2 Alginate & Gypsum
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
why are mounted diagnostic casts on an articulator important?
complement tool in addition to clinical exam
legal proof of pt’s current occlusion
allow clinician to
modify occlusal pre-treatment plan prior to establish definitive Tx plan
evaluate occlusion in centric and eccentric positions
determine inter-arch distance, teeth vs alveolar ridge
make alteration without pt being there physically
what materials are most commonly used to make impressions?
Hydrocolloids and synthetic elastomeric polymers
what is alginate made from?
cell wall constituents of brown algae (chemistry involves salt of alginic acid Na or Ca alginate)
what can be evaluated with casts of the mouth?
relative alignement between maxillary/mandibular arches
occlusal relationship
fabrication of restoration and prostheses
The impression material is usually carried to the mouth by means of …?
a tray (plastic or metal; pre-fabricated or individual)
what are desireable qualities to consider when picking impression materials?
Pleasant odor, taste, and color
Absence of toxic or irritant constituents Adequate shelf life
Economic
Easy to use
Good setting characteristicsSatisfactory consistency and texture
Readily wets oral tissues
Resistance to permanent distortion
Adequate strength
Dimensional stability over temperature and humidity normally found in clinical and laboratory setting
Compatibility with cast and die materials
Accuracy in clinical use
Readily disinfected without loss of accuracy
No release of gas during the setting of the impression or cast and die materials
what are different types of impression materials?
Alginate hydrocolloid (A.K.A. irreversible hydrocolloid)
Agar hydrocolloid (A.K.A. reversible hydrocolloid)
Elastomeric materials
Zinc oxide-eugenol materials
Gypsum
Compound impression materials
what are the most widely used impression material in dentistry?
Alginates
what are some advantages of alginate hydrocolloids?
hydrophilic
accurate if handled properly
inexpensive
easy manipulation
pleasant taste
able to displace blood and body fluids
easily pourable
can use with stock trays
what are some disadvantages of alginate hydrocolloids?
dimensionally unstable (syneresis vs imbibition)
low tear resistance
must be poured immediately
limited detail reproduction
can only be used for a single cast
incompatible w epoxy resin die materials
what 2 main chemical reactions occur when alginate hydrocolloid powder is mixed with water to obtain a paste?
Na3PO4 = retarder (delays reaction so we have more time to work w it)
CaSO4 = active ingredient
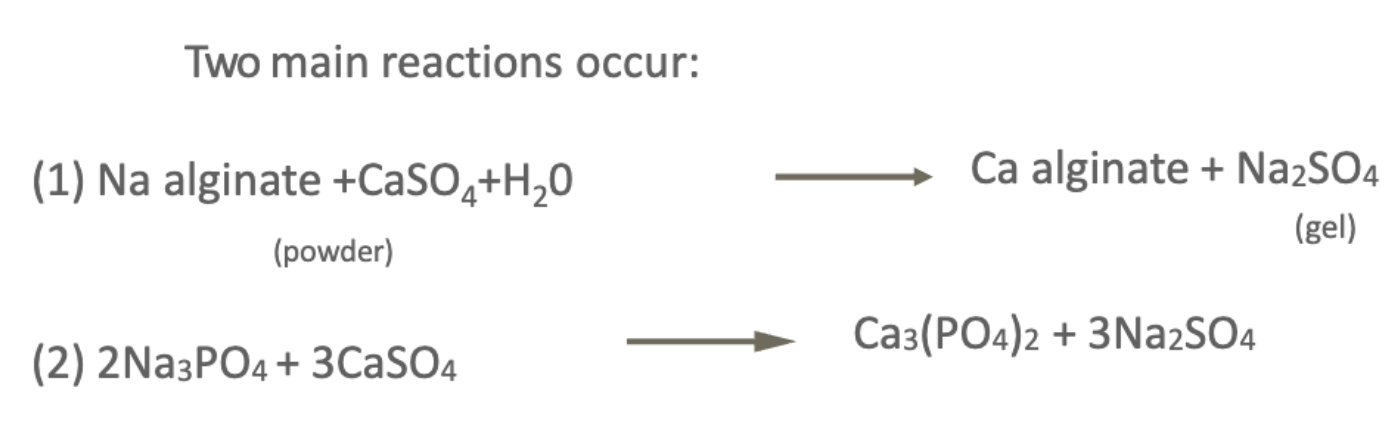
describe the process of mixing alginate and water.
