#2: Water & the pH Scale
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
____________ ______ link atoms in molecules together
covalent bonds
_________________ ____________ play a key role in living organisms because they can be continuously broken and reformed in the many dynamic processes that a cell undergoes
non-covalent interactions
What are 6 examples of processes where non-covalent interactions are important?
dissolution of salt in water, 3D structure of proteins, base-pairing and base-stacking in the DNA double helix, aggregation of lipids into membrane bilayers, affinity of sugar molecules for taste receptors, binding of a medicine to its target protein
Rank the 5 main non-covalent interactions from STRONGEST to WEAKEST
charge-charge (ionic), hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole, dipole-induced dipole, dispersion
Name the non-covalent interaction:
Both molecules have a net-neutral charge, but the more electronegative atom pulls the electrons towards it, causing it to have a partial negative charge and the less electronegative atom to have a partial positive charge
dipole-dipole
Name the non-covalent interaction:
one net-neutral molecule has a dipole which causes a dipole on a molecule that normally doesn’t have a dipole
dipole-induced dipole
Name the non-covalent interaction:
A molecule without a dipole will sporadically have a small, randomly oriented flickering dipole which can then induce a dipole in another
dispersion
Which of the 5 non-covalent interactions are considered van der Waals forces? (interactions between uncharged molecules)
dipole-dipole, dipole-induced dipole, dispersion
Stronger non-covalent interactions lead to a _________ melting point because more energy is needed to overcome these forces and melt the substance
higher
Neutral molecules where the center of gravity of the negative charges does not coincide with the center of gravity of the positive charges are said to have a ________
dipole
The water molecule is ___________ and carries a ___________ _________ _________
non-linear, permanent dipole moment
Two atoms from different molecules rarely come closer together than the sum of their ____________________ _______ — with the very important exception of the ___________ ______
van der Waals radii, hydrogen bond
What is the most important non-bonded interaction in biochemistry?
hydrogen bond
What is the approximate distance of the hydrogen bond between the oxygen of one water molecule and the hydrogen of another?
1.77 angstroms
What is the approximate length of the van der Waals radius of the hydrogen in a water molecule?
1.2 angstroms
What is the approximate length of the van der Waals radius of the oxygen in a water molecule?
1.4 angstroms
As ice, water molecules interacts ______________ with ___ other water molecules
tetrahedrally, 4
Water has a very ______ boiling point compared to similar sized molecules due to the high number of hydrogen bonds it can make
high
It’s open lattice structure makes ice _____ dense than water, which is unusual
less
The arrangement of water molecules in bulk liquid water is very ________
dynamic
In liquid form, what is the rough average # of hydrogen bonds that each molecule can make?
3.2
In which state can water form MORE hydrogen bonds: liquid or ice?
ice
Biomolecules are surrounded by bulk water. All surface-exposed hydrogen-bond _______ and _______ are engaged in hydrogen bonds with surrounding _______ molecules.
donors, acceptors, water
hydroxyl groups can be both a hydrogen _________ and ________ simultaneously
donor, acceptor
weakly acidic molecules that are able to give away a hydrogen
donor
weakly basic molecules that are able to receive a hydrogen
acceptor
Is OH and NH a hydrogen bond ACCEPTOR or DONOR?
donor
Is O and N a hydrogen bond ACCEPTOR or DONOR?
acceptor
Ions in solution are __________ by water molecules
hydrated (or solvated)
The __________ ________ of water molecules interact very favorable with charged ions in solution, forming a ____________ _______
permanent dipole, hydration shell
In hydrophobic interactions, nonpolar molecules arrange themselves in such a way as to minimize its __________ _______ with the polar molecules
surface area
______________ _________ cause nonpolar groups to come together in aqueous solutions
hydrophobic interactions
What are 4 examples of processes where hydrophobic interactions are important?
folding of protein molecules, binding of small hydrophobic molecules to hydrophobic clefts on the protein surface, stacking of bases in the DNA double helix and RNA tertiary structures, formation of the lipid bilayer surrounding cells
Say you have a reaction where you go from a nonpolar molecule dissolved in H2O to having the nonpolar molecule and water separated.
What is the ΔH?
0
Say you have a reaction where you go from a nonpolar molecule dissolved in H2O to having the nonpolar molecule and water separated.
What is the sign of ΔG? Will this be a spontaneous or nonspontaneous reaction?
negative, spontaneous
Say you have a reaction where you go from a nonpolar molecule dissolved in H2O to having the nonpolar molecule and water separated.
