Business GCSE topic 2.2 - Making Marketing Decisions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
4PS
Product
Place
Price
Promotion
Product
Good that satisfies a want or need
4 elements of product
Design
Packaging
Branding
Product Life Cycle
Design mix
Combination of aesthetics, function, cost that are the combined design priorities of a product
Branding
Creating an identity for a product that clearly distinguishes it from its competitors
Benefits of branding
Recognition → From logos, slogans, advertisements
Desire → From high quality marketing, good reputation
Brand loyalty → From high quality product, good reputation, good customer service
Higher Prices → From customer loyalty, good quality, good customer service
Why products get packaged
Protection
Inform → Information of the product so people would know what it is and how to use it
Aesthetics → Look appealing to encourage customers to buy it
Product Life Cycle
Theory of every product going through the same stages
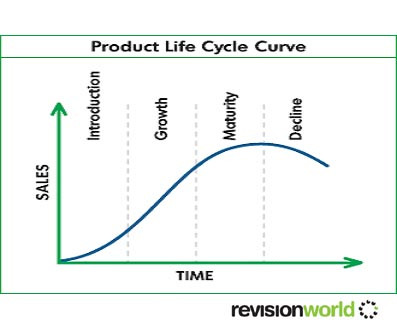
4 stages of the product life cycle
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
Introduction stage
Low sales
High cost for customer
Financial losses
Few competitors (No competitors)
Growth stage
Increasing sales
Cost for customer falls
Profits rise
Increasing number of customers
More competitors
Maturity stage
Peak sales
Cost for customer lowest
Profits high
Product in mass market
Stable number of competitors
Decline stage
Sales falls
Cost for customer low
Profits fall
Customer base falls
Number of competitors fall
Extending the product life cycle
An attempt to extend the sales of a product to avoid the decline phase
Ways of extending the product life cycle
Introduce new variations of the product
Sell into new markets
Make small changes to product’s design, colour, packaging
New advertising campaign
Introduce a new and improved version of the product
These would all lead to an increase customer base → wider market share → Ahead of competitors → Increased sales revenue → Higher profitability
Price
How much a consumer pays for a product
Pricing strategies
Skimming
Penetration
Competitive
Cost-Plus
Promotional
Skimming
Launching with a high price but reduce later. This is used to recoup research costs
Penetration
Starts at low price to build brand loyalty and then increases
Competitive
Charging similar prices as competitors
Cost-Plus
Adding a mark up to the cost to make a profit
Promotional
Temporarily reducing price to increase interest
Factors influencing pricing strategies
Technology → Consumers can compare prices between two stores easily so it is important that business is competitively priced
Competition → The fewer competitors a business has, the more they are able to set their own fare
Market segments → Need to consider the income of their customers
Cost of production
Level of demand
Place
How the business products gets to the consumer and which other businesses it needs to pass through