CMS III Final: Peds pt 2
1/365
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
366 Terms
which bone is the first to ossify?
clavicle → last to fuse
if a 10 year old male presents with a painless limp and Trendelenburg gait, what dx should you suspect?
Legg-calves-perthes → AVN of femoral head
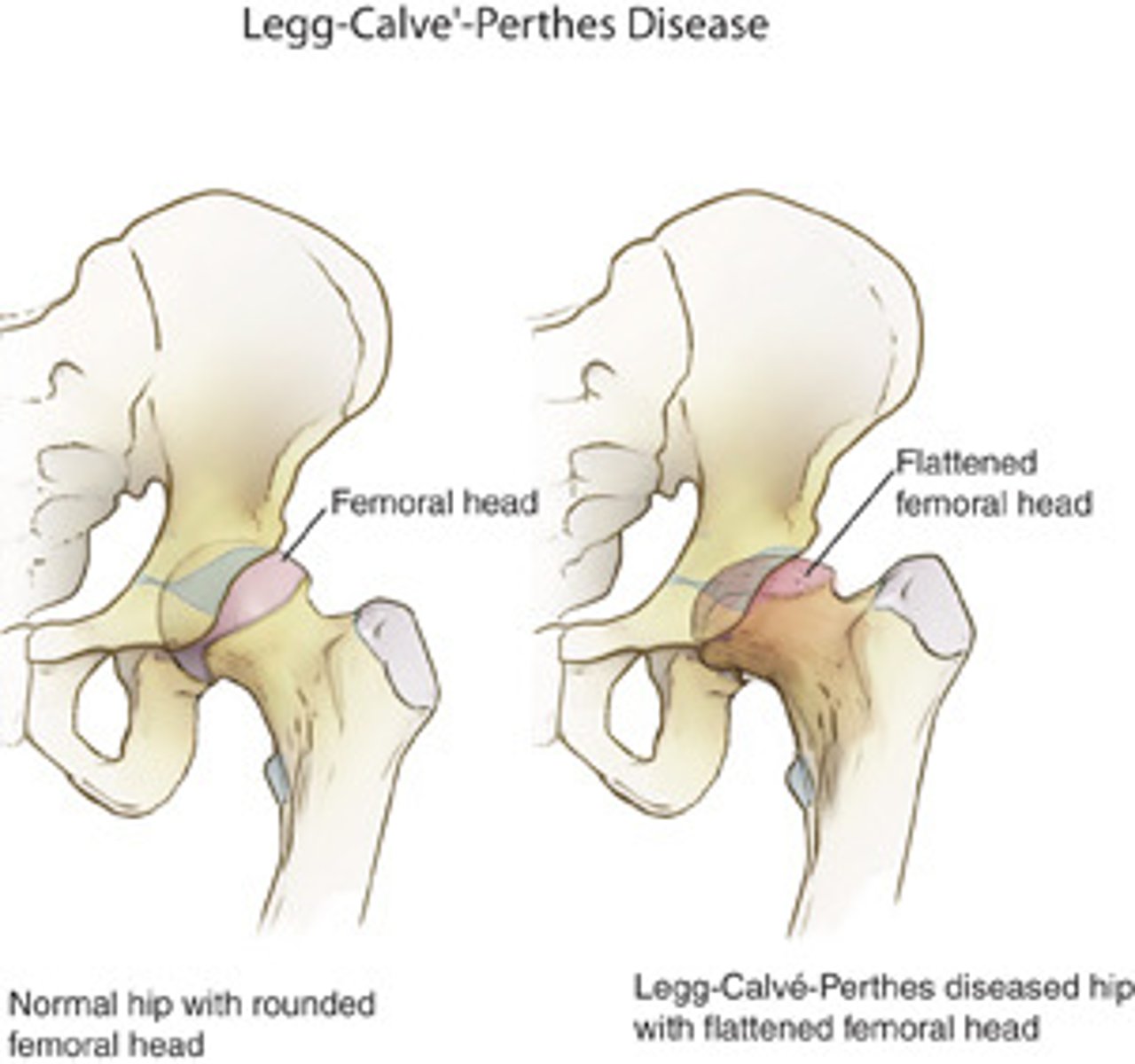
if a 14 year old male presents with a painful limp without hx of trauma, what dx should you suspect?
SCFE ***→ displacement of femoral head from neck
also see:
LE externally rotated
shortening of limb
antalgic gait with abductor lurch
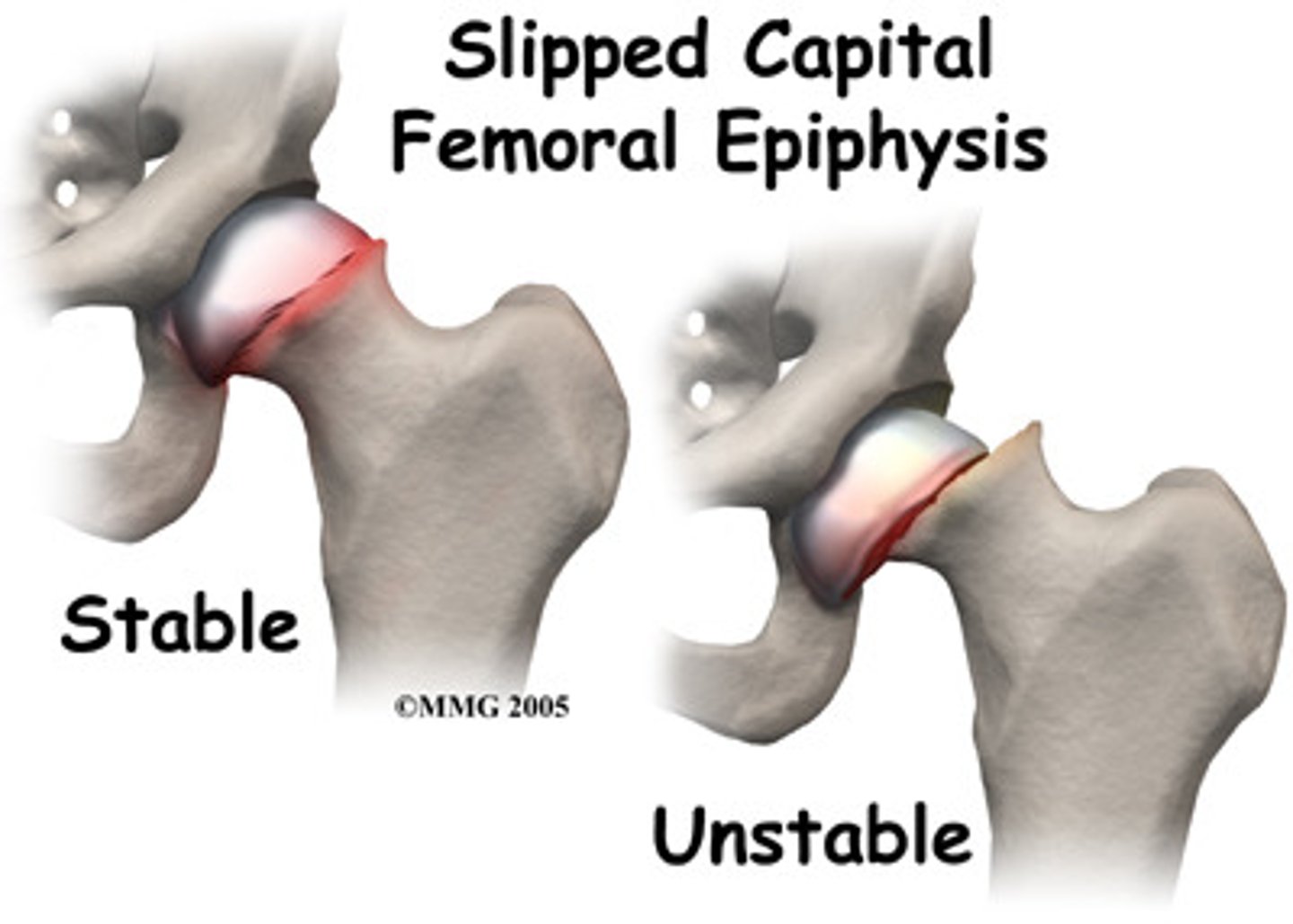
what is seen on imaging in SCFE?
