Biol 1406 Exam 2 DC
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes both the "mosaic" arrangement of proteins embedded throughout the lipid bilayer as well as the "fluid" movement of lipids and proteins alike.
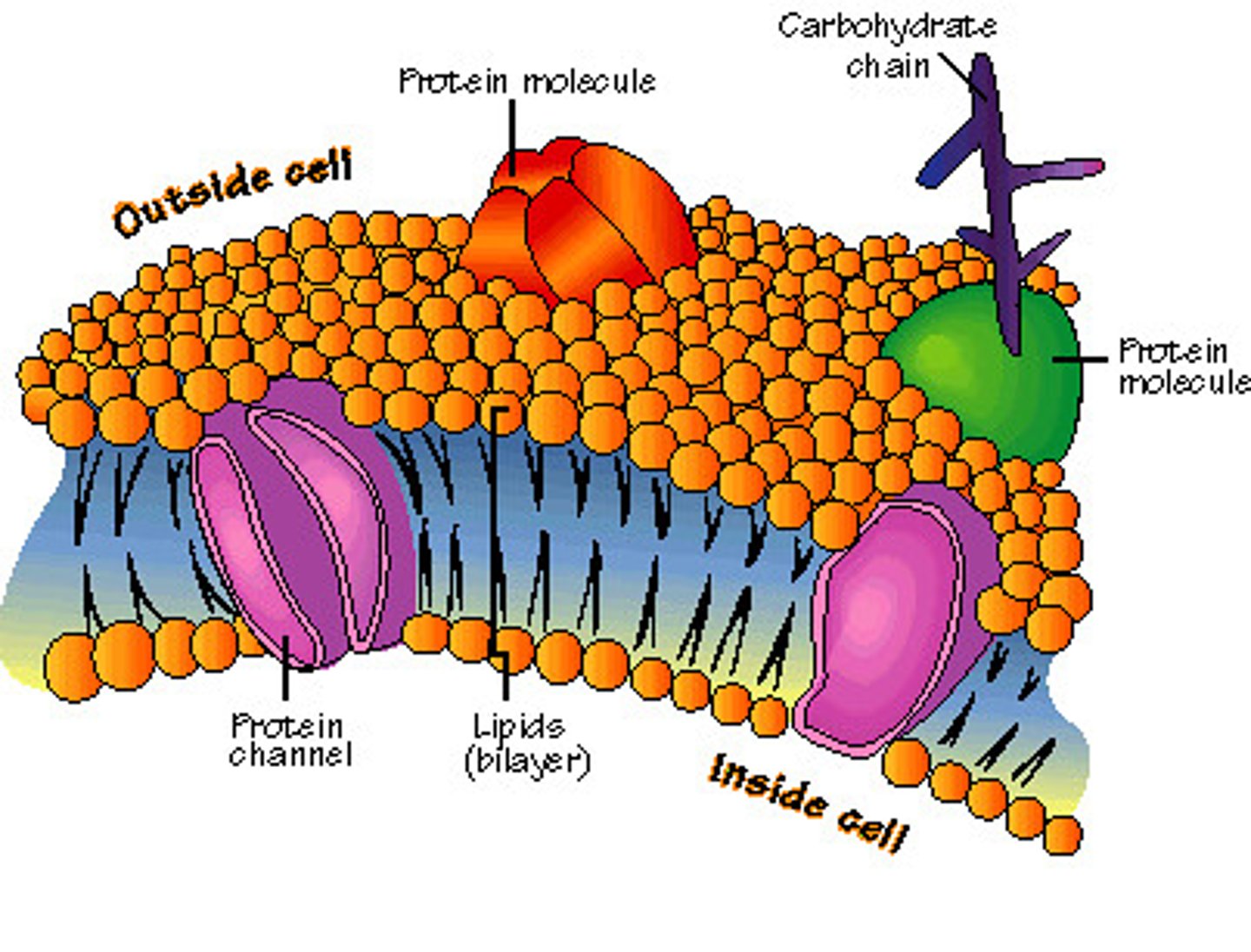
Selective permeability
Describes how the cell membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell -- not everything can get in or out -- it selects what can get in and out
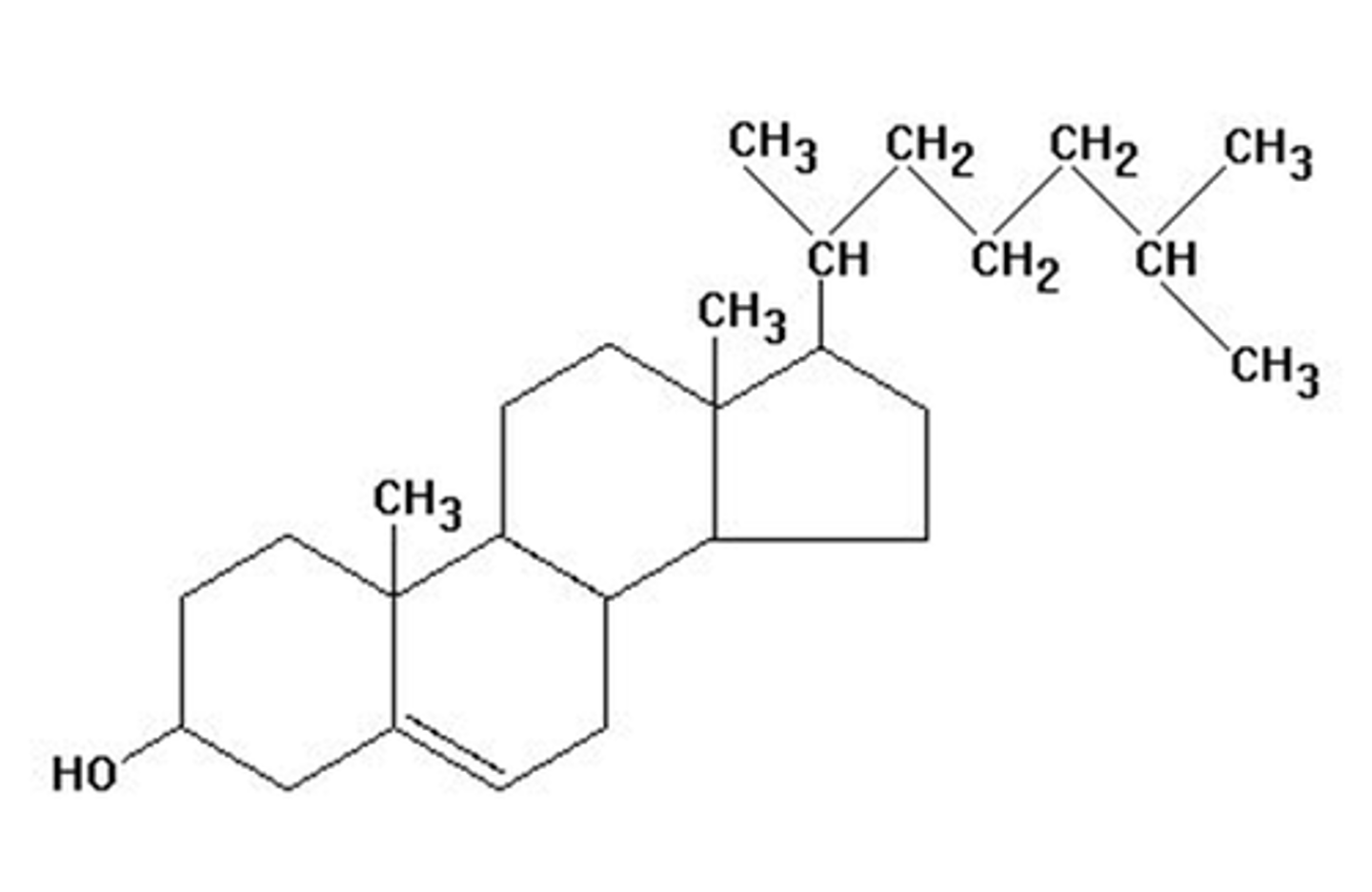
Cholesterol
Lipid molecule found in animal cell membranes that contributes to the stability and fluidity of the cell membrane.
