Physics cohort
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Energy store(CEMENT KG)
Chemical
Elastic
Magnetic
Electrostatic
Nuclear
Thermal
Kinetic
Gravitational potential
Energy transfer(HOSE ME)
Heating
Other
Sound
Electrical current
Mechanical work done
Electromagnetic
Kinetic energy
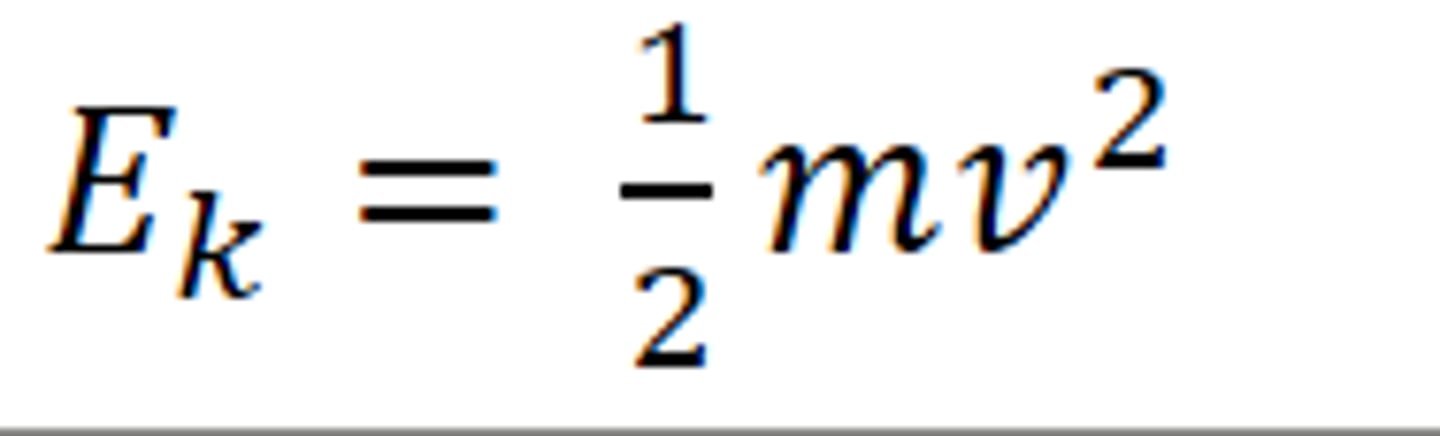
Gravitational Potential energy
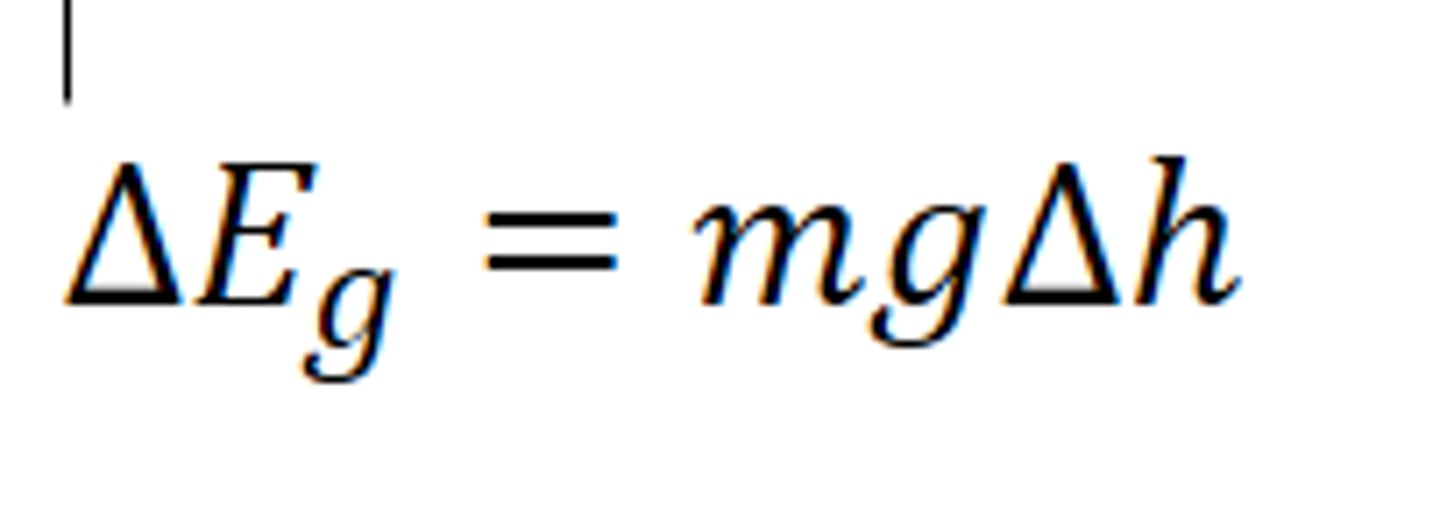
Mechanical working/Work done
W=Fd
Efficiency
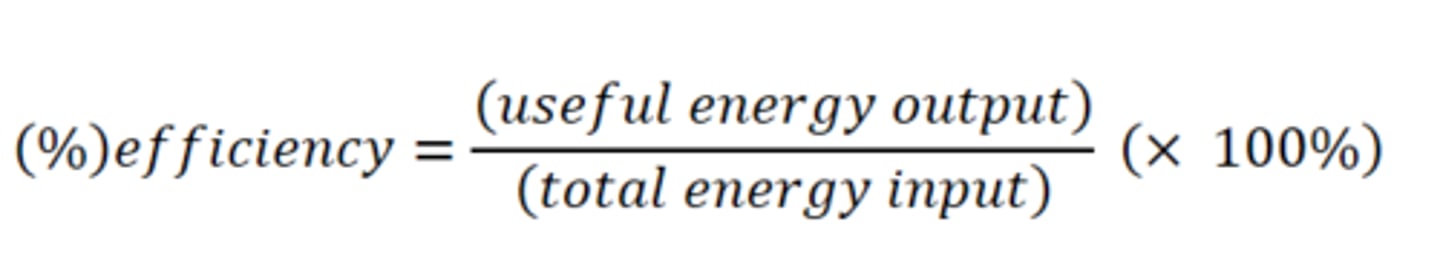
Speed
s=d/t
Newton's 1st law
When the resultant force is zero, there is no acceleration; objects continue at a constant speed and in a constant direction or stay stationary.
Newton's 2nd law
When there is a resultant force, objects will change their motion. We call this an acceleration. It includes: a. speeding up b. slowing down c. changing direction
How to measure volume(By displacement)
Fill a measuring cylinder with water to a known volume. Submerge the object. The new water level minus the initial water level equals the object's volume.
How to show electrostatic charges by friction
Rub a polythene rod with a duster then put it near confetti and the confetti should attract to the rod.
How does friction create charge
Friction creates charge by transferring electrons between the surfaces of two different materials that are rubbed together.(duster loses electrons, rod gains electrons.)
What is electrical conduction in metals(in terms of free moving electrons)
As the electrons are free, They aren't bound to specific atoms and can move easily. When an electrical voltage is applied, these free electrons flow, creating an electric current.
Flow of electrons
In diagrams Positive to negative.