widened and radiolucent physis, deformed/displaced femoral head
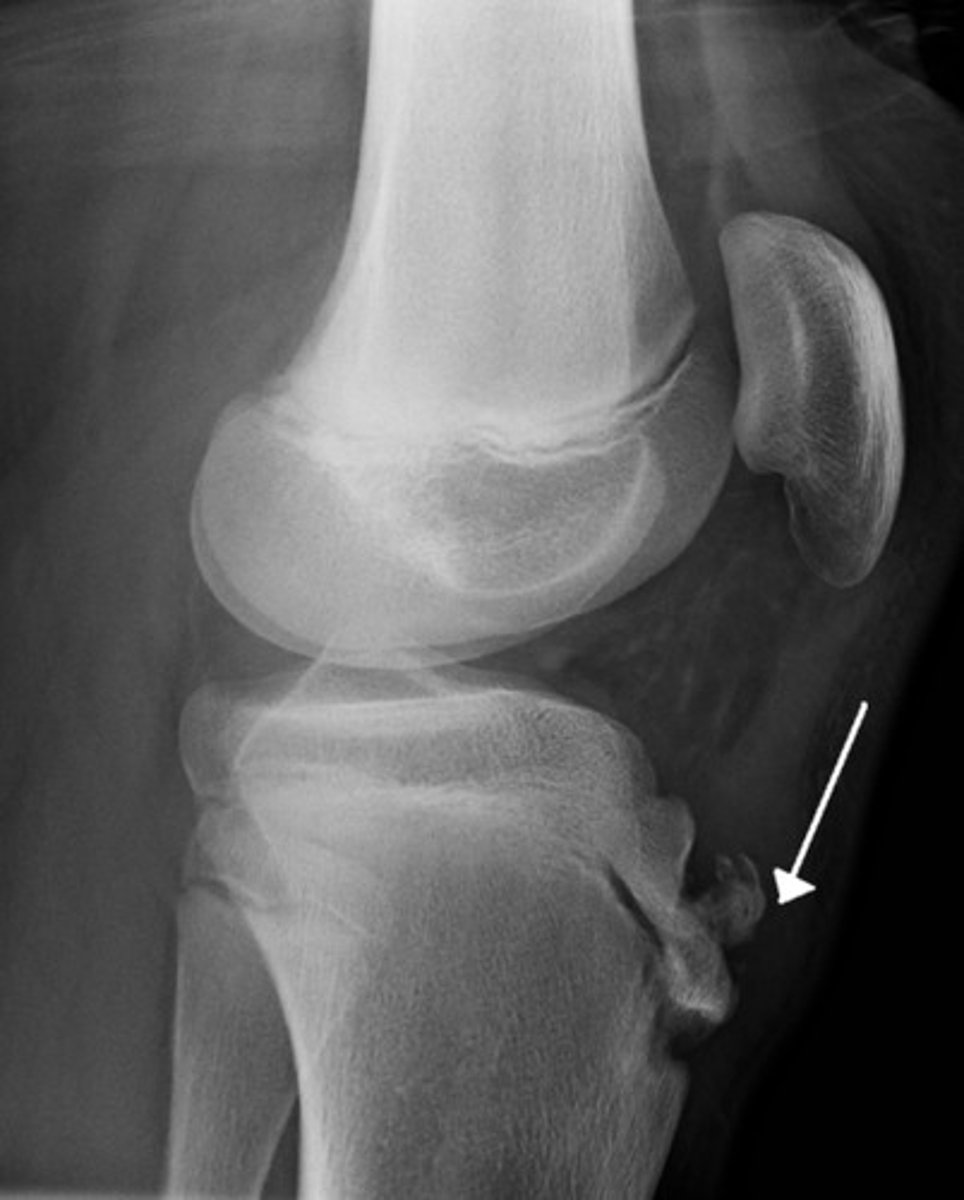
which dx has swelling, tenderness, and increased prominence of tibial tubercle on PE?
osgood-schlatter*** → response to stress on tibial tuberosity
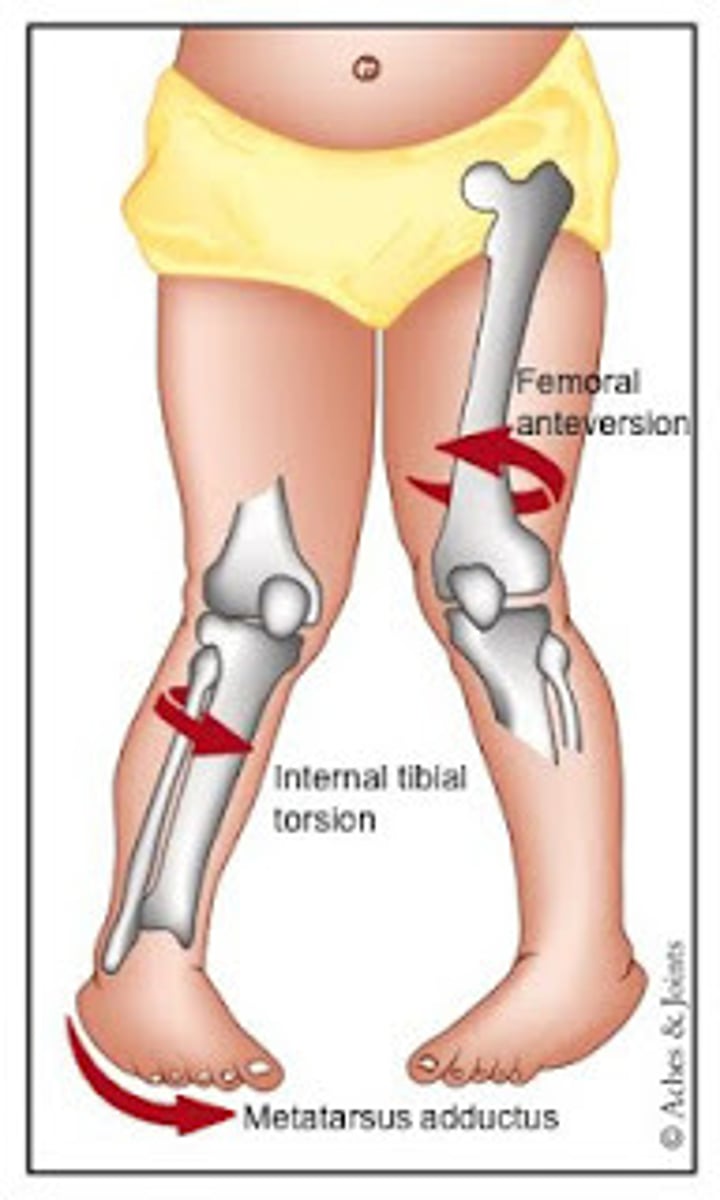
which abnormality shows pts that stands with their thighs, knees, and feet turned inward?