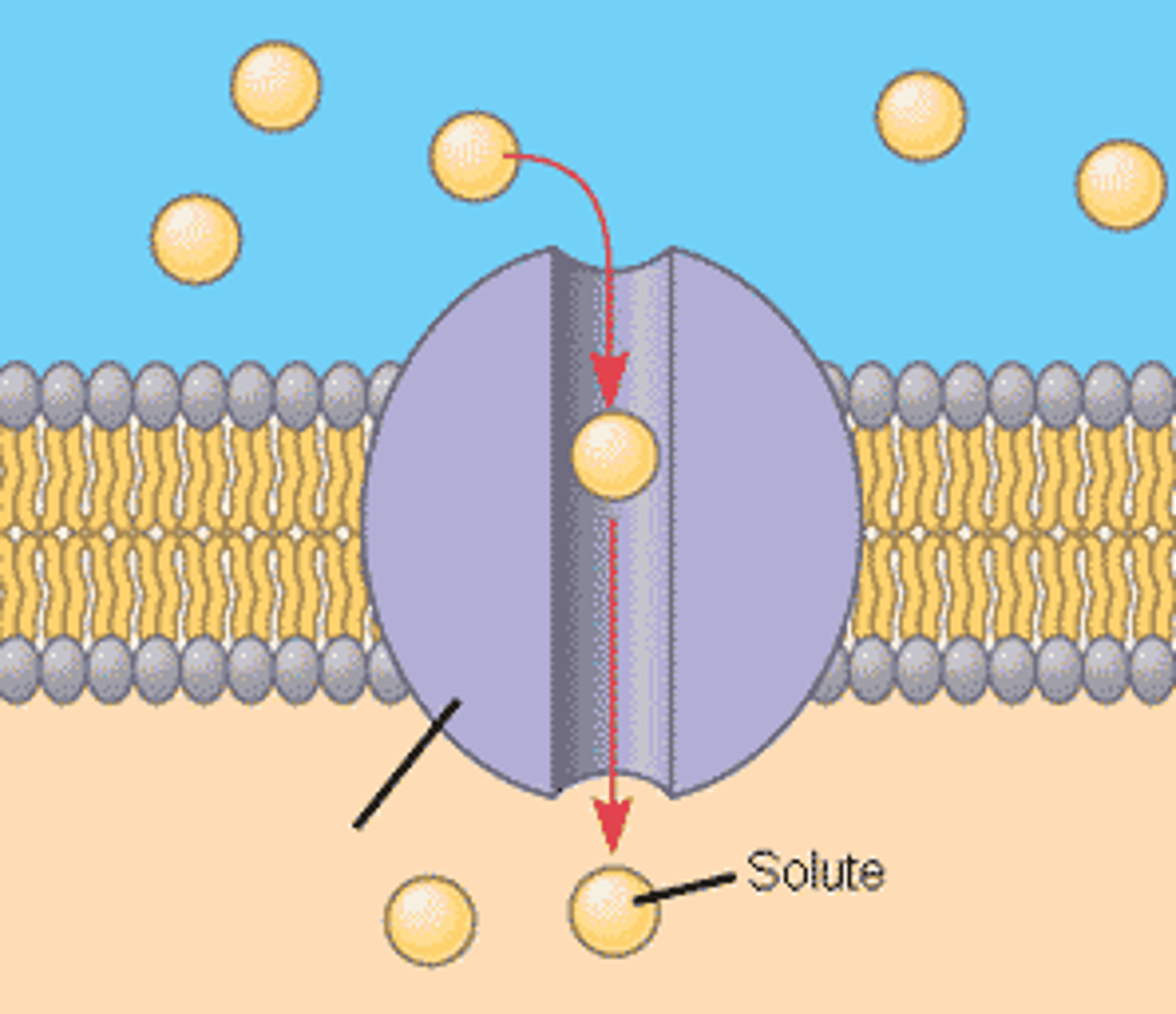
Channel Protein
Integral protein involved in facilitated diffusion.
Glycoprotein (protein with carb chain)
Peripheral protein with a carbohydrate association that is involved in cell recognition and identification of cell type.
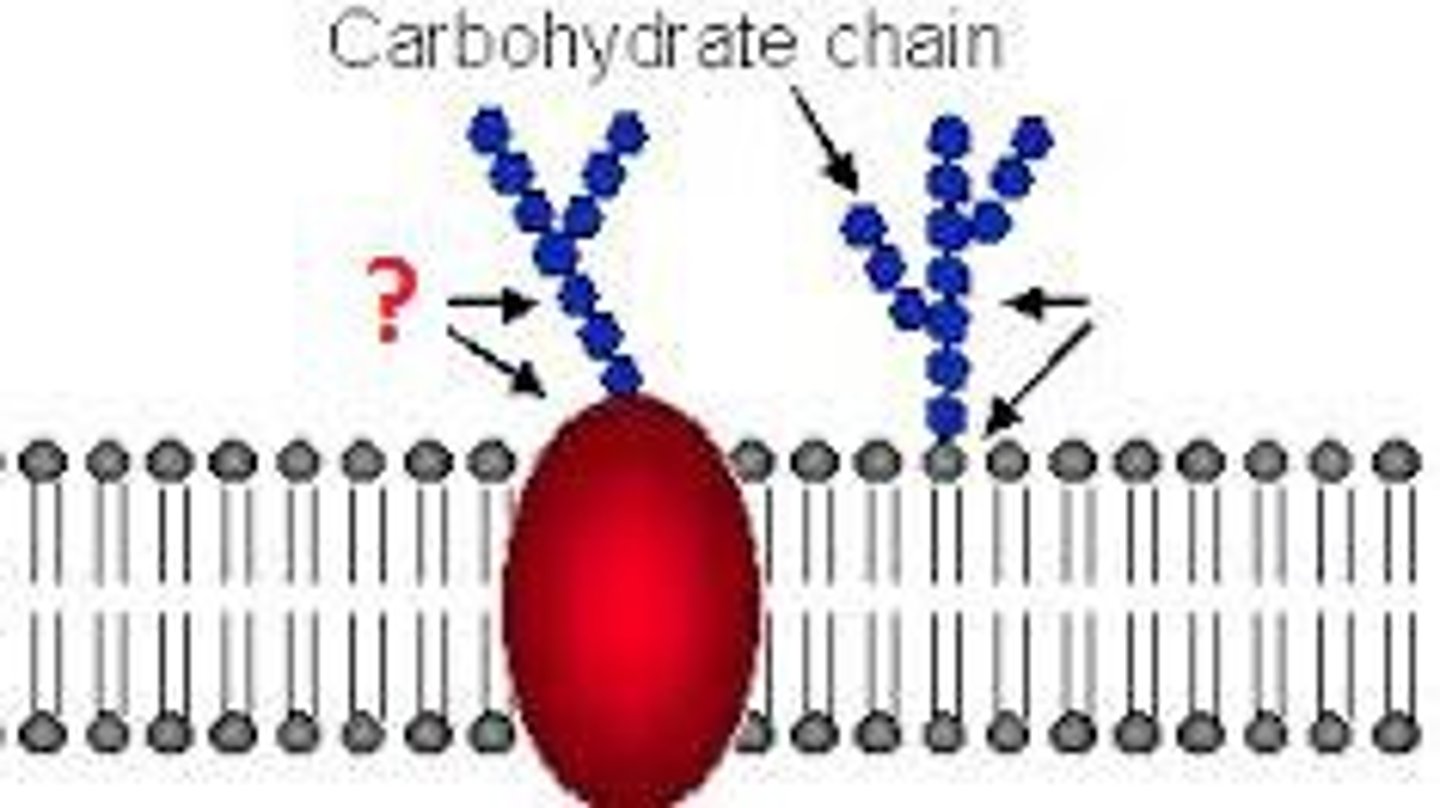
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water.
Hydrophobic
Repelled by water.
Phosphate head
Polar region of the phospholipid that is hydrophilic.
Fatty acid tails
Nonpolar region of the phospholipid that is hydrophobic.
Phospholipid
The major component of the cell membrane consisting of a hydrophilic (polar) head and hydrophobic (nonpolar) tails.
