TV4101 - Cytology 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Cytology Pros?
Quick
Atraumatic
Cheap
No anaesthetic
Well tolerated mostly
Cytology Cons?
Screening - may need furhter tests
Suscept to sample bias
May be inconclusive due to low cellularity or artefacts
Unable to evaluate tissue architecture
Cytological criteria of malignancy overlap with
dysplasia
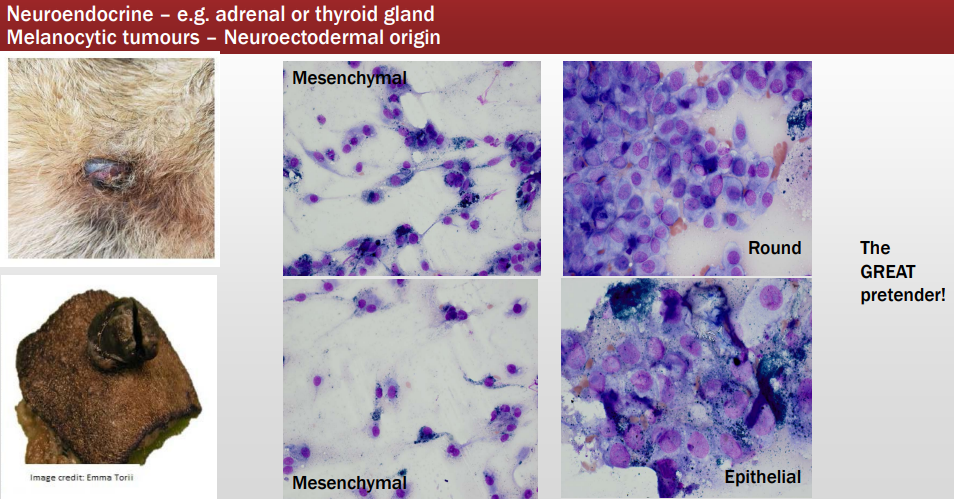
Types of Tissue Cells
Which is which?
Left - Round cells
Middle - Epithelial Cells
Right - Mesenchymal Cells
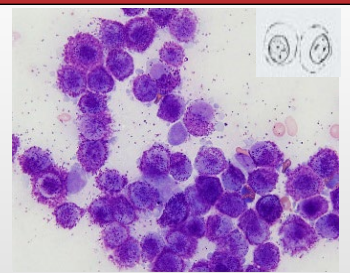
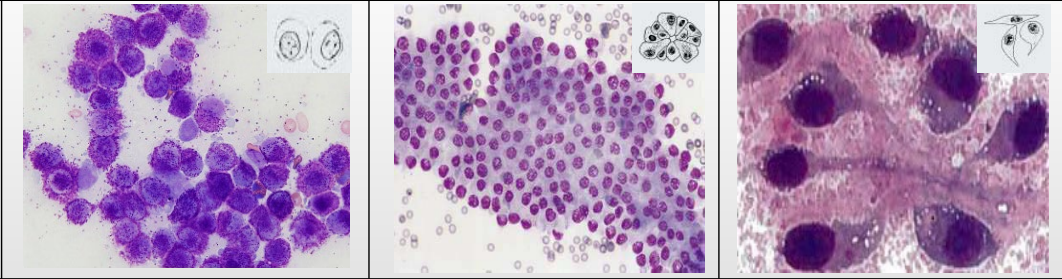
Types of Tissue Cells - Round cells
Describe shape?
Cellularity of slides?
Distribution on slide?
Round
Well defined border
High cellularity
Distribution: Exfoliate individually, evenly across slides
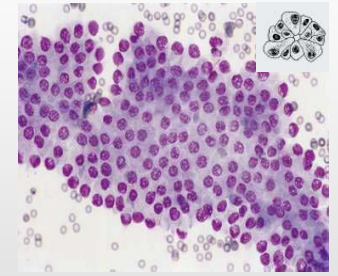
Types of Tissue Cells - Epithelial Cells
Features?
Cellularity of slides?
