Disorders of Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Blood Vessel Structure
Anatomy and function of blood vessels.
Systemic Arterial BP Regulation
Mechanisms controlling blood pressure in arteries.
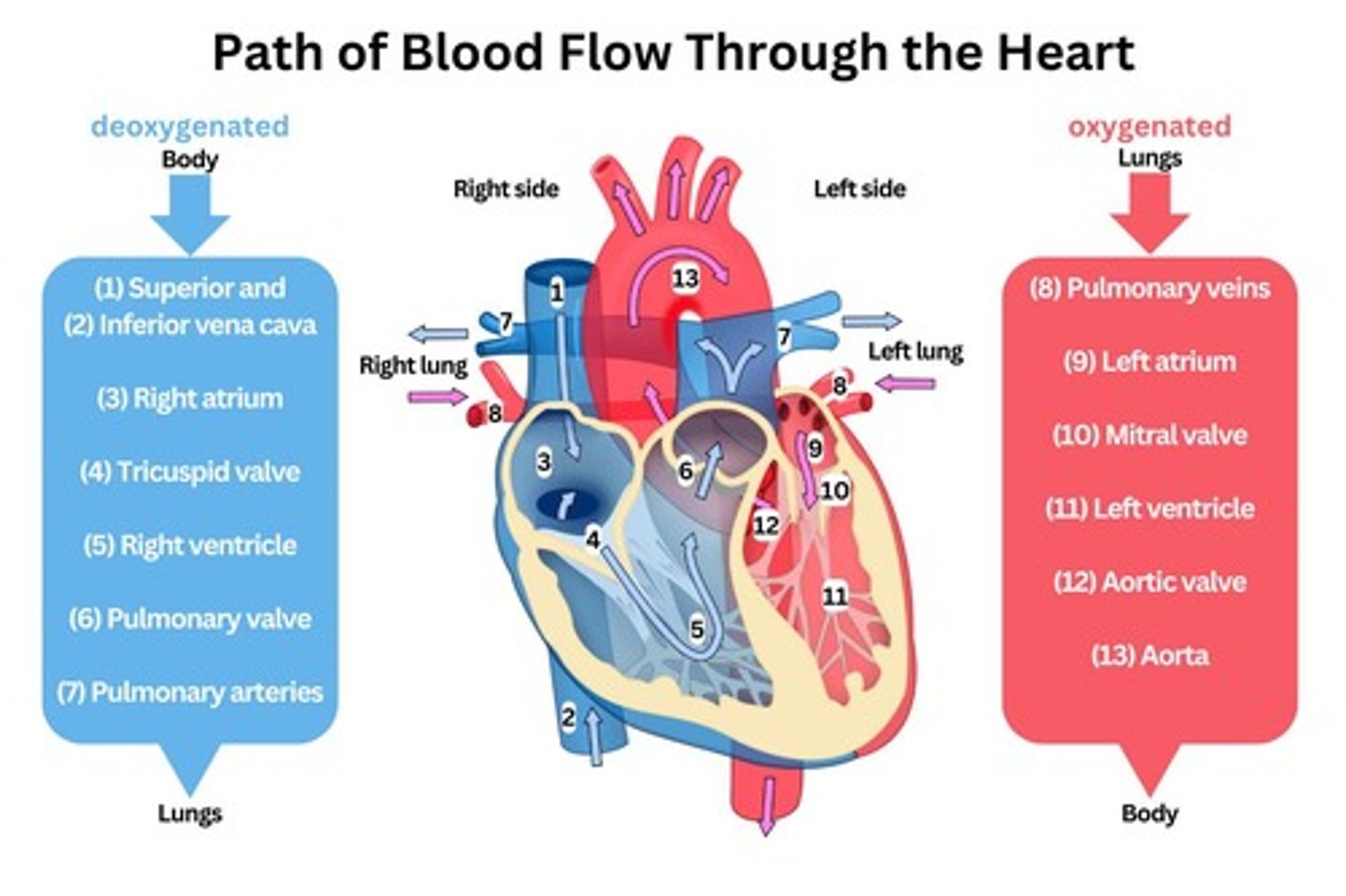
Deoxygenated Blood
Blood lacking oxygen, collected by vena cavae.
Right Atrium
Chamber receiving deoxygenated blood from body.
Tricuspid Valve
Valve between right atrium and right ventricle.
Right Ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Pulmonary Artery
Carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Oxygenated Blood
Blood enriched with oxygen from the lungs.
Left Atrium
Chamber receiving oxygenated blood from lungs.
Mitral Valve
Valve between left atrium and left ventricle.
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
Aorta
Main artery delivering blood to the body.
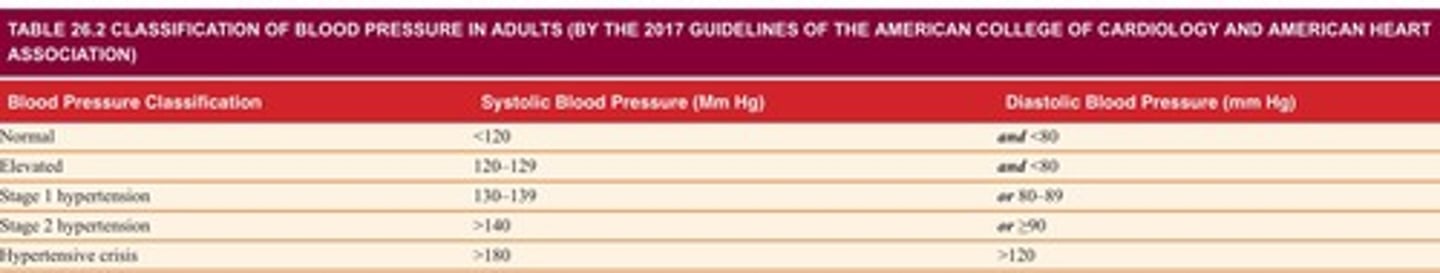
Systolic BP
Pressure during ventricular contraction.
