programming methodologies
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
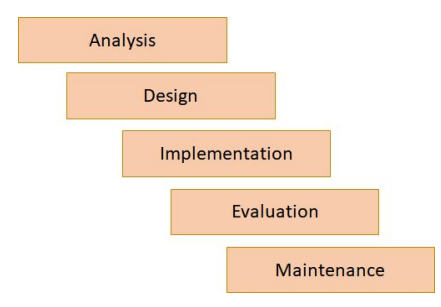
analysis
stakeholders stake their requirements which are used to define the problem and system requirements
design
the different aspects of the new system are designed (e.g. inputs, outputs, security features)
development
the project is split into individual and self-contained modules and allocated to teams
testing
the program is tested against the test plan formed in the design stage
alpha testing
carried out by in-house software development teams within the company. bugs are pinpointed and fixed.
beta testing
carried out by end-users after alpha testing has been completed. feedback from users is used to inform the next stage of development
white box testing
carried out by the software development team, who know the internal structure of the program, and so all possible routes throughout the program are tested
black box testing
the testers aren’t aware of the internal structure of the program
implementation
once the software has been tested and reviewed, it is installed onto the users’ systems
evaluation
the effectiveness of the system is evaluated against the system requirements. different criteria are considered (e.g. robustness, reliability, portability, and maintainability)
maintenance
any errors or improvements that could be made to the system are flagged by end users. programmers regularly send out software updates to fix bugs, security issues, or make improvements.
waterfall lifecycle
if a change needs to be made within a project, developers must revisit all levels between the current stage and where the change needs to be made
users have little input as they are only involved at the very beginning and end (during analysis and evaluation)
agile methodologies
a collection of methodologies
aim to improve the flexibility of software development + adapt to user requirement changes faster
problem is broken down into sections which are developed in parallel
different sections of software can be at different levels of development
a working prototype will be given early during development, and the prototype is built on in an iterative manner
less of a focus on documentation
priority given to user satisfaction
extreme programming
agile model
team of a pair of programmers, and a representative end user
model built on system requirements that are specified by the end user
paired programmers produce high-quality code and work no longer than 40 hour weeks
hard to produce high quality documentation
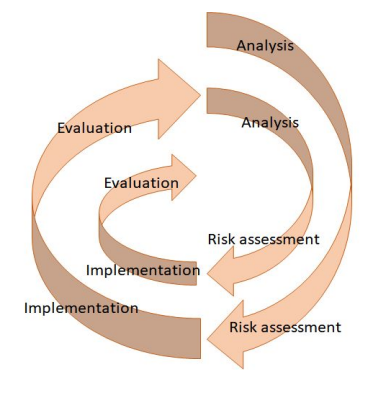
spiral model
analysing system requirements > pinpointing and mitigating risks > development, testing + implementation > evaluating to inform the next iteration
if the project is found to be too risky at any point is it terminated
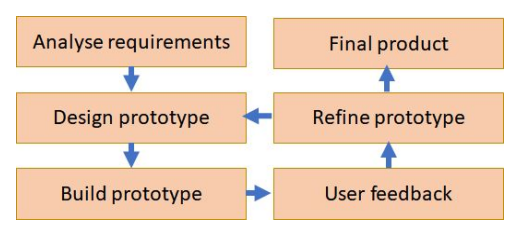
rapid application development
iterative methodology
partially functioning prototypes which are constantly built-upon
user requirements are gathered by using focus groups
incomplete version of the solution is built and given to the user to trial
user feedback is used to generate the next, improved prototype
this continues until a final products made
common to use where requirements are initially unclear
constant changed can make code inefficient
strengths of waterfall
straightforward to manage
clearly documented
drawbacks of waterfall
lack flexibility
no risk analysis
limited user involvement
waterfall uses
static, low-risk projects which need little user input
strengths of agile
produces high quality code
flexible to changing requirements
regular user input
drawbacks of agile
poor documentation
requires consistent interaction between user and programmer
uses of agile
small to medium projects with unclear initial requirements
strengths of extreme programming
produces high quality code
constant user involvement means high usability
drawbacks of extreme
high cost of two people working on one project
teamwork is essential
end-user mat not be able to be present
uses of extreme
small to medium projects with unclear initial requirements requiring excellent usability
strengths of spiral
thorough risk analysis and mitigation
caters to changing user needs
produces prototypes throughout
drawbacks of spiral
expensive to hire risk assessors
lack of focus on code efficiency
high costs due to constant prototyping
uses of spiral
large, risk-intensive projects with a high budget
strengths of RAD
caters to changing user requirements
highly usable finished product
focus on core features, reducing development time
drawbacks of RAD
poorer quality documentation
fact pace may reduce code quality
uses of RAD
small to medium, low budget projects with short time frames