Distribution on slide?
Polygonal to cuboidal or columnar
Usually distinct cell borders/margins
High cellularity
Distribution
In clusters or sheets
Some adherenace btw cells
Malignant cells may lose adhesion
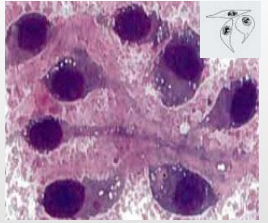
Types of Tissue Cells - Mesenchymal Cells
Shape?
Borders?
Cellularity?
Fusiform, spindle or oval to stellate (some may be more plump and round e.g. cells from bone) '
Cell borders may be indistinct or wispy cytoplasmic tails
Cellularity: Usually low due to adherence of cell in matrix, but malignant tumours might have a moderate to high yield.
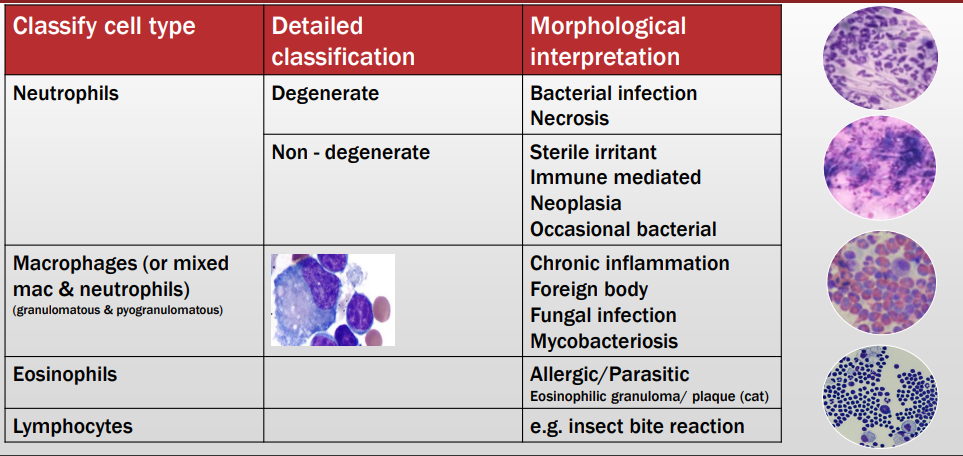
Types of inflam cells
Detailed classification
Morphological Interpretation?
What is this?
Describe the cells
Behaviour?
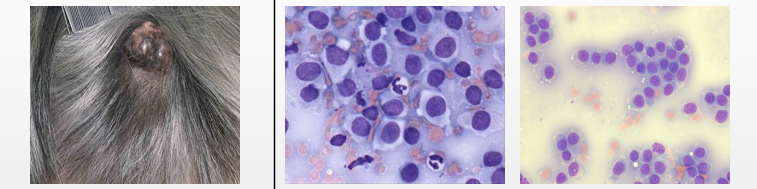
Histiocytoma (round cells)
Round cells - uniform, lots of cytoplasma that is clear, fine chromatin pattern, round nucleus (Like fried eggs)
Benign and respond spontaneously (If not gone in 2 months or inc and dec in size → is not histio but mast cell tumour_
What is this?
Describe the cells
What do?
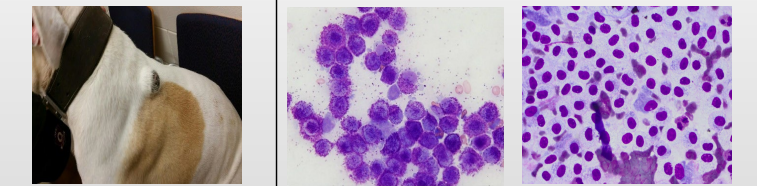
Mast Cell Tumour (MCT) - Round cells
Middle photo - Well granulated with purple granules
Right photo - Agranular version
Have clinically and medically staged and graded - have they got to the local lns (FNA or biopsy)
Sx removal then ask pathologist for margins and grading
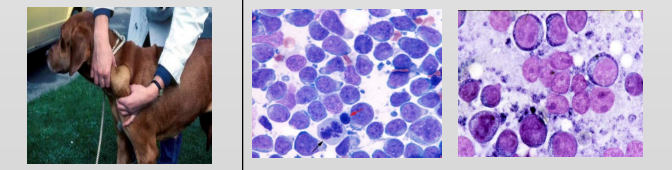
What is this?