Diastolic BP
Pressure during ventricular relaxation and filling.
Pulse Pressure
Difference between systolic and diastolic BP.
Normal Pulse Pressure
Approximately 40 mmHg in healthy adults.
Widened Pulse Pressure
Indicates risk for coronary artery disease.
Stroke Volume
Blood ejected from left ventricle per beat.
Mean Arterial BP (MAP)
Average arterial pressure during cardiac cycle.
MAP Normal Range
90-100 mmHg for healthy individuals.
MAP Calculation
MAP = (Cardiac output) x (Peripheral vascular resistance).
Cardiac Output
Total blood pumped by heart per minute.
Peripheral Vascular Resistance (PVR)
Resistance blood encounters in circulatory system.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Regulates vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
Blood Pressure (BP)
Product of cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance.
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
Peripheral Vascular Resistance (PVR)
Resistance in blood vessels affecting blood flow.
Systolic BP
Pressure in arteries during heartbeats.
Arterial Stiffness
Loss of elasticity in arteries, replaced by collagen.
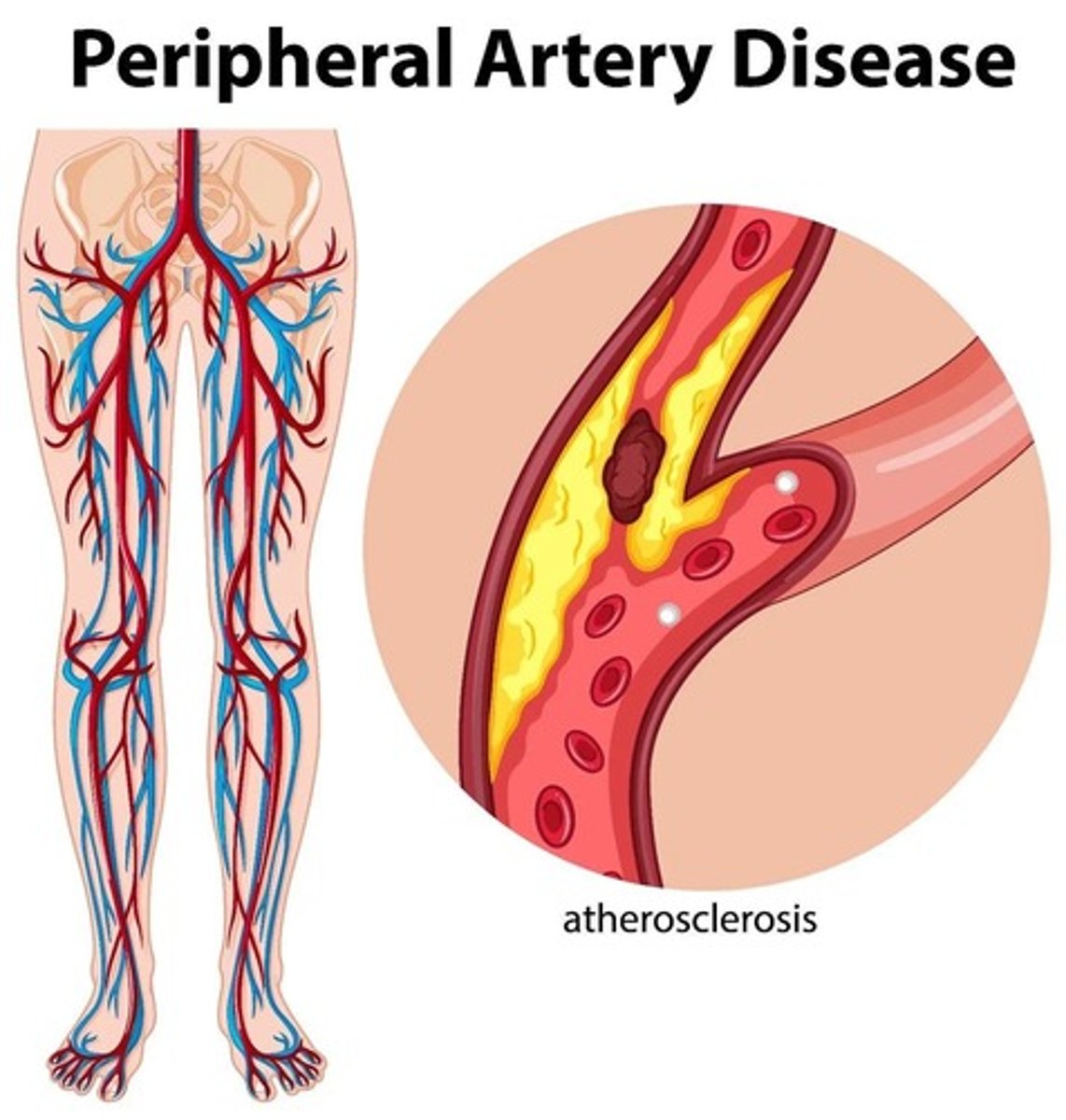
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Chronic disorder causing restricted blood flow in extremities.