hip anteversion
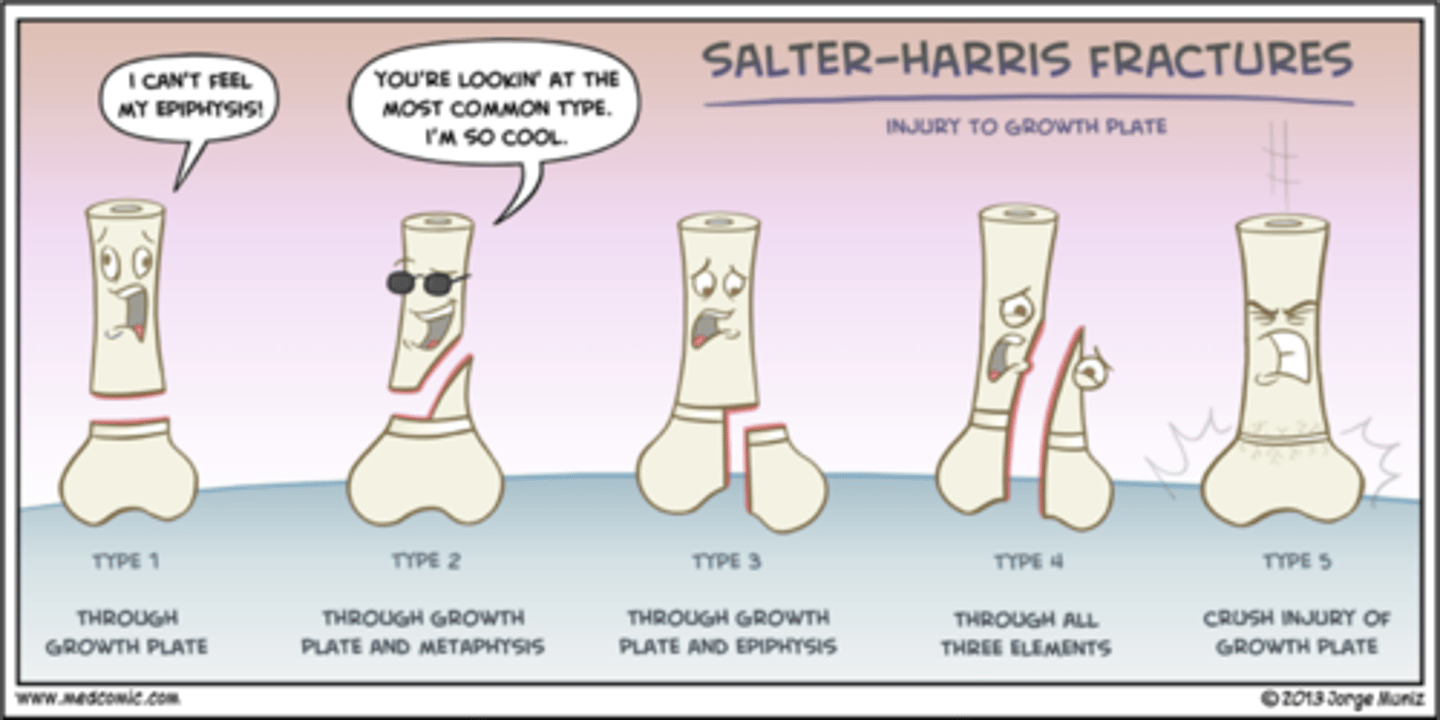
salter harris fractures
how many times are we gonna see this
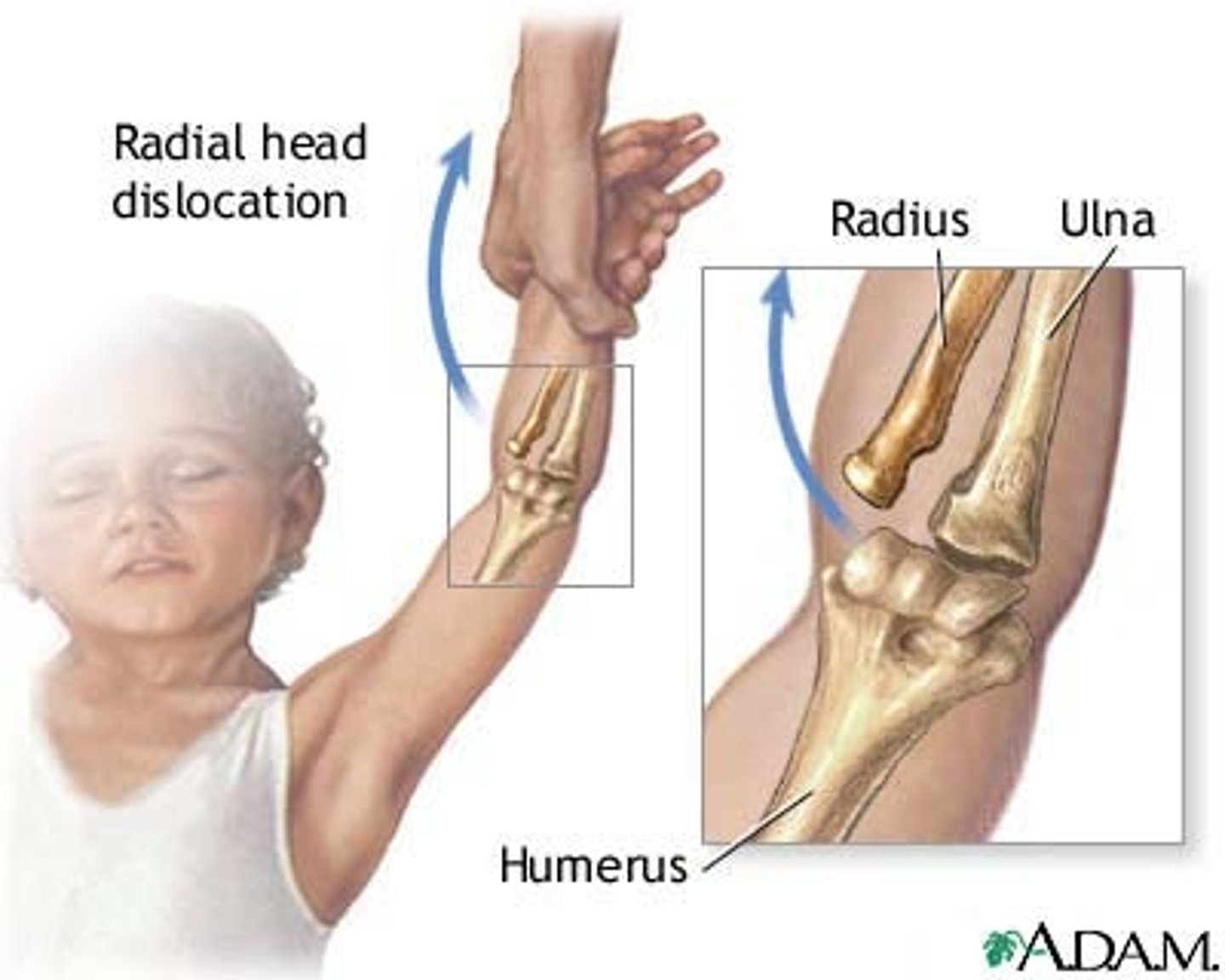
in which dx does the annular ligament sublux from the radial head?
