Lecture 8: Plant development from seed to maturity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Plant Embryo division
begins with division of zygote
1st division is asymmetrical and transverse
apical cell: smaller cell on top, gives rise to most of the mature embryo
basal cell: larger cell, produces suspensor, anchors embryo at micropyle and is the source of nutrient exchange. Expands longitudinally by multiple transverse divisions to form the suspensor
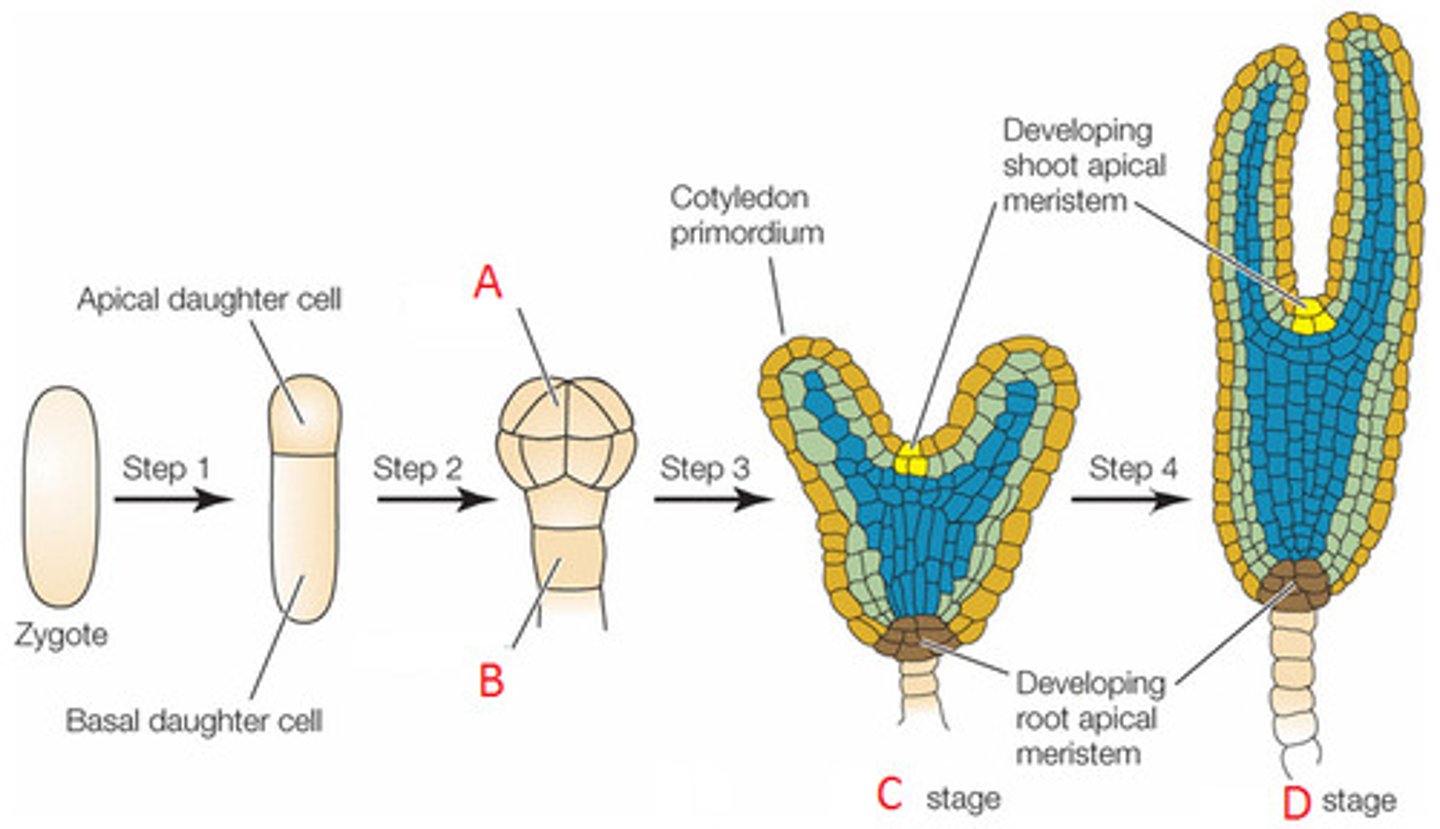
Suspensor and hypophysis
produced by basal cell through multiple transverse divisions. Top cell of suspensor is the hypophysis