Describe the cells
Lymphoma
Round cell, prominent nucleoli
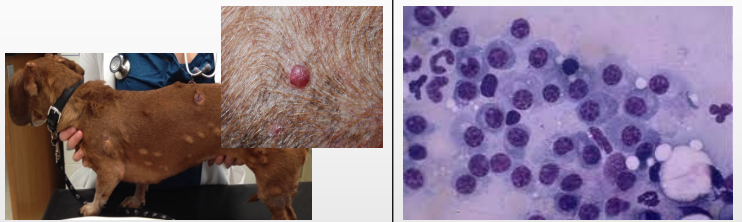
What is this?
Describe the cells
Behaviour?
Plasmacytoma - Round cells
Cells have eccentric nuclei
Course chromatin pattern aka clock face
Very blue cytoplasm
Benign but require Sx removal (generally curative)
If in BM v bad as causes multiple myeloma
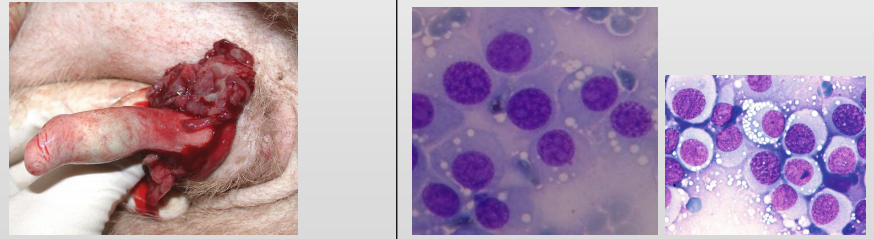
What is this?
Describe the cells
TX?
Transmissible venereal tumour
Round cells - vacuolated
Surgically debulked then tx with vinchrinstine
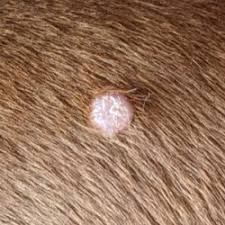
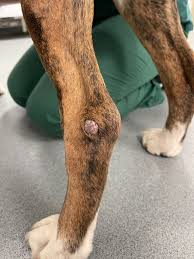
Round cell tumours - Histiocytoma
Common app?
Single smooth pink raised hairless mass oft on head, pinnae
Round cell tumours - MCT
Common app?
Single/multiple white-light yellow or haemorrgic masses/plaques
Ulcers common
Visceral involvement possible
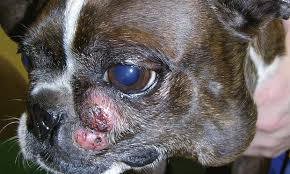
Round cell tumours - Lymphoma
Common app?
Multi offwhite/red to purple nodules on skin
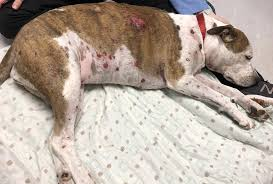
Round cell tumours - Plasma Cell Tumour
Common app?
Single raised pink nodule on head, trunk or limbs
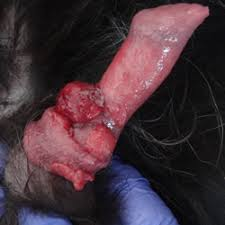
Round cell tumours - Transmissable veneral tumour
Common app?
Single or more oft multi pedunculated to cauliflower-like masses on ext genits of sexually active dog
Round cell tumours
Cyto charactersitics?