nursemaid's elbow*** →tx with hyperpronation of arm with pressure over radial head
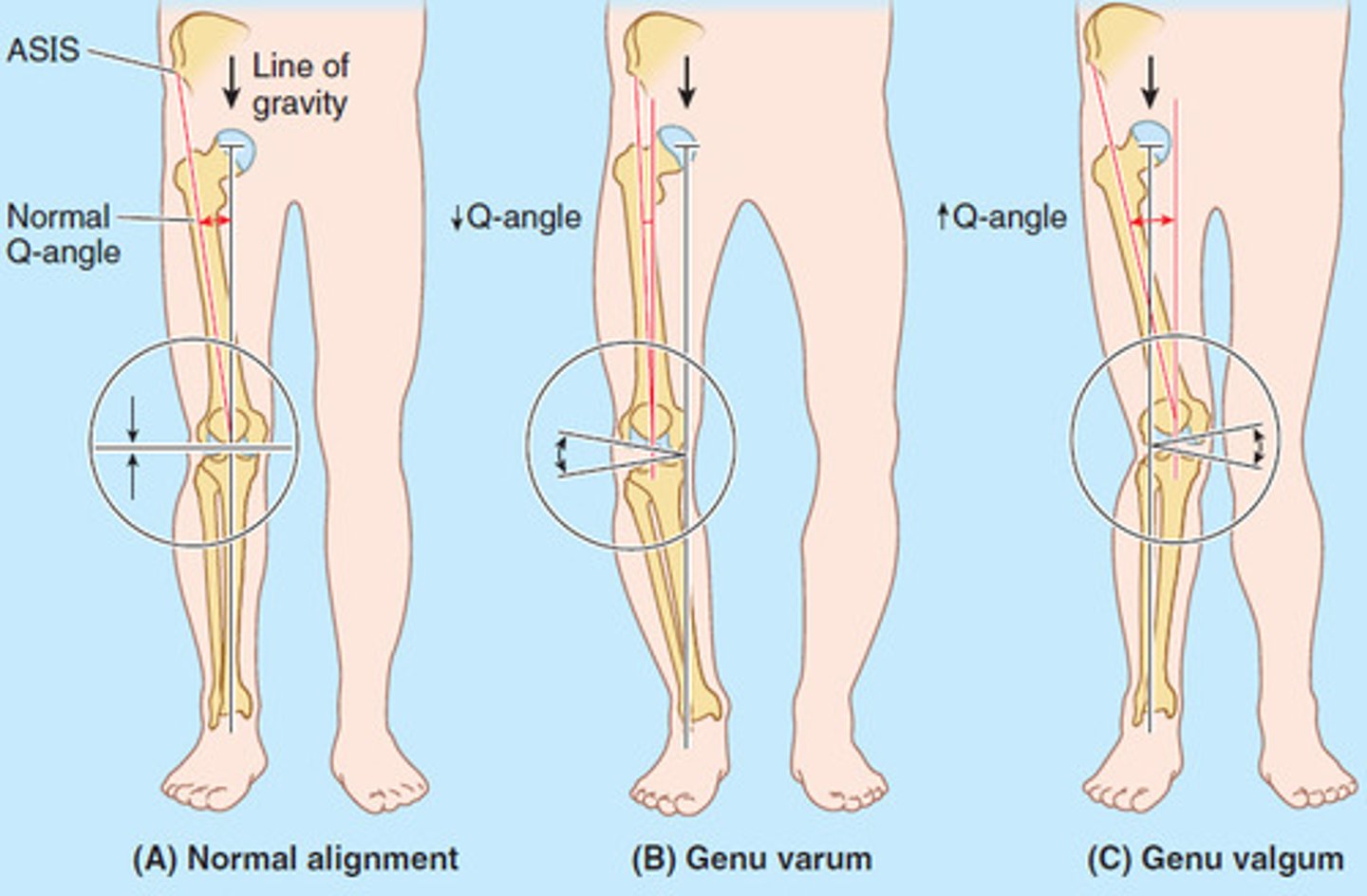
what is the different between genu varum and genu valgus?
varum = bowlegs
valgus = knock knees
resolve on their own***
which subtype of JIA is more common in knees and ankles?
oligoarthritis***
which subtype of JIA commonly involves DIP joints and presents with uveitis?
psoriatic arthritis
arthritis + FHx of psoriasis , dactylitis or nail changes
what is the tx for kawasaki syndrome?
IVIG and ASA
what is the dx criteria for kawasaki syndrome?
fever x4 days with 2 of the following:
conjunctivitis
LAD
rash
mucous membrane changes
peripheral extremity changes
what is a major complication of Kawasaki syndrome?
coronary artery aneurysm
what are the stages of Kawasaki dz?***
acute 7-14 days = fever, irritability, conjunctivitis, oropharynx erythema, rash, LAD, edema
subacute 10-25 days = desquamation, coronary artery aneurysm, thrombocytosis
convalescent 21-60 days = low risk for aneurysm, coronary artery risk
what is the tx for idiopathic scoliosis?
PT, boston brace, surgery if >40 degrees
when should you refer to ortho for scoliosis?
immature > 20***
mature > 40
sus pain/neuro sx
which dx involves increased angulation of thoracic spine MC due to poor posture?
kyphosis (humpback)
in which hereditary dx are the vertebrae more curved and have a wedged shape?
Scheuermann disease → schmorl nodes
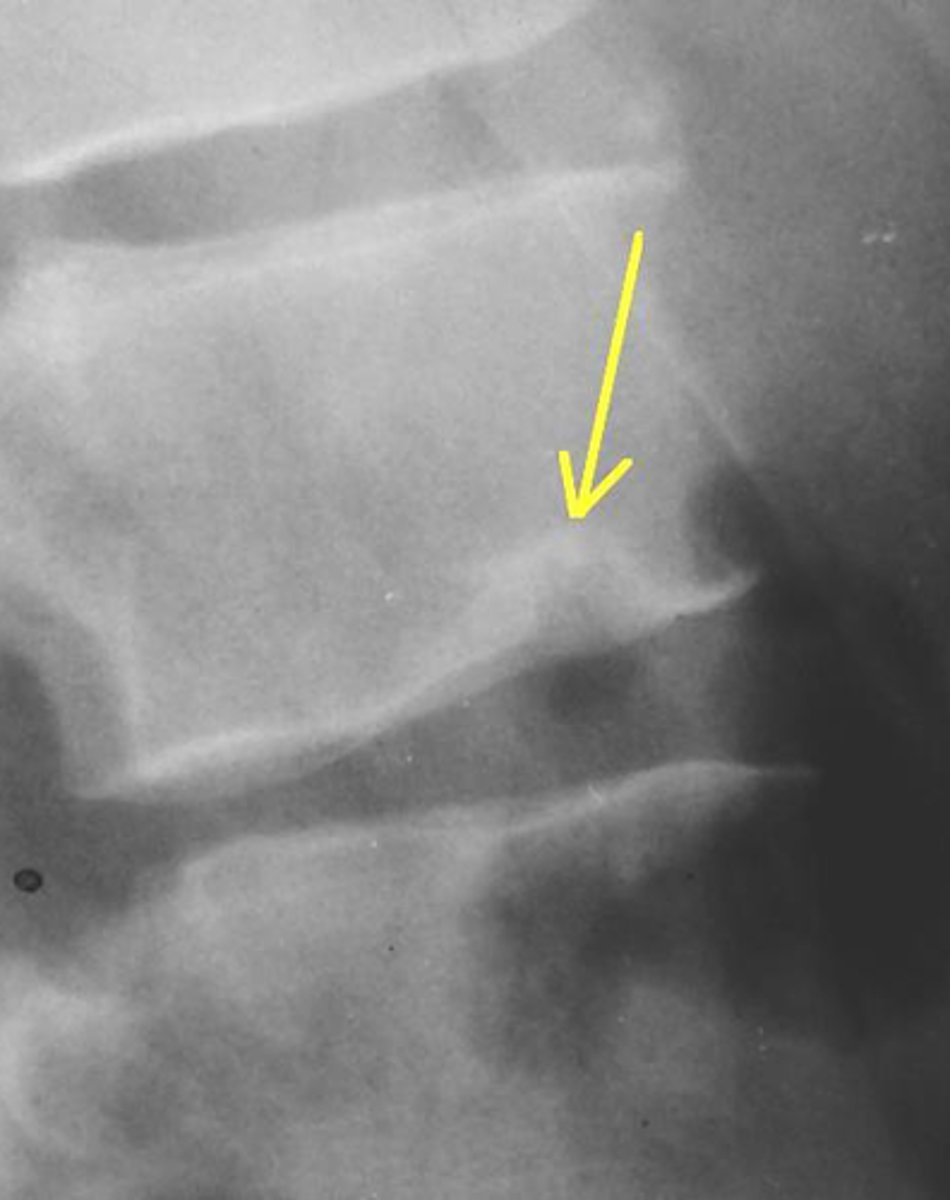
which dx is commonly seen in athletes who hyperextended the spine?
