Reproductive system
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Male reproductive anatomy
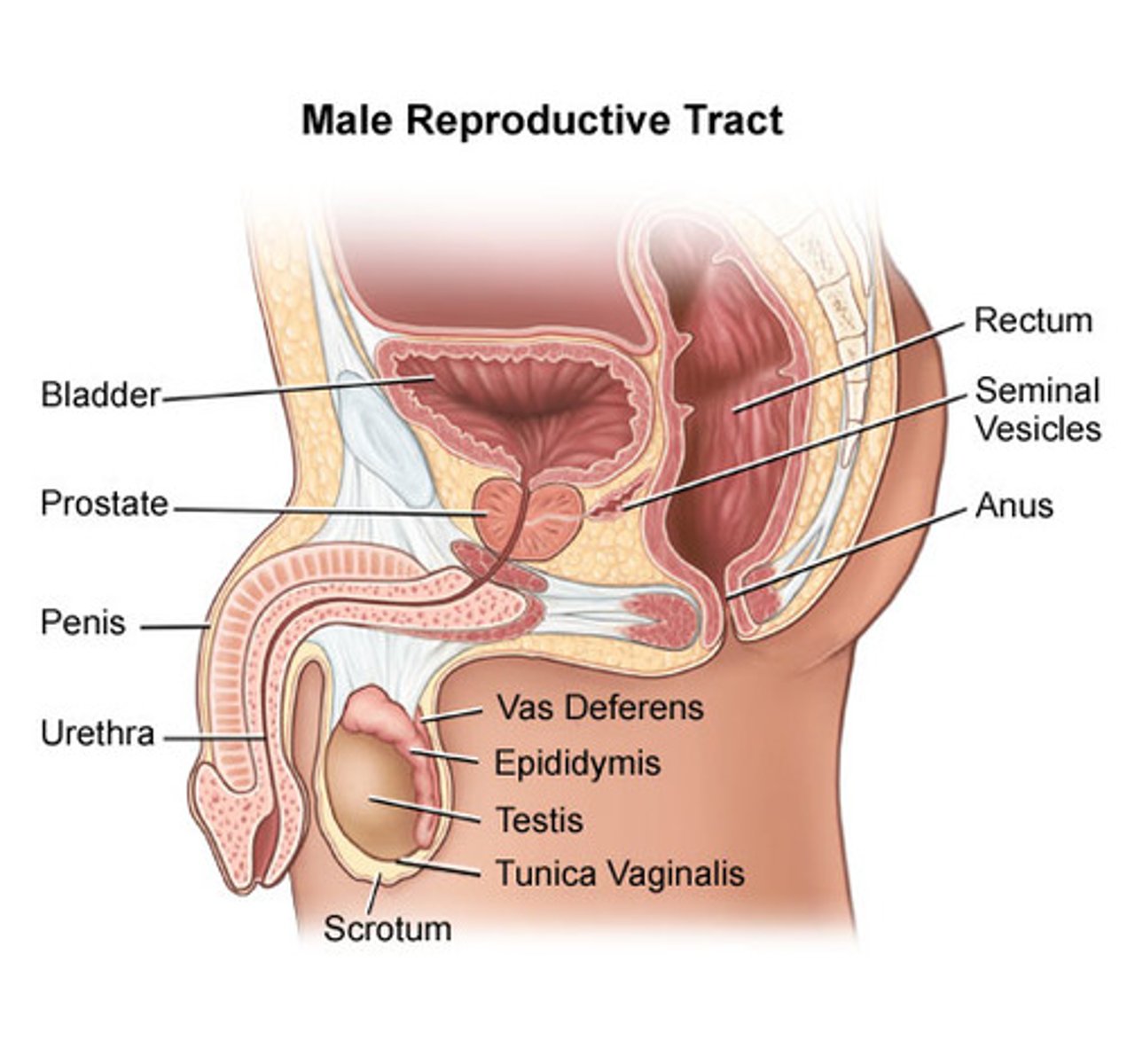
Scrotum
sac that contains testes
2 testes
> site of sperm storage and production
> secretes testosterone
Penis
consists of erectile tissue connected to nervous system
Accessory glands
> prostate gland
> seminal vesicle
> secretions added to sperm
Functions of the male reproductive system
> testes produce sperm and testosterone
> ducts transport, store and assist in maturation of sperm
> accessory glands secrete liquid portion of semen
> penis provides passageway for ejaculation via urethra which also excretes urine
Female reproductive system (side angle)
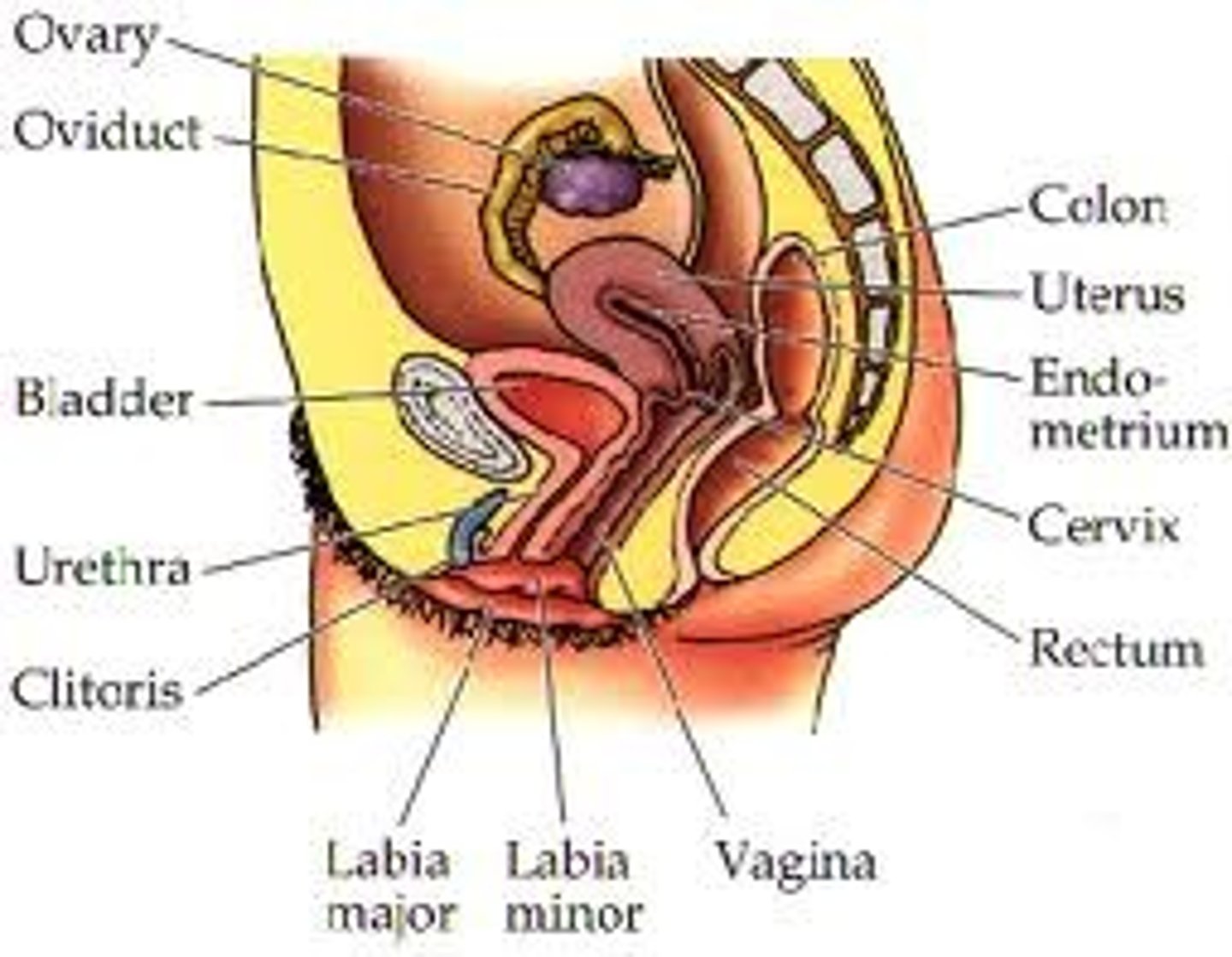
Female reproductive system (front angle)
> consists of 2 cycles - ovarian and uterine
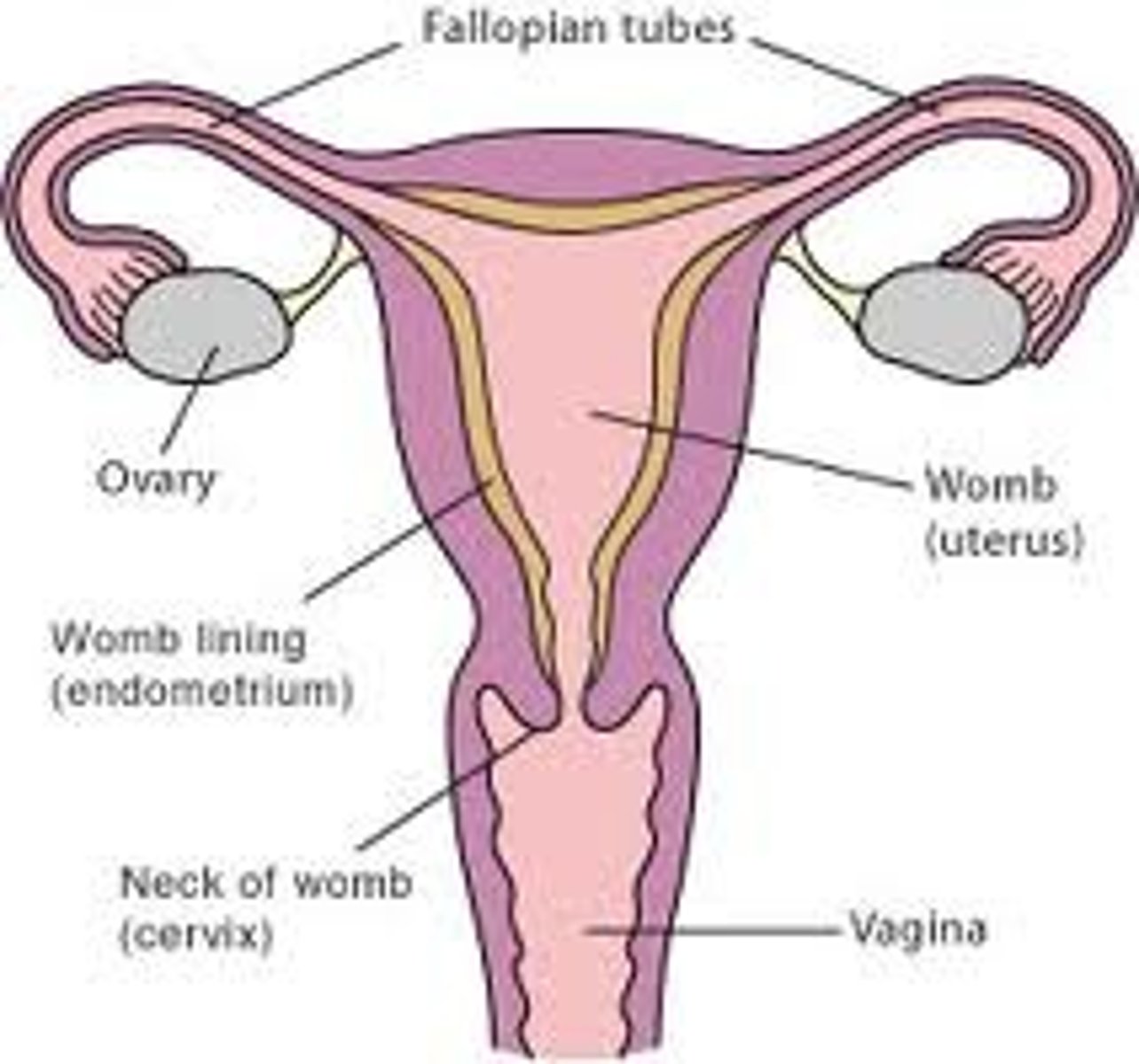
2 ovaries
> produce eggs
> hormones
> progesterone
> oestrogen
> attached to pelvis by ligament