In real life Negative positive
Electrical charge
Q=It
Energy
E=QV or E=ItV
Voltage
V=IR
Power
P=IV
Work done
W=Fd
Weight
W=mg
Spring extension
F=kx
Wave speed
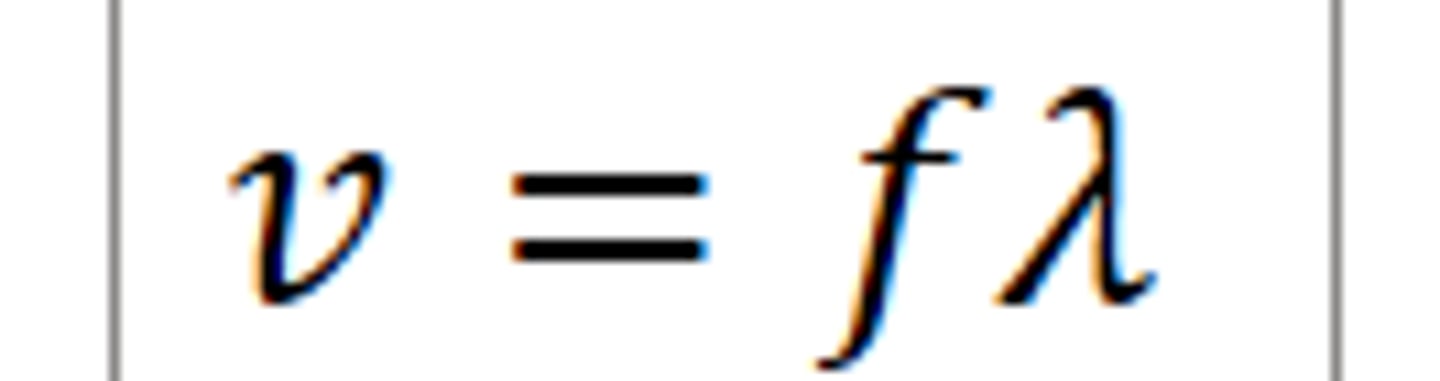
Human hearing
20Hz to 20000Hz
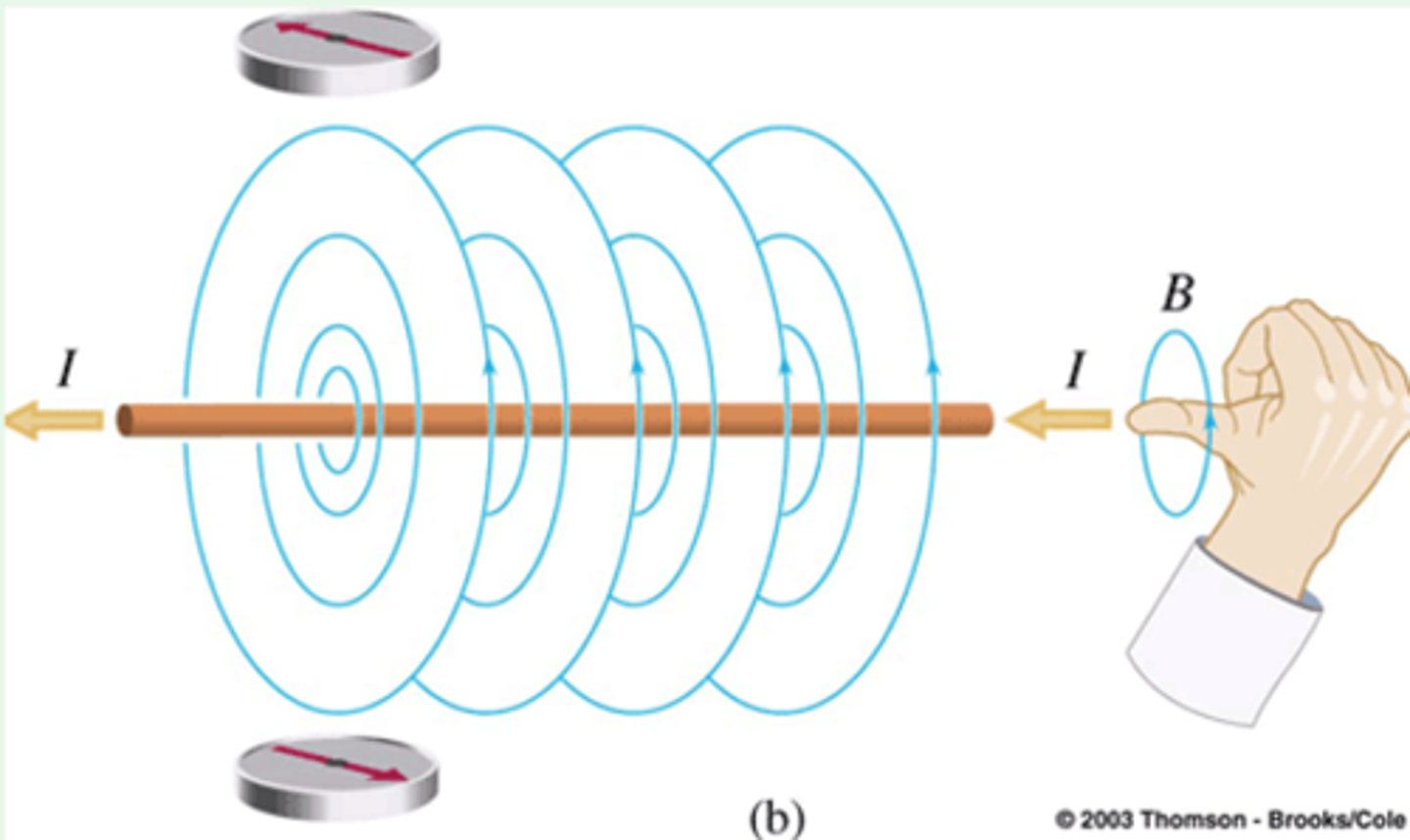