What drives this process? Why?
entropy, entropy is smaller (thus, less favorable) for a hydrocarbon in water than when surrounded by hydrocarbons
Is there an enthalpy change when going from a nonpolar molecule dissolved in H2O to having the nonpolar molecule and water separated?
no
molecules with both polar and nonpolar segments
amphiphilic (or amphipathic)
Amphiphilic molecules are at the same time ____________ and ___________
hydrophobic, hydrophilic
If the __________ segments are substantial in an amphiphilic molecule, these segments tend to cluster together
hydrophobic
When you place a lipid molecule in water, the water molecules next to the hydrophobic tail are restricted in ____________ ___________ (although they are still very mobile) because the hydrophobic tail is unable to participate in __________ _________. This also means the entropy of the water molecules is __________.
rotational freedom, hydrogen bonding, reduced
The hydrophobic effect is driven by the __________ of water
entropy
When you have a cluster of amphiphilic molecules (like fatty acids) in water, it is most entropically and energetically favorable to minimize the area where ___________ groups interact with water. To do this, molecules try to almost hide their _________ groups from the water, which increases ___________ and consequently decreases _______ ______.
hydrophobic, hydrophobic, entropy, free energy.
When many lipids are placed in water, they tend to form _______ because all the hydrophobic groups are sequestered from water.
micelles
Which increases the entropy of the system the MOST: micelles or clusters?
micelles
Whether or not a lipid molecule forms a micelle or bilayer depends on the molecule’s ___________
properties
the pH scale quantifies water’s ability to _________
ionize
The neutral water molecule has a very slight tendency to ________
ionize
The ________ ________ within water facilitates its ionization
hydrogen bonding
How many moles are in 1 liter of water?
55.5
What is the specific Keq equation for water? (answer in pic)
pic
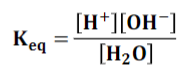
Kw is called the “____ _______ of water’
ion product
In 1 liter of pure water, there are at any time _________ moles of H3O+ and _________ moles of OH-
1×10-7, 1×10-7
What is the equation to go from the Keq of water to the Kw of water?
55.5 x Keq = [H+][OH-] = [10^-7][10^-7] = Kw = 10^-14
What is the value of Kw for 1 liter of pure water?
10-14
What is the pH scale formula? (answer in pic)
pic
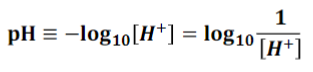
the concentration of the acidic portion of water ([H+]) and the concentration of the basic portion of water ([OH-]) have an ___________ relationship
inverse
Solutions with [H+] = [OH-] = 10-7 are _________ and have a pH ______ _____ 7
neutral, equal to
Solutions with more H+ than OH- are ________ and have a pH _______ ______ 7
acidic, less than
Solutions with more OH- than H+ are _________ and have a pH _______ ______ 7
basic, greater than
weak acids/bases exist in _____________ between a ___________ and ___________ state
equilibrium, protonated, deprotonated
What is the dissociation constant (Ka) formula? (answer in pic)
pic
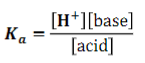
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation? (answer in pic)
pic
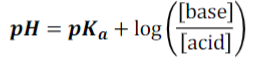
When there is _____ H+ than OH- in a solution, pH < pKa
more
When there is _____ H+ than OH- in a solution, pH > pKa
less
-log[10-7] = ____
7
log(106) = __
6
log(10-5) = __
-5
if log(x) = 5, then x = _____
105
if log (x) = -2.23, then x = _____
10-2.23
When [conjugate base] = [acid], then pH = __________ = ____
pKa + log(1) = pKa
What is the Bronsted acid-base equilibrium? (answer in pic)
pic

log(1) = ____
0
log(16/3) = ____________
log(16) - log(3)
When pH = pKa, then [conjugate base] = _______
[acid]
When [conjugate base] = 10 x [acid], then pH = __________ = _____
pKa + log(10) = pKa + 1
log(10) =
1
When pH = pKa + 1, then [conjugate base] = __________
10 x [acid]
When [acid] = 100 x [conjugate base], then pH = __________ = ____
pKa + log(1/100) = pKa - 2
log(1/100) =
-2
When pH = pKa - 2, then [acid] = __________
100 x [conjugate base]
________ consist of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base. By having this mixture, it serves to maintain a _____ near the ______ of the acid base system. This sort of weak acid and base serves as a source or sink for generating ________.
buffers, pH, pKa, protons
What are 2 major ways protons are used in biology?
induce a large conformational change of a protein, store energy as a proton concentration gradient across a membrane
What is an example of how a small change in pH via protons can induce a large conformational change of a protein, causing a dramatic effect?
influenza virus’ haemagglutinin which enables the flu virus to enter/infect a cell
What is an example of how even a small change in pH via protons can change how energy is stored via proton gradients?