spondylolysis → defect of pars interarticularis withOUT forward slippage
which dx involves forward slippage or displacement of vertebrae?
spondylolisthesis
what is seen on PE in spondylolisthesis?
palpable "step off" at lumbosacral area, hamstring tightness, localized back pain worse with standing straight
if a 14 year old female presents with papules on elbow and knees as well as a rash on her eyelids, how would you treat?
juvenile dermatomyositis → tx with prednisone
rash = heliotrope rash
papules = gottrons papules
what is considered a fever in a peds patient?
100.4 F*** or 38C
which route for temperature is best for age 0-3 months? which routes are most accurate?
0-3 →rectal (axillary second line)
most accurate = rectal and oral
which dx starts as a sandpaper rash and involves strawberry tongue with circumoral pallor?
scarlet fever → rash spreads over trunk/extremities and desquamates
what is the 1st line tx for scarlet fever?
PCN G***
2nd line = cefdinir, clinda, azithro
what are the complications of scarlet fever?
rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis
which dx appears as honey-colored crust?
impetigo → affects epidermis only
what is the etio of impetigo?
S. aureus is MC***
also s. pyogenes
what is the tx for impetigo?
mild = mupirocin
severe = keflex/clarithro
where is folliculitis MC found? what is the etiology?
scalp, face, extensors of extremities
S. aureus
what is seen in the different stages of lyme disease?
early localized → erythema migrans
early disseminated → flu-like sx, neuro/cardio sx
late → arthritis (knee MC)
how is lyme disease diagnosed?
ELISA and Western Blot to confirm
tx with doxy
which dx has a rash that begins on wrists/ankles and spreads centripetally and becomes petechial?
RMSF → rickettsia rickettsi***
tx with doxy
which dx involves a fine, maculopapular rash that starts on the face and spreads cephalocaudally?
Rubella (german measels) → spares palms/soles
which dx has forchheimer spots?
Rubella
which dx involves koplik spots and a red blanching rash that spreads cephalocaudally?
rubeola (measels) → multinucleated giant cells seen
what can decrease the length of sx in rubeola?
vitamin A
what is the varicella prodrome?
fever, malaise, anorexia
proceeds to "dewdrop on a rose petal" vesicles that begin on face and spread to trunk and extremities***
what is the only exanthem that begins on the trunk?
roseola infantum "6th dz" → HHV6 etio
which dx involves a malar exanthem and lacy red rash on extensors, trunk, and butt?
erythema infectiosum "5th dz" → etio parvo B19
which dx involves a blueberry muffin rash, cataracts, microcephaly, and sensorineural hearing loss?
congenital rubella→ also has congenital heart dz and stillbirth
what is the prodrome for rubeola?
fever, malaise, dry cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis***
which dx has a malar exanthem with circumoral pallor?
erythema infectiosum "5th dz and slapped cheek"***
which dx is defined by breast tissue development in children aged 1-4 without pubic hair or linear growth?
premature thelarche
normal if < 2 y/o***
which dx has sx of moon face, buffalo hump, central obesity, impaired growth, and thin/bruised skin?
Cushing syndrome
what test is used to dx cushing's syndrome?
24 hr urine free cortisol and dexamethasone suppression test***
what is the MC cause of hyperthyroidism?
Grave's dz → heat intolerance, exophthalamos, HA, fatigue, diarrhea, appetite changes
what is the treatment for hyperthyroidism?
methimazole
what is the MC cause of hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis → short stature, brittle nails, thin hair and eyebrows, bradycardia, delayed DTRs
which dx is characterized by infertility, ovulatory dysfunction, and hyperandrogenism?
PCOS → acne, hirsutism, amenorrhea, thin scalp hair, acanthosis nigricans, ovarian cysts
what do labs looks like in PCOS?
↑ prolactin, LH, DHEA & testosterone
↓ TSH & FSH
what is the tx for PCOS?
metformin**, diet/exercise, endo referral**
which dx is characterized by excessive GH after epiphyseal closure?
acromegaly → large doughy hands, coarse face features, cardiomegaly, tooth space widened, wide feet
what is measured to diagnose acromegaly?
IGF-1
OGTT
MRI (pituitary tumor)
what is the tx for acromegaly?
octreotide, cabergoline
which dx involves weight loss, SQ wasting, hyperpigmentation in flexural regions and has tx of lifelong corticosteroids?
Addison disease
what is the MCC of primary adrenal insufficiency?
congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) → d/t 21-hydroxylase deficiency
what is the MC bone dysplasia?
Achondroplasia → autosomal dominant mutation of FGFR3 gene
in which dx do patients have disproportionate short stature, short limbs, and a long narrow trunk?
achondroplasia
what are the s/sx of diabetes insipidus in children?
infant = poor feeding, slow growth, FTT
older children = polyuria, polydipsia
general: enuresis, pale dry skin, inability to sweat
what is the treatment for central DI?
DDAVP
how is DI diagnosed?
24 hr urine, serum Na and ADH, water deprivation
what is the treatment for nephrogenic DI?
thiazides, K+ supp, indomethacin
which dx has serum antibodies against pancreatic islet cells?
T1DM → labs show low fasting c-peptide and insulin with concomitant hyperglycemia
which dx presents with proteinuria, hyperglycemia, and hyponatremia?
DKA → also kussmaul respiration, fruity breath, AMS
what is a complication of DKA? how do you treat?
cerebral edema → IV mannitol, stat neurosurg consult
which dx has hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, relative impariment in insulin secretion?
T2DM
which dx is characterized by delayed bone age but normal growth velocity?
constitutional growth delay *** → non-pathological cause of short stature "late bloomers"
in which dx do patients have low linear growth within in the first 3 years then resume to normal rate?
constitutional growth delay
do patients with familial short stature have delayed puberty and abnormal growth velocity?
no, everything is normal just growth curve at/below 3-5th percentile
is bone age consistent with chronological age in familial short stature?