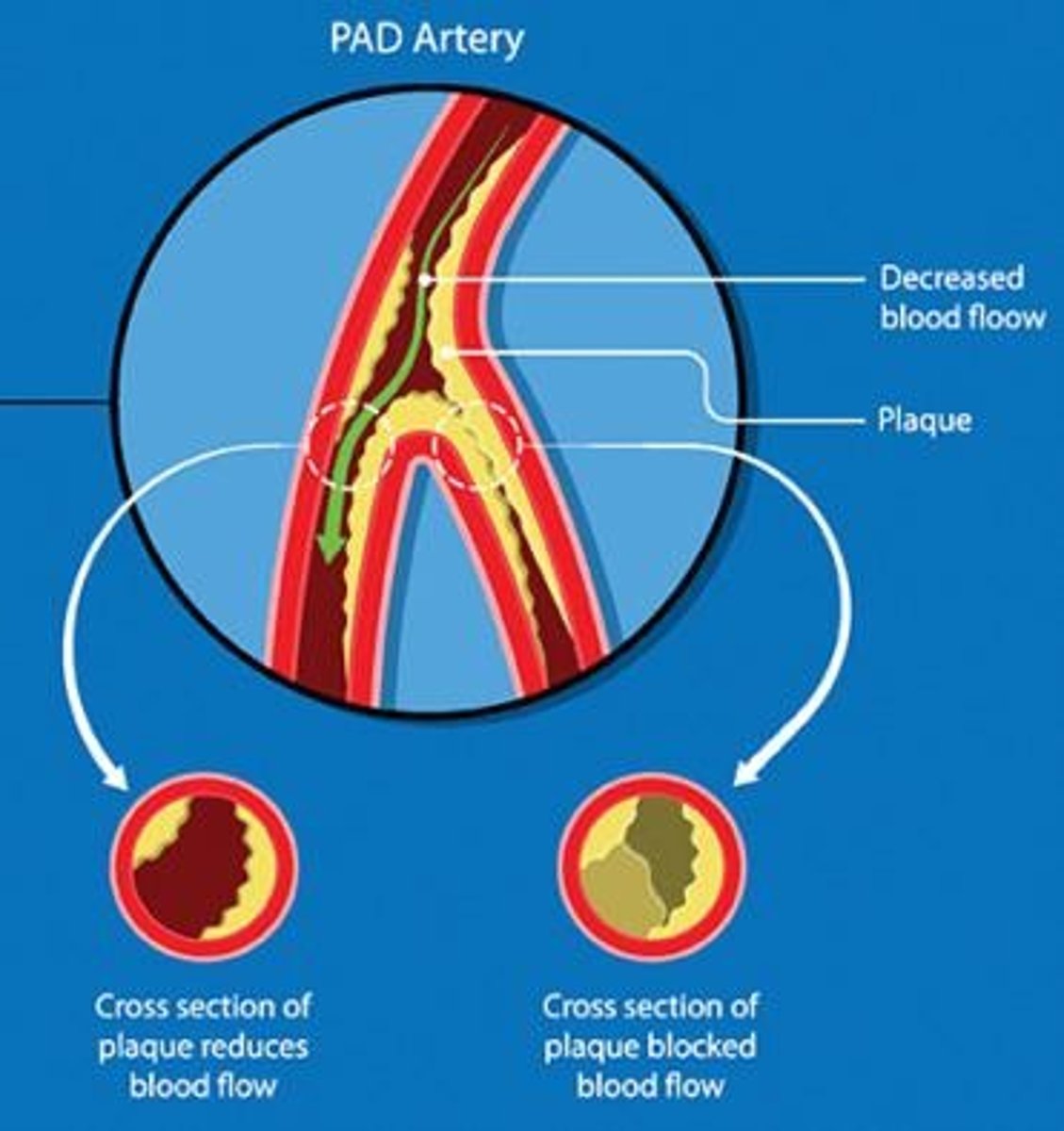
Atherosclerotic Plaque
Buildup of fats and cholesterol in arteries.
Intermittent Claudication
Pain in legs during exercise due to insufficient blood flow.
Ischemia
Insufficient blood supply to tissues, causing damage.
Atrophic Changes
Thinning of skin and subcutaneous tissues due to ischemia.
Dependent Rubor
Deep red color in limbs when lowered, indicating blood flow.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
Compares BP in ankle and arm to assess circulation.
Doppler Ultrasound
Non-invasive method to assess blood flow in vessels.
Anti-platelet Agents
Medications like aspirin that reduce blood clotting risk.
Statins
Medications that lower cholesterol levels in the blood.
Walking Therapy
Exercise to promote collateral circulation in PAD patients.
