2.5 - a/symmetric information, market structures, profit & loss, game theory, collusive and non-collusive, concentration ratio
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
perfect/ symmetric information
all consumers and producers have equal access to all relevant information
optimal decision-making
imperfect/ asymmetric information
one party in a transaction has more/ better information than the other
suboptimal decision-making
government responses to assymetric information
regulation
provision of information
licensure (obtaining a license by service/ good provider)
private responses to asymmetric information
screening/ research by buyers
signalling by sellers
eg. warranties, brand name, service records
moral hazard
one party takes risks
doesn’t face full costs of the risks
the full costs are borne by the other party
eg. insurance
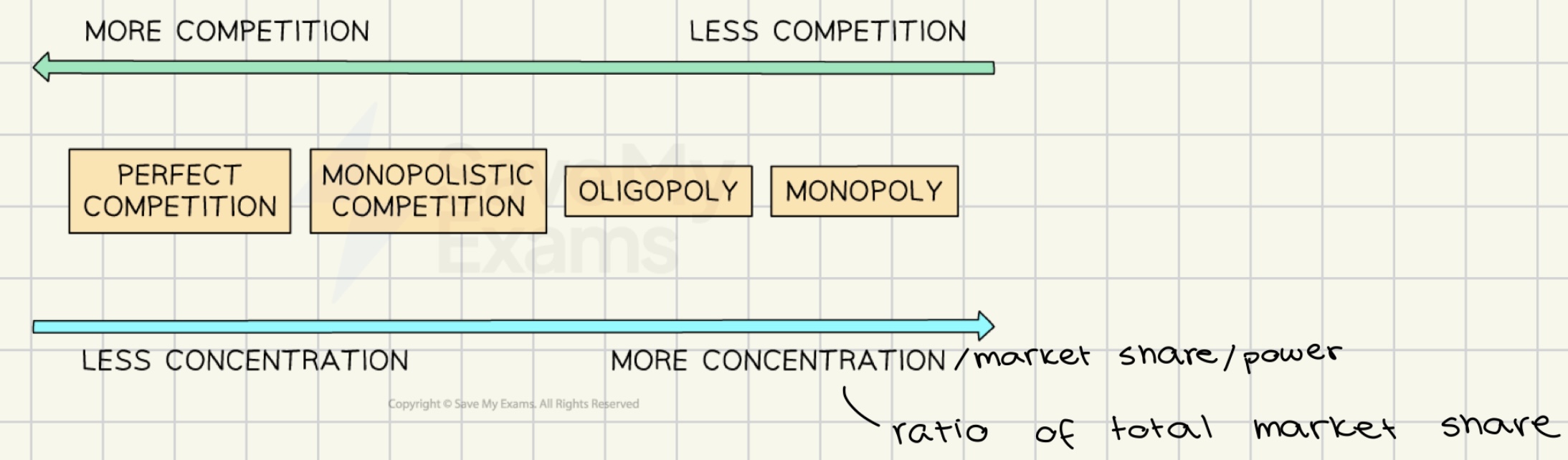
market structures
perfect competition
imperfect competition
monopolistic competition
oligopoly
monopoly
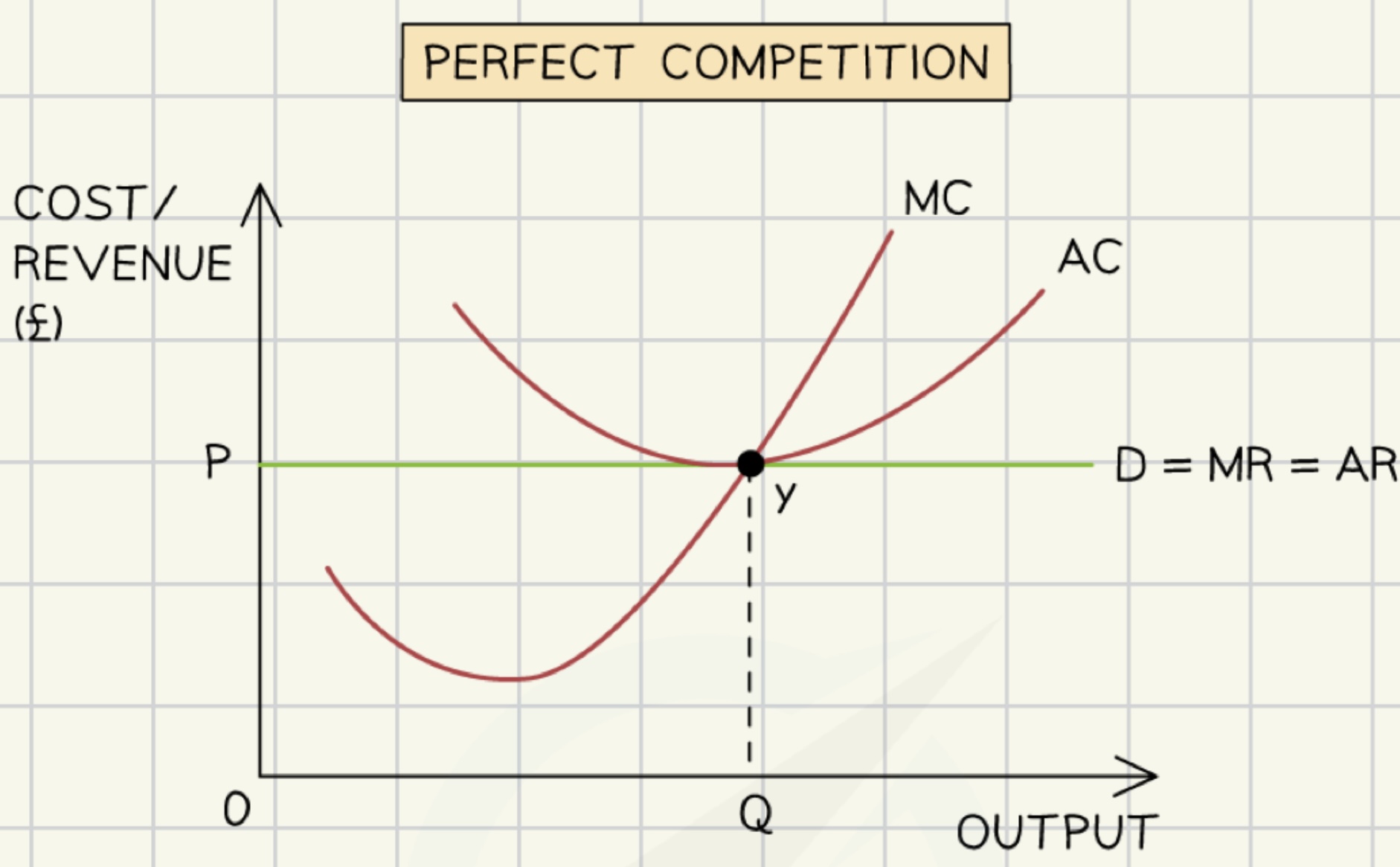
perfect competition
many small firms
homogeneous products
no barriers to entry or exit
no market power
perfect knowledge
perfect competition
leading to optimal outcomes for consumers and producers.
eg. agriculture
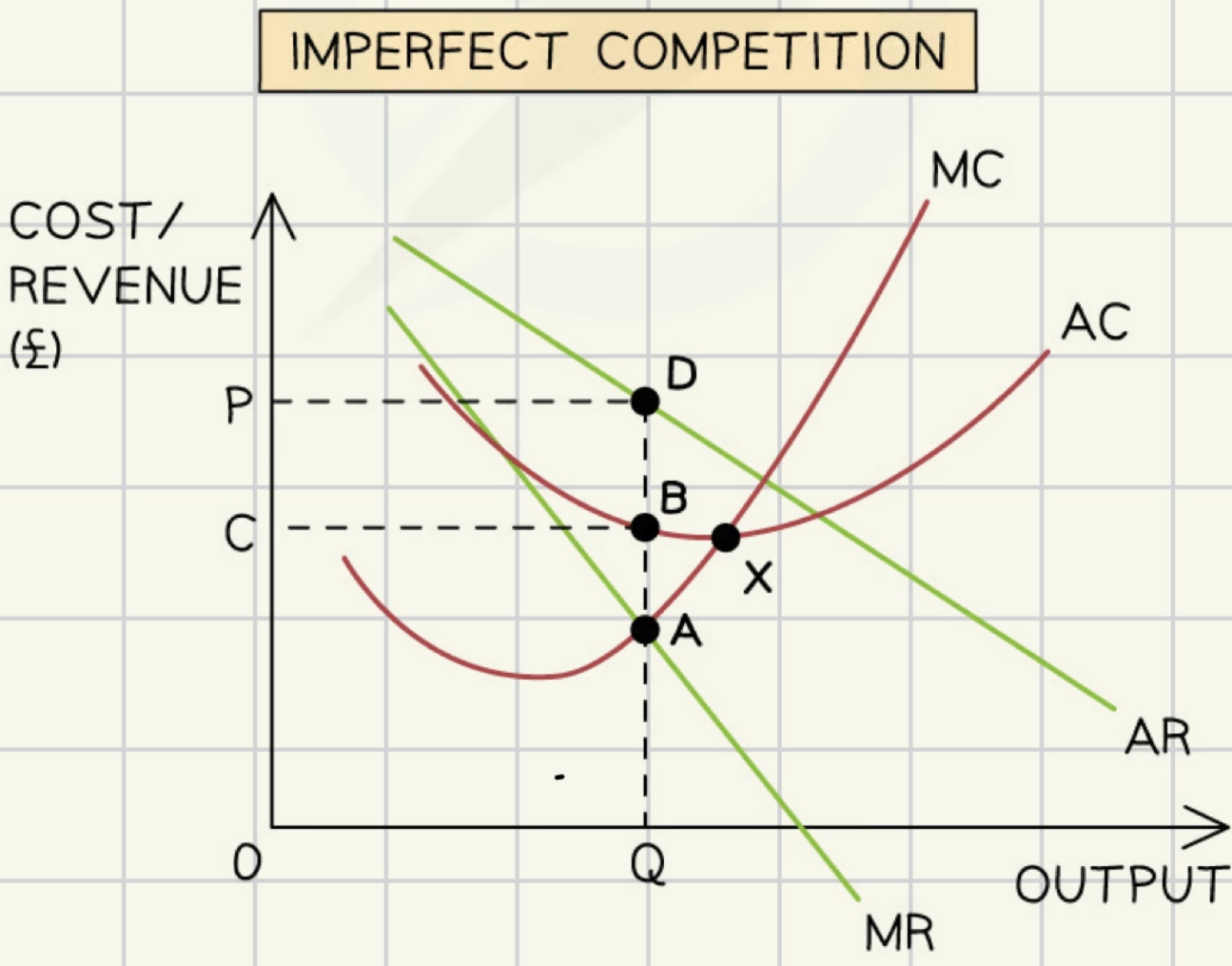
imperfect competition
market structure where individual firms have
some control over price
