Lecture #22 & #23| Tumor Growth and Metastasis
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Metastasis
The ability of cancer cells to penetrate into lymphatic and blood vessels, circulate through the bloodstream, and the invade and grow in normal tissues everywhere else
lethality of benign tumors
Do not kill host
well organized and differentiated
- have fewer “luxury molecules” normal cells but sometimes they have too many
even a large benign tumor in most places will not kill you
exceptions: blocking airways
Lethality of metastases
Do kill the host
its what’s the tumor cells do to the body
organ failure
cachexia (wasting away)
infections: most common cause of death in cancer patients
Hemorrhage: rare, excessive bleeding
Heart failure: even rarer, rarely has tumors
hard to treat, not amendable by surgery
Comparison between metatstes and original tissues
Retain some properties of original tissue
metastatic tumors cells look different from their new surrounding
retain some of the characteristics of the original tissues that helps to determine the origin of the primary tumor
Effect of metastases on organ function
typically organs have a lot of excess capacity
2 lungs, 2 kidneys; so metastases can be present for a long time before symptoms arise
Metastic tumor cells destroy the architecture of the organs
when pts starts to show symptoms it is often too late
leukemias often have symptoms earlier
Steps of metaastasis
Hypoxia → angiogenesis (growth of new blood vessels)
Invasion of circulatory system
Migration to a new site
Establishment in a new tissue
Rapid proliferation of tumor cells
Step #1 Hypoxia and angiogenesis
Tumor cells may not need growth factors but they do need nutrient and oxygen
they enduce the growth of new blood vessels
when the tumor is around 10,000 cells, necrosis of center tumor cells occurs
in order to survive and proliferate, they need to supply more nutrients
Hypoxia increases expression of p53
so it is trying to avoid hypoxia
selects for aggressive, unstable p53 -/- cells
Angiogenesis
It is signaled by factors secreted by tumor and normal cells
local signaling to endothelial cells
sprouting-extension of pseudopodia
invasion through basal lamina
cell division behind sprout
formation of capillary tube
balance between activators and inhibitors

Activators are growth factors, inhibitors help inhibit formation of new blood vessels
How do tumor cells migrate?
Must lose adhesion to neighboring cells
Lose expression of APC and E-cadherin
Instead express N-cadherin that allows them to migrate
Escape tissue of origin and burrow thru neighboring tissue through the expression of new genes that allow it to move like integrins
Cells in tissues are surrounded by extracellular matrix made up of proteins
Cross basal lamina which is made up of lamina, collagen, integrins
Tumor cells must degrade ECM but also make holes (through proteases) in basal lamina → allows invasion of capillaries
EMT=epithelial to mesenchymal transition then MET=mesenchymal to epithelial transition
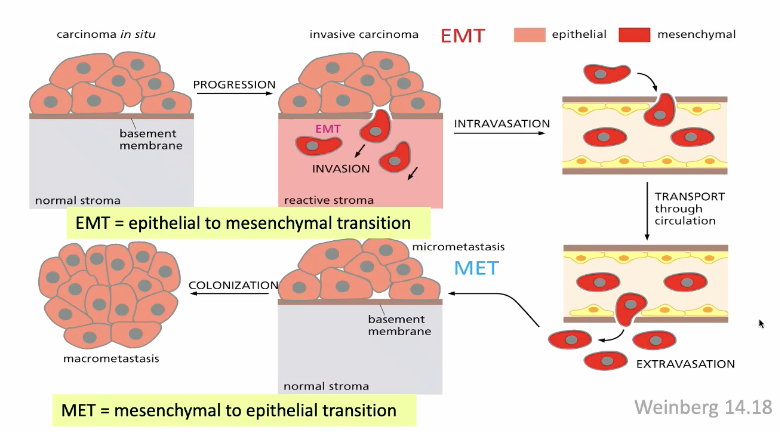
Proteases that degrade basal lamina to make holes
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Serine proteases
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Affect cell migration by degrading ECM and change cell adhesion
Alter cell-ECM interaction: regulate cell shape, proliferation, apoptosis
Release latent growth factors attached to ECM
Directly regulate activity of extracellular enzymes
Notice that around cancer cells there is less ECM
Expression of MMP results in hyperplasia and invasive metazoic tumors in mouse models
Angiostatin inhibits angiogenesis. What is its connection to basement membrane?