powder lightly shaken for aeration
add water to mixing bowl first
1 scoop of powder used for 1 measure of water
1 minute of thorough mixing for regular setting
45 seconds for fast setting
set time = 3.5 minutes

1 scoop of alginate powder is __ g
16
1 measure of water is __ ml
38 ml
what happens if you use a lower water to powder ratio?
increased strength
increased tear strength
“better” consistency
decreased working time
decreased setting time
decreased flexibility
what happens if you use a higher water to powder ratio?
decreased strength
decreased tear strength
runny consistency
increased working time
increased setting time
increased flexibility
how does cold vs hot water affect alginate?
colder water increases working/setting times
t/f: Insufficient mixing results in a grainy mix and poor recording of details
true
Disinfection can be accomplished by immersion in …?
sodium hypochlorite or iodophors
If needed, impression can be stored in 100% humidity for __ minutes prior to pouring
30
Storage in either air (syneresis) or water (imbibition) results in significant dimensional change. what is syneresis? water is imbibition?
Syneresis: Loss of water due to dehydration that causes shrinkage
Imbibition: Tendency to absorb water that results in swelling
what are some common problems that are related to inadeqaute working or setting time?
temperature of mixing water (ideally 65-75 F)
incomplete spatulation
incorrect water-powder ratio
improper storage of alginate powder
what are some common problems that occur with impressions?
distortion
inadequate working/setting time
tearing
distortion can occur due to…?
movement of the tray during setting of the material
premature removal of impression
improper storage of impression after removal
length of time between impression making and pouring
Delayed cast separation
tearing can occur to impression due to…?
premature removal from the mouth
speed of impression removal
incorrect water-powder ratio
undercuts
not enough material
Consistency is related to what 3 factors?
(1) water-powder ratio,
(2) water temperature,
(3) spatulation
Porosity can be related to incorrect ________
spatulation
Poor stone surface is related to an extended period of contact between the set gypsum and the alginate (separation should occur between ___ minutes after pouring)
45 to 60
describe infection control guidlines for any impression
in operatory:
Rinse impression using cold running water to remove blood and debris
Rub impression using Cavi Wipe
Wrap it with Cavi-Wipe and place in plastic bag
in laboratory:
Place impression on a paper towel
Spray with Cavicide in 4th Fl Lab and leave it for 3 mins
Rinse impression using cold running water
Pour impression with Type III or IV dental stone
should alginate impressions be boxed?
no!
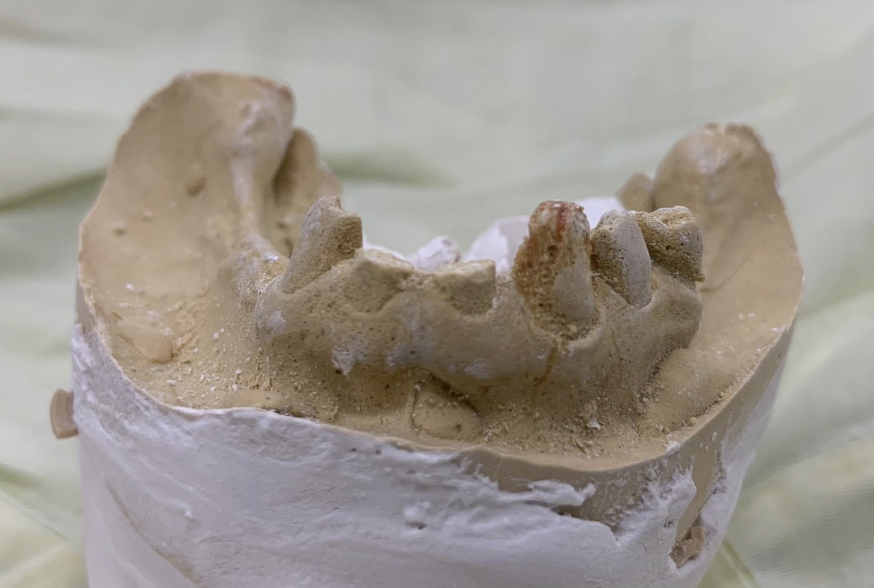
what happend?