Histiocytoma
Moderately pale
Slightly granular cytoplasm
Round to slight indented nucleus
Mast Cell Tumour
Purple cytoplasmic granules in pale cytoplasm
Lymphoma
Slightly blue cytoplasm
Mitotic figures common (in high grade ones)
High nucleus-to- cytoplasm (N:C) ratio
Finely granular chromatin
Plasma cell
Large round eccentric nucleus
Abundant blue cytoplasm oft with perinculear clear zone
Mitotic figures maybe
Venereal Tumour
Round nuclei
Moderate amount of pale cytoplasm with few
Small distinct cytoplasmic vacuoles
Mitotic figures maybe
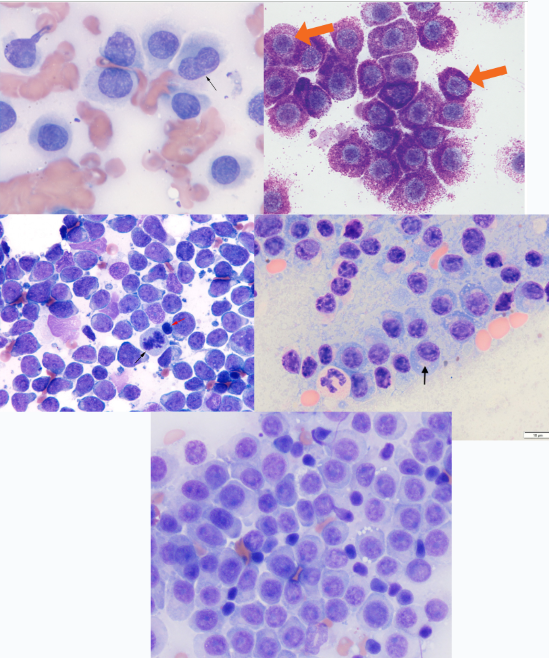
Round cells - Which is which?
Top Left - Histiocytoma
Top right - MCT
Middle Left - Lymphoma
Middle Right - Plasma Cell Tumour
Bottom - Transmissable Venereal Tumour

What is this?
Behaviour?
What do?
Sebaceous adenoma/hyperplasia - Sebaceous epith cells
Benign
Sx removal if bothering animal
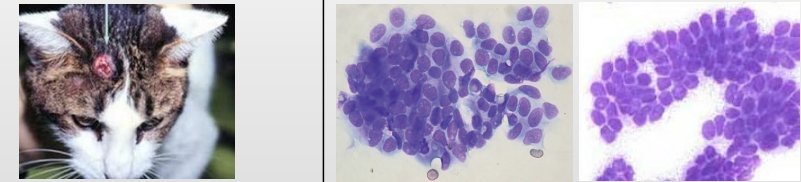
What is this?
Features?
Trichoblastoma (Basal cell tumour)
Basal eptihelium cells
Pretty uniform
High nucelo to cytoplasmic ratio

What is this?
Features?
Perianal gland hepatoid adenoma - Epithelial cells
Hepatoid as cells mimic hepatocytes

What is this?
Features?
Lipoma (benign) or Liposarcoma (malignant) - Mesenchymal (Spindle) cells
Lipoma most common - Generally don’t have to remove unless issues in locomation or bothersome
Neoplastic mass of adipocytes

What is this?
Features?
Fibrosarcoma (Spindle/Mesenchymal cells)
Spindle cells making fibroid
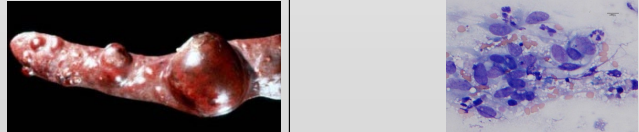
What is this?
Features?
Haemangiosarcoma (HSA)
Very Malignant
Seen at spleen, liver, heart and skin
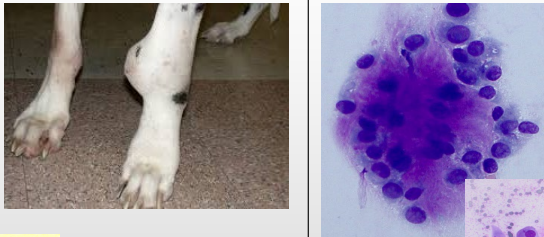
What is this?
