critical care final
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
ABG - respiratory acidosis
r/t COPD, Trauma, CNS depression
Tx. Narcan, HOB raise, ABCs, mechanical vent. support breathing.
metabolic alkalosis
loss of CO2 ^ bicarb. vagal maneuvers, pain meds. decrease fTot, vT.
alarm high pressure r/t
obstruction = PIP. bitting, secretions, low lung compliance.
Tx. drain, check tubing. suction w/ hyperoxygenation first.
a flutter
CCB, BBs.
amiodarone 150mg @ 1mg/min > 48hr
anticoag q3wks if > 48 hrs
a fib
CCB, BBs, anticoagulation therapy Q3wk if. cardiovert if unstable
palliative care
for all patients serious, life-limiting illnesses, focusing on providing relief from symptoms and stress to improve quality of life.
propofol, fentanyl, precedex
goal. lightest sedation possible. reorient pt.
propofol - lipid. change tubing Q12h.
frequent v/s because RR depressant.
SVT
Adenosine is ONLY for SVTs.
UNSTABLE 90/60, aLOC, SOB> cardiovert
Stable> vagal! adenosine 6mg } 12mg } 12mg } cardiovert
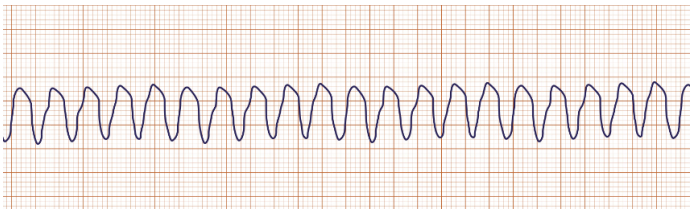
v tach
HR 100 < “tombs”
check pulse. stable> amiodarone 150 mg } 300 mg } cardiovert
unstable > lidocaine 1-1.5 mg } max 3mg } cardiovert

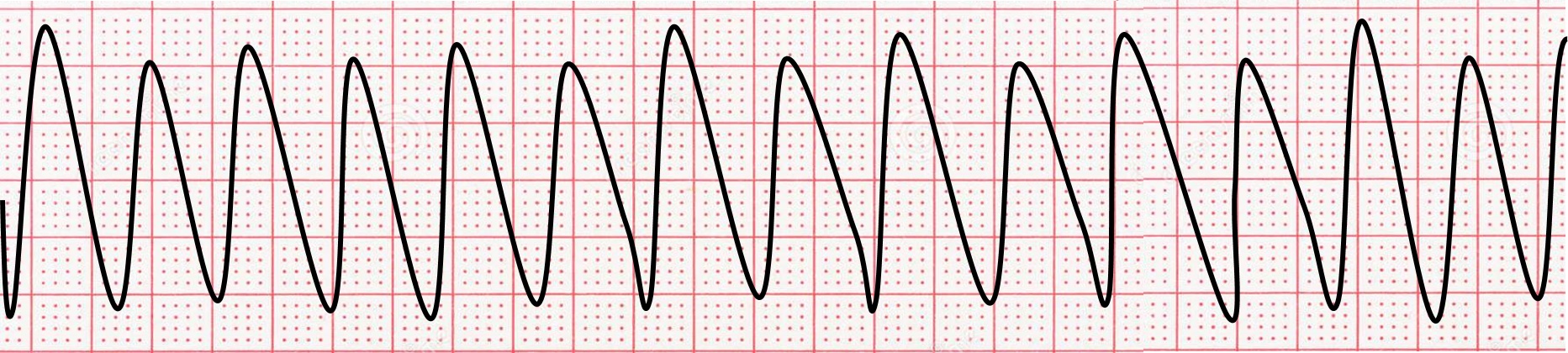
pulseless v tach & torsades.
v tach = shock (defib). compressions > epi 1mg q3min no max. + amiodarone 300 mg > 150 mg > intubate
torsades > add magnesium 1-2 g IV.