YES → not in congenital growth delay
which dx presents with cafe au lait spots, axillary/body/pubic hair, breast tissue or scrotal thinning in females <8** and males <9**?
precocious puberty → sex hormones not appropriate for age → bone XR advanced beyond chronological age
what is the tx for precocious puberty?
histrelin or leuprolide (GRH agonists) therapy
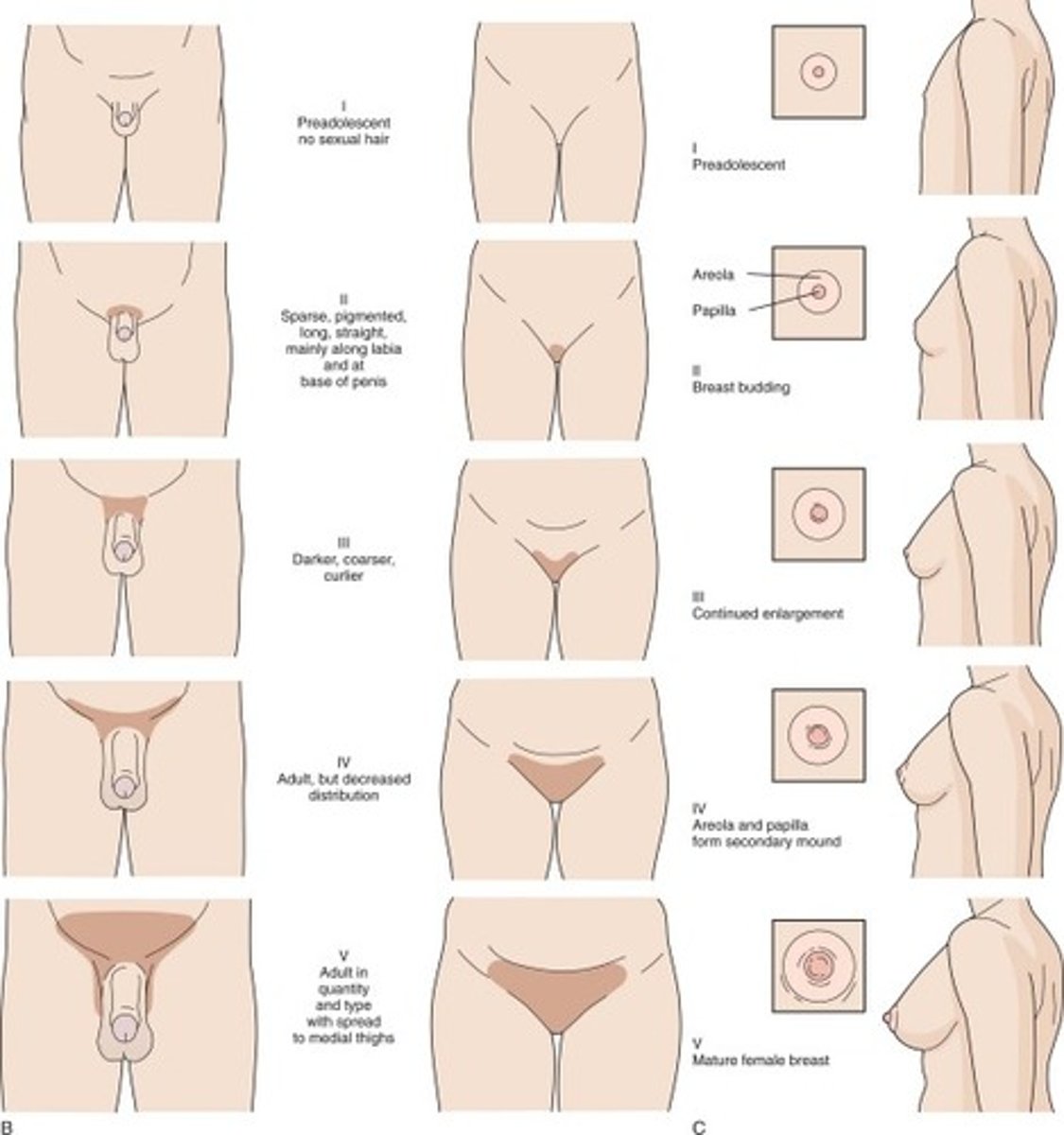
tanner stages
***
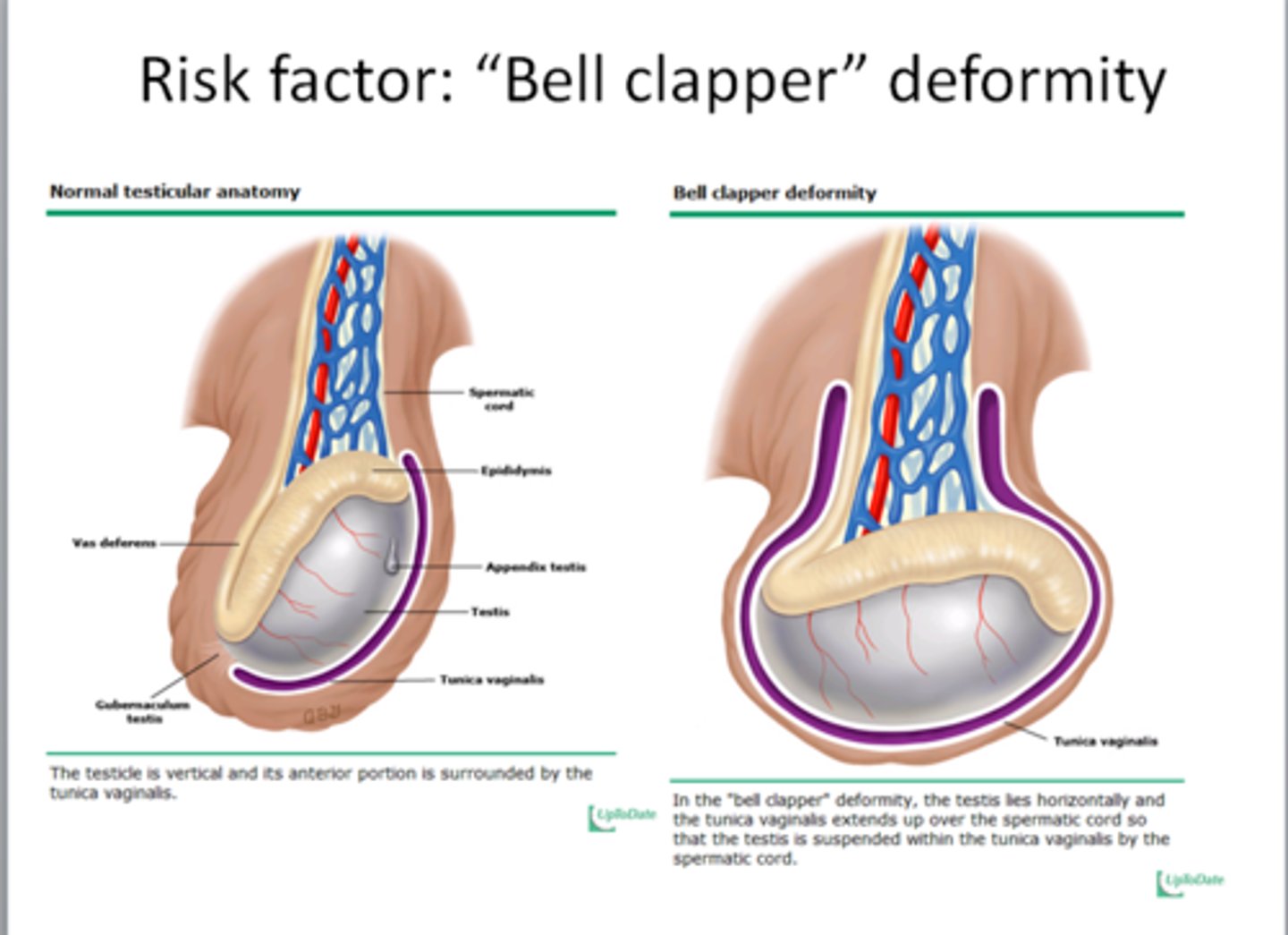
if an adolescent presents with acute testicular pain and swelling and absent cremasteric reflex, what would you order to confirm the dx?