Features?
Where can it be found commonly in dogs?
Osteosarcoma (Mesenchymal/Spindle cells)

Types of tissue cells - what can we see
Slide not drying due to fat = Lipoma or Liposarcoma
Criteria of malignancy
(predominantly applied to ?)
What broad parts of the cells do we observe and rank which are more important / give more confidence whether mass is benign or not?
Predominantly applied to epithelial & mesenchymal tumours
Nucleoli
Nuclear
Cytoplasmic (be careful of dysplasia)
Criteria of malignancy - Nucleoli
Features that are abnormal?
Description?
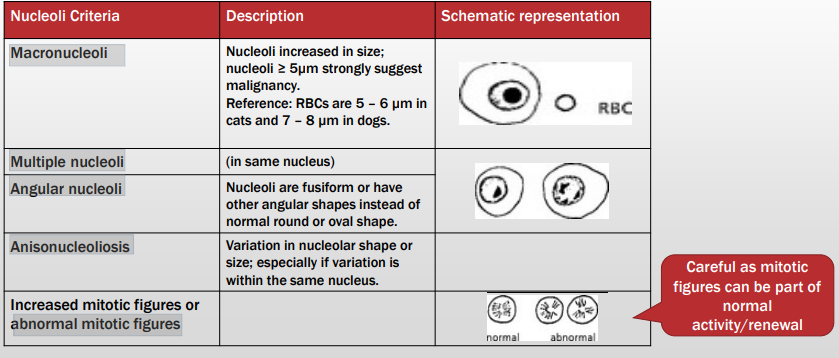
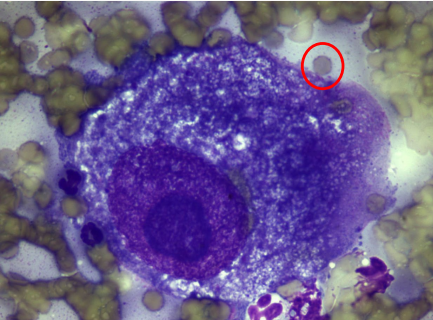
Criteria of malignancy - Nucleoli
Describe the cell - malignant or no? Why?
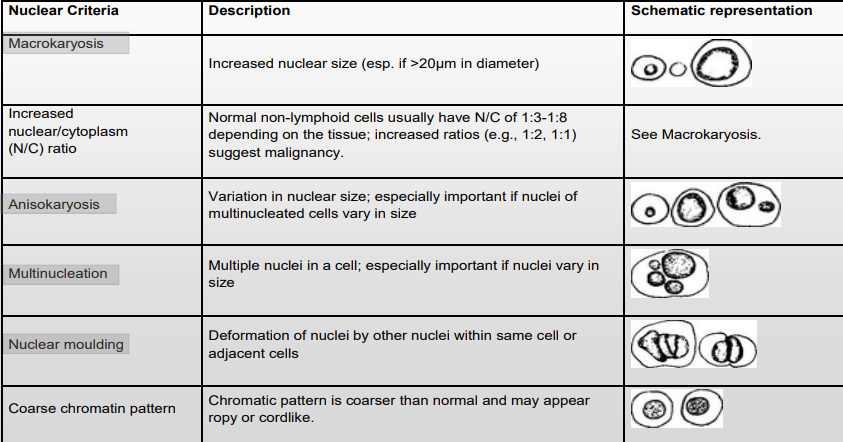
Macrokaryosis
Macronucleoli
Macrocytosis
(Increased nucleolar, nuclear & cell size)
Malignant
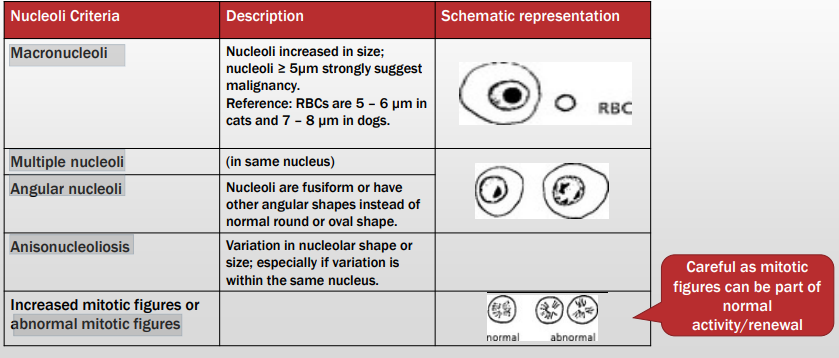
Criteria of malignancy - Nucleoli
Describe the cell - malignant or no? Why?