pro-embryo
8-cell stage
Protoderm, ground meristem, procambium
protoderm: becomes epidermis, periclinal divisions
ground Meristem: ""ground tissue, surrounds procambium
procambium: ""vascular tissue
Globular stage
cell division of the proembryo soon leads to the globular stage that is radially symmetrical and has little internal cellular organization, hypophysis formed
Heart stage
Cotyledon, cotyledon shoulder, central domain, hypophysis
Late Heart stage, Torpedo
Shoot apical meristem at the top, hypocotyl in the middle
Final stage with cotyledons
has SAM and RAM
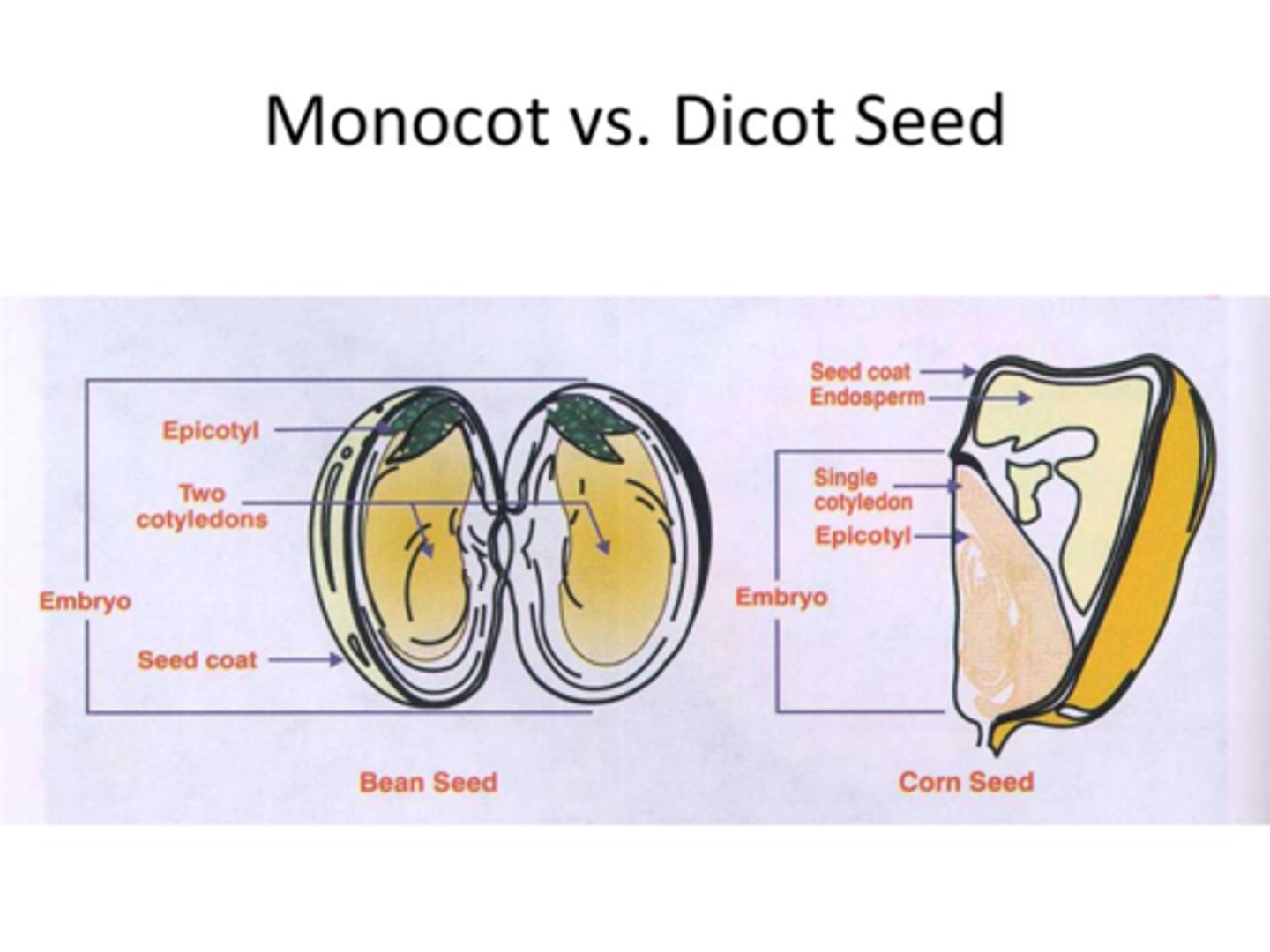
Monocot vs Dicot Embryo
Monocot: 1 cotyledon
- plumule: becomes leaves
- hypocotyl: stemmy region below(hypo) cotyeldon
- radicle: becomes root, first tissue to emerge
- endosperm
-coleoptile: protective sheath
Dicot: 2 cotyledon
- plumule
- hypocotyl
- radicle
- endosperm
Germination
nutritional dependence (embryo)-> nutritional independence (roots and leaves)
Quiescence vs Dormancy
Quiescence: seed doesn't germinate because env conditions bad
Dormancy: seed doesn't germinate because needs a trigger
Dormancy Triggers