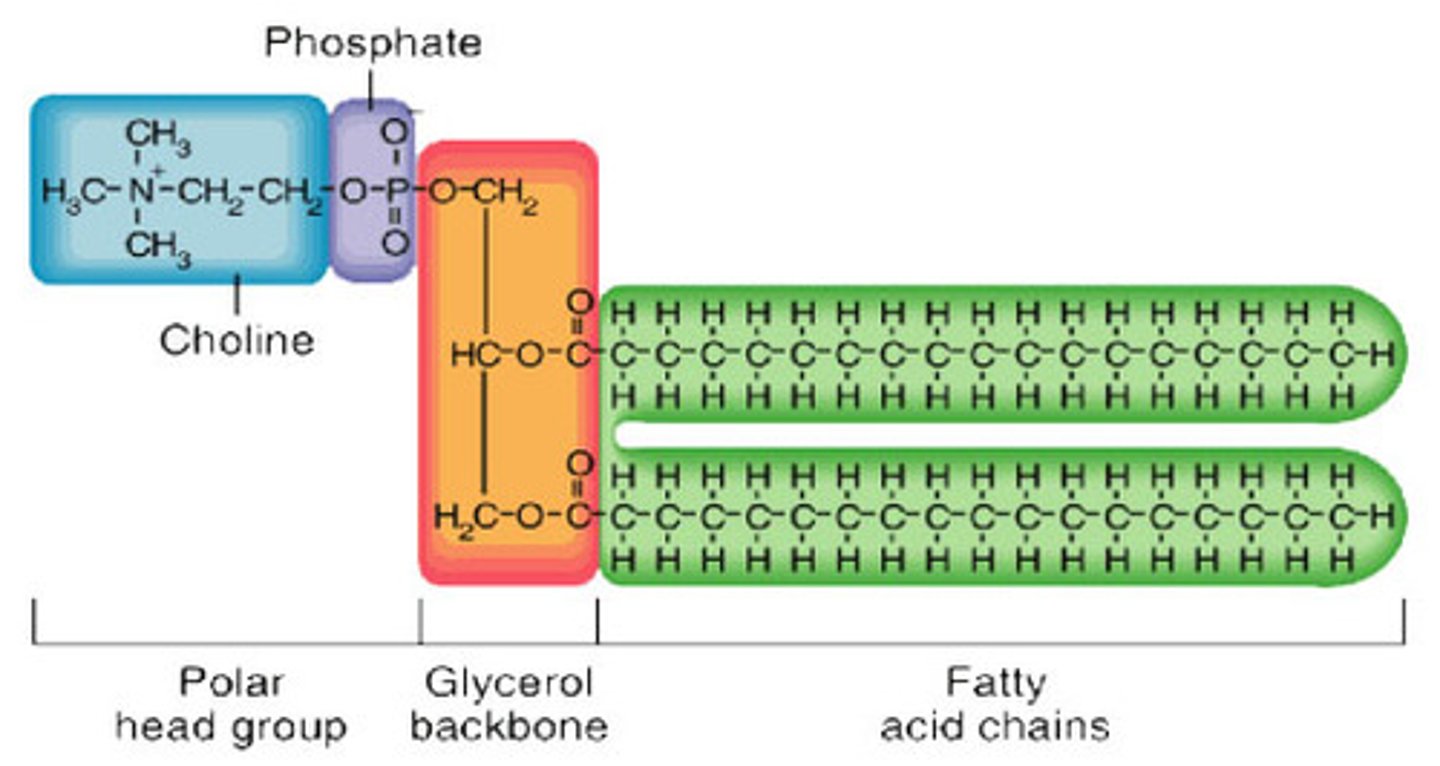
Phospholipid Bilayer
Describes how the phospholipids line up tail to tail
Passive Transport
This type of transport does not require energy because the molecules are moving down the concentration gradient (from an area of High concentration to an area of Low concentration).
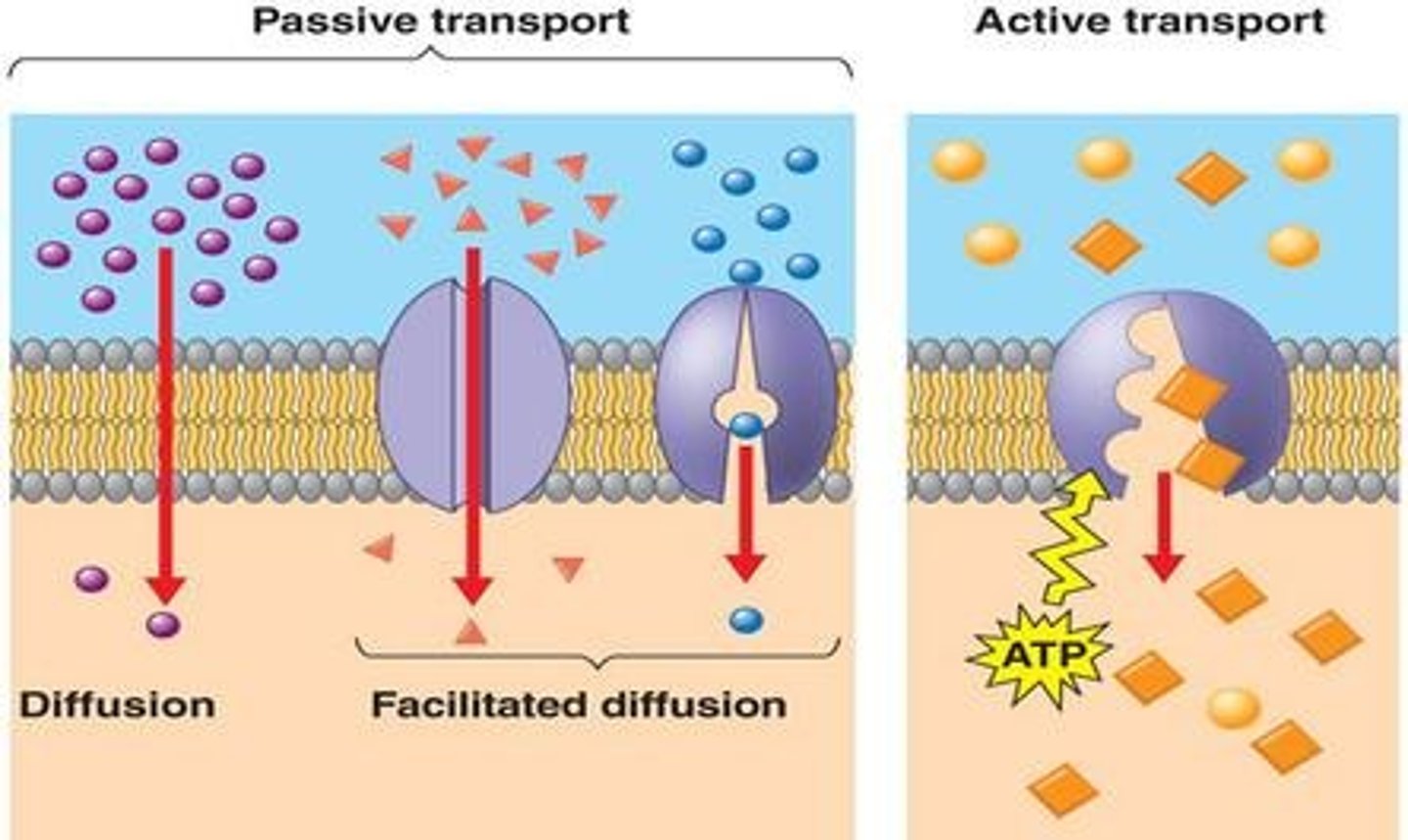
Active Transport
This type of transport requires energy because the molecules are being moved against their concentration gradient (from an area of Low concentration to an area of High concentration).