Pleomorphic nucleoli with varying size and shape
Macronucleoli
Angular nucleoli
= malignant neoplasia
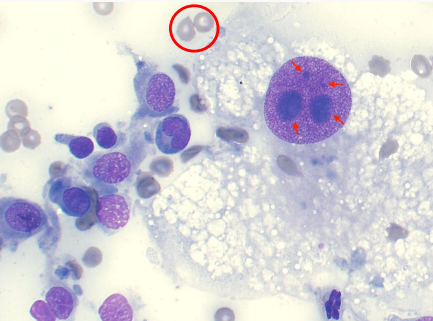
Criteria of malignancy - Nucleoli
Describe the cell - malignant or no? Why?
Multiple nucleoli
Anisonucleoliosis
= malignant neoplasia
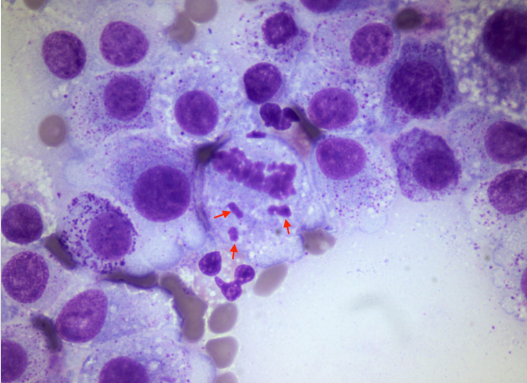
Criteria of malignancy - Nucleoli
Describe the cell - malignant or no? Why?
Abnormal mitotic figures
Malignant
Criteria of malignancy - Nuclear Features
Includes?
Description?
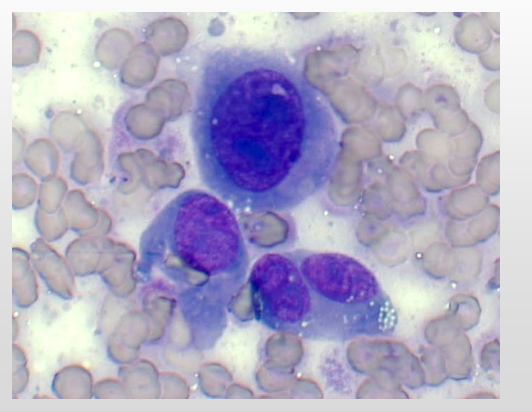
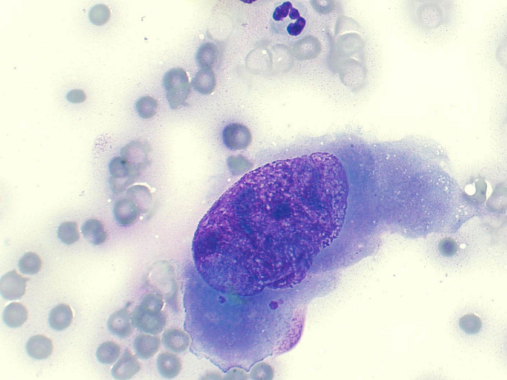
Criteria of malignancy - Nuclear Features
Describe the cell - malignant or no? Why?