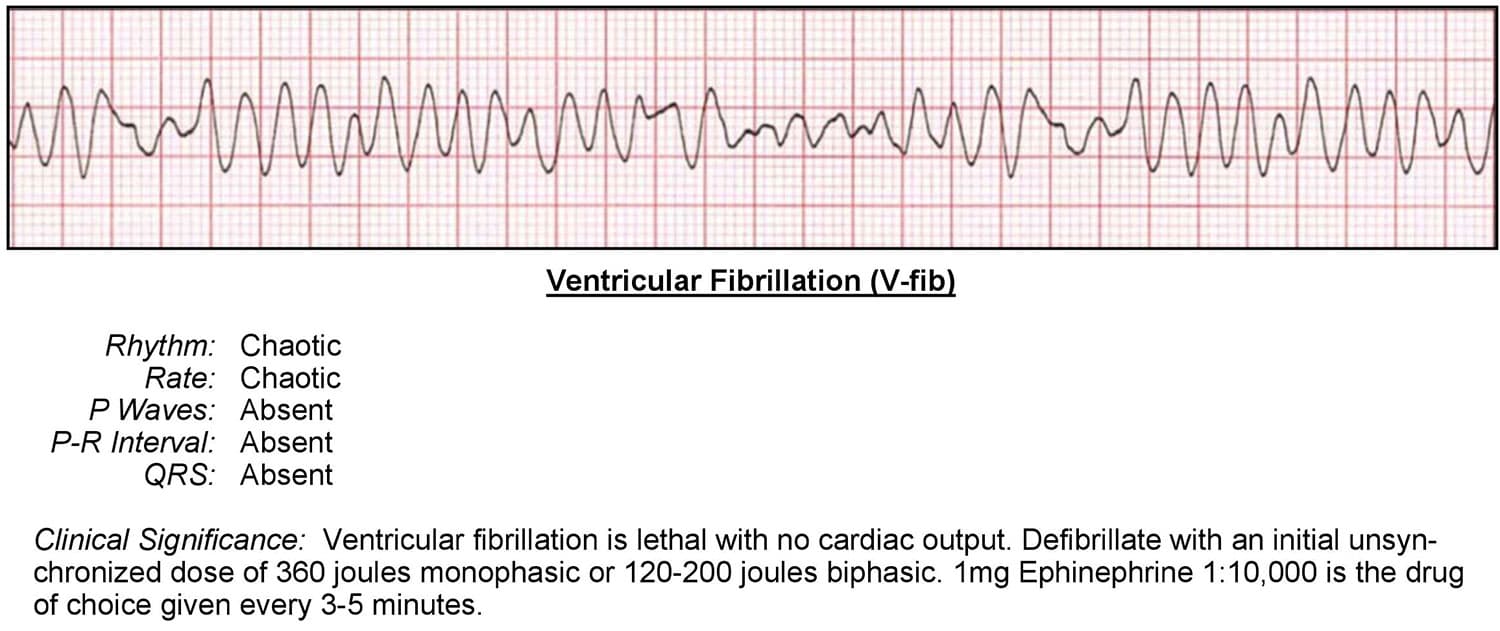
v fib
v tach = shock (defib). compressions > epi 1mg q3min no max. + amiodarone 300 mg > 150 mg > intubate
torsades > add magnesium 1-2 g IV.
PEA & asystole
NEVER CARDIOVERT/DEFIB.
Dx cause > hypovolemic most common. CPR and epi1 mg q3min no max. Consider advanced airway management.
