STEM Summative
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
alleles
different forms of genes for a single trait
dominant allele
one whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present; always expressed
recessive allele
one whose trait is hidden whenever the other allele is present; only expressed in the homozygous state
heterozygous
genotypes made of two different alleles
homozygous
genotypes made of the same alleles
heredity
the passing of physical characteristics from parent to offspring
genetics
the scientific study of heredity
trait
each specific characteristic, such as stem height or seed
gene
used to describe the factors that control a trait; section of DNA molecule that contains information to code for one specific protein
purebread
the offspring of many generations that have the same form of a trait
hybrid
an organism that has two different alleles for a trait
fertilization
a process in which new organism begins to form when egg and sperm cells join together
genotype
an organism’s genetic makeup, or allelles
phenotype
an organism’s physical appearance, or visible traits; how a trait looks or is expressed
Punnett square
a chart that shows all of the possible ways that alleles can combine in a genetic cross
probability
a number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur
incomplete dominance
occurs when one allele is only partially dominant
example of incomplete dominance
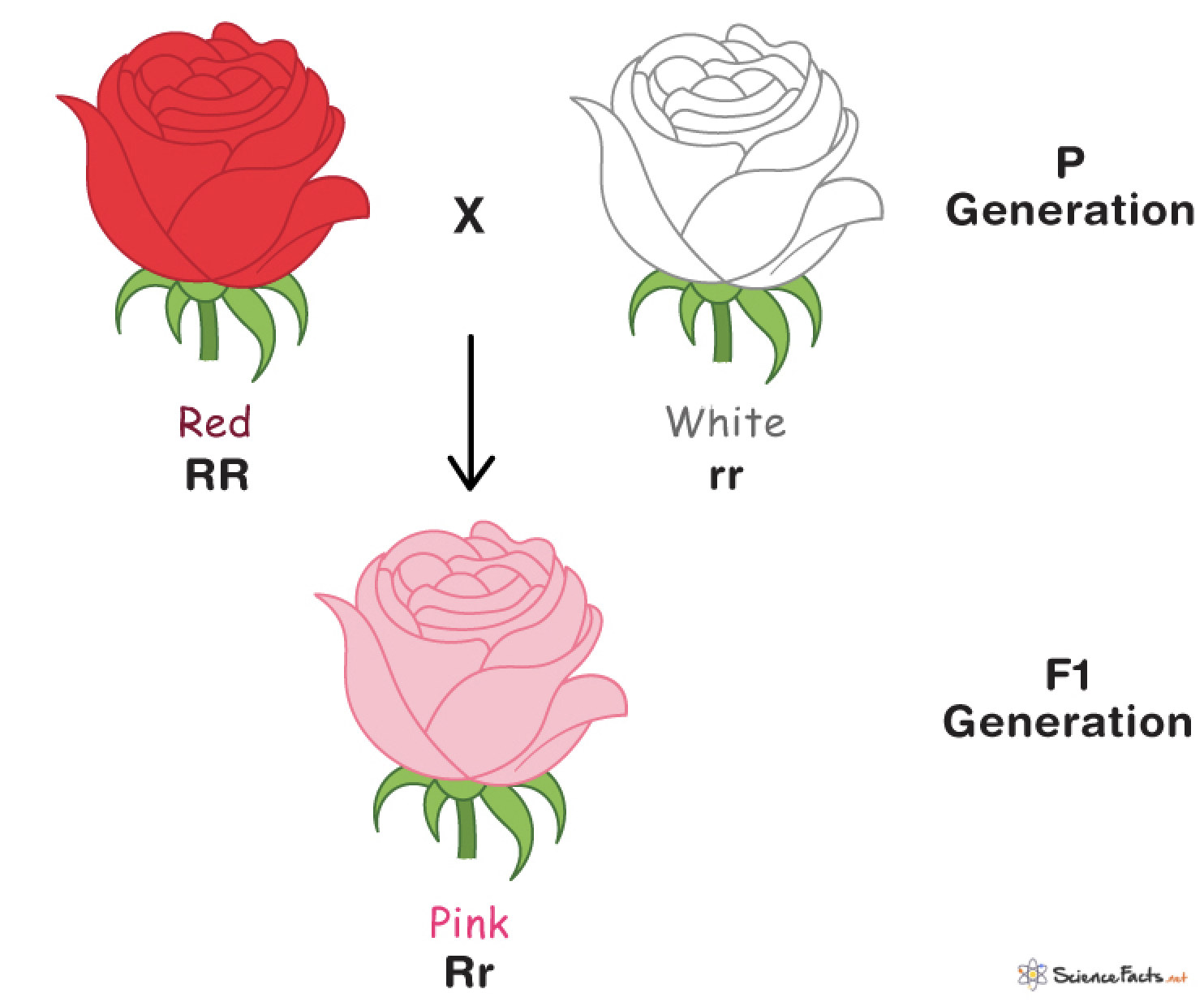
codominance
occurs when both alleles for a gene are expressed equally
example of codominance
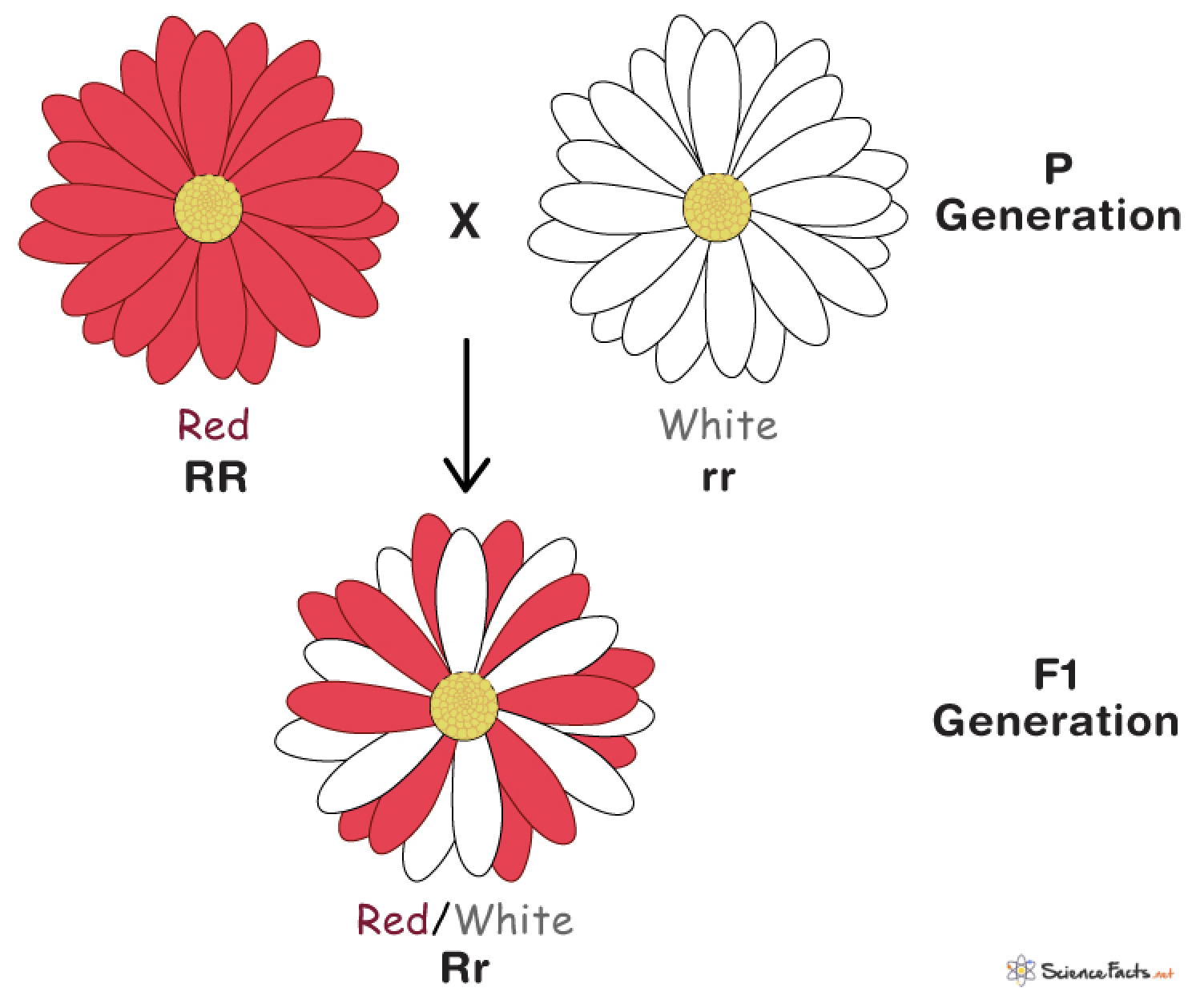
multiple alleles
three or more possible alleles determine the trait
example of multiple alleles