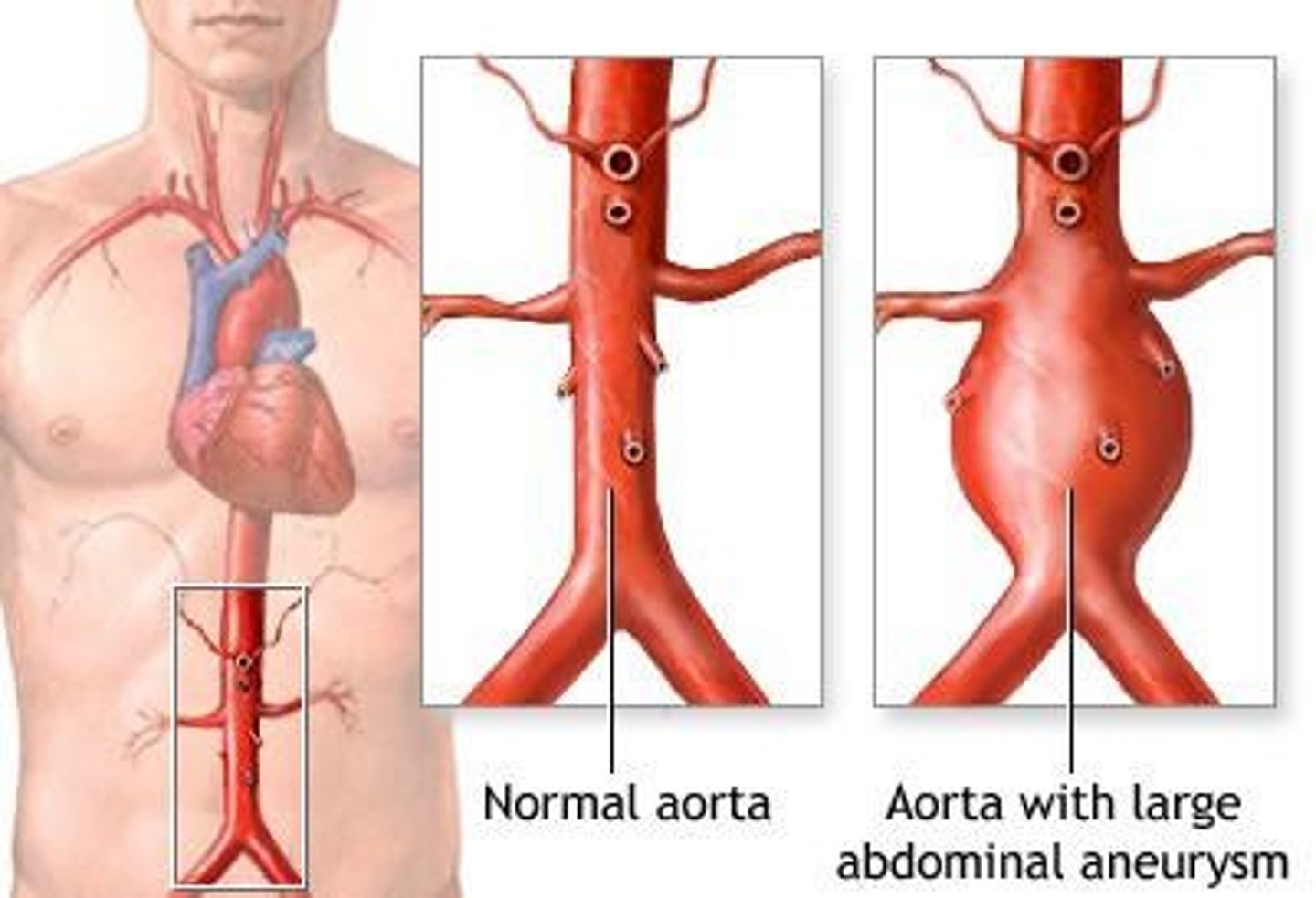
Aortic Aneurysm
Weakening of aorta's layers, potentially leading to rupture.
Pulsating Mass
Possible sign of an aortic aneurysm in patients.
Risk Factors for Aneurysms
Hypertension, elevated lipids, atherosclerosis, smoking history.
Rupture Prevention
Critical to avoid as aorta supplies blood to the body.
Clinical Manifestations of PAD
Symptoms include pale skin, weak pulses, and non-healing sores.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Rare condition presenting with abdominal/back pain and bulge.
Triple A
Abbreviation for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.
Internal Hemorrhage
Severe bleeding inside the body, life-threatening.
CT Scan
Imaging technique for diagnosing aortic conditions.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging for detailed internal views.
Pulsating Aneurysm
Aneurysm with rhythmic expansion, risk of rupture.
Surgical Repair
Emergency procedure for ruptured aneurysms.
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm
Aneurysm located in the thoracic region of the aorta.
Substernal Pain
Pain below the sternum, indicative of thoracic issues.
Tracheal Compression
Pressure on trachea causing breathing difficulties.
Laryngeal Nerve Pressure
Causes hoarseness due to nerve compression.
Esophageal Compression
Difficulty swallowing due to pressure on the esophagus.
Superior Vena Cava Compression
Leads to neck vein distention and facial edema.
Blood Stasis
Reduced blood flow, increases risk of thrombus formation.