product differentiation
potentially inefficient outcomes.
monopolistic competition
many relatively small companies
differentiated products
low barriers to entry
some market power
imperfect knowledge among consumers
good amount of competition
eg. restaurants, computer games, books, furniture
oligopoly
few large companies
mutual interdependence
differentiated or homogeneous products
high barriers of entry
significant market power
imperfect knowledge
some competition
eg. cars,household appliances, detergents, cereal
monopoly
one large company
unique product
no close substitutes
high to impossible barriers of entry
complete market power
imperfect knowledge
no competition
eg. public utilities
marginal costs MC
change in total costs resulting from additional unit produced
marginal revenue MR
the increase in revenue resulting from an additional unit produced
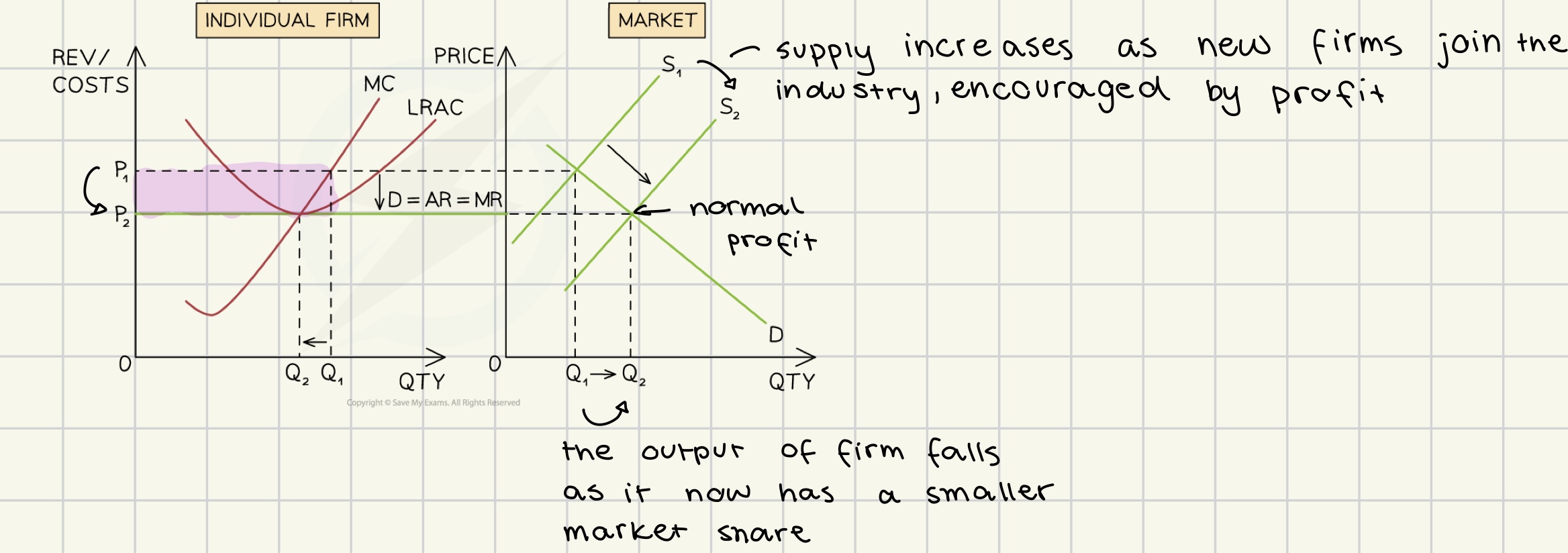
abnormal profit in perfect competition
in short run
profits will always return to long term equilibrium
total revenue > total costs
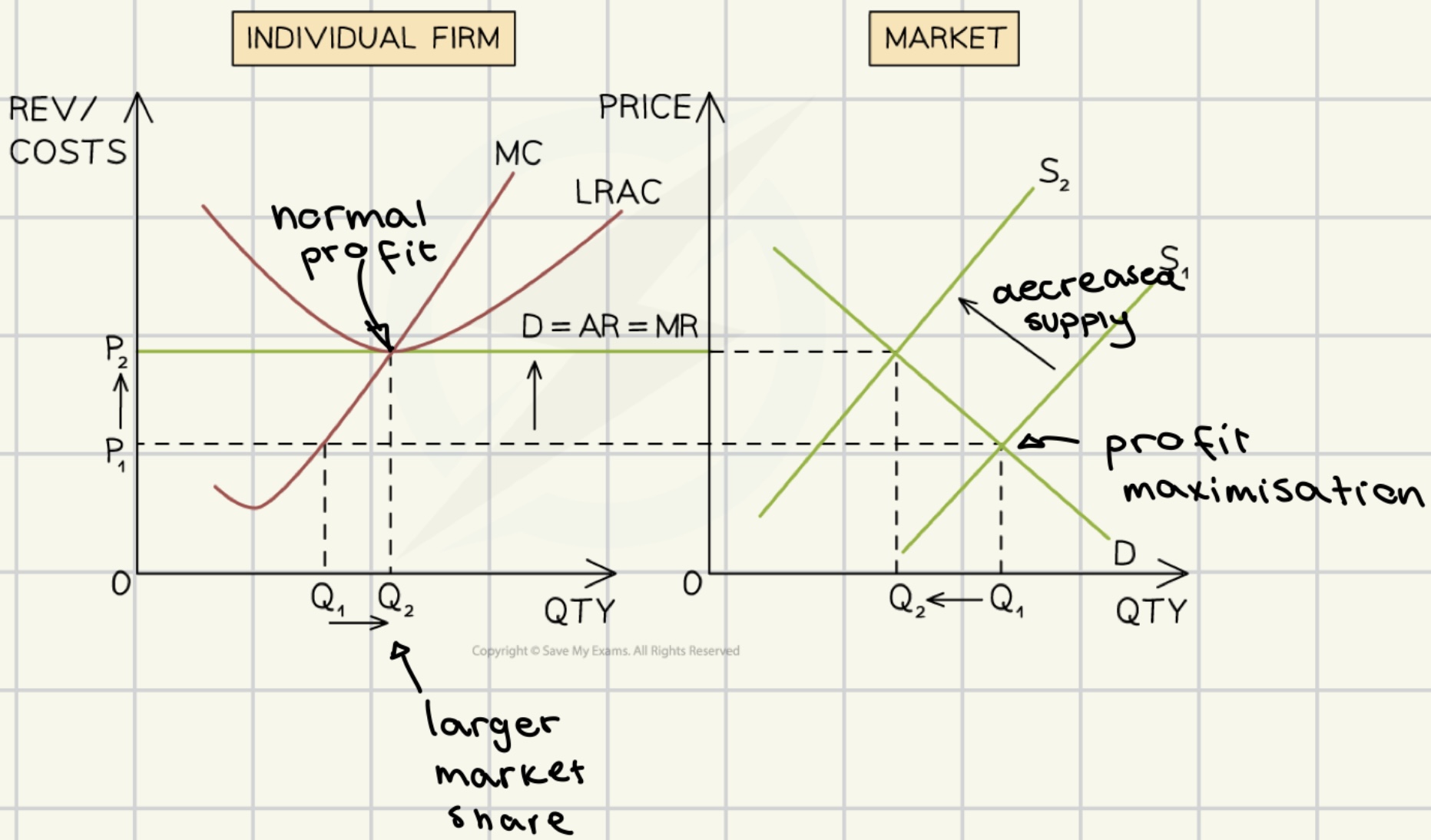
moving abnormal profit to normal profit in long run for perfect competition
abnormal profit → -firms making abnormal profit loose $ - new entrants attracted by profit opportunities -no barriers to entry → normal profit → - firms making losses leave - firms that stay make more profit → abnormal profit ….