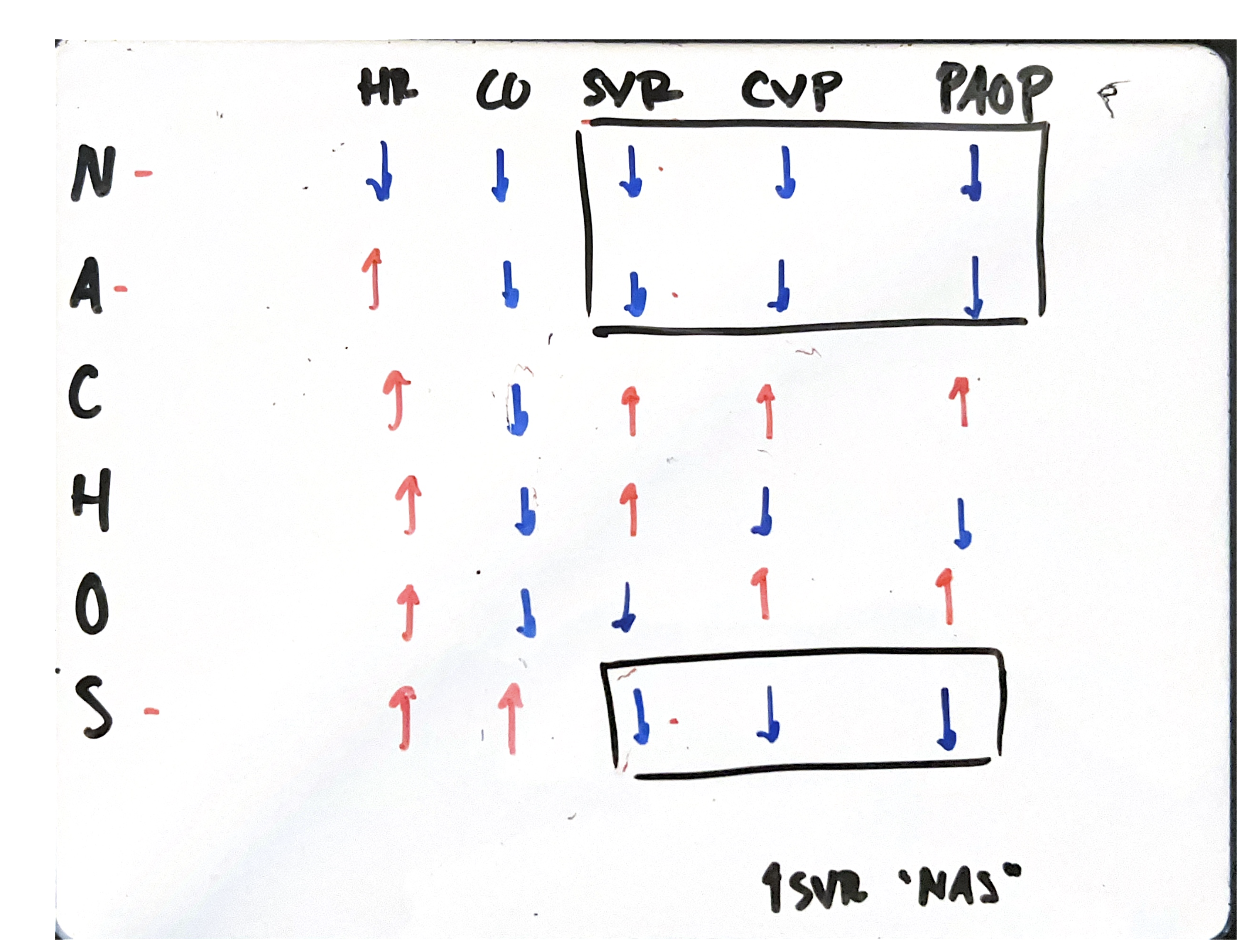
CVP
SVR
CO
PAP
PAOP
✅ CVP (Central Venous Pressure) volume: 2–6 mmHg
CHF > diuretics and vasodilators
✅ PAP (Pulmonary Artery Pressure):
Systolic 15–25 mmHg
Diastolic 8–15 mmHg
✅ PAOP (Pulmonary Artery Occlusion Pressure, aka wedge pressure): 6–12 mmHg
✅ SVR (Systemic Vascular Resistance): 770–1500 dyn·s/cm⁵
✅ CO (Cardiac Output): 4–8 L/min
Pulmonary artery catheter
measures CVP, CO, PAP, PAWP.
