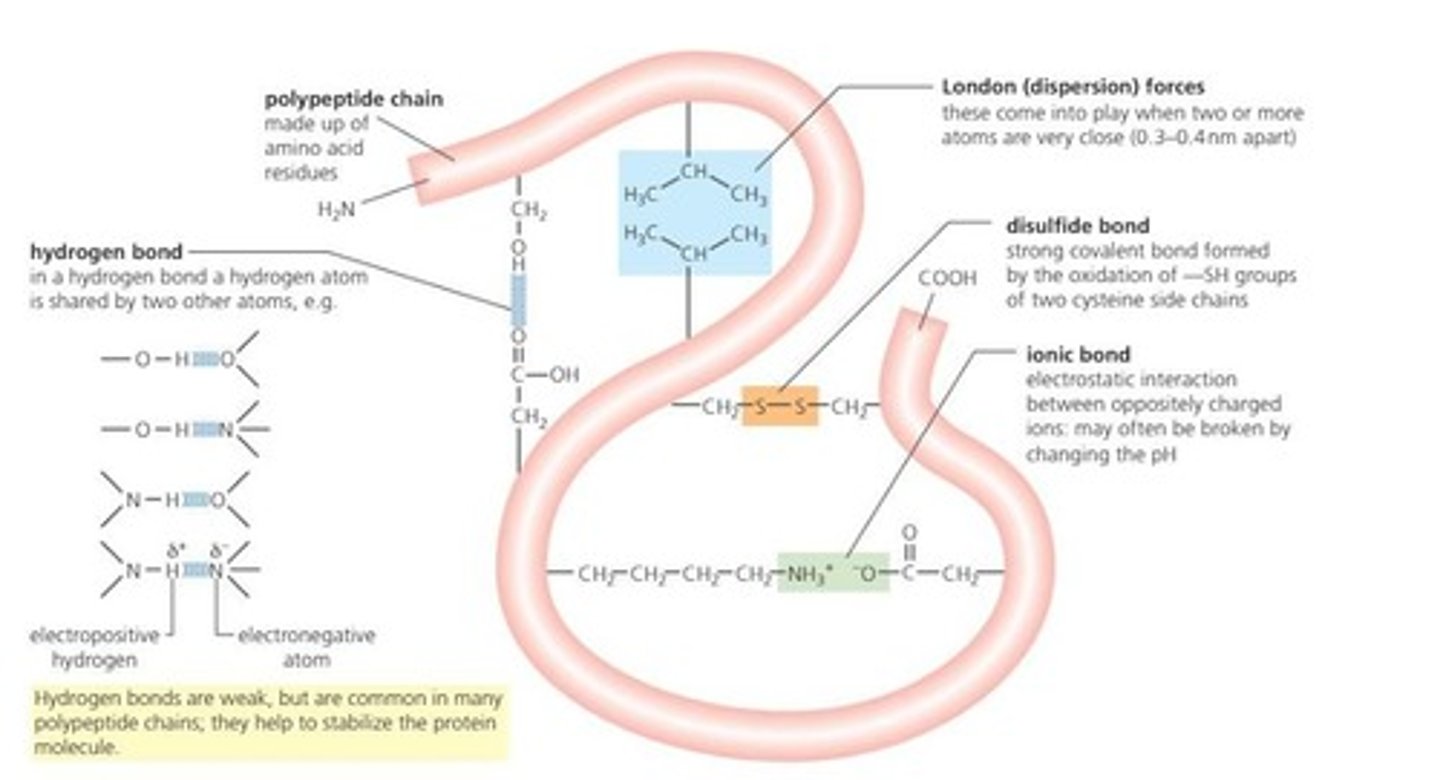
Ionic Bonds
Attractions between charged side chains affecting protein shape.