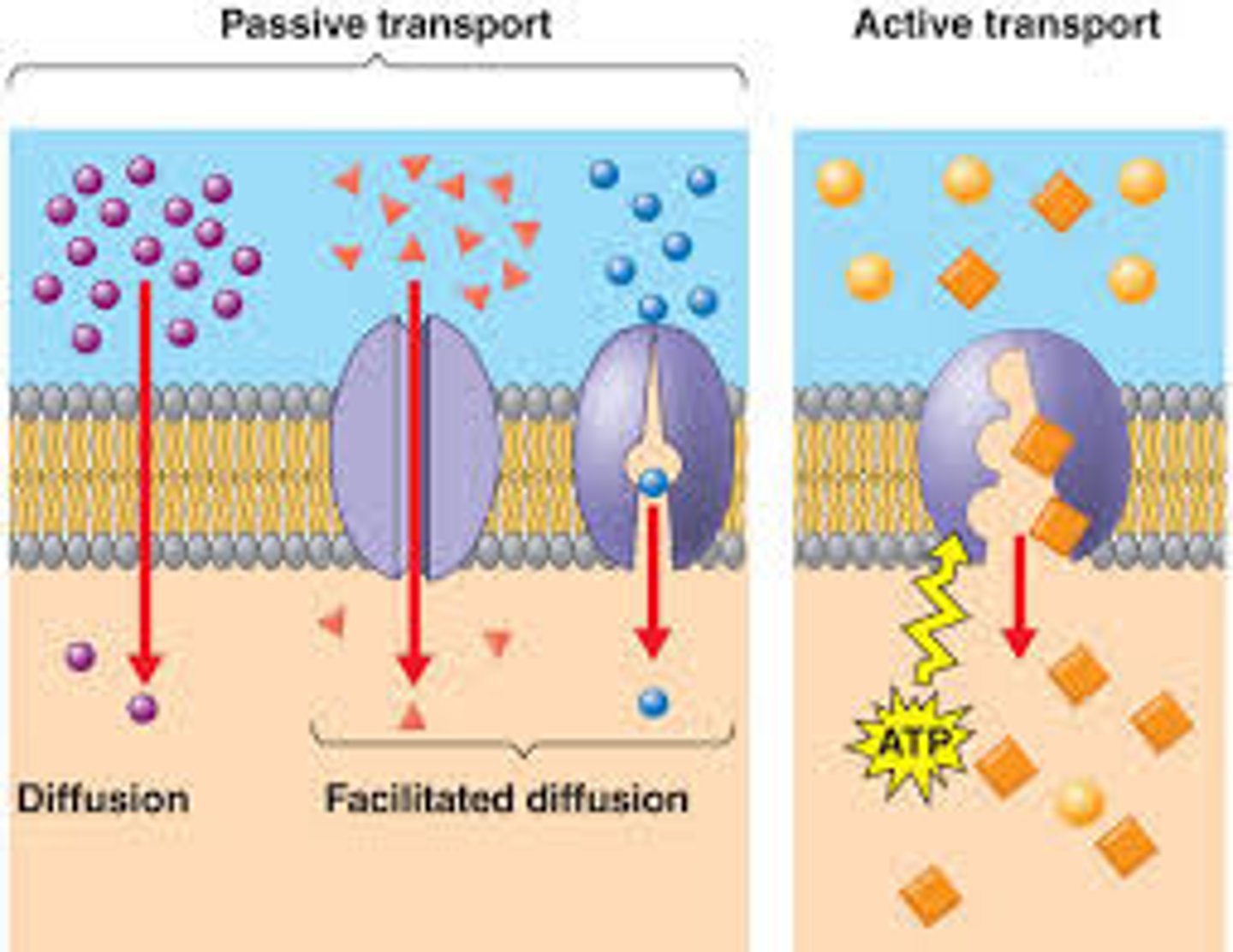
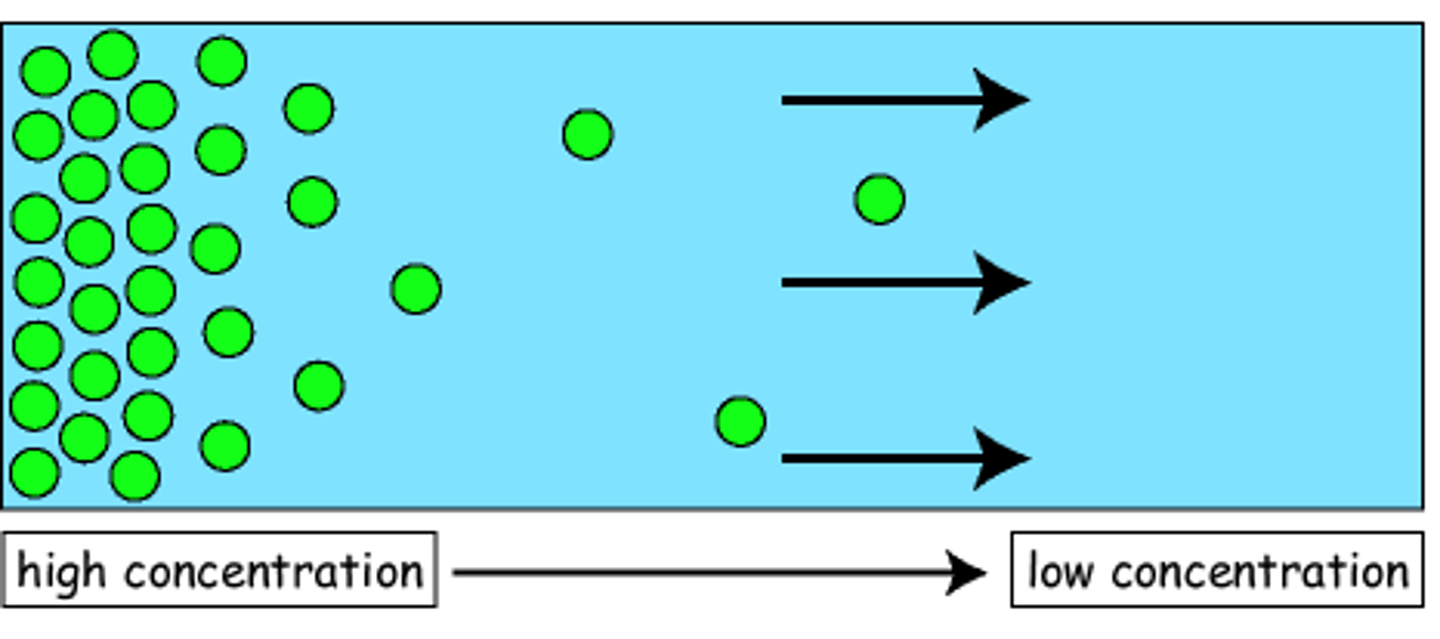
Diffusion
A type of passive transport that involves the movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration.
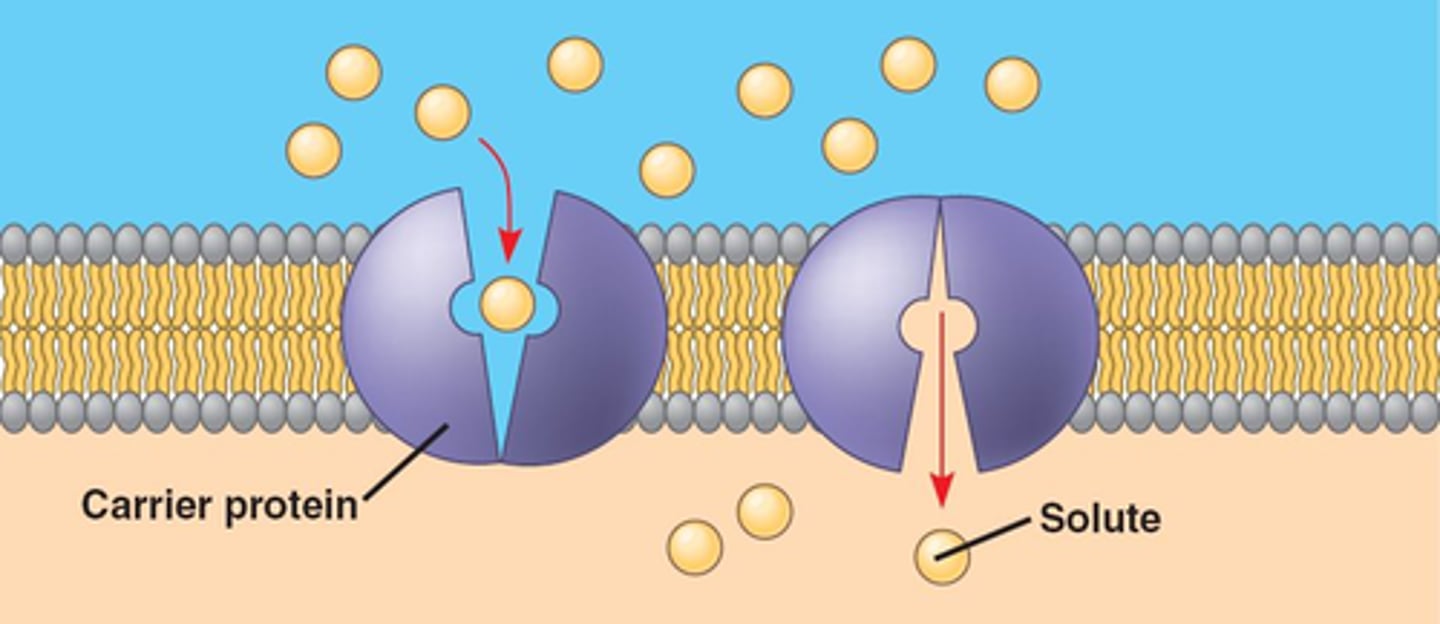
Facilitated Diffusion
A type of passive transport where special proteins in the cell help molecules move from a high concentration to a low concentration.
Osmosis
A type of passive transport - the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane.
Hypertonic Solution (hyperosmotic)
A solution that has a higher amount of solute. "SALT SUCKS" Ex: salt water, sugar water (Koolaid)
Hypotonic Solution (hypoosmotic)
A solution that has a lower amount of solute. Ex: distilled water
Isotonic Solution (isosmotic)
A solution that has an equal amount of solute as the inside of the cell. Water in - Water out.
antiporter
A carrier protein that transports two molecules across the plasma membrane in opposite directions.
symporters
move two molecules in the same direction
Uniporter
A carrier protein that transports a single molecule across the plasma membrane.