eye color
polygenic inheritance
occurs when more than one gene affects a trait
example of polygenic inheritance
height
nitrogen bases
molecules that contain nitrogen and other elements
What are the four nitrogen bases?
adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
how nitrogen bases mix
A goes with T; C goes with G
What does DNA stand for?
deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA replication
the process in which an identical copy of a DNA strand is formed for a new cell; because of the way the nitrogen bases pair up, the order of the bases in each new DNA strand exactly matches up the order in the original DNA strand
orders of structures (smallest to biggest)
nitrogen bases, DNA, chromosomes, cell
good path of cell division
makes an identical copy
bad path of cell division
leads to mutations (change in cell) which can cause cancer
What did Mendel observe?
the offspring of the F1 generation were always tall and the offspring of the F2 generation always had the recessive trait a quarter of the time
significance of Mendel’s observations
showed that the offspring traits are determined by individual, separate alleles inherited from each parent
What are DNA strands connected by?
nitrogen bases
Where are chromosomes found?
the nucleus of a cell
What is DNA made of?
strands are made of deoxyrybo sugar separated by phosphate; rows are made of the nitrogen bases
What are chromosomes made of?
genes
sequence for ATCGGC
TAGCCG
What genetic structure allows genes to pass from parents to offspring?
chromosomes
Where does the male’s genotype go on a Punnett square?
the top
Where does the female’s genotype go on a Punnett square?
the left side