Anisokaryosis = nuclear variation in size
Malignant
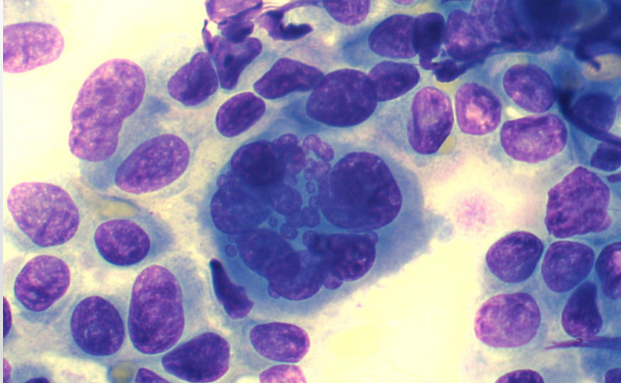
Criteria of malignancy - Nuclear Features
Describe the cell - malignant or no? Why?
Multiple nuclei = malignant neoplasia
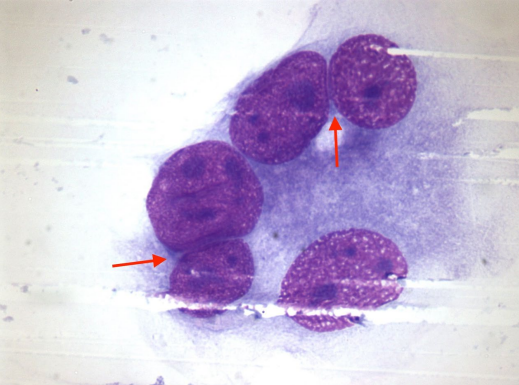
Criteria of malignancy - Nuclear Features
Describe the cell - malignant or no? Why?
Nuclear molding (hugging nuclei) - Malignant
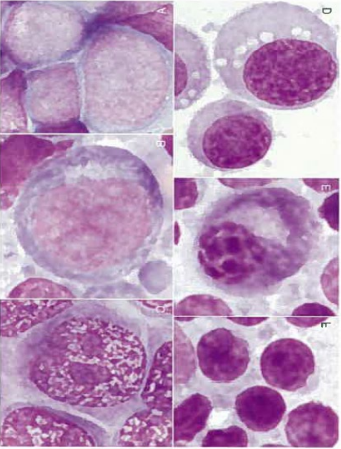
Criteria of malignancy - Nuclear Features
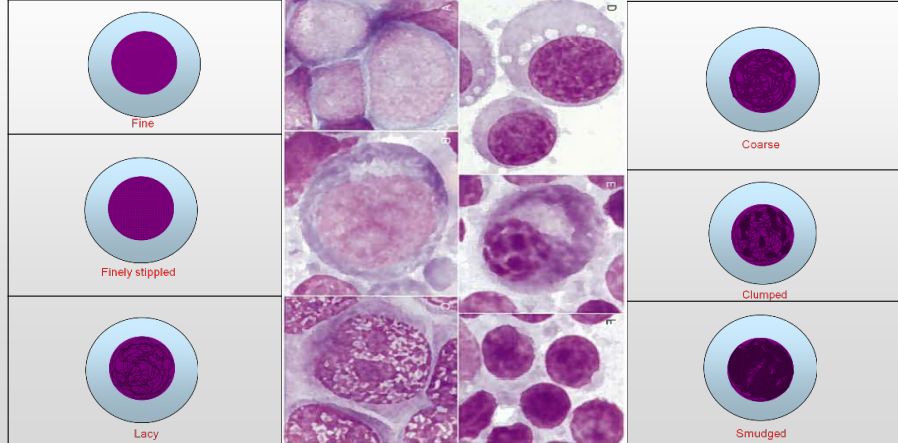
What are we comparing?
Theory behind it?
Describe each
Nuclear features – chromatin pattern (theory: coarser than usual suggests malignancy)
How do diff tissue cells metastatise?
▪ Round cells & epithelial tumours metastasize via lymphatics
▪ Mesenchymal predominantly metastasize via blood vessels (but occasionally via lymphatics – usually a sign of more aggressive disease)
Types of TIssue cells - the other category