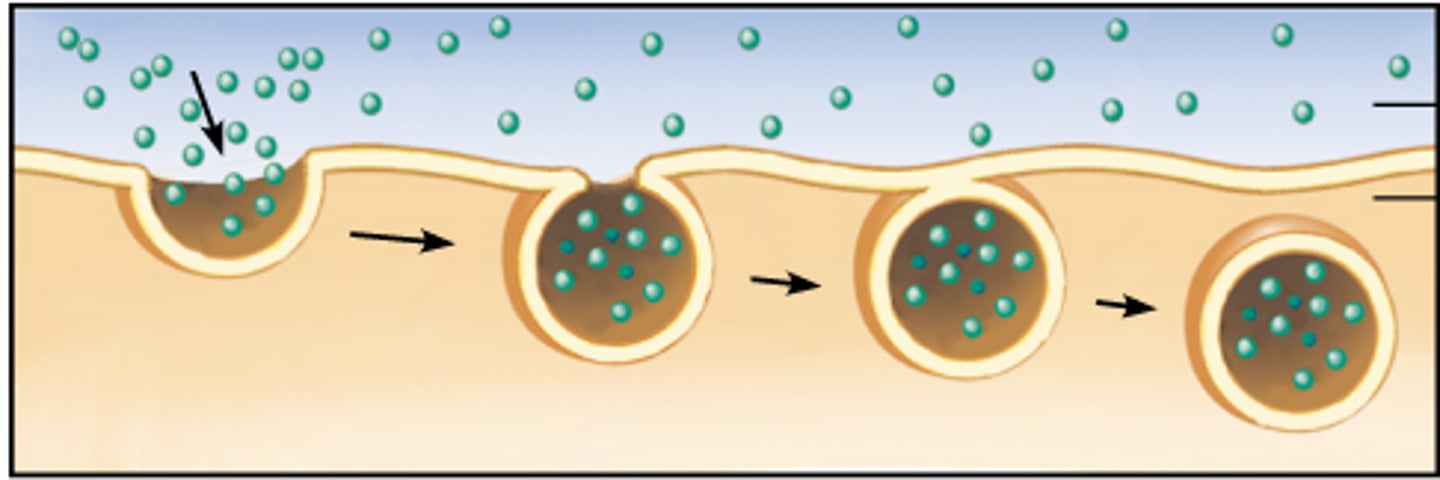
Endocytosis
A form of active transport where the cell engulfs large substances and takes them into the cell.
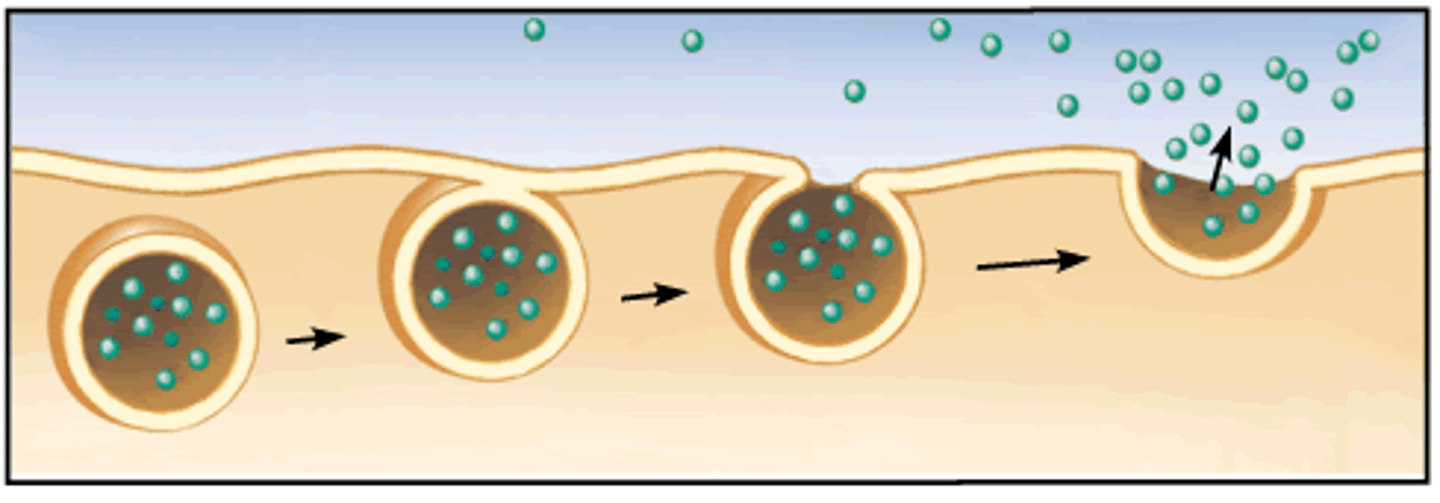
Exocytosis
A form of active transport where the cell secretes large substance out of the cell.
Phagocytosis
"cell eating" - type of endocytosis
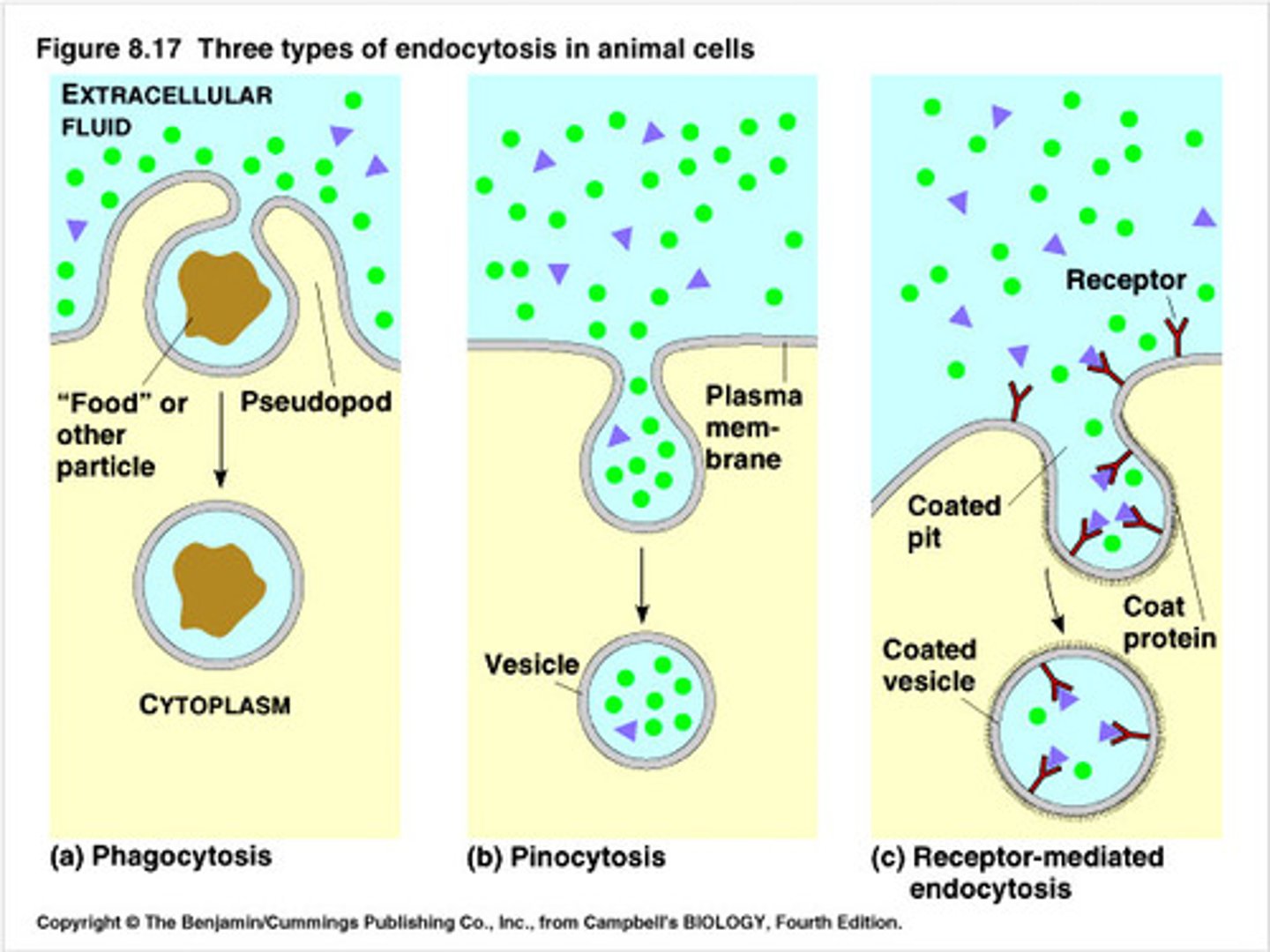
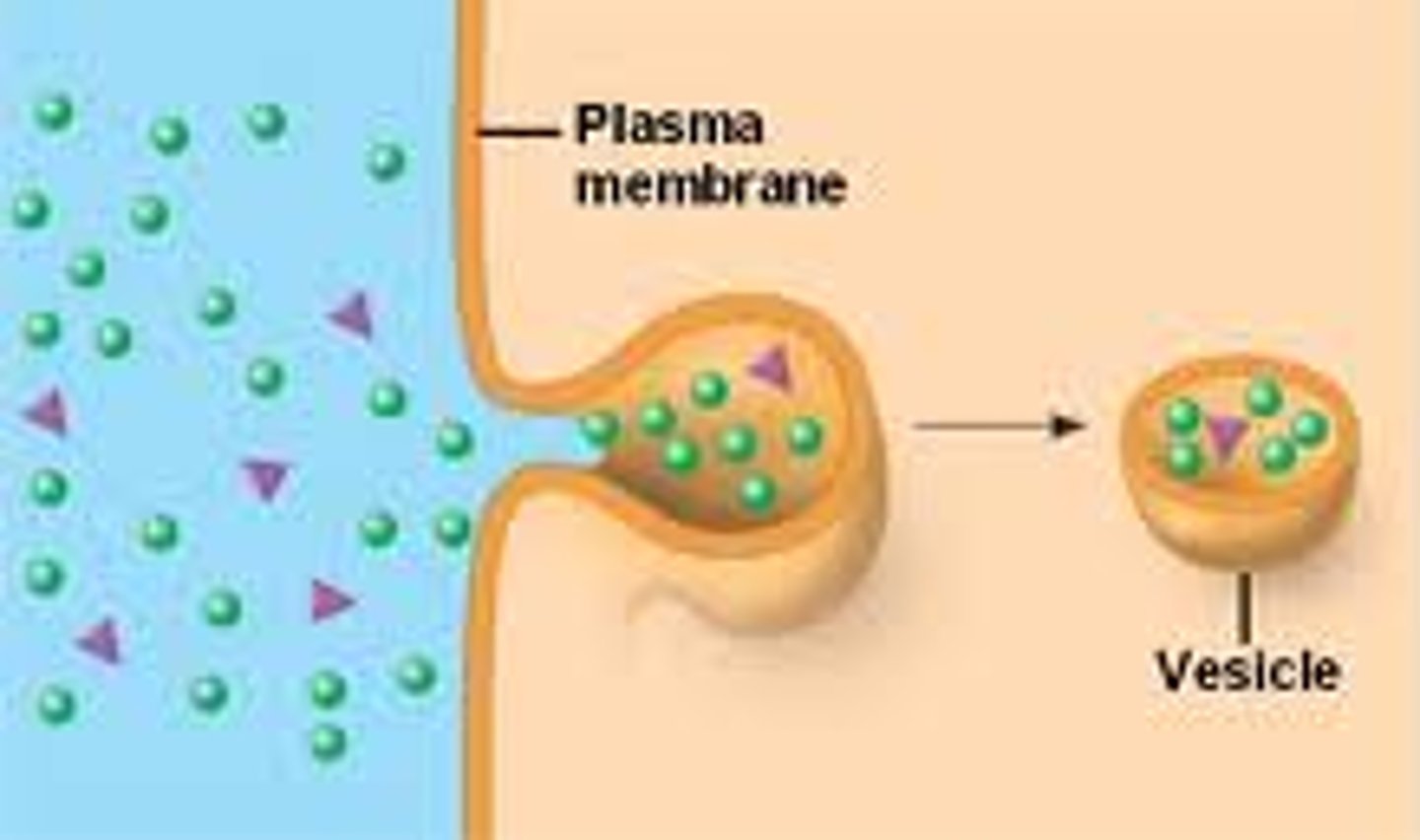
Pinocytosis
"cell drinking" - type of endocytosis taking in small amounts