CVP 2-6, PAP 15-25/8-15
PAOP 8-12
VAP “POTHEADS”
P - PUD prophylaxis, PPIs
O - oral care w/ CHG
T - transmission control, hand washing
HOB 30 <
Enjoy sedation vacation
Aspiration precautions - suction at bedside
DVT prophylaxis. SCDs, heparin
S - subglottic suction PRN
anaphylactic - remove irritan. epinephrine, antihist.
septic - lactic lvls, ABX, levophed.
neurogenic - atropine, D5W/glucagon, dopamine.
obstructive. tension pneumo = needle decompress, chest tube. cardiac tamponade = pericardiocentesis
cardioenic - nitro, lasix, dixoxin/dobutamine
post renal
obstruction of flow. stones, tumors, BPH. foley, stent, cont. bladder irrigation. L1-L2 fracture
admin blood products
only w/ NS 18-20 gauge
Q15M. D/C if reactions. NS bolus, keep bag for identification/send pharmacy.
DIC -
Plt decrs
PTT ^ prolonged
D – dimer ^
Fibrinogen decrs
Antithrombin decrs
Fix clotting issue w/ Plasma & cryo contain clotting factors. Then treat H&H. correct acidosis.

MONA for ACS, MI
Morphine - 2-4mg IV
O2 4-6L and rest
Nitro - vasodilation, h/a is s/e. SL route @ 3 doses max q5mins
aspirin 325mg max
tidaling & bubbling
Cont bubbling is normal only in suction control OK. Not OK in the water seal chamber.
Tidaling in water seal chamber with each breath = proper function. Continuous bubbling suggests a leak or problem in the system.
failure to sense
spike but no wave d/t insufficient charge. increase milliamps, roll patient to left side
IABP
assess UOP, monitor H/D, provide cardiac support through counterpulsation (during diastole).
IABP – supports the heart
Inflates on diastole. Deflates during systole.
Interventions. Flat 10> log roll, leg immobile. Prevent bleeding out
Loss pulse on left radial !! s/s complication > freq neurovasc. leg circumference
IABP interventions.
stable BP, atropine at bedside. hold manual pressure 30 mins. bed rest w/ reverse trend. log rol, leg immobilization.
acute pancreatitis.
s/s LUQ epigastric pain, radiation to back. positive turner’s (bruised flank), Cullen’s, ^ amylase/lipase/glucose/bili and hypocalcemia
tx manage RR dysfuction r/t hypocalcemia. sz precaution. NPO or NG, F/E replace
GI bleed
s/s of hypovolemic shock. 2 large bore IVs
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Cool, clammy skin
Decreased urine output
Mental status changes
EN vs PN
EN > directly into GI tract. preferred over PN. done when functional GI but impaired swallow. OG for ETT pt. NGT for concious pt.
PN > IV Central line. TPN given through central line. contains complete nutrition. use dedicated port to avoid contamination. Q24h tubing change or Q12h for lipids.
cardiac contusion s/s and tx
bruising r/t blunt trauma to heart.
s/s dysrhythmias, PVCs, afib, ST changes, MI. ^CK, CKMB, troponin.
tx. digoxin, dopamine/dobutamine, EKG changes monitor freq. angina, tachy, low BP.
flail chest
s/s paradoxical chest mvt. tachypnea, dyspnea, hypoxemia.
tx intubation, ventilation
open pneumothorax
s/s sucking sound, hypoxemia
tx. 3 sided dressing, chest tube insert
burn injury ABCs
IV pain meds.
Airway, early oxygenation to recover lungs
Breathing - escharotomies to allow fluid release
Circulatory - 4mL x KG x TBSA % = fluid resuscitation 0.5/kg/hr = ideal UOP
ICP pt
keppra, cerebrex for sz
3 NS for fluids w/ strict I/O
mannitol for volume control
glucocorticoids for cerebral edema
^ RR and decrease PEEP on ventilation. hyperventilation (↑ RR) → reduces CO₂ → vasoconstricts cerebral vessels → lowers ICP (used short-term)
craniectomy.
NO NG tubes if TBI suspect. CPP = MAP - ICP. 60 = 100 is goal.
seizure pt
turn on side to keep patent airway. lorazepam IVP.
safety - padding rails, low position.