ATP synthase
Which of the following molecules do you expect to have the HIGHEST melting temperature?
A. CH4
B. CF4
C. CO2
D. OCH2
E. They all have similar melting temperatures
D (OCH2)
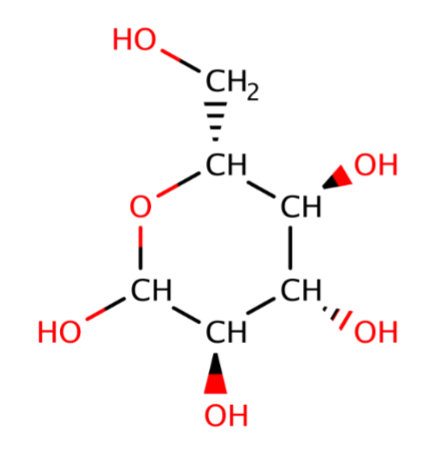
How many hydrogen bonds with water can the displayed molecule (glucose) make simultaneously?
A. 6
B. 12
C. 15
D. 16
E. 17
F. 18
E (17)
Select all of the following processes that are primarily driven by the hydrophobic effect?
A. The spontaneous formation of a bilayer from lipid molecules
B. The folding of proteins into a 3D structure where nonpolar chemical groups are at the center
C. The interactions between strands of DNA
D. The interaction between proteins in protein complexes
A, B, D
Phosphates (PO₄³⁻) can be protonated 3 times, each with a different pKa:
H₃PO₄ ⇌ H⁺ + H₂PO₄⁻ (pKa = 2.1)
H₂PO₄⁻ ⇌ H⁺ HPO₄²⁻ (pKa = 7.2)
HPO₄²⁻ ⇌ H⁺ + PO₄³⁻ (pKa = 12.4)
At pH = 6.2, what is the most common protonation state?
A. H₃PO₄
B. H₂PO₄⁻
C. HPO₄²
D. PO₄³⁻
B (H₂PO₄⁻)
Phosphates (PO₄³⁻) can be protonated 3 times, each with a different pKa:
H₃PO₄ ⇌ H⁺ + H₂PO₄⁻ (pKa = 2.1)
H₂PO₄⁻ ⇌ H⁺ HPO₄²⁻ (pKa = 7.2)
HPO₄²⁻ ⇌ H⁺ + PO₄³⁻ (pKa = 12.4)
At pH = 6.2, what is the ratio [H₂PO₄⁻]/[HPO₄²-]?
A. 10/1
B. 2/1
C. 1/1
D. 1/2
E. 1/10
A (10/1)
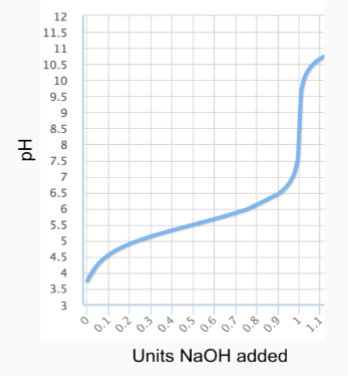
Consider the titration curve shown below of a buffered solution. What is the approximate pKa of the buffer?
A. 3.5
B. 5.5
C. 7.5
D. 9.5
E. 11.5
B (5.5)
Given what you know about nonbonded interactions, which of the following do you expect to have the LOWEST boiling point?
A. methane (CH4)
B. methanol (CH3OH)
C. methylamine (CH3NH2)
D. formaldehyde (CH2O)
A (methane CH4)
Which of the following molecules have BOTH a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor?
A. formaldehyde (CH2O)
B. methanol (CH3OH)
C. acetonitrile (CH3CN)
D. ethane (C2H6)
B (methanol CH3OH)
The pKa of acetic acid (CH3COOH) is 4.76. What is the ratio of [CH3COO-] to [CH3COOH] at a pH of 6.76?
A. 100:1
B. 2:1
C. 1:2
D. 1:100
A (100:1)
Sort the pH of the following mixtures from LOWEST (most acidic) to HIGHEST (most basic):
(1) 0.001 mol of HCl added to 1 L water
(2) 0.001 mol HCl added to a buffer solution of 0.1 M HCOOH and 0.1 M NaHCOO (pKa=3.75)
(3) 0.001 mol HCl added to a buffer solution of 0.1 M NH4Cl and NH3 (pKa=9.25)
1, 2, 3
Which of the following statements is TRUE about a protein with an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.5?
A. it has a net negative charge at pH 4 and net negative charge at pH 9
B. it is neutral at pH 4 and has a net negative charge at pH 9
C. it has a net negative charge at pH 4 and net positive charge at pH 9
D. it has a net positive charge at pH 4 and net negative charge at pH 9
D