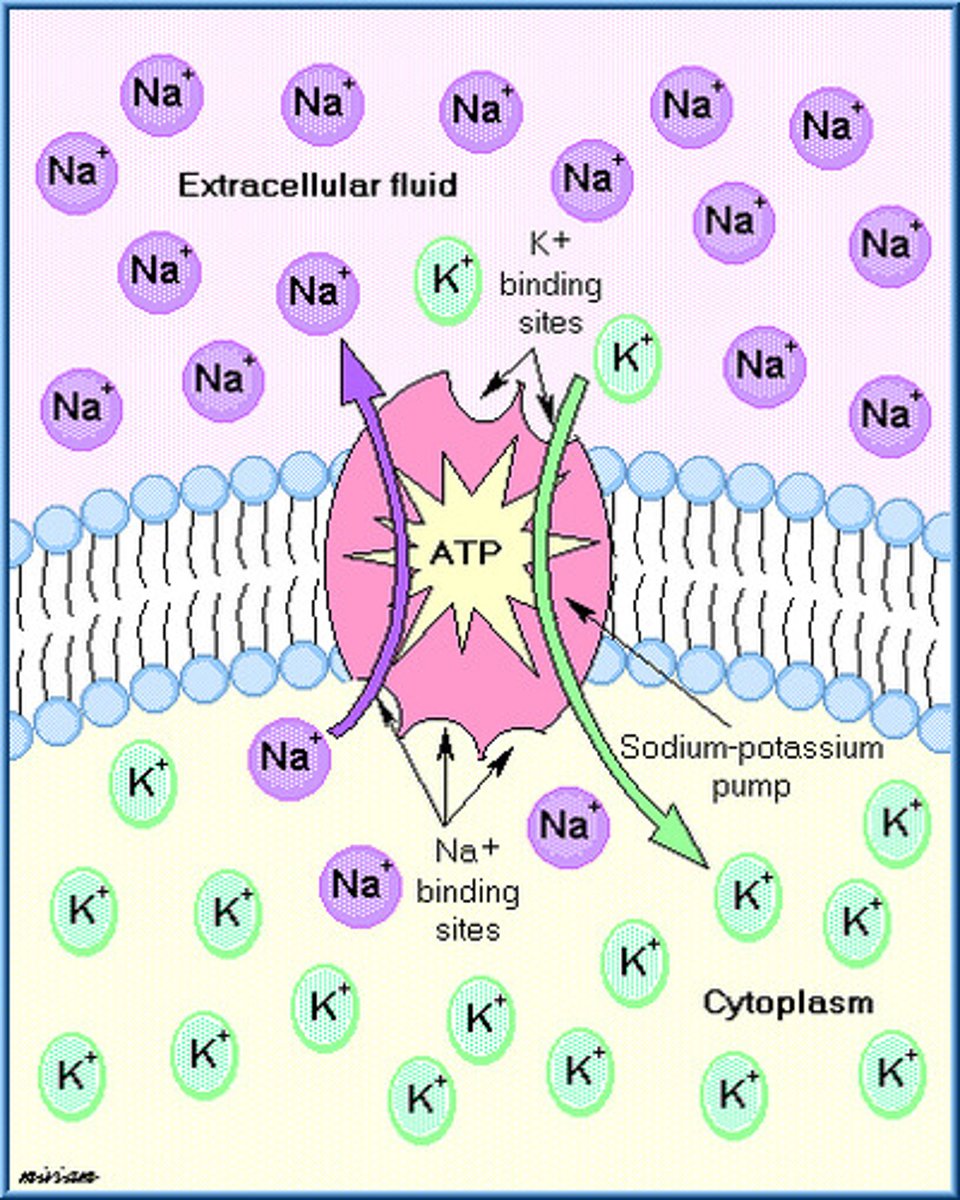
Sodium/Potassium Pump
Form of active transport that moves Na+ and K+ against their concentration gradient - important for the function of nerve cells.
Nonpolar amino acids in membrane proteins
hydrophobic and not soluble in water
Turgor Pressure
When a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution and gains a lot of water, the cell wall presses back on the cell membrane to prevent the cell from bursting.
