Haloalkanes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Do haloalkanes have a polar bond?
Yes, all C-X bonds are polar as halogens have a higher electronegativity than carbon
What is the order of polarity of C-X bonds and what determines this?
C-F most polar
C-Cl
C-Br
C-I least polar
F has the highest electronegativity difference to C, which means the C-X has stronger partial charges and the biggest dipole. This decreases down the group.
Are haloalkanes soluble in water? Why?
No, they are insoluble in water as the R group is non-polar
What intermolecular forces do haloalkanes have?
Van der waals forces and permanent dipole-dipole
What can haloalkanes be dissolved in?
Hydrocarbons - as these are non polar
How does chain length affect boiling point of haloalkanes?
Longer chain = higher boiling point
This is because VdW forces and no. of electrons increase with chain length
How does branching affect boiling point in haloalkanes?
Branching reduces boiling point
This is because it decreases the surface area - so VdW forces are weaker
How does boiling point change down the group?
It increases down the group as the halogen is larger so has more electrons and stronger VdW forces
What is the most important factor in determining their reactivity?
C-X bond enthalpy
What's the order of reactivity of haloalkanes?
Reactivity increases down the group
What happens when haloalkanes react with acidified AgNO3?
Hydrolysis reaction
C-X bond breaks
X- ion released into solution
AgX(s) precipitate formed
What colour precipitates would chlorobutane, bromobutane and iodobutane form when reacted with acidified AgNO3?
Chlorobutane: white ppt
Bromobutane: cream ppt
Iodobutane: yellow ppt
What is a nucleophile?
An electron-rich species with a lone pair of electrons on an electronegative atom which can be donated to form a new covalent bond with an electron-deficient species
Give 3 examples of nucleophiles
:OH-
:CN-
:NH3
What is nucleophilic substitution?
A reaction where a nucleophile donates a lone pair of electrons to an electron-deficient carbon atom and an electron-rich atom leaves the molecule as it is replaced by a nucleophile
What are the reagents and conditions needed for the nucleophilic substitution with :OH-?
Reagent: NaOH/KOH
Conditions: aqueous and ethanol, warm
What are the reagents and conditions needed for the nucleophilic substitution with :CN-?
Reagent: aqueous ethanolic KCN
Conditions: aqueous and ethanol, warm
What are the reagents and conditions needed for the nucleophilic substitution with :NH3?
Reagent: excess conc NH3 solution
Conditions: ethanol and high pressure, excess sol
What is elimination?
A reaction where a large molecule loses atoms or groups of atoms
What nucleophile is used in elimination?
:OH- which acts as a base
What are the reagents and conditions needed for the elimination reaction of haloalkanes?
Reagent: KOH (ethanol)
Condition: heated
What is formed in the elimination reaction of haloalkanes?
An alkene, water and a halogen ion
What's the mechanism for elimination reaction of haloalkanes?
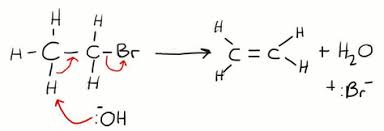
How do you decide whether a haloalkane undergoes nucleophilic substitution or elimination?
It depends on the reaction conditions:
Aqueous NaOH/KOH, warm → nucleophilic substitution
Ethanolic NaOH/KOH, hot → elimination
What are CFCs?
Haloalkanes containing C, F and Cl only (no H)
What is the problem with CFCs?
They catalyse the breakdown of ozone in the atmosphere via free radial substitution
What are CFCs being replaced with?
HCFCs and HFCs