W7: Accommodation and Cycloplegic Refraction
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Discuss the tests used to assess accommodation in paediatric patients and their normative values.
Name the tests used to assess accommodation in paediatric patients
Amplitude of Accommodation (AoA)
Accommodative Facility
Relative Accommodation
Fusional Reserves version of Accommodation
What is Amplitude of Accommodation?
Measure of max amount of accom that can be exerted
Diff in D btwn far + near point of accom relative to a reference point
AoA dec’s as we get older
Bc’s symptomatic at approx 45 years-presbyopia
hyperopes notice it sooner as may alr have been accom comp to myopes
What factors affect the measurement of amplitude of accommodation?
Technique used can affect AoA
Subjective tech’s don’t allow for ocular depth of focus e.g RAF rule
Effect of pupil
As we get older-pupil gets smaller,inc’d DOF ,inc’s tolerance of accom ,certain amount of leeway that accom system doesnt need to take into account -AoA may be overestimated when using subj tech’s
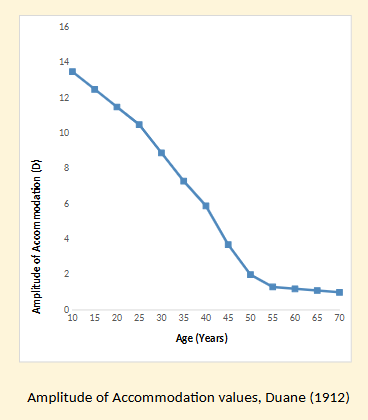
Describe the findings from Duanes (1912) study of amplitude of accomodation values
Starts from 10 years old
At 10 years -13-14D
Every 5 years declines fairly linearly until 25 years old more sharp decline ,at 45 years mark 2D of accom left
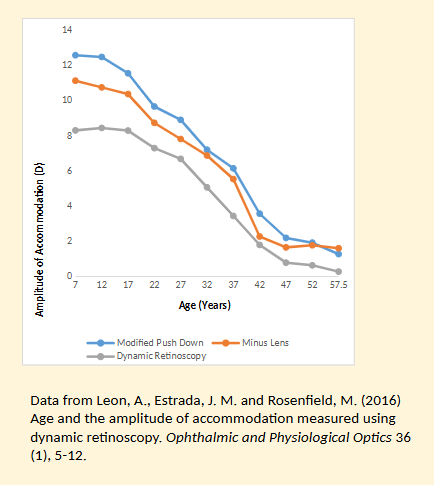
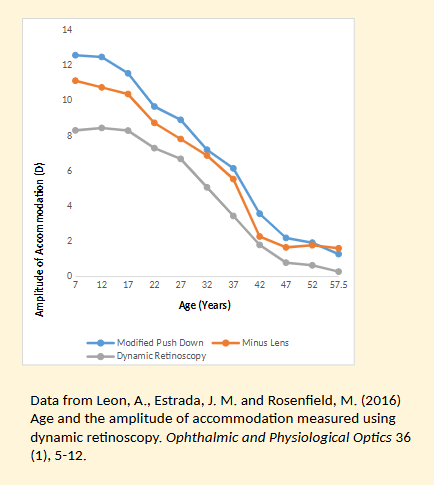
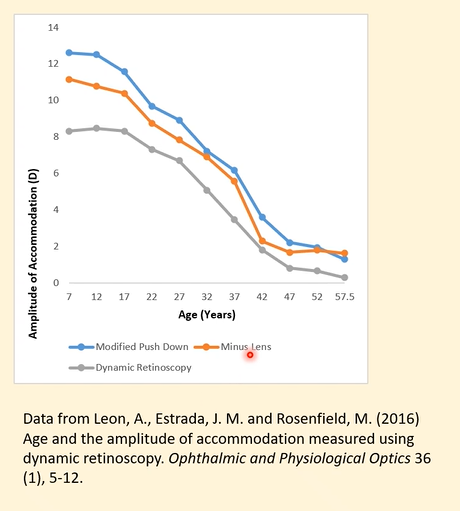
Explain the findings from Leon et al’s (2016) study into age and the amplitude of accomodation measured using dynamic retinoscopy ?
All three methods show a decline in amplitude of accommodation (AoA) with age, with a steep fall from childhood to the mid-40s and very low values in presbyopia.
Subjective techniques (modified push-down – blue, and minus lens – orange) consistently produce higher AoA values than the objective method.
Minus lens (orange) is slightly lower than push-down (blue) across most ages because the minus-lens method depends on adding lenses until blur occurs and the accommodative system can no longer overcome the demand.
Dynamic retinoscopy (grey) shows the lowest AoA across all ages because it is an objective measurement and does not include the effect of depth of focus (DOF).
In presbyopic ages, subjective methods still show some apparent accommodation, but this is largely due to DOF—objective dynamic ret shows near-zero accommodation, indicating that the true accommodative ability is minimal.
