Lecture 17: Atomic Physics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Outline Einstein’s theory of relativity
Replaced newtonian mechanics when dealing with particle speeds comparable to the speed of light
Outline quantum theory
Understanding behaviour of atoms in absorption and emission of radiation
What is blackbody radiation?
Blackbody: a body that emits all radiation when hot
all objects emit radiation whose total intensity is proportional to the 4th power of their Kelvin temp
blackbody would also absorb all radiation that are incident on it and will reflect none, thus appears black
example: the sun is a blackbody
What is quantum physics?
What happens to the total power of the emitted radiation as T increases
Total power of emitted radiation increases
What happens to the peak of the spectra as T increases
The peak of the spectra shifts towards shorter wavelength
Outline the physics of an ear thermometer
doctors often use an ear thermometer to measure temperature
this type of thermometer measures the amount of infrared radiation emitted by the ear drum
it then converts the amount of radiation into a temperature reading
this thermometer is very sensitive as compared to ordinary mercury thermometer, this is because the power emitted by the ear drum is proportional to the fourth power of temperature (T^4)
Describe attempts to explain blackbody radiation
early attempts to use classical ideas to explain the shape of the curves failed
in 1900 max planck developed a theory of blackbody radiation that is in complete agreement with the observed curve
planck assumed that energy of atomic oscillator is discrete (quantized) and not continuous as assumed in classical theory
Describe quantized vs not quantized energy
Quantized energy: energy that can only take on discrete values
eg. staircase, piano
Non-quantized energy: energy that can take on any value within a range
eg. slide, violin
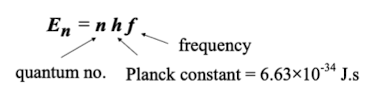
Outline planck’s quantum hypothesis
the energy of an atomic oscillator can have only certain discrete values En (that is, energy of oscillator is quantized)
oscillator emit and absorb energy when making a transition from one quantum state to another in the form of a single quantum of energy (i.e. energy of radiation is quantized)
What is the equation derived from Planck’s quantum hypothesis
what is the photoelectric effect?
electrons are ejected when light strikes a metal surface
an increase in intensity of the light beam means more photons are incident, so more electrons will be ejected but energy of each photon is not changed
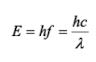
outline some features of the photoelectric effect
no electrons are emitted if f < fc
as f increases, KEmax of electrons also increases
KEmax can be measured by reversing the terminals of the battery
KEmax = eVs
what did einstein propose about the photoelectric effect?
argued that when light is emitted by a molecular oscillator, the molecule’s vibrational energy of nhf must decrease by an amount of hf (or 2hf, etc.) to another integer times hf
to conserve energy light must be emitted in packets, or quanta
what is work functions (Wo)?
minimum energy required to eject an electron from a material
eg. Na - 2.28 eV, Ba = 2.48 eV, Cu = 4.70 eV
what is stopping voltage (Vs)?
the voltage at which an electron reaches the collector
describe einstein’s photon theory
classical theory cannot explain the photoelectric effect, but quantum theory can
outline atomic spectra: the key to the structure of the atom
a gas heated in a discharge tube emits light only at characteristic frequency
this is called line spectrum
the line spectrum works as a ‘fingerprint’ for identification of the gas
outline the energy level diagram for a hydrogen atom
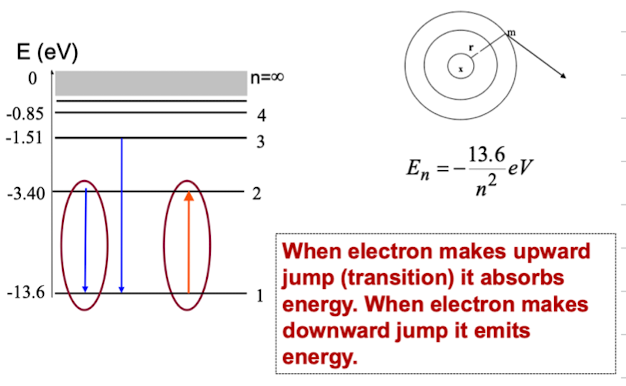
what is ionisation energy?
the minimum energy required to ionise the atom in the ground state (in case of a hydrogen atom it is 13.6 eV)