profit loss in short run in perfect competition
total revenue < total costs
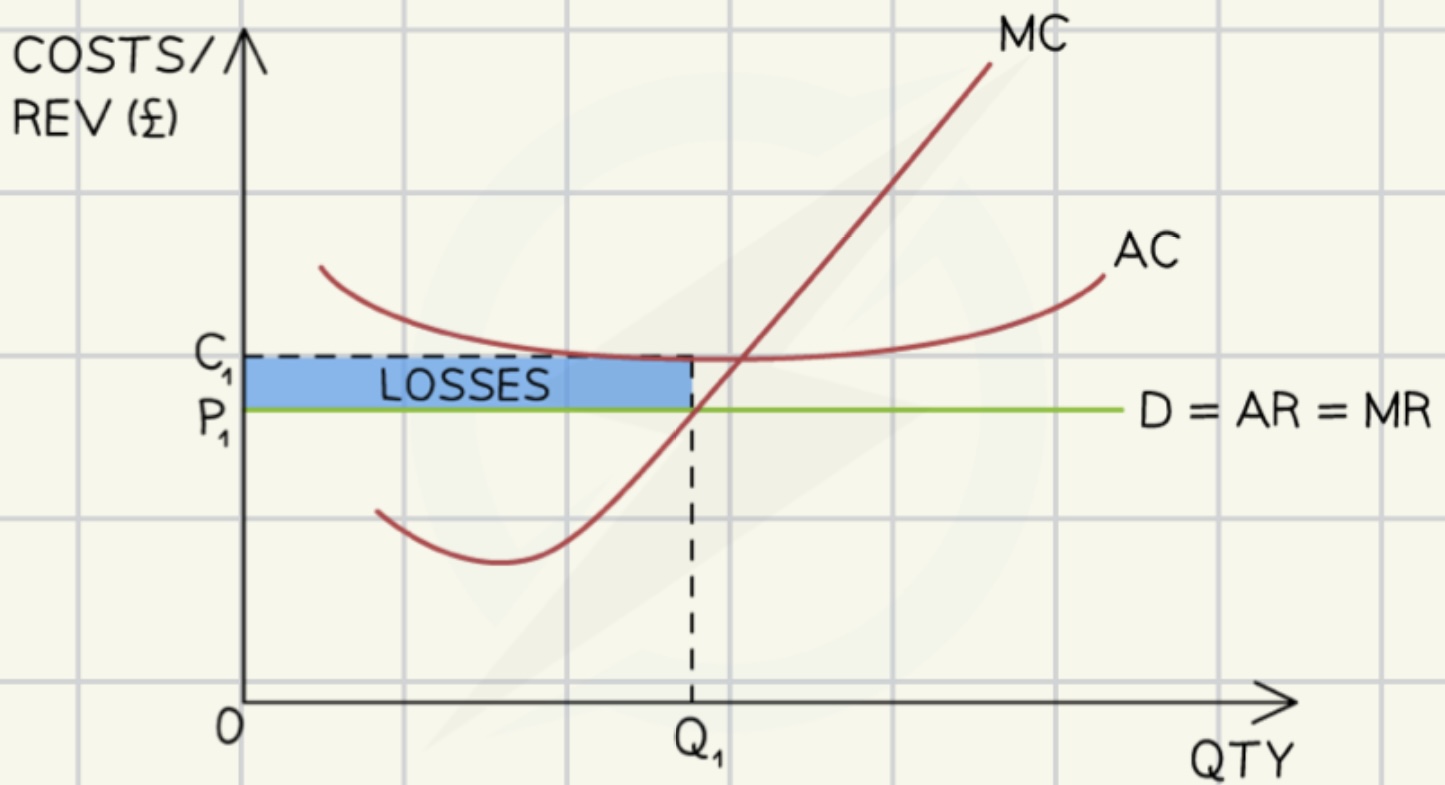
moving from loss in short term to normal profits in long run in perfect competition
if firms in perfect competition make losses in the short run they will shut down
shut down rule:
if average revenue = average costs, the firm should shut down
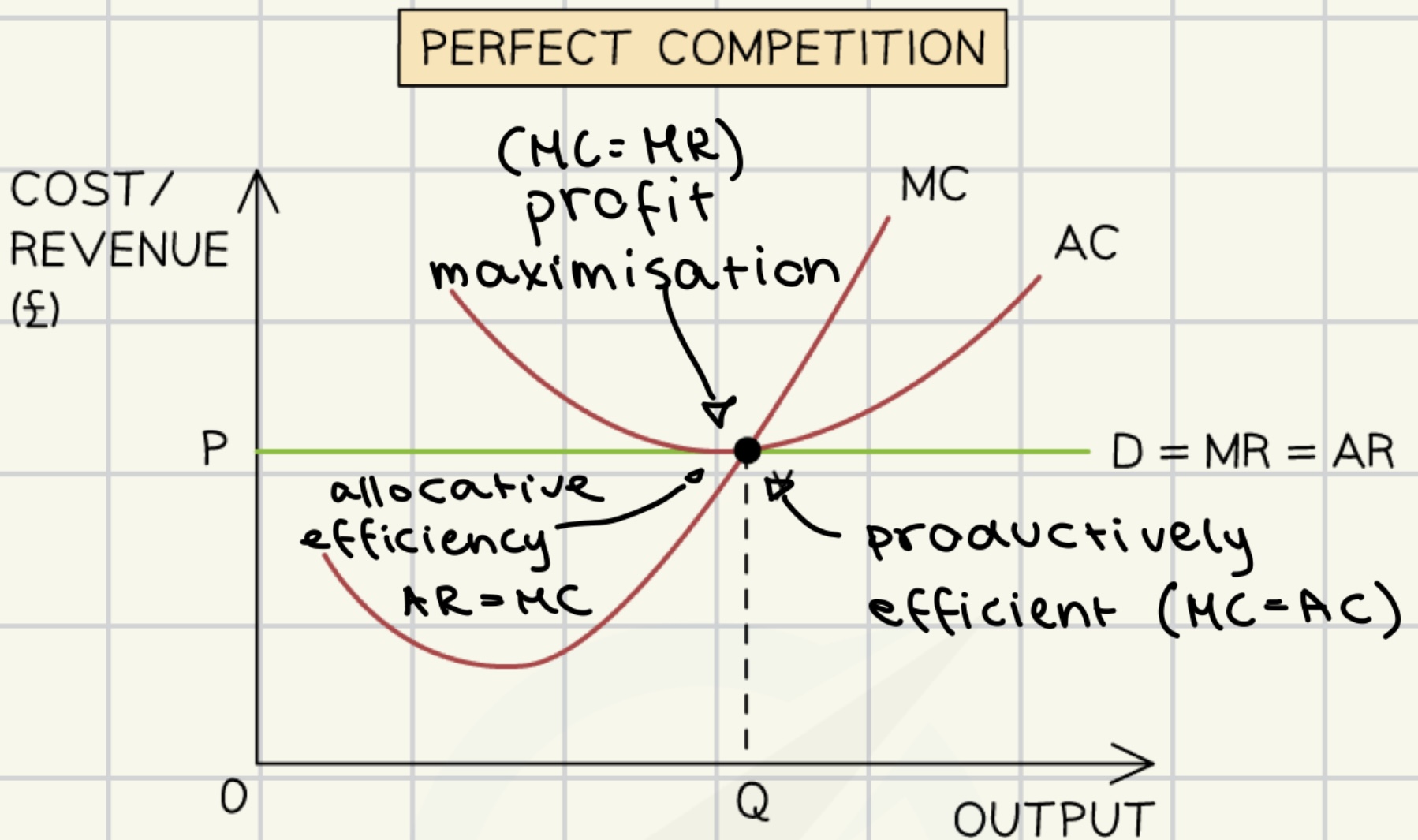
allocative efficiency in perfect competition
allocative efficiency → AR=MC
consumers and producers get maximum possible benefits
no excess demand/supply