DOF also influences younger age groups, as subjective methods show much higher AoA than objective dynamic ret, even though the actual change in lens power may not be as large as subjective results suggest.
Overall, the study shows that DOF affects subjective measures throughout the lifespan, causing them to overestimate true lens-based accommodation compared to dynamic retinoscopy.
How is amplitude of accommodation clinically determined?
Measure the dist of the near point of accom to the spectacle plane while RE= fully corrected.
e.g myopic -appear to have a higher AoA bc some of accom power may have alr been used to maintain clear vision
If refractive correction is not worn the measured AoA would have to be adjusted
How is the near point of accommodation measured and converted to amplitude?
NPA can be measured by push-up or push- down method (mono + binoc)
PU -overestimates,PD-underestimates AoA-avg both
The dioptric equiv of the NPA (punctum proximum) is the AoA
What are Hofstetter’s formulas for estimating expected amplitude of accommodation?
Used to derive expected AoA for Caucasian subjects up to 60 years
Max amplitude: 25 – 0.4 × age (years).
Avg amplitude: 18.5 – 0.3 × age (years).
Min amplitude: 15 – 0.25 × age (years).
What are the Hofstetter-calculated amplitudes for a 10-year-old emmetrope?
Max amplitude: 25 – 0.4(10) = 21 D.
Avg amplitude: 18.5 – 0.3(10) = 15.5 D.
Min amplitude: 15 – 0.25(10) = 12.5 D.
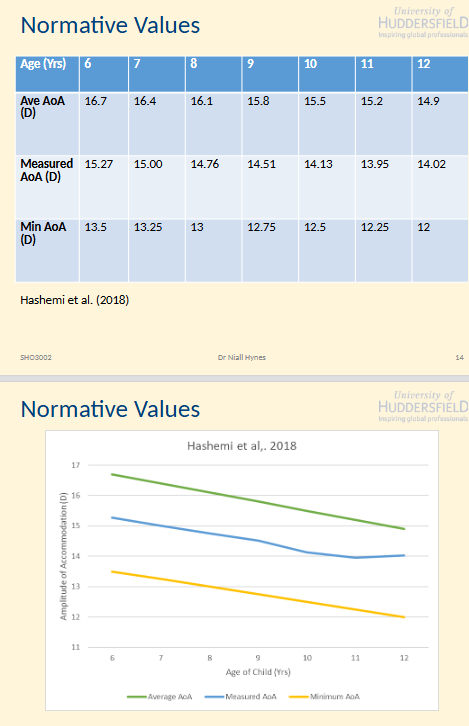
Normative values
Age 6-12 years (Hashemi et al 2018)
Average AoA
Measured AoA
Min AoA
Fairly linear rel
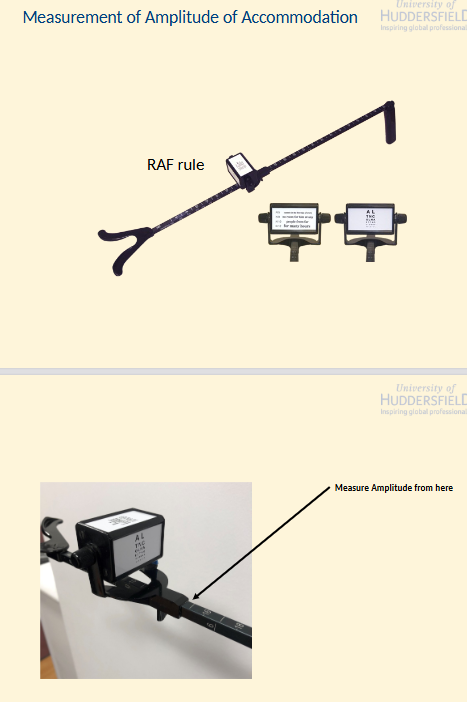
How would you measure Amplitude of Accommodation using a RAF rule?
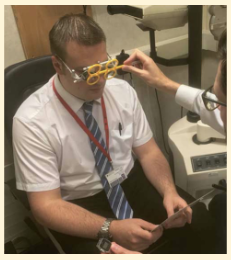
What is accommodative facility?
Ability of patient to rapidly change accommodation.
How is accommodative facility measured?
Usually measured at 40cm.
Target is N5 or N6 letter or words.
RE=fully corrected
±2.00D lenses are flipped before the eye.
Test is started w/ the pt trying to clear the letters through the +2.00D lens (accommodative stimulus = 0.5D).
Then through the -2.00D lens (accommodative stimulus = 4.50D
What should clinicians consider regarding normative data for accommodation facility?
Diffic as evidence base isn’t great.
Range of ages
Poor exclusion criteria
Adv to form own impression of what is normal.
Clinical pass rates
7 cpm Monocular
5 cpm Binocular
Discuss conditions that affect accommodation
Give examples of accommodative disorders?
Accommodative Insufficiency
Accommodative Fatigue
Accommodative Spasm
Accommodative Inertia
What is accommodative insufficiency and what symptoms does it cause?
