Biology Shell Summer Exam
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Characteristics of living things
MRS H GREN
Plants
Multicellular organisms
They have chloroplasts and cellulose cell walls
They carry out photosynthesis
They store carbohydrates as starch or sucrose
Examples include maize, peas and beans.
Animals
Multicellular organisms
No chloroplasts, cell walls or photosynthesis
They store carbohydrate as glycogen
Animals include humans, houseflies and mosquitoes.
Fungi
Some are single celled
No photosynthesis but chitin cell walls
Made from mycelium which is made from hyphae (contain many nuclei)
They use saprotrophic nutrition
carbohydrate stored as glycogen
Examples include mucor and yeast.
Protoctists
Microscopic single-celled organisms
Some resemble plant structured cells and others animals
Examples are chlorella and plasmodium
Bacteria
Microscopic single-celled organisms
Have cell wall and membrane
No nucleus but some carry out photosynthesis
Example includes lactobacillus and pneumococcus (causes pneumonia)
Pathogen
An organism causing disease (fungi, bacteria, protoctist or virus)
Viruses
They are small non-living organisms
No cellular structure
Only reproduce inside living cells
Examples include tobacco mosaic virus causing leaf discolouring and HIV causing AIDS
Level of organisation in organsims
Organelle, cell, tissue, organ, system.
Differences between plant and animal cells.
Plants have cell walls, chloroplasts and a vacuole, whereas animal cells do not.
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and responsible for growth and reproduction.
Cytoplasm
A fluid inside the cell which protects the organelles within.
Cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
Cell wall
A structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of energy production.
Chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell
Ribosomes
Makes proteins (protein synthesis).
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area
Elements in carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Elements in proteins
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
Elements in lipids
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Structure of starch
long chain of glucose molecules
Structure of protein
Long chain of amino acids
Enzymes role
Increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy without being used up themselves.
Photosynthesis word equation
carbon dioxide + water --> glucose + oxygen
Photosynthesis balanced symbol equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Structure of a leaf
Waxy cuticle - reduces water losss
Upper epidermis - transparent to allow light through
Palisade layer - contains most chloroplasts
Spongy layer
Lower epidermis
Guard cells around stomata - lets CO2 diffuse
Required Ions
Plants require mineral ions for growth
Magnesium ions are needed for chlorophyll
Nitrate ions are needed for amino acids
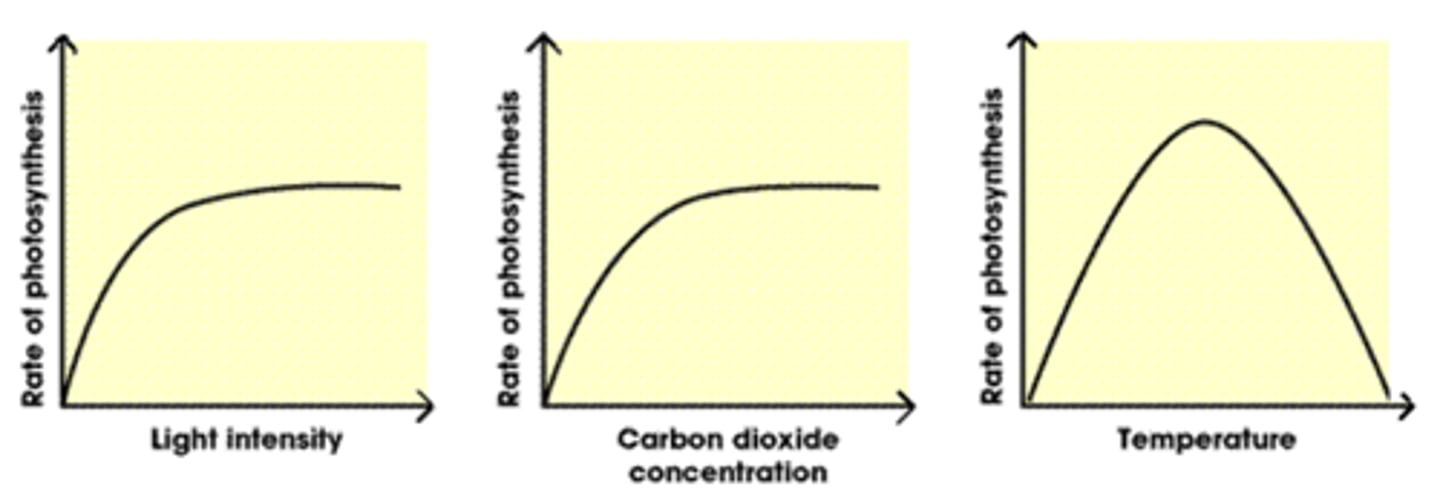
Effects on the rate of photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide concentration, light intensity and temperature
How do glasshouses and polythene tunnels increase crop yield?