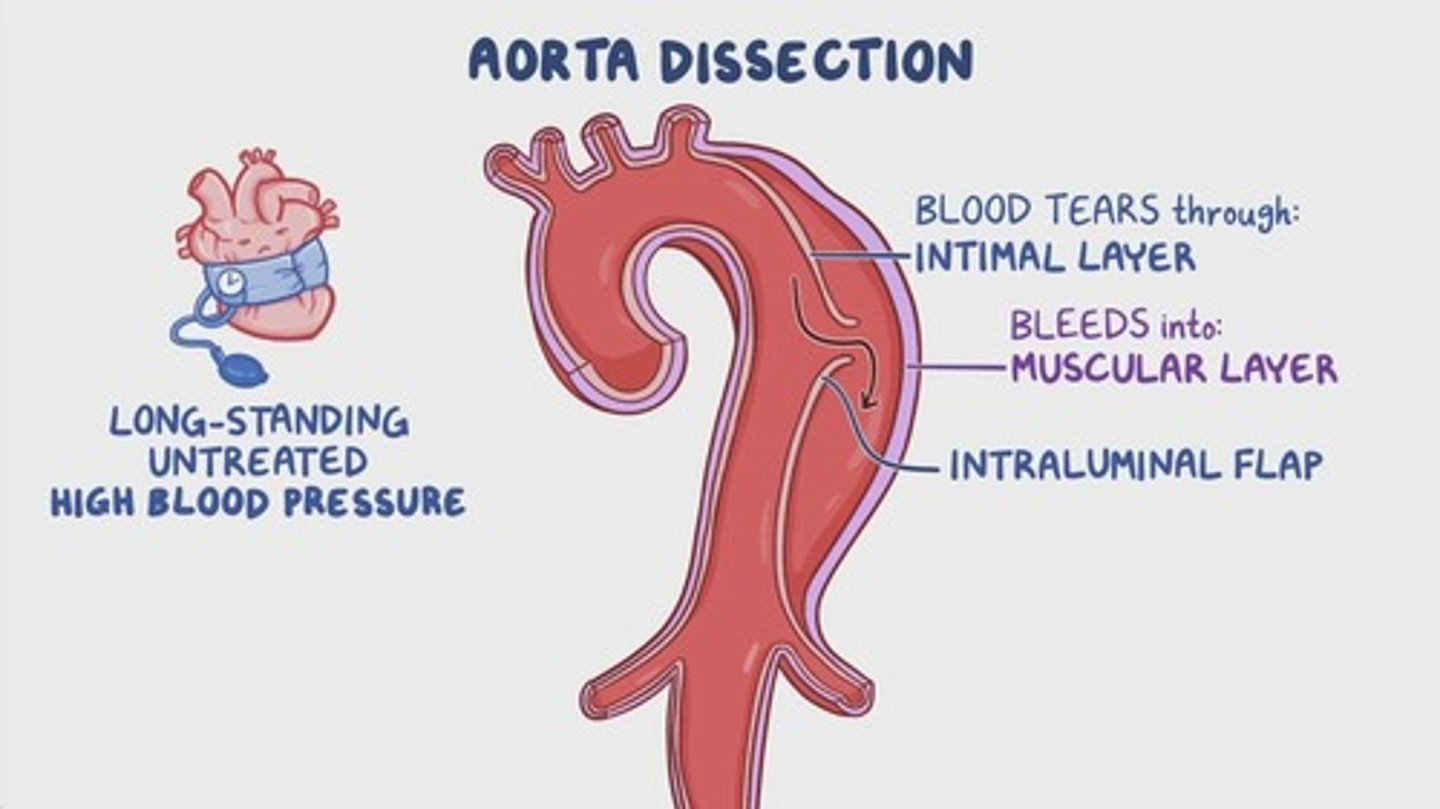
Aortic Dissection
Life-threatening tear in the aorta's vessel wall.
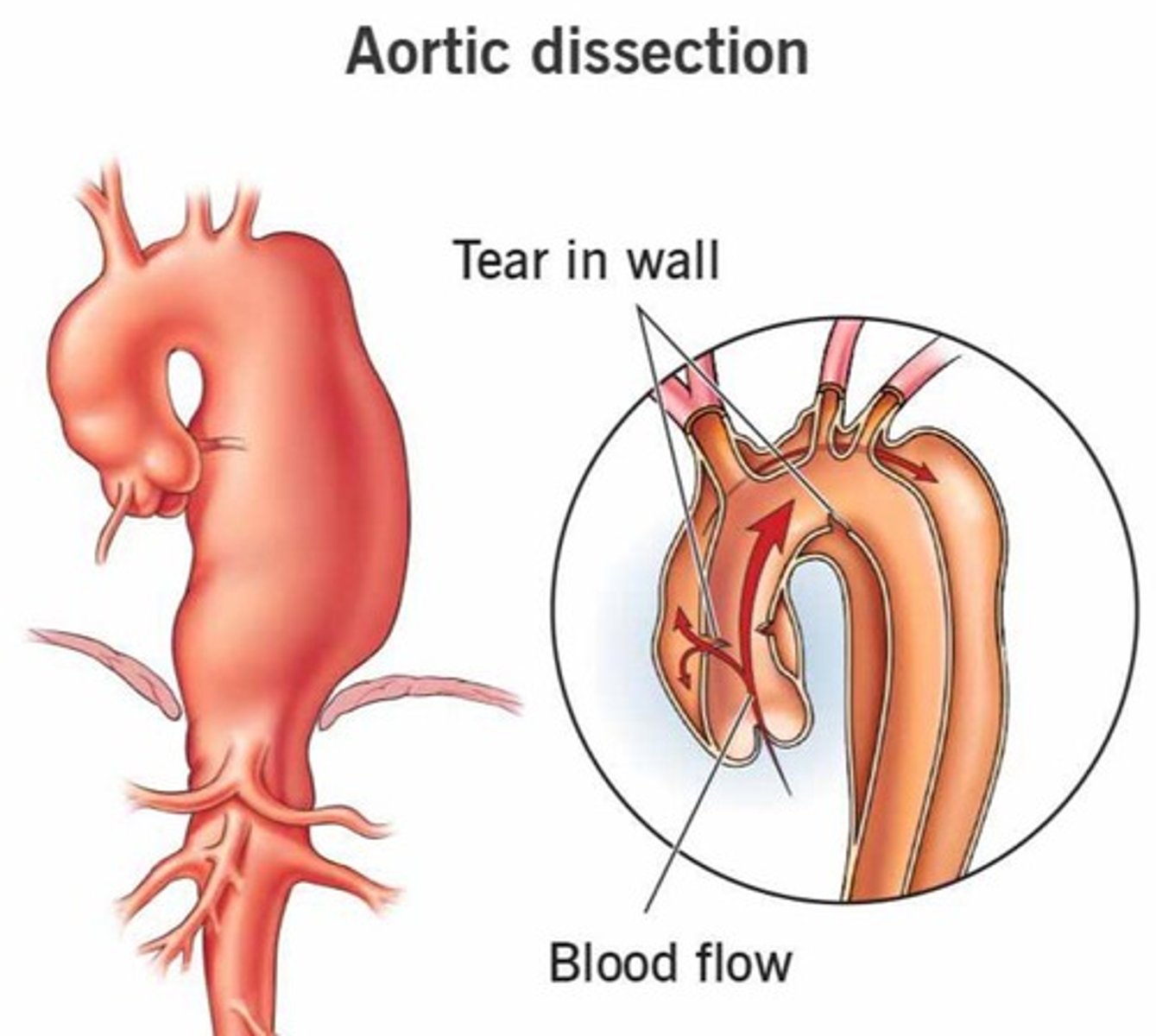
Excruciating Pain
Severe pain described as tearing or ripping sensation.
Syncopal Episodes
Fainting due to obstructed blood flow to the brain.
Hypertension
High blood pressure, a risk factor for dissections.
Systolic BP Control
Management of blood pressure to reduce dissection risk.
Prosthetic Graft
Artificial replacement for damaged aortic segments.
Mortality Rate
High risk of death associated with aortic dissection.