When accom is less than expected for their age
Symptoms:
Blurred NV
Frontal HA’s
What diagnostic criteria help identify accommodative insufficiency?
AoA less than min AoA as det by Hofstetter’s formula (Borsting et al., 2003, Abdi et al., 2005)
Accommodative Fatigue
Similar symptoms but more transient
What clinical signs are associated with accommodative insufficiency?
Reduced AoA
Reduced Accommodative Facility
can’t go from D to N as efficiently as we would like
Reduced NV/ VA
When fully corrected
XOP @ Near, bc’s relatively esophoric if Pt tries to exert more accom
Near triad rel btwen accom + convergence- bc not accom enough=exo, eyes turn in for every D we accom .this isn’t happening when they try hard they’re overaccom as a result
What treatment options exist for accommodative insufficiency?
Hyperopic Rx
Low add may be needed-temp measure
If too high may prevent accommodative response acting as it should
Pen to nose exercises
Can be related to Convergence Insufficiency
What is accommodative inertia and who is most affected?
More prevalent in adults over 30 years.
Accommodative system has diffic switching from dist to near vision and back again
Accom Facility test =important
What are the causes and signs of accommodative inertia?
Causes:
Prolonged near work
Poor GH
Anisometropia
Early presbyopia
Holmes-Adie syndrome (unilateral cases)
Signs:
Reduced AoA
Reduced accommodative facility
How is accommodative inertia treated?
Any underlying conditions should be treated
RE corrected.
Push up exercises/flipper exercises can help w/ accommodative facility
What is accommodative spasm?
AKA Accommodative Excess
Constant contraction of the ciliary muscle leads to exertion of accommodation
What are the causes of accommodative spasm?
Uncorrected hyperopia
Prolonged near work
Underlying emotional cause
Lesions of the brain
Multiple sclerosis
Meningitis
Head trauma
What symptoms occur in accommodative spasm?
Pseudomyopia
Exerting accom too much→ can lead to temp shortsightedness
Cycloplegic Refraction should det myopia not present.
HA’s
Ocular Discomfort
Esotropia + pupil miosis in more defined cases
Too much accom=too much convergence
bc accom=pupil miosis
How is accommodative spasm treated?
Hyperopia should be gradually corrected.
Causes eyes to relax
In more pronounced cases cycloplegics can be used.
Orthoptic exercises needed to prevent a reoccurrence
Discuss the indications for cycloplegia of paediatric patients
When is cycloplegia indicated in children?
Young children: (bc accom is more uncontrolled at this age,check for any uncorrected/latent hyperopia)
<7 years
1st ST
<4 years
First ST+ repeat eye exams in children
When subjective refraction is limited.
When dry ret = diffic
For a more stable ret reflex
Discuss the indications for cycloplegia of paediatric patients
When is the need for cycloplegia indicated?
Latent Hyperopia
Dry subjective signif less +ve than ret
E.g., Ret R + L +4.00 D, Subj +1.50 D R and L
Case History
problems focusing
Suspected accommodative disorders
Reduced AoA
Reduced accommodative facility
Dynamic Ret
Lead of accom
Lag of accommodation >1.00 D
When should you consider the use of a cycloplegic agent according to the College Guidelines?
To give:
a) an accurate assessment of the RE (major factor in amblyopia or squint)
b) the best poss view of the fundus, w/in the limits of the co-operation of the child.
What is cyclopentolate?
Muscarinic antagonist
Prevents eye from accommodating.
Dilates eye
What are the recommended cyclopentolate doses for children?
3 months – 11 years
Apply 1 drop, 30–60 minutes before examination, using 1% eye drops.
brown eyes=more resistant
12 – 17 years
Apply 1 drop, 30–60 minutes before examination, using 0.5% eye drops
What are the side effects of cyclopentolate?
Blurred vision
Photophobia
Psychosis, Hallucinations, Ataxia + incoherent speech
2% conc.
Multiple drops of 1% (not advised)
What should be explained to the patient before instilling cyclopentolate?
Obtain informed consent.
Explain why you want to use cycloplegia.
Explain visual effects
NV blur
Pupil dilation
Inc’d light sensitivity
What precautions should be taken before instilling cyclopentolate?
Explain that drops will sting a little!
Important to maintain trust.
Sometime better for another optom to put the drops in.
Good optom / Bad optom!
Check for allergies
Consider near ret for prev reactions to drops
What should be checked after instilling cyclopentolate?
Drops take about 30 mins to work.
Check accom has relaxed.
AoA
Check for Anisocoria
May indicate unequal cycloplegia
What information must be recorded when using cycloplegic drugs?
Drug
Dose
Batch number
Expiry date
Example: Cyclopentolate, 1.0%, BN 1234, Exp 02/2022
What should be considered during retinoscopy under cycloplegia?
Concentrate on centre 3-4 mm.
Pupil periphery may be affected by aberrations + have a diff reflex.