It inhibits the protease that turns inactive plasminogen into active plasmin
ECM/BM is cleaved by processes such as plasmin
VEGF
Pro-angeiogenic factor that binds to endothelial cell receptor kinase and singles cell to proliferate
released from normal and tumor cells under hypoxia
can be surpasses by antagonists of receptor
What is HIF
Hypoxia inducible factor which regulates the transcription of VEGF
so hypoxia stabilizes transcription factor HIF to increase the expression of VEGF
Regulation of proteases
Secreted by inactive precursors
confined to specific areas by TIMP (tissue inhibitor of MMPs (plasmin activates pro-MMP to MMP) and serpins (serine protease inhibitors)
many cells have receptors on their surface that bind protease and limit their range of action
Migration to a new site
Follow the circulatory system
Lung get metastases from many tissues because all the blood goes there for oxygenation
Portal vein goes directly to liver
Large cancer cells can get stuck in blood vessel causing a blood clot
Cancer cells also travel through the lymphatic system → metastases in lymph nodes
Homing and coloration of a cancer cell to a distant organ is a complex process that depends on the target tissue as well as the tumor cells and other unknown
Establishment in a new tissue
Proper environment is required that depends on hormones
Rapid proliferation of a new tissue
Takes time to adapt
genetic instability will accelerate the process
How can knowledge of metastasis be used tonight cancer
Diagnostically: determine the stage of the tumor and therefore how to treat it
MMP
Metastatic gene signatures
Therapeutically
Target any of the 5 steps of metastasis
Diagnostic applications of metastasis knowledge
MMPs are diagnostic of metastatic potential
detection of MMP in tissues indicate whether the tumor has the potential to metastasize, used as a screening tool
DNA sequencing to see if there is a metastatic signature which allows staining of the whole genome
Signatures allows prediction of metastasis and survival for many cancers
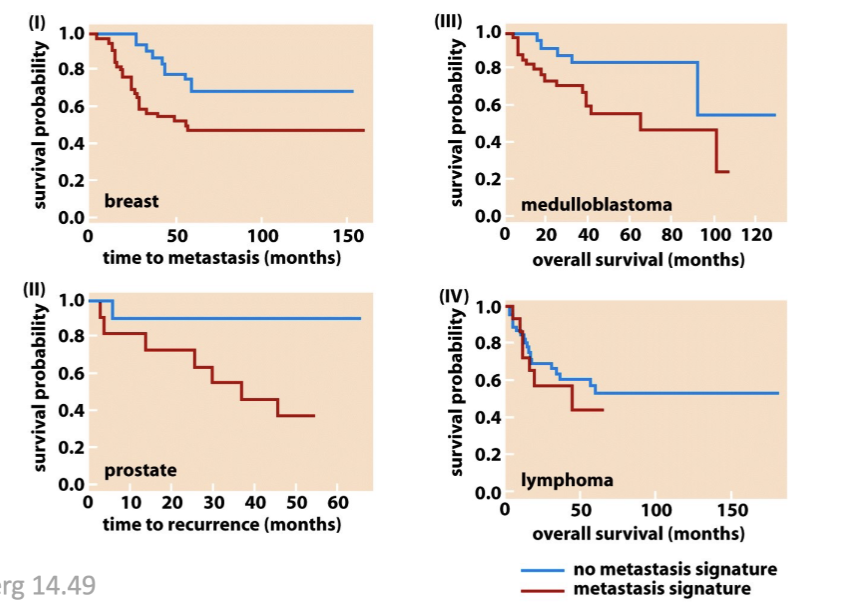
does not work well for lymphoma
Therapeutic application using knowledge of metastasis to fight cancer
Direct inhibition of proteases through TIMP
Target the cells that produce the proteases, normal cells rather than tumor cells
Angiogenesis → a good drug target for cancer
Angiostatin can decrease tumor size but requires repeated treatment
Tumor blood vessels are leaky and disorganized
Taken advantage of in treatment
Even hypoxia can be taken advantage of but tumor hypoxia can cause cancer cells to become resistant to standard therapies → solution: bioreductive prodrugs that become activated only in oxygen poor core of solid tumors
Drugs approved by the FDA for good drugs to target cancer
Monoclonal antibody for VEGF
anti-angiogenesis drug that slows tumors
Avastin
Chemical inhibitor of angiogenesis
given in combo with other drugs
ex: thalidomide inhibits angiogenesis, Ub ligases and generates ROS → impacted babies