Degenerative Changes
Deterioration of aortic wall layers, increasing dissection risk.
Type A Aortic Dissection
More common, severe; involves ascending aorta.
Type B Aortic Dissection
Begins distal to subclavian artery; does not involve ascending aorta.
Hypertension
Sustained elevated blood pressure in arteries.
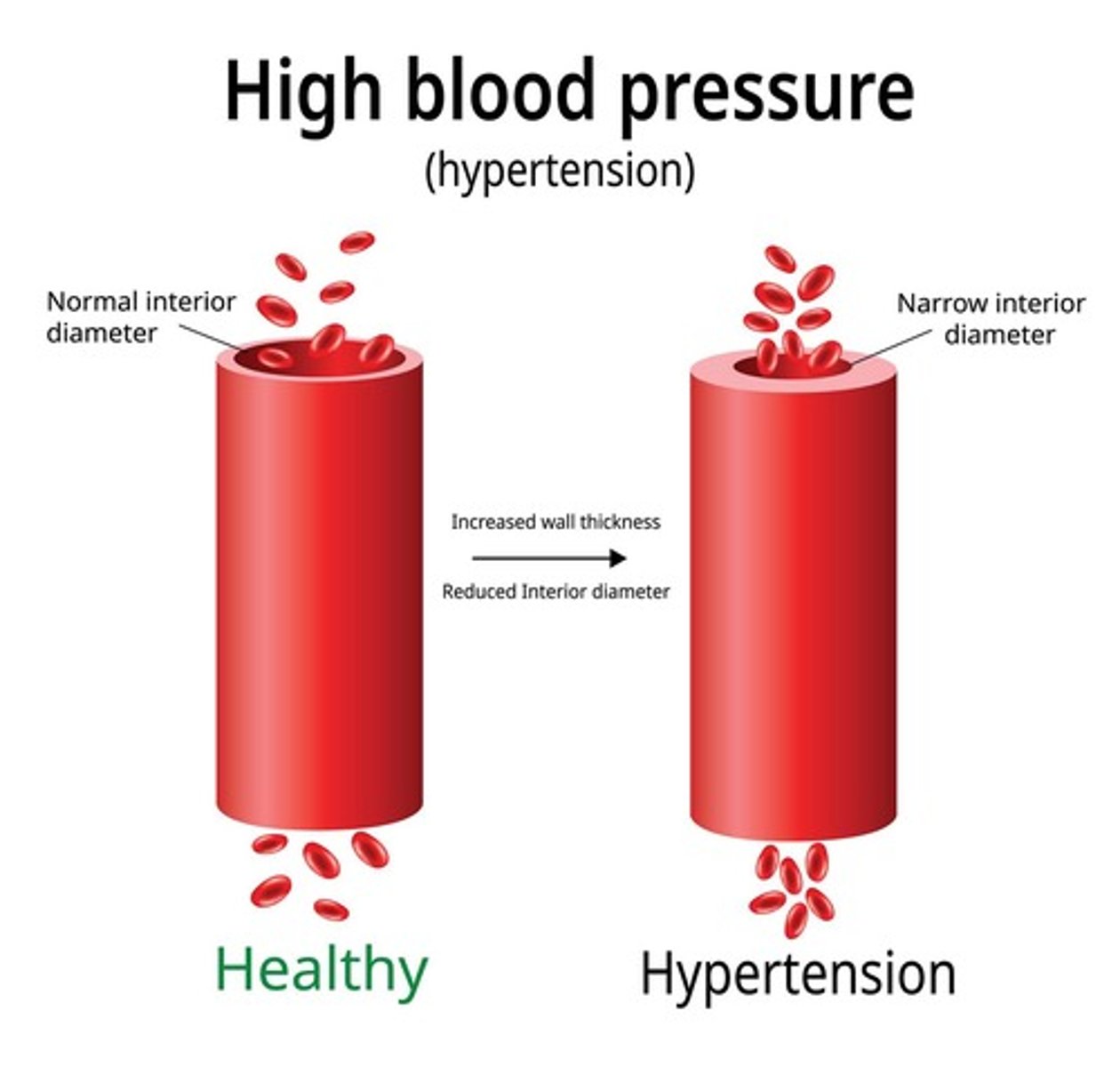
Primary Risk Factor
Leading cause of cardiovascular disease globally.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Age, ethnicity, family history, genetics.
Modifiable Risk Factors