no one can be better off without the other being worse off
average costs are minimised
no waste
high productivity
barriers to entry for monopoly
monopoly → 25% or more of the market
legal (patent/license/ copyright)
aggressive competition
economies of scale of existing companies
control of scarce resources
natural/ cost barriers
monopoly vs perfect competition graphs
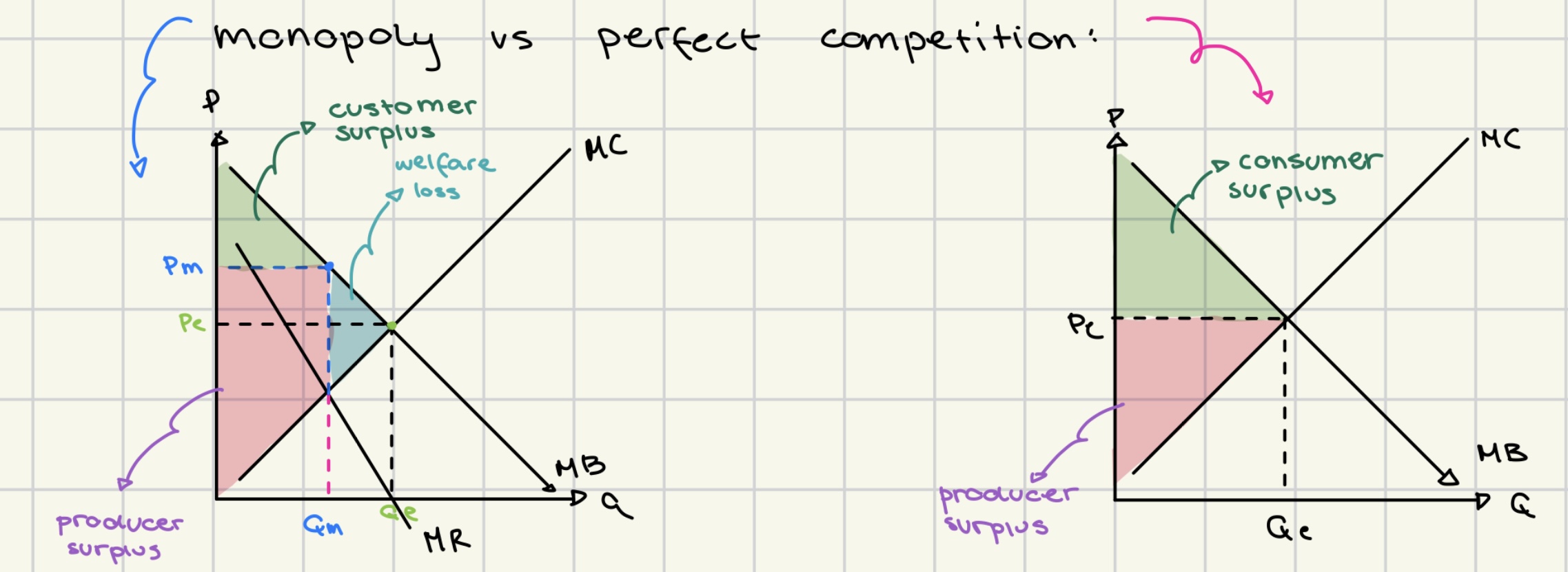
benefits of monopoly
super profit allows investment in research and development
may have lower prices
economies of scale
natural monopoly
disadvantages of monopolies
no need to be more efficient
stifled innovation
no incentive to improve quality
higher price
lower output
loss of consumer and producer surplus
welfare loss
allocative inefficiency
market failure
negative impact on distribution of income
ways of dealing with monopolies
anti- trust laws to break up a monopoly
mandatory pricing regulations imposed by governments
price controls
competition policies
natural monopoly
when a single firm can provide a good or service at
lower cost than multiple competing firms
due to high fixed costs and economies of scale.
