PSYCH 1: L9 Memory
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Hermann Ebbinghaus
examined memory scientifically --> how we acquire and forget info
--> memory capacity and malleability of our minds
Structure of Hermann Ebbinghaus studies
used himself (1 subject) as control for indv differences
used nonsense syllables as control for stimulus differences
varied list sizes
Results of Hermann Ebbinghaus studies
memory capacity = 7 +/- 2 items
learning and forgetting curves
--> (recall dec as retention interval inc)
--> (repetitions req for learning inc as # of syllables per list inc)
What of Hermann Ebbinghaus studies DIDN'T explore
ability to display memory of info when asked to reproduce it in approach
diff types of memory that exist
if memory capacity changes for meaningful info
if/how we alter memory of info
Memory tests
Free recall test (Ebbinghaus's test
cued recall test (states ex)
recognition tests (dwarfs ex)
savings tests (elemental tables example)
implicit memory tests
--> stimulus/ response pairs
What are the 3 steps of displaying memory?
encoding, storage, retrieval
encoding
the process of converting information into a form that allow us to retrieve that info later
Storage
the process of retaining critical info for later use
Retrieval
the process of accessing the stored information that we have encoded in order to use it in a situation
Temporal memory stages
External events → sensory memory → short-term memory → long-term memory
Sensory memory
Considered a hypothetical stage of memory for years
Involves all our senses
Most of info is said to only last in our memory for a fraction of a second
Infinity capacity (or at least large)
After fraction of a second, you attend to/remember only the info deemed relevant
Sperling's sensory memory experiment
stimulus array flashed on screen for 0.05 seconds
tone within 0.3s tells what row to speak
participants recall correct row
Conclusions: Showed that we are unable to retain much information within a short amount of time
Short term memory
Has a capacity of 7 +- 2 items (Nonsense syllables confirmation)
Contains info that we deemed relevant (Both past and new info)
-Info can be stored in this stage of memory from anywhere between 10 s to a few daysAfter, memories are stored either:
--> Forgotten info
--> long-term memory store
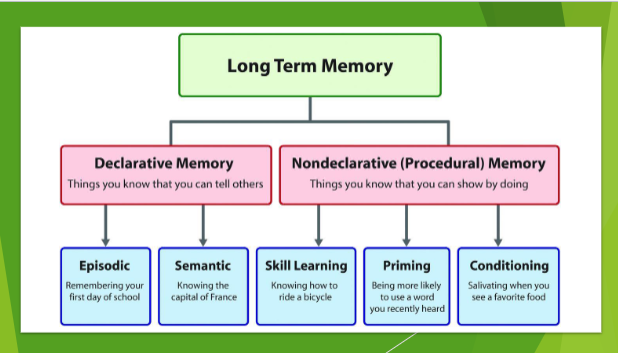
long term memory
Consists of info from STM that we identified as important - and had the ability and time to store
Info in this part of our memory can be very complex
very susceptible to distortions and complete fabrications