Cognitive Psychology - Memory - Catching the Moment
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Semantic Memory
Memory of context-independent facts
Episodic Memory
Memory of unique events
What are the components of Episodic Memory?
Details
Context
Associations
What is the effect of Amnesia?
Impaired episodic memory due to hippocampal damage.
Why is the hippocampus crucial to Episodic Memory?
Because it binds details of content → context to create memories.
How is Episodic Memory tested in the Lab?
Study Phase: Encoding Mini-Events
Test Phase: Retrieving the Mini-Events
What are the stages of Memory?
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
What is the effect of Divided Attention on Memory?
Divided Attention during encoding impairs memory.
What does fMRI scanning show about encoding attended (vs unattended) event features?
Attended features:
Had boosted memory (when attention was paid)
Increased hippocampus activation for encoding features
Suggests attention is critical for encoding new memories and modifying input to hippocampus.
Dual Code Theory (Paivio, 1971)
Theory suggesting:
Image + verbal code → richer memory traces.
Distinctiveness Theory (Von Restorff)
Theory suggesting memory is boosted by processing differences in the context of similarity (like identifying “odd ones out”)
Evidence for Distinctiveness Theory and the Picture Superiority Effect
Ensor et al (2019): Made memory distinctive words using colour and fonts.
What features make information memorable? (Borkin et al., 2013)
Objects, colour and complexity made data visualisations memorable. Whereas scientific figures do not perform well.
What are some models (evidence) of Image Memorability?
Image Feature Model (Bylinski et al., 2015): Distinctive images that stand out from their context are more memorable.
Naspi et al (2021): Images are less memorable when their concepts share more features with other concepts.
How does schema-related information affect memory? (Van Kesteren, et al., 2014)
Memory improves for course-related schema information studied within degree courses.
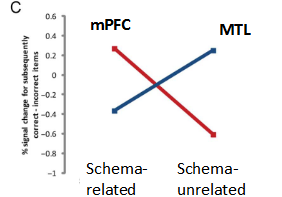
What brain areas are activated for new schema-related facts? (Van Kesteren et al., 2014)
PFC: More activation.
MTL: Less activation.
What is the Baker-Baker Paradox?
Phenomenon where processing information for meaning (semantic/deep processing) improves memory encoding.
What area of the brain is associated with processing?
Brain network including the Ventrolateral PFC is activated by non-semantic and semantic (even more) processing. Region is also activated when words are successfully encoded in memory.
How does elaboration improve Memory processing?
Semantic processing involves relating new material to your prior knowledge - even just naming
Deliberate elaboration means going further and may work by distinctive processing as well as meaning
What is memory encoding a by-product of?
Processing
What are the roles of the DLPFC and VLPFC in memory?
DLPFC: Aids encoding and organises recall by meaning.
VLPFC: Aids in semantic (deep) encoding.
What is the effect of distinctiveness on facial recognition? (Carr et al., 2013)
fMRI has shown that faces are more likely to be recollected if they are distinctive compared with similar faces. When encoding memories, processing for distinctiveness boosted hippocampus activity.