Module 5: integumentary System
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEDCERTS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Skin
Skin Forms the first line of defense for the immune system. It also waterproofs the body and is a major receptor for sense of touch. cutane(o)-, dermat(o)-, derm(o)-
Sebaceous glands
Secrete oil (sebum) to lubricate the skin and prevent growth of bacteria.
seb(o)-
Sweat Glands
Secrete sweat to regulate body temperature and water content. They excrete some wastes from metabolism.
hidr(o)-
Hair
Hair Alerts us to the presence of insects on the skin and prevents us from losing body heat. pil(i)-, pil(o)-, trich(o)-
Nails
Protect the last bone of each finger and toe. onych(o)-, ungu(o)- Combining Form(s) Meaning Example(s)
Alopec(i)-
Baldness
Cry(o)-
cold
erythr(o)-, ethem(o)-
red
Koil(o)-
hollow, concave
Lip(o)-
Fat
Melan(o)-
Black
Myc(o)-
Fungus
Onych(o)-
Nail
Pil(i)- or Pil(o)-
Hair
Scler(o)-
Hard, Hardening
Seb(o)-
Sebum (oil)
Trich(o)-
Hair
Urtic(o)-
Rash, Hives
Xer(o)-
Dry
AA
Alopecia areata
BCC, BCCA
basal cell cancer or carcinoma
caut
Cauterization
CRYO
Cryosurgery
Debm
Debridement
Ecz, Ez
Eczema
LE
lupus erythematosus
MM, mm
Malignant Melanoma
NF
Necrotizing fasciitis
PS, ps
Psoriasis
ST
sclerotherapy
SCC
Squamous cell cancer or carinoma
Primary Functions of the Skin
Immune defense for blocking entrance of harmful microorganisms (pathogens).
Barrier for fluid loss and waterproofing of the body.
Sensation for temperature, touch, and pain.
Vitamin D production with the help of the sun’s ultraviolet light.
Epidermis
Outermost layer of the skin
keratin
A fibrous, water-repellent protein. In the epidermis, we have a soft keratin (hair) and hard keratin (nails)
Melanocytes
Located in the bottom layer of the epidermis. Produce a color pigment (melanin) that ranges from yellow-brown to black. Clusters of melanin produce freckles or moles on the skin
Carotenes
yellow to orange-colored fat-soluble pigments obtained from food, particularly fruits and vegetables. I understand these pigments are stored in the skin and contribute slightly to our skin color
Hemoglobin
Inside our red blood cells. When we are hot or flushed, the increased blood flow colors our skin pink.
subcutaneous layer
Lies below the dermis, which is why it is also referred to as the hypodermis (hypobelow, dermis skin). This layer is mainly made of fat or adipose tissue and connects the skin to the underlying surface muscles to provide anchoring. In addition, it stores nutrients for our body.
Sweat glands (Sudoriferous glands)
They are subdivided into two main types: eccrine (or merocrine) glands are most numerous on the palms of the hands, the soles of the feet, and the forehead. These glands are responsible for sweating, which is also known as perspiring. Apocrine glands are confined to the axillary and anogenital areas and their ducts connect to hair follicles. The only become active after puberty.
Perspiration is mostly water with a small amount of sald and metabolic waste products
Hidrosis
The production and excretion of sweat.
Major function of hair
Alert the body to the presence of insects on the skin
First Degree Burn (Superficial burn)
Damage to the upper most layer (epidermis) only. It is characterized by local redness, edema (swelling), and pain
Second degree burn (partial thickness burn)
Damage only to the epidermis and the upper part of the dermis. Second degree burns blister and are red.
Third degree burn (full thickness burn)
Damage to the epidermis, the entire dermis, the hypodermis, and often the tissues below (including muscle or bone). The skin will look charred and black-brown. Because the nerve fibers are damaged, third degree burns are not painful. Skin grafting will be required. Dehydration with electrolyte imbalance (including shock) is an immediate threat that requires treatment
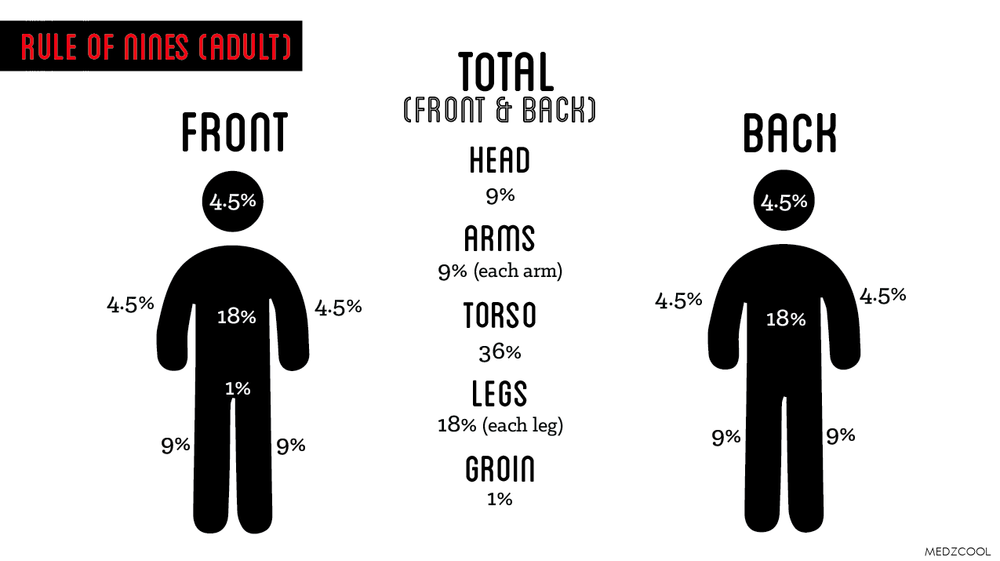
Rule of Nines
Help medical care providers estimate the amount of fluid loss in second and third degree burns of adults. The body surface is subdivided into 11 areas of 9% each.
ABCDE
mnemonic to help us remember the risk factors for recognizing melanoma.
Asymmetry
Border irregular, not smooth
Color much darker than other moles or unusual color
Diameter greater than the size of a pencil eraser
Evolving mole