left out too long
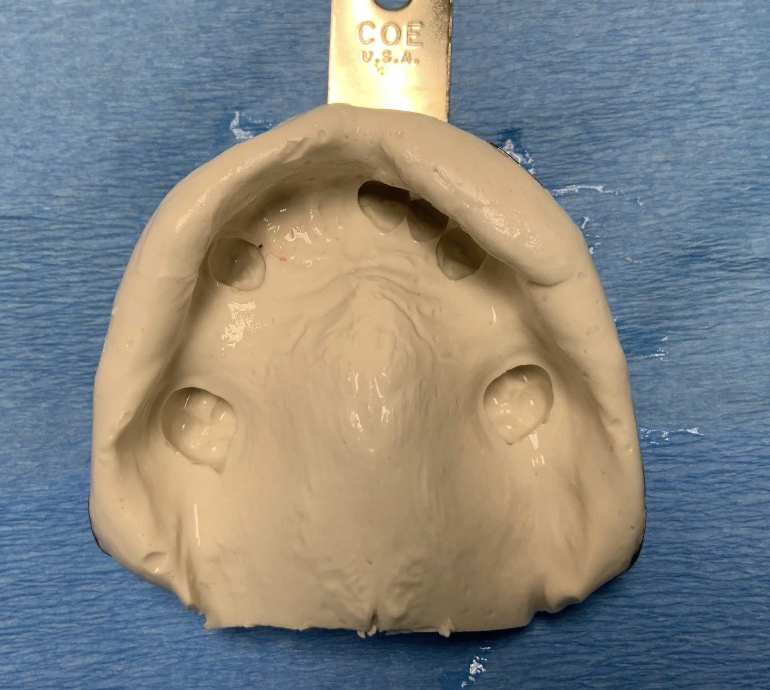
is this a good impression?
yes (9 out of 10)
Gypsum products generally refer to the various forms of …?
calcium sulfate (hydrous and anhydrous)
gypsum products are manufactured by the calcination of …?
calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO 4 . 2H 2 0)
OR
calcining “synthetic” or “chemical” gypsum, a by-product of the manufacture of phosphoric acid
how are gypsum products classified?