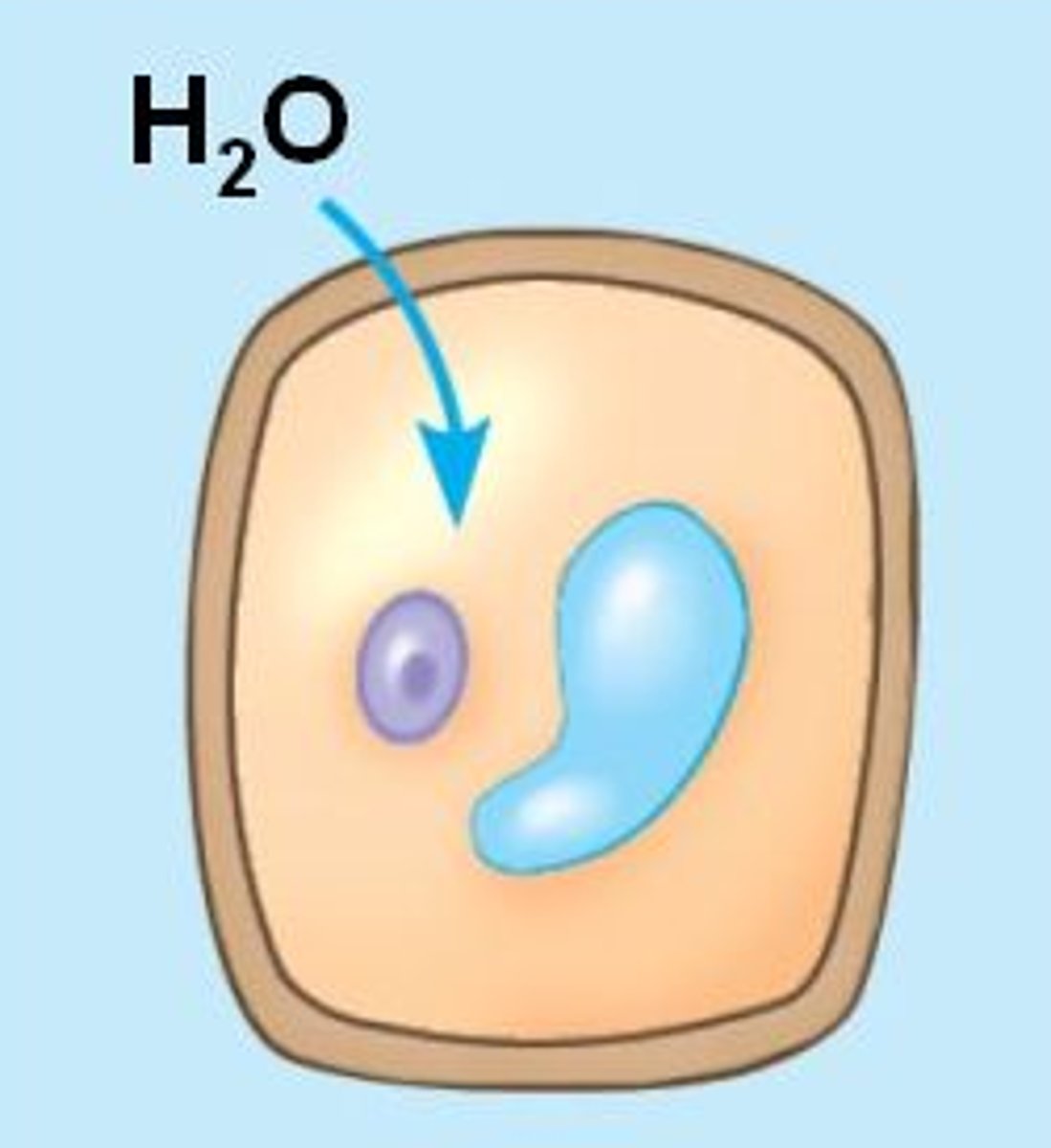
Plasmolysis
When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution and loses all of its water --- very limp
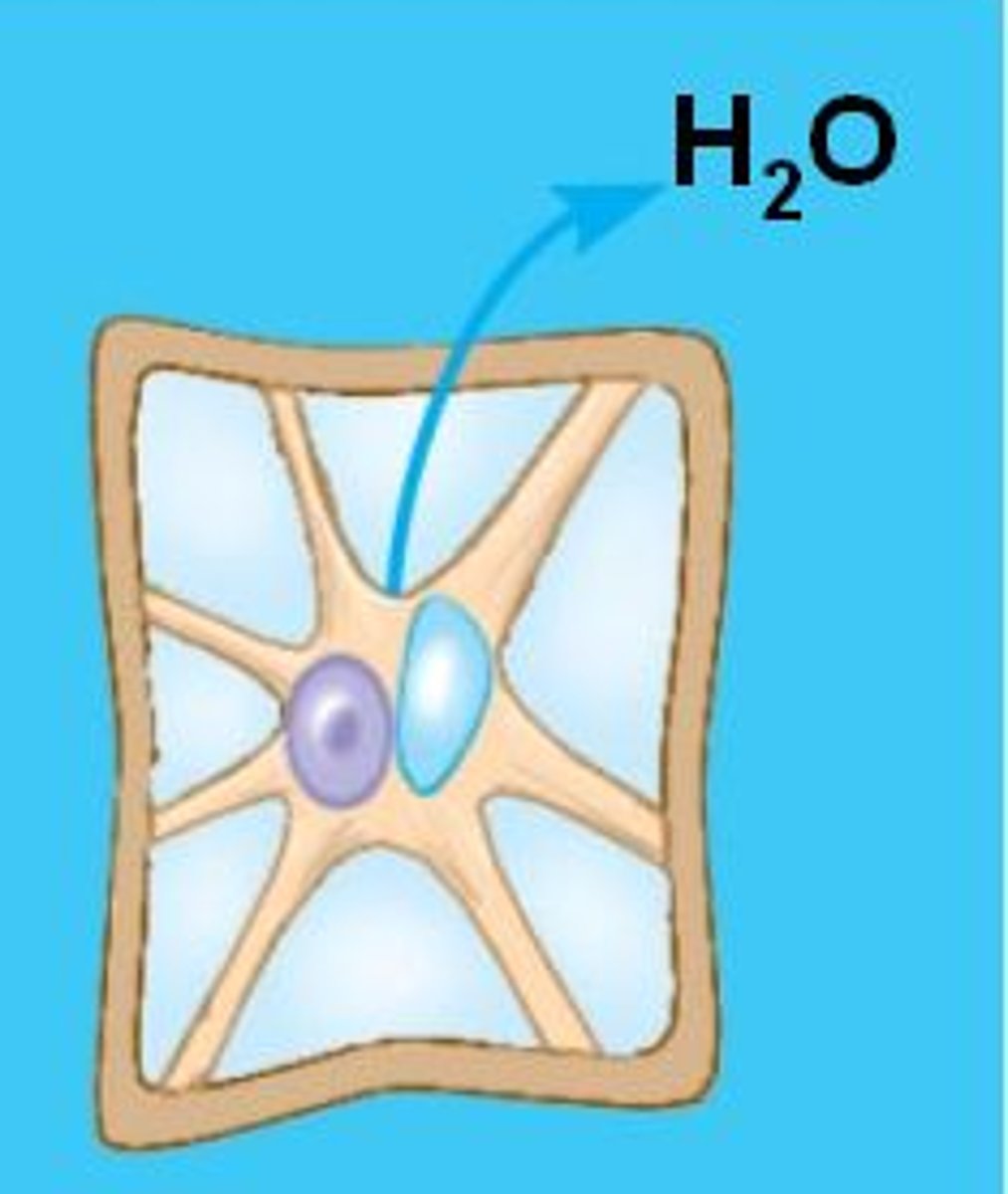
What happens to an animal cell in a Hypotonic solution?
The cell swells and may burst/lyse.
What happens to an animal cell in a Hypertonic solution?
The cell will shrivel.
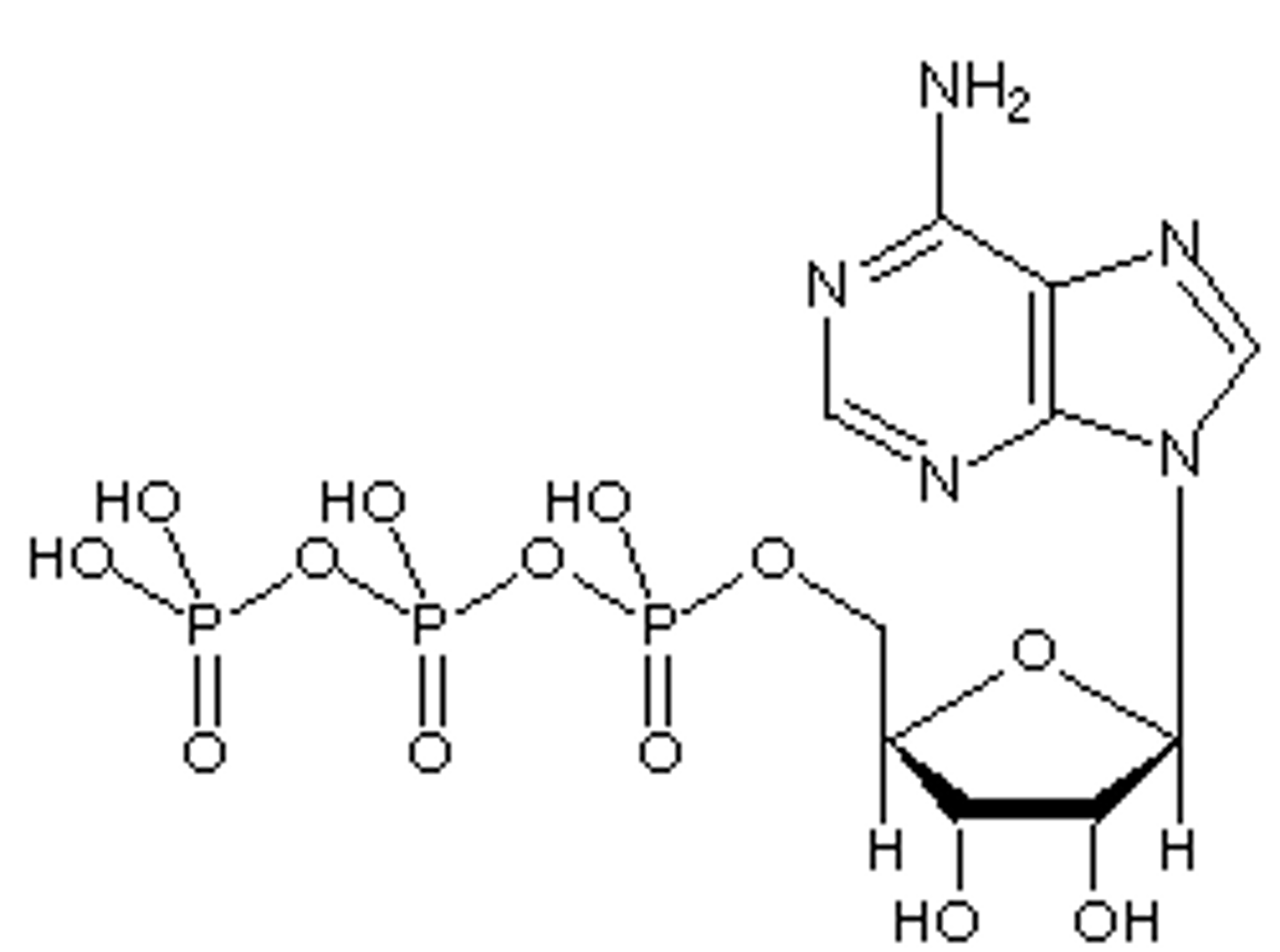
ATP
the cell's energy currency
cell mediated endocytosis
a receptor protein helps trap the molecules that needs to be brought into the cell
Endergonic
requires energy, positive delta G, anabolic reactions
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Used to fuel endergonic reactions
kinetic energy
energy of motion
potential energy
stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object, Ex: top of a hill
redox reaction
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another; also called oxidation-reduction reaction.