testicular torsion ***→ scrotal US with doppler
which dx is associated with a bell and clapper deformity?
testicular torsion
what is the blue dot sign?
when gangrenous appendix of testis is seen through the scrotum in torsion
what is the treatment for testicular torsion?
stat uro consult, manual detorsion, surgical orchiopexy
torsion of appendix testis = no tx, resolves
what is the etiology of orchitis?
coxsackie B
mumps (unvaxxed)***
trauma
what is the typical presentation of orchitis?
typically occurs 5-10 days after parotitis, testicles are swollen and tender, fever
what is the failure of midline penile fusion?
epispadias → assoc with bladder exstrophy
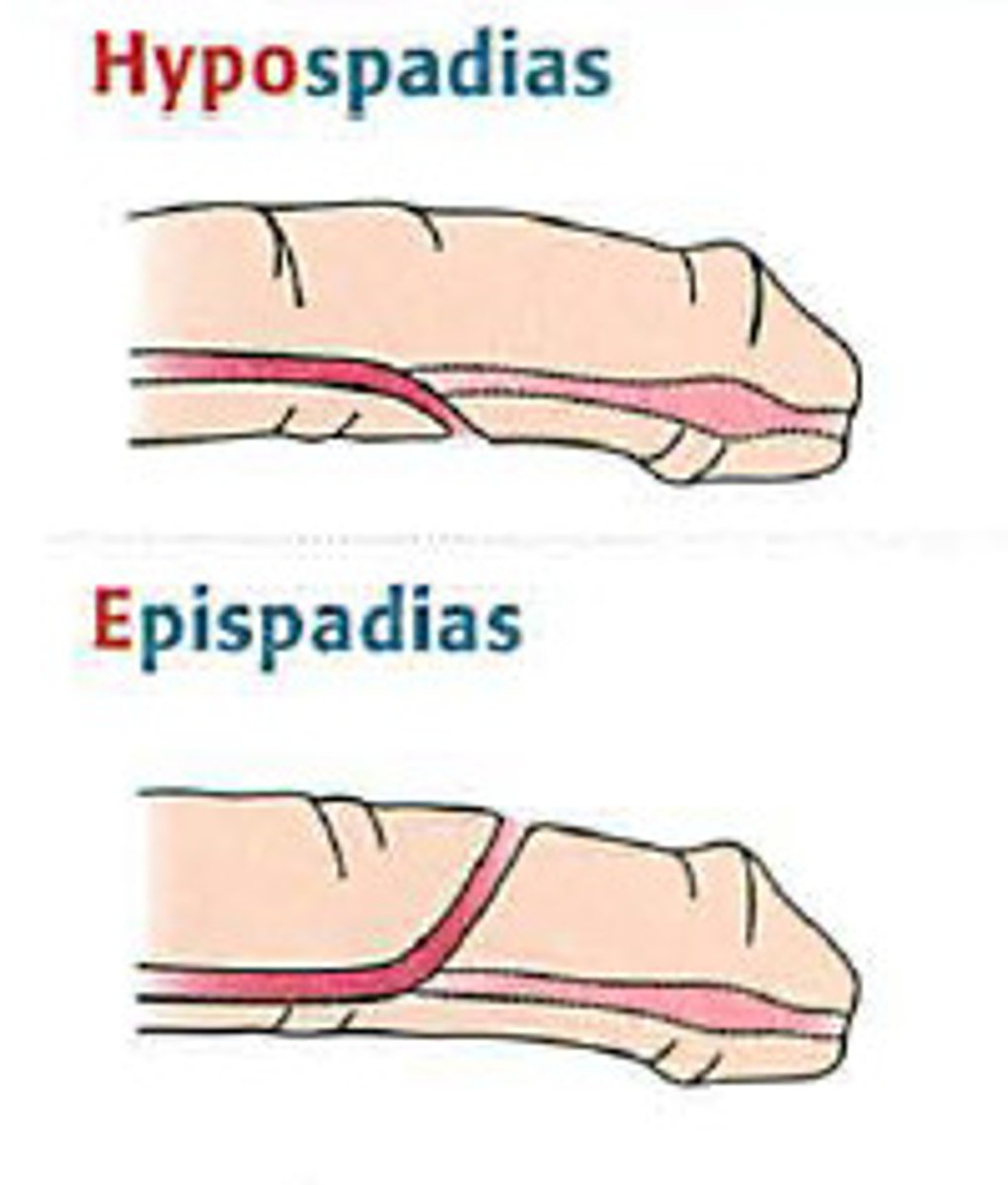
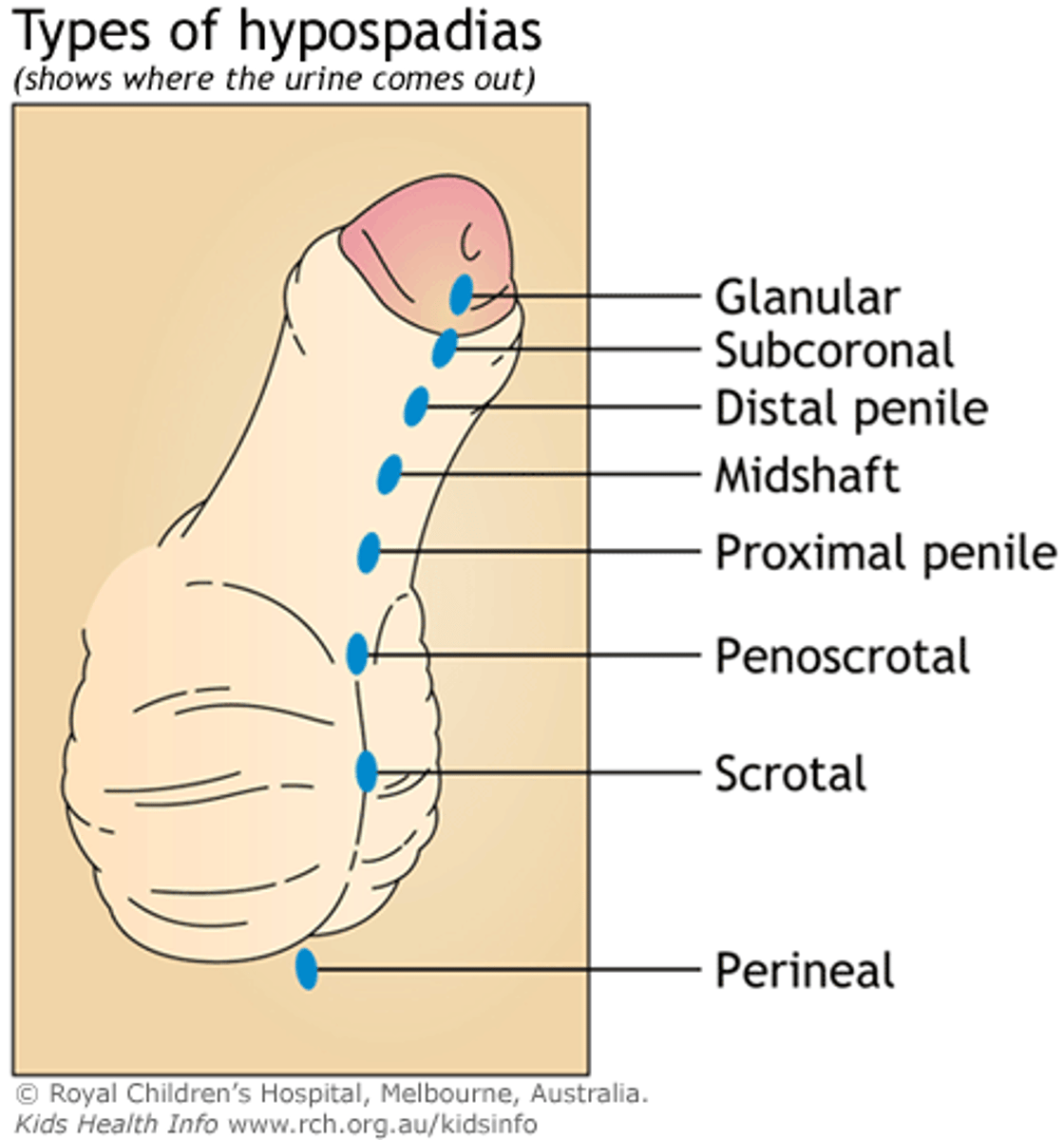
what is the MC urethral anomaly?