by International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
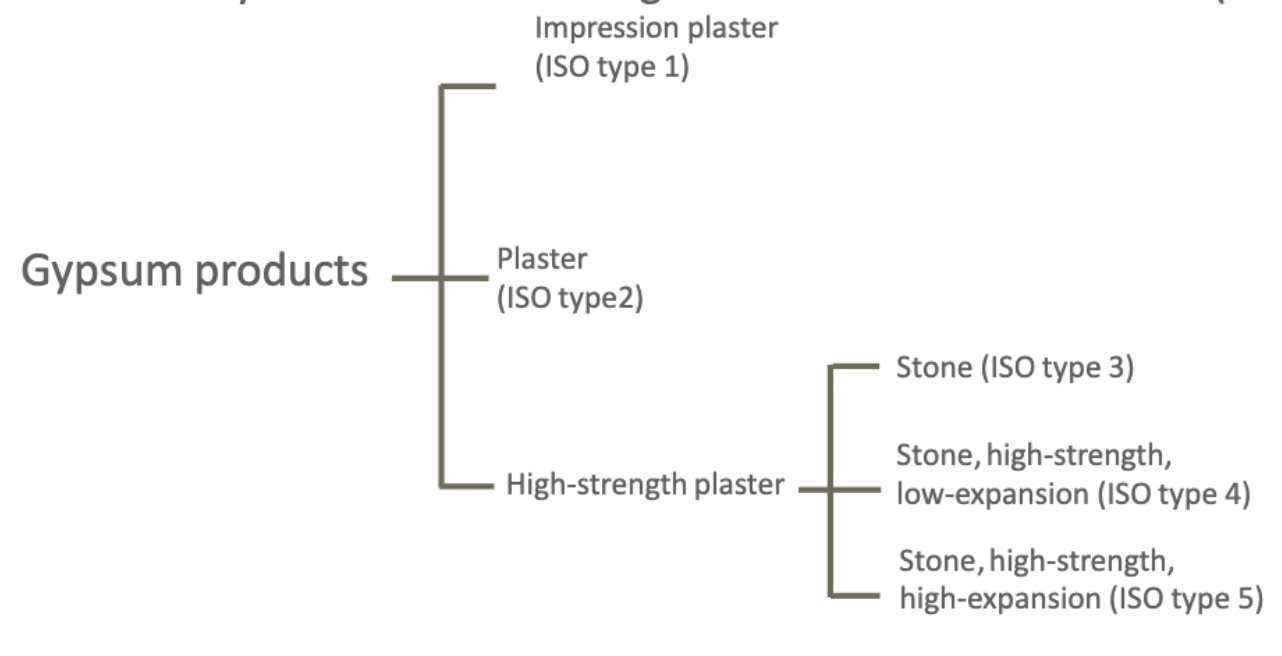
Both plaster and stone are products of…?
partial dehydration of gypsum (Differences in properties result from differences in the physical nature of the powders)
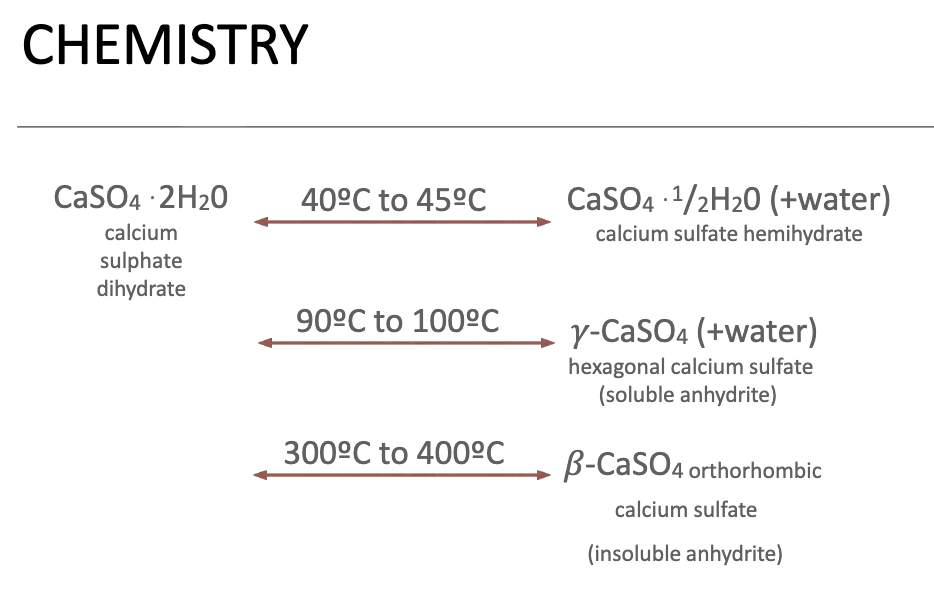
Traditional hemihydrate plaster is produced by what process?
dry calcination (sometimes refer to Beta Hemihydrate)
Medium- and high- strength plasters (stones) manufactured by wet calcination have a stronger/weaker set mass (sometimes refer to Alpha Hemihydrate)
stronger
slide 61