Light: Detects daylenth to avoid spawing in wrong season
Chilling(stratification): needs to be chilled to avoid spawnign in winter
Abrasion: needs to be abrased to germinate only after being dispersed
First structure to emerge post germination
radicle/root, anchor plant to soil, absorbs water,
then:
shoot
these exhaust nutrients from endosperm
Post germination
1) seed is imbibed and swells
2) GA induces hydrolytic enzymes, enzymes secreted
3) alpha amylase breaks down starch in endosperm to release root
4) Root emerges
5) shoot greens up
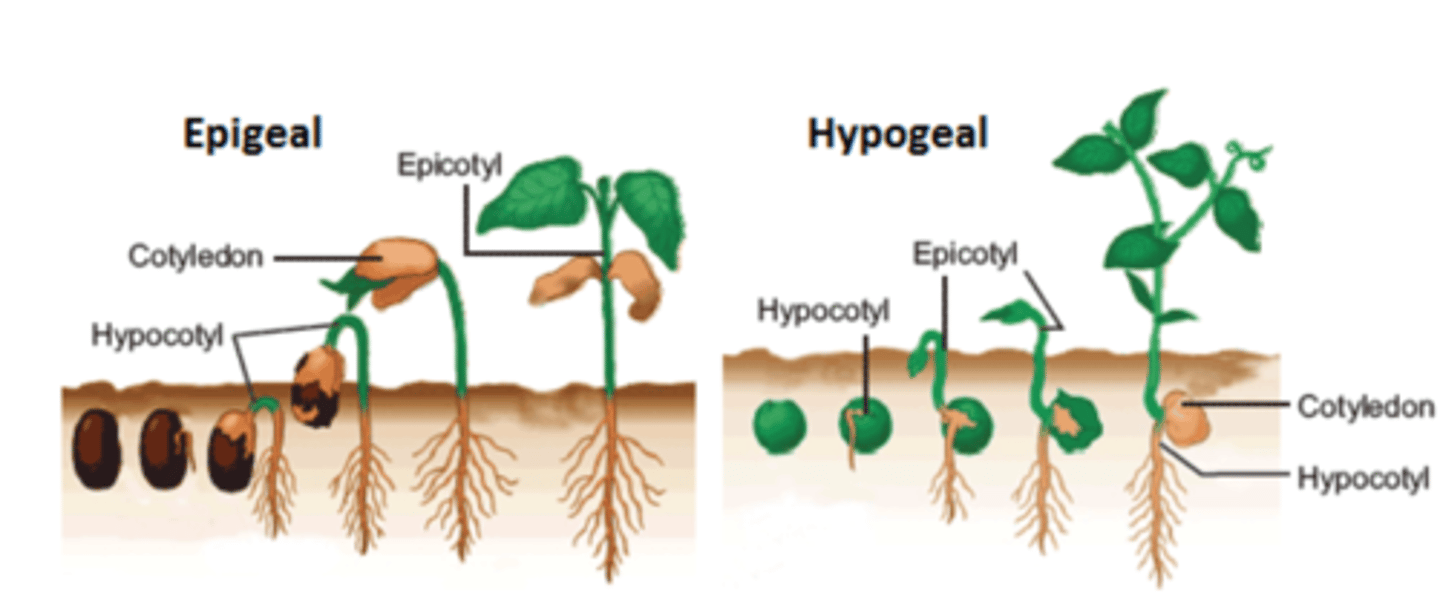
Epigeal vs Hypogeal