reasons for economies of scale
specialisation of labor
specialisation of management
bulk buying
financing economies
spreading of costs
reasons for diseconomies of scale
co-ordination and monitoring difficulties
communication difficulties
poor worker motivation
oligopoly strategic behavior (due to interdependence)
based on plans of action that take into account rivals’ possible courses of action
incentives in oligopoly market
conflicting incentives
incentive to collude (agreement between firms to limit competition between them)
incentive to compete/ cheat
game theory
analyses and displays the behavior of decision-makers who are dependent on each other
their behavior may trigger price wars
game theory graph/ payoff matrix
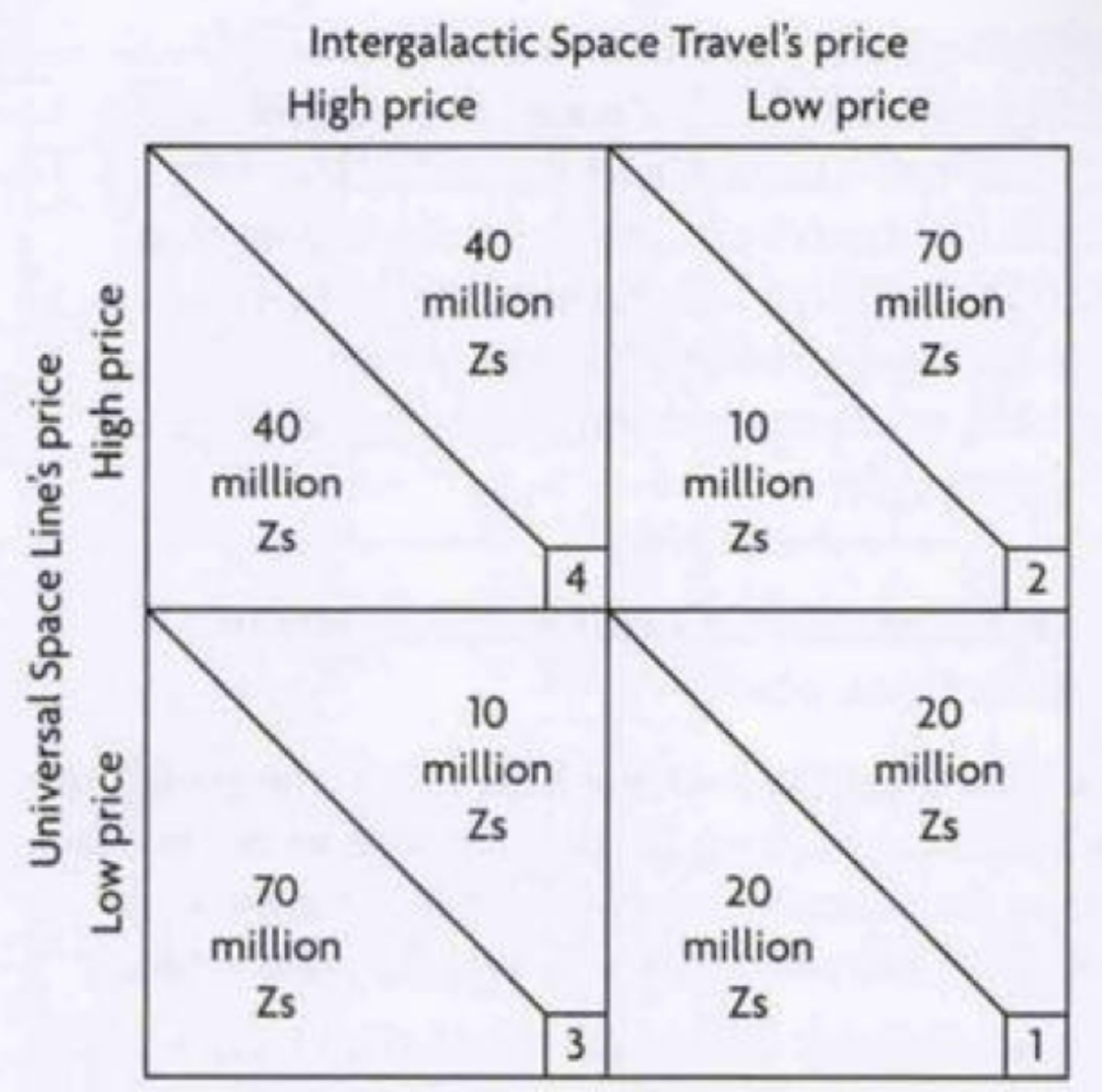
Nash equilibrium
final position that results from the game
non-price competition in oligopoly
product development
advertising
branding
quality customer services
warranties
provision of credit
discounts on upgrades
collusive oligopoly
a market structure where firms collude to
limit competition
increase market power
maximize joint profits.
eg. cartels → OPEC
ILLEGAL due to its anti-competitive nature.
informal collusion
where firms coordinate their actions
without a formal agreement,
through signaling
tacit understandings
to achieve similar objective
price leadership collusion
informal collusion
one leading firm sets prices that other firms in the industry follow
effective coordination of pricing strategies
without explicit agreements.
non-collusive oligopoly
firms compete without colluding, resulting in
independent pricing
independent production decisions.
concentration ratio
a measure of the market share held by the largest firms in an industry
concentration ratio ↑ = competition in industry ↓
** if 4 largest firms control 40% of the output an industry is considered oligopolistic
weakness and usefulness of concentration ratios
do not reflect competition from abroad
no indication of the importance of firms in global market
do not account for competition from other industries
do not distinguish between different possible sizes of largest firms
disadvantages of oligopoly
welfare loss
allocative inefficiency
market failure
higher prices and lower quantities of output than under competitive conditions
loss of consumer surplus due to higher prices
negative impacts on the distribution of income
possibly less innovative
benefits of oligopoly
economies of scale due to large size
product development and technical innovations due to high abnormal profits
improved efficiency and lower costs
increased product variety