They keep them away from pests and diseases in a controlled environment so that efficiency can be maximised.
How do fertilisers increase crop yield?
Fertilisers provide nutrients for the plant
which are needed for growth.
Advantages of pest control
-Quick and efficient
-Crop yield is increased
Disadvantages of pest control
- Expensive
- Environmental damage
- Poisonous to humans and wildlife
- Can cause water pollution
What is fish farming?
It is when fish are farmed and bred in a controlled environment to maximised yield, size and taste.
They can be fed specifically the right food and the water can be monitored.
The water can also be removed and filtered.
Sources of carbohydrates
Pasta, rice, sugar (provides energy)
Sources of proteins
Meat and fish (Growth and repair)
Sources of lipids
Butter and oily fish (energy store and insulation)
Sources of Vitamin A
Liver (Improves vision and skin)
Sources of Vitamin C
Fruit (prevents scurvy)
Sources of Vitamin D
Eggs and sunlight (calcium absorbtion)
Sources of Water
Food and drink (basically every bodily function)
Sources of calcium
Milk and cheese (makes bones and teeth)
Sources of iron
Red meat (healthy blood)
How do energy requirements vary?
They vary with activity levels, age and pregnancy.
Processes food can go through:
ingestion, digestion, absorbtion, assimilation and egestion
What is peristalsis?
The process of circular muscle contractions moving food through the gut
What is the role of digestive enzymes?
They break down large molecules into smaller ones.
Enzyms include amylase, maltase, protease and lipase.
Where is bile produced and stored?
It is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
What is bile's role in digestion?
It neutralises stomach acids and emulsifies fats to speed up digestion.
How is the small intestine adapted for absorption?
It is long, has a large surface area and a layer of permeable cells with a good blood supply.
What does a balanced diet include?
A balanced amount of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals and water.
Structure of the alimentary canal:
- mouth (breaks down food)
- oesophagus (connects mouth and stomach)
-stomach (pummels food and produces enzymes)
-small intestine (produces enzymes and absorbs nutrients)
-large intestine (excess water is absorbed)
-pancreas (produces enzyme)
Structure of an insect pollination plant
They are sticky, brightly coloured and scented.
Structure of an wind pollination plant
Small, dull, scentless petals.
Long filaments and lots of pollen to be carried away by the wind.
Conditions needed for seed germination
water, oxygen, warmth
What do germinating seeds utilize before they can carry out photosynthesis?
Food reserves
Population
All the different organisms of one species in a habitat.
Habitat
The place where an organism lives.
Community
All the different species living in a habitat.
Ecosystem
All the different organisms living in a particular area and all the non-living abiotic conditions.
Biodiversity
The variety of different species of organisms on Earth, or within an ecosystem.
Biotic factors:
-Availability of food
-Number of predators
-Competition
Abiotic factors:
-Environmental conditions
-Toxic chemicals
What can biodiversity be measured using?
Quadrats
What equation would you use?
Mean= total number of organsims/number of quadrats
Trophic level names:
-producer
-primary consumer
-secondary consumer
-tertiary consumer
-decomposers
How much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next?
10%
REMEMBER WHEN DESCRIBING PRACTICALS
Compare
Organism
Repeat
Measure (unit and time)
Same (give 2)