Diet, tobacco, alcohol, obesity, fitness.
Target Organ Damage
Increased risk for heart disease and stroke.
Hypertensive Emergency
BP over 180/120 with acute organ damage.
Acute Organ Damage
Can lead to ischemic stroke or retinal hemorrhage.
Cardiomyopathy
Diverse diseases affecting heart muscle function.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
Thickened heart wall; impairs relaxation and filling.
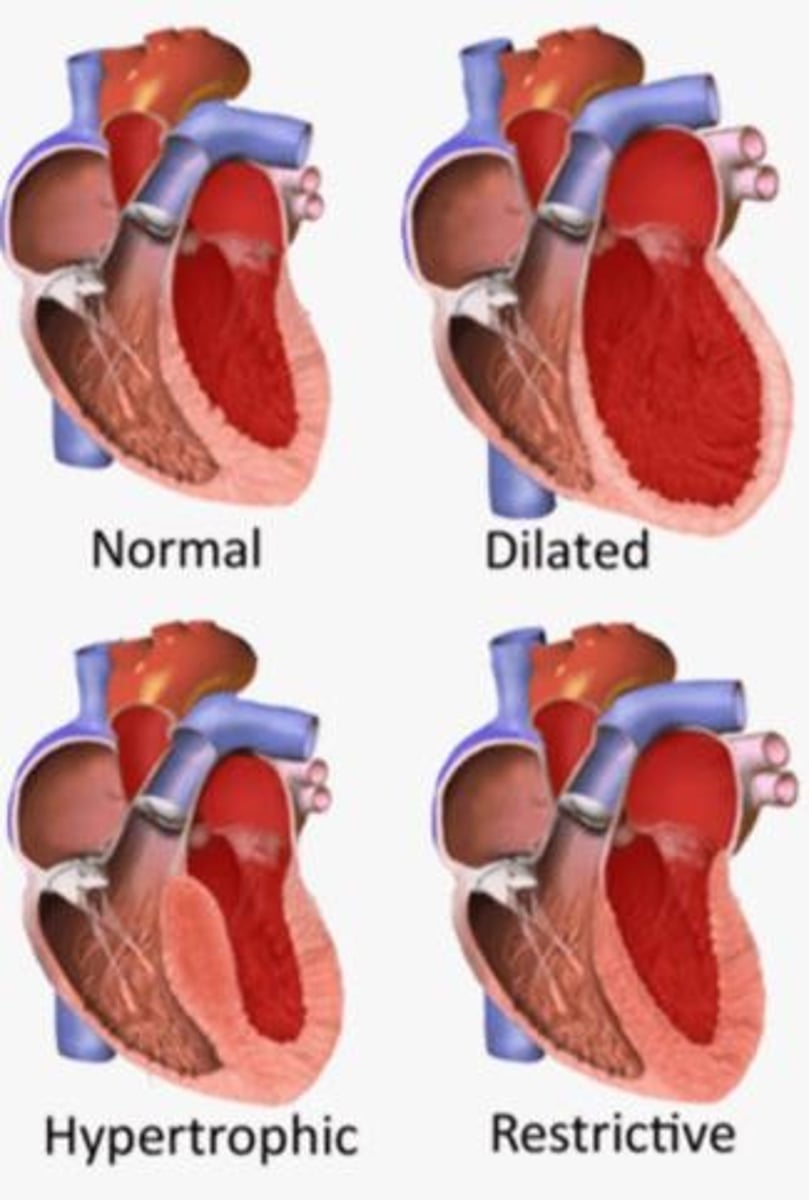
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Both genetic and non-genetic origins; heart dilation.