hypospadias ***→ birth defect of abnormally placed urinary meatus
what is the MC congenital abnormality of the GU tract?
cryptorchidism → undescended testicle (sometimes absent) (unilateral or bilateral)
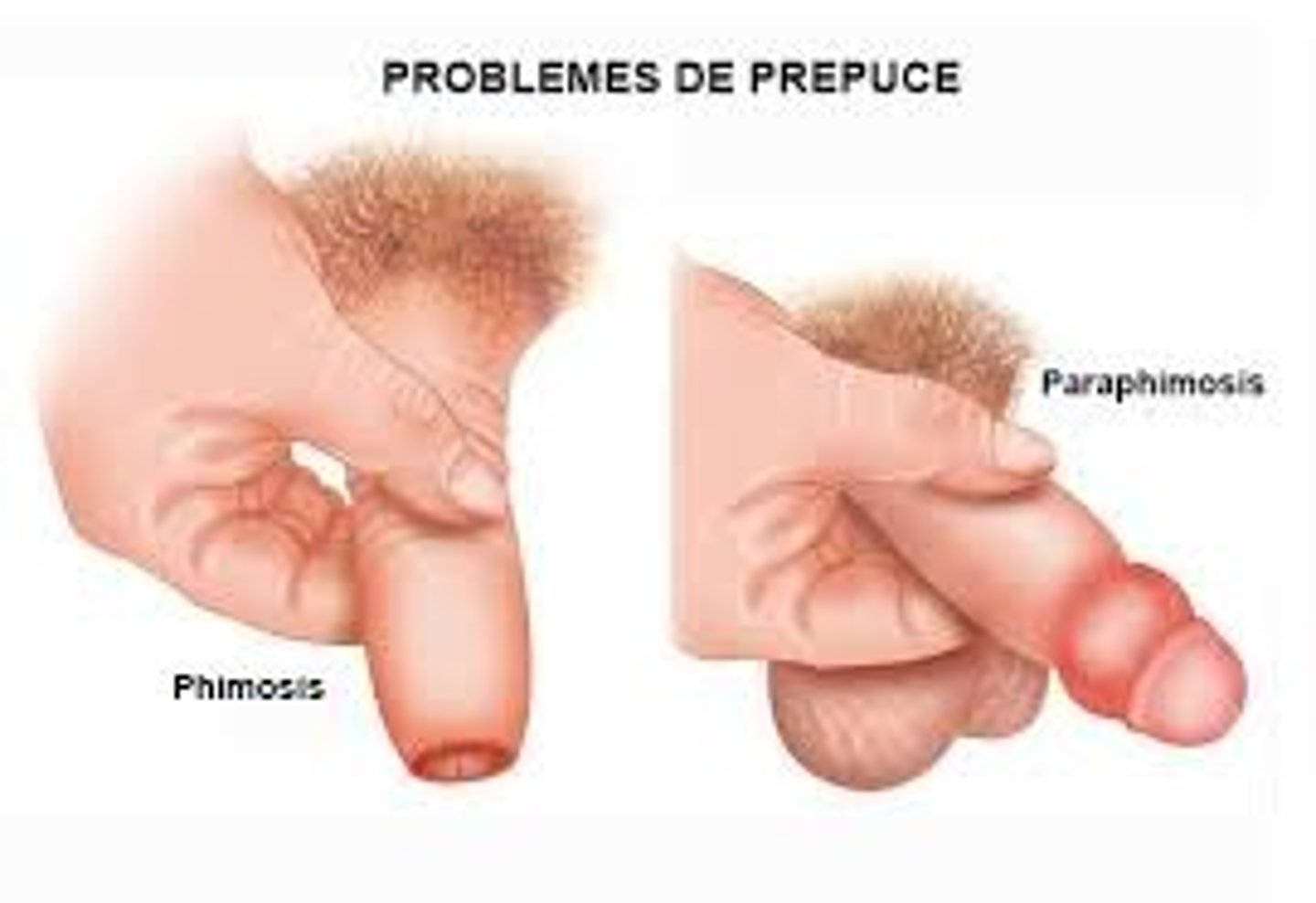
what is defined by the inability to retract foreskin?
phimosis → can result form repeated balanitis → tx with circumcision
who is more likely to experience nocturnal enuresis?
males <12
what is the treatment for nocturnal enuresis?
desmopressin (DDVAP) or imipramine
what are causes and contributing factors for nocturnal enuresis?
causes → UTI, T1DM, stress, DI, CKD, hormones, sleep apnea
contributing factors → small bladder, excess urine formation during sleep, problem with sleep arousal, uninhibited detrusor contractions
what is retracted foreskin that cannot be returned to normal position?
paraphimosis
what is the MC type of acute kidney injury (AKI) in peds population?
prerenal** → caused by dehydration*, HF, sepsis, anaphylaxis
what is the MCC of renal (intrinsic) AKI?
acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
what are causes of post renal AKI?
obstruction → stones, neurogenic bladder, anticholinergics
what is the hallmark finding of AKI?
oliguria
which dx is characterized by injury to the kidney resulting in increased BUN and Cr?
acute tubular necrosis → damage to the renal tubules
what is seen on UA in ATN?
muddy brown
granular casts
epithelial casts
which dx is characterized by injury/disease that increases permeability to the glomerular filtration barrier?
nephrotic syndrome
what is seen on labs and PE in nephrotic syndrome?
proteinuria
hypoalbuminemia
edema
HLD
dyspnea
ascites
periorbital edema
in which dx does UA show proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia?
nephrotic syndrome→ tx with salt restriction, diuretics, adequate protein, etc
what is the MC form of primary glomerulonephritis?
IgA nephropathy (Berger's dz)→ characterized by IgA deposits in glomerulus of kidney