Magnetic field wire
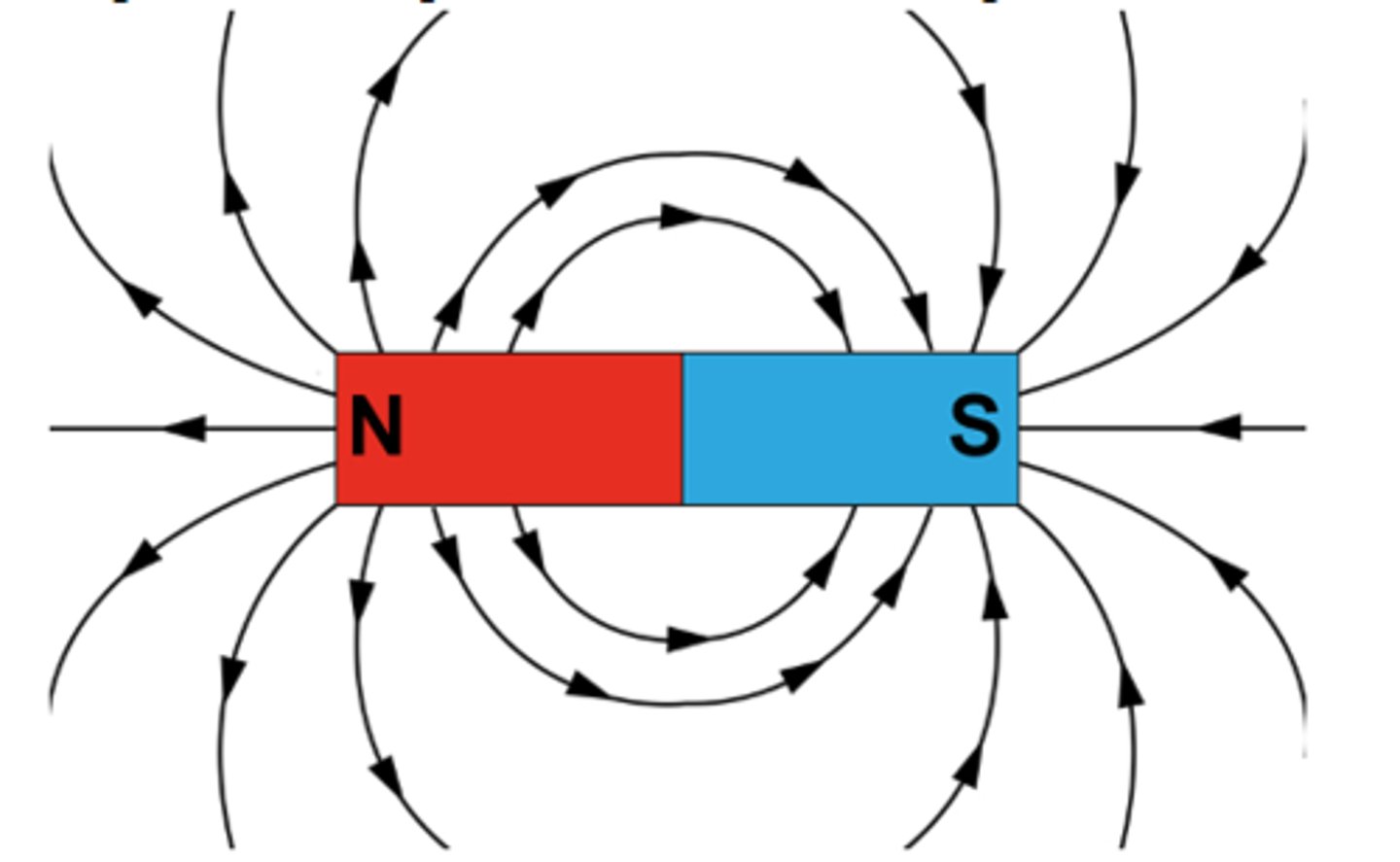
Magnetic field Bar
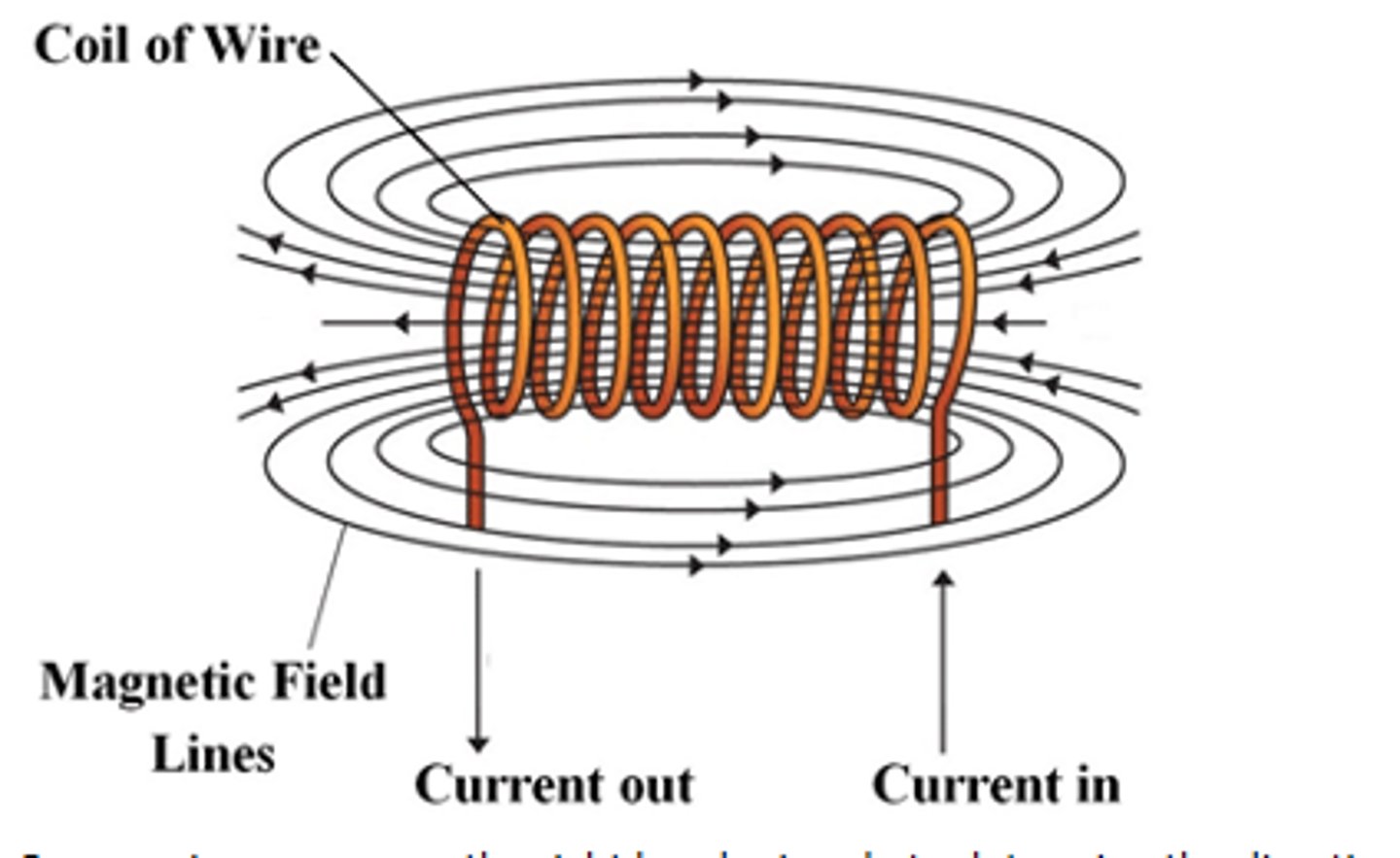
Magnetic field coil