Epigeal: cotyledons above ground
Hypogeal: cotyledons below ground NEVER photosynthesize
Meristem
where plant grows from: area of continuous cell division
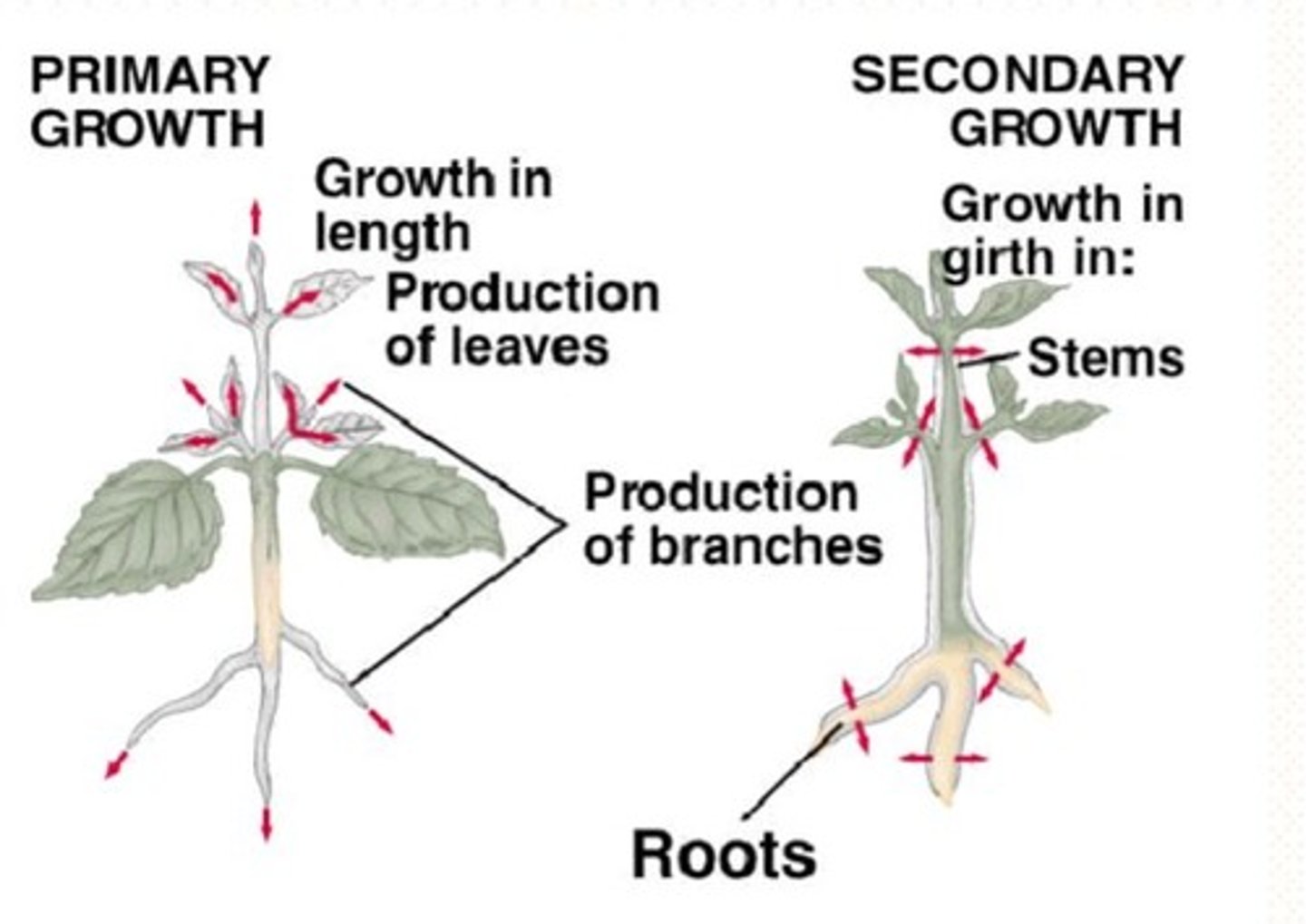
Primary vs secondary growth
Primary growth: vertical, occurs from SAM and RAM
Secondary growth: Girthiness, vascular cambium
SAM
at the top of the shoot, where meristem elongation occurs
stem from auxillary buds
Apical Dome
Apical shoulders: leaf primordia
Apical dome composed of protoderm, procambium and ground tissue
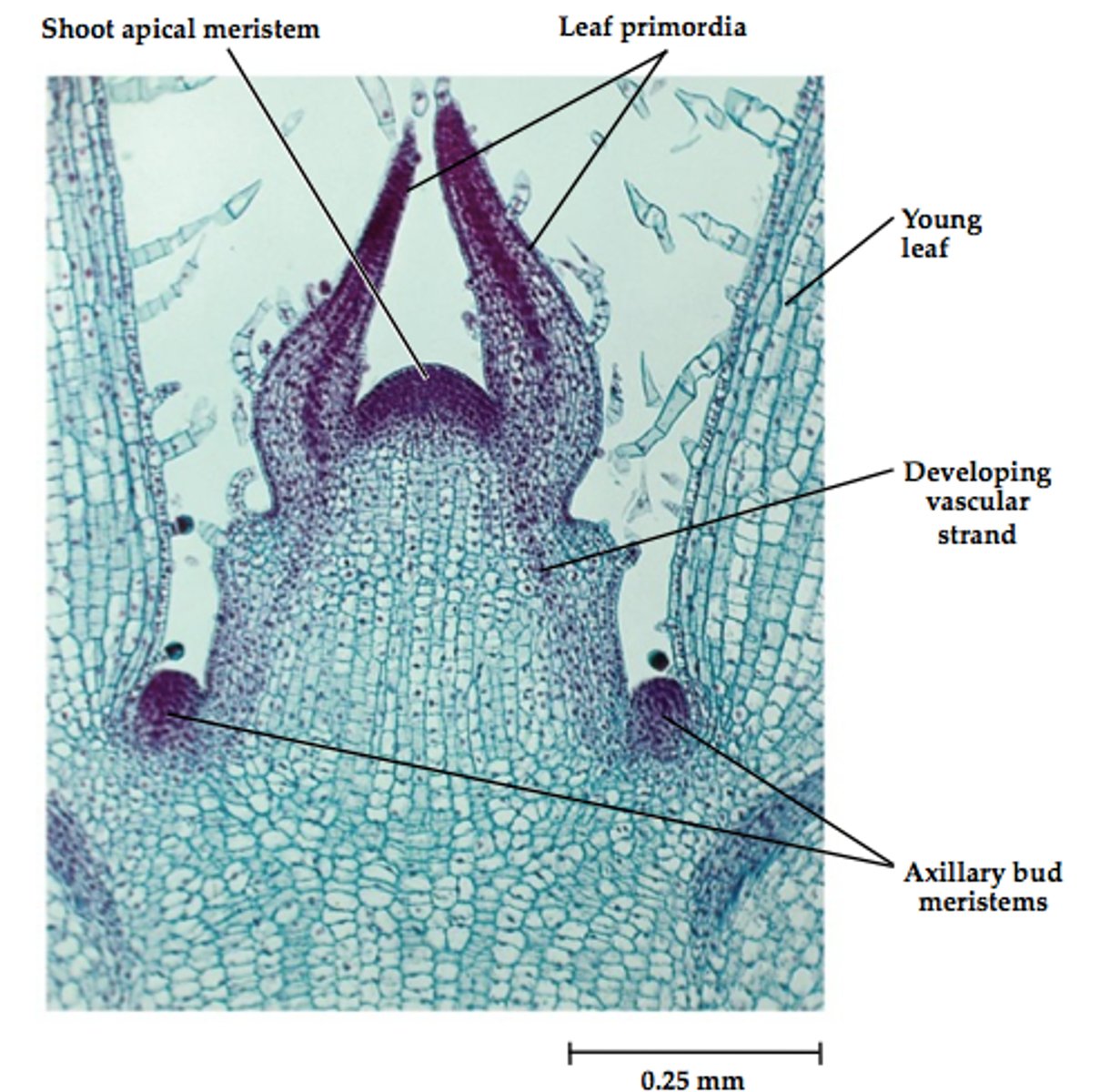
Plants grow up by:
elongating cells at the shoot tip