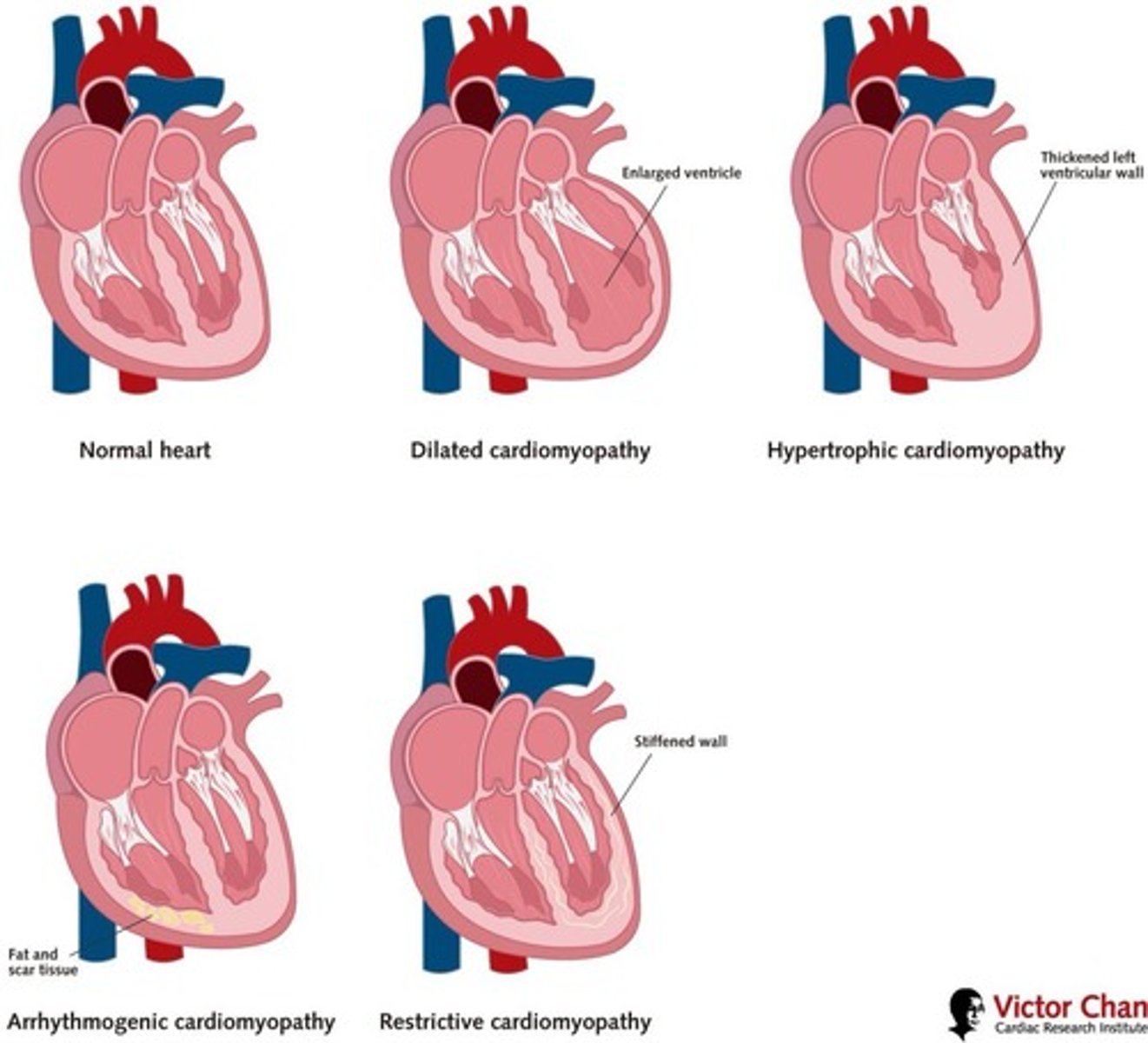
Idiopathic Cardiomyopathy
No known cause for heart muscle disease.
Hypertensive Retinopathy
Eye damage due to uncontrolled hypertension.
Ventricular Hypertrophy
Thickening of heart muscle walls.
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Spectrum of conditions from unstable angina to heart attack.
Chronic Kidney Disease
Long-term damage from uncontrolled hypertension.
Ischemic Stroke
Blood clot blocks blood flow to the brain.
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Irregular heartbeats; can occur in HCM.
Left Ventricular Outflow Obstruction
Blockage of blood flow from left ventricle.
Pregnancy-Related Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy occurring during or after pregnancy.
Blood Pressure Control
Management strategy for reducing hypertension effects.
Ventricular Fibrillation
Most common cause of sudden cardiac death in athletes.
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Genetic transmission pattern affecting sarcomere protein genes.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Characterized by asymmetric septal hypertrophy and obstruction.
Diastolic Dysfunction
Occurs due to stiff, non-compliant left ventricle.
Systolic Function
Normal function despite diastolic dysfunction presence.
Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms include dyspnea, chest pain, syncope, arrhythmias.
Beta-Blockers
Medications used to improve diastolic filling.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Medications that reduce left ventricular outflow tract obstruction.
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract (LVOT)
Path for blood exiting the left ventricle to aorta.
Myocardial Ischemia
Increased risk despite normal coronary arteries.
Disopyramide
Medication that increases risk of ventricular arrhythmias.