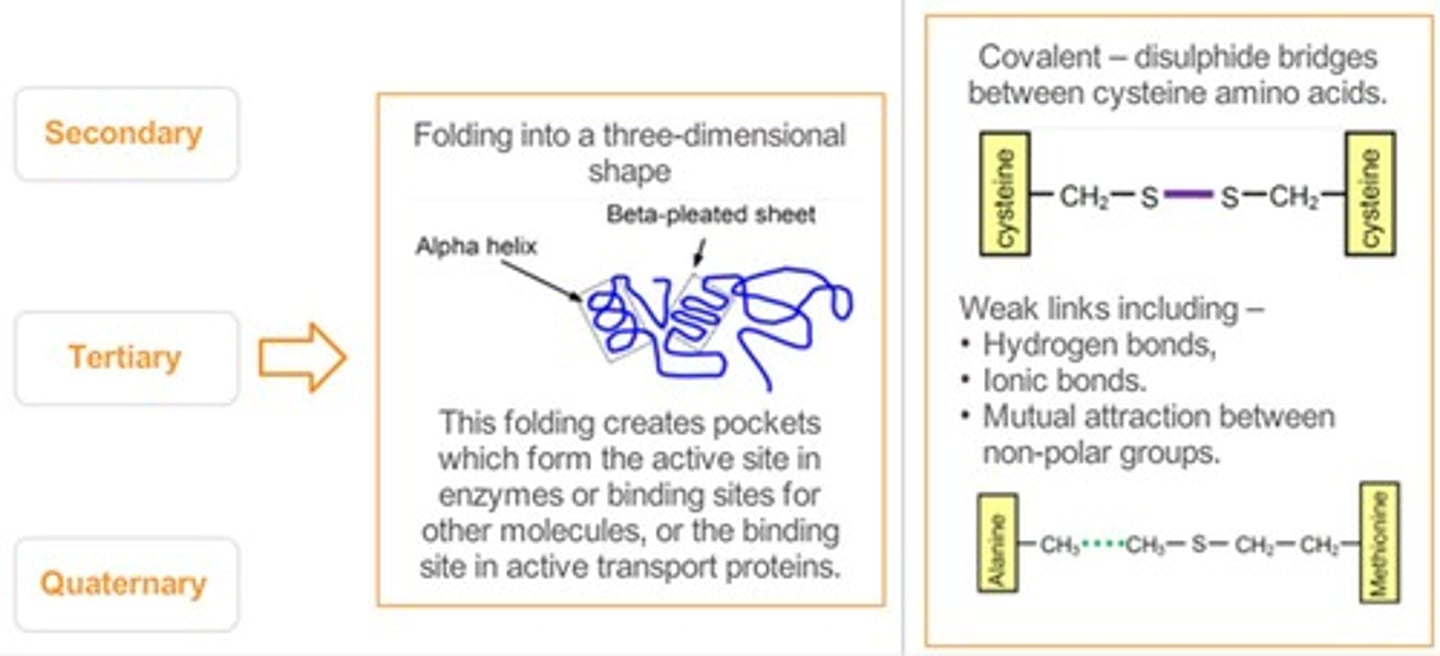
Disulfide Bridges
Covalent bonds between cysteine residues stabilizing protein structure.
Zwitterions
Amino acids with both positive and negative charges.
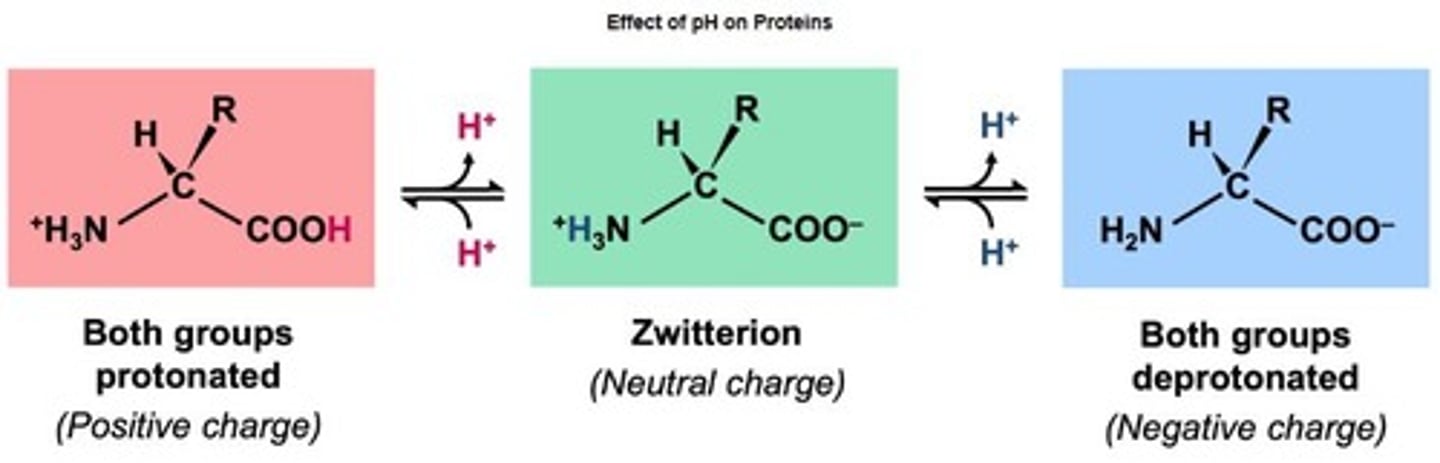
Optimal pH
pH level at which a protein functions best.
Thermal Energy
High temperatures disrupt hydrogen bonds in proteins.