Reduction
gain of electrons NAD --> NADH
Oxidation
loss of electrons NADH --> NAD
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Ex: Energy in food converted to chemical/kinetic energy and lost as heat.
second law of thermodynamics
when energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is always degraded into lower quality energy (usually heat)
exergonic reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy. Negative delta G, catabolic reactions
Reactant for enzymes
Substrate
Enzyme with mutation
Will not function correctly, mutations change shape of enzyme thereby changing shape of active site
allosteric activator
binds to allosteric site and increases enzyme activity
noncompetitive inhibitor
A substance that impedes the activity of an enzyme without entering an active site. By binding elsewhere on the enzyme, a noncompetitive inhibitor changes the shape of the enzyme so that the active site no longer functions.
feedback inhibition (negative feedback)
A metabolic pathway is switched off by the inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway.
Active site of an enzyme
the region of an enzyme that attaches to a substrate, substrate fits like a 'lock in a key'
allosteric inhibition
binds to allosteric site (not active site) and decreases enzyme activity by changing active site shape.
Environmental influences on enzymes
pH, temp and substrate concentration
Competitive inhibition of enzymes
occurs when a substance other than the substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme
Cofactors
Minerals that assist in the normal functioning of enzymes
coupled transport
Uses the energy released when a molecule moves by diffusion to supply energy to active transport of a different molecule. Ex: amino acids and sugar
Coenzymes are
organic nonprotein components that aid in enzyme functioning
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
cis Golgi network
Section of the Golgi apparatus that receives materials from the endoplasmic reticulum.
trans golgi
shipping side
plasma membrane (cell membrane)
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell and separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment
Vesicle
Small membrane-bound sac that functions in moving products into, out of, and within a cell.
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
cell wall function
protection, structural support
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility. Many bacteria are flagellated, and sperm are flagellated.
Cilia
The hairlike projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner
Pili
Appendages that allow bacteria to attach to each other and to transfer DNA
central vacuole
A large vacuole that rests at the center of most plant cells and is filled with a solution that contains a high concentration of solutes. Storage.
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
Rough ER
A network of interconnected membranous sacs in a eukaryotic cell's cytoplasm; covered with ribosomes that make membrane proteins and secretory proteins.
Smooth ER
That portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes. Makes lipids and stores calcium
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Centrioloes
a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division. Aids in cell division. Animal cells
endosymbiotic theory
a theory that states that certain kinds of prokaryotes began living inside of larger cells and evolved into the organelles (mitochondria and chloroplasts) of modern-day eukaryotes. DNA evidence. Double membraned.
extracellular matrix (ECM)
The meshwork surrounding animal cells, consisting of glycoproteins, polysaccharides, and proteoglycans synthesized and secreted by the cells.
Purpose of cell surface proteins
recognition and communication
types of cell junctions
tight junctions, gap junctions, desmosomes
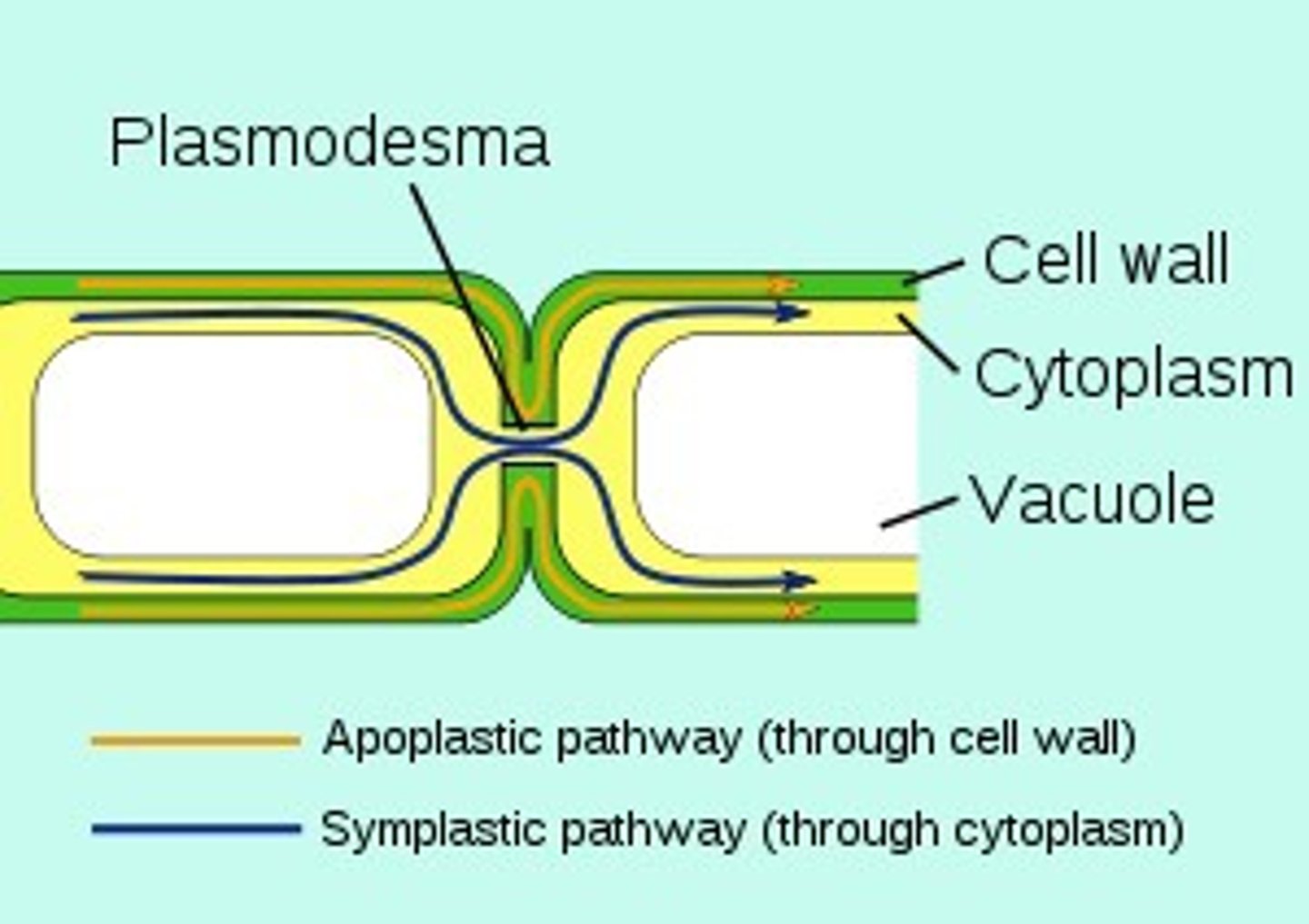
Plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent plant cells