> held close to fallopian tube
Fallopian tubes
connect ovaries to uterus
Uterus (womb)
> muscular organ (smooth muscle) with endometrium (lining with blood supply)
> nourish
> protect
> expel foetus
Cervix (neck of womb)
usually blocked by mucus (breaks down during intercourse and during ovulation)
Ovarian cycle
develops secondary oocyte (egg) for fertilisation
Uterine cycle
prepares endometrium to receive fertilised egg
Ovulation
release of oocyte into pelvic cavity
Phases of reproductive cycle
> menstrual phase
> pre-ovulatory phase
> ovulation
> post-ovulation
Fertilisation
1. sperm makes contact with egg
2. acrosome reacts with zona pellucida
3. acrosome reacts with perivitelline space
4. plasma membranes of sperm and egg fuse
5. sperm nucleus enters egg
6. cortical granules fuse with egg plasma membrane, which renders the vitelline layer impenetrable to sperm
Physiological changes in pregnancy
> physiological rather than pathological
> significant changes body undergoes can lead to pathologic states or leave her susceptible to other health conditions and more vulnerable
When is viability considered?
24 weeks
Cardiovascular changes in pregnancy
> diminished arterial bp
> increased cardiac output
> increased circulating vol.
> supine hypotensive syndrome
Hematologic changes in pregnancy
> relative anaemia
> leucocytosis
> diminished platelets
> elevated fibrinogen, normal coagulation
Pulmonary changes in pregnancy
> elevated diaphragm
> increased minute ventilation and todal vol.
> partially compensated respiratory alkalosis
> diminished functional residue capacity
GI changes in pregnancy
> increased uterine vol.
> displacement fo abdo contents
> relatively insensitive abdo wall
> delayed gastric emptying
> diminished gastroesophageal sphincter tone
Musculoskeletal changes in pregnancy
> increased ligamentous laxity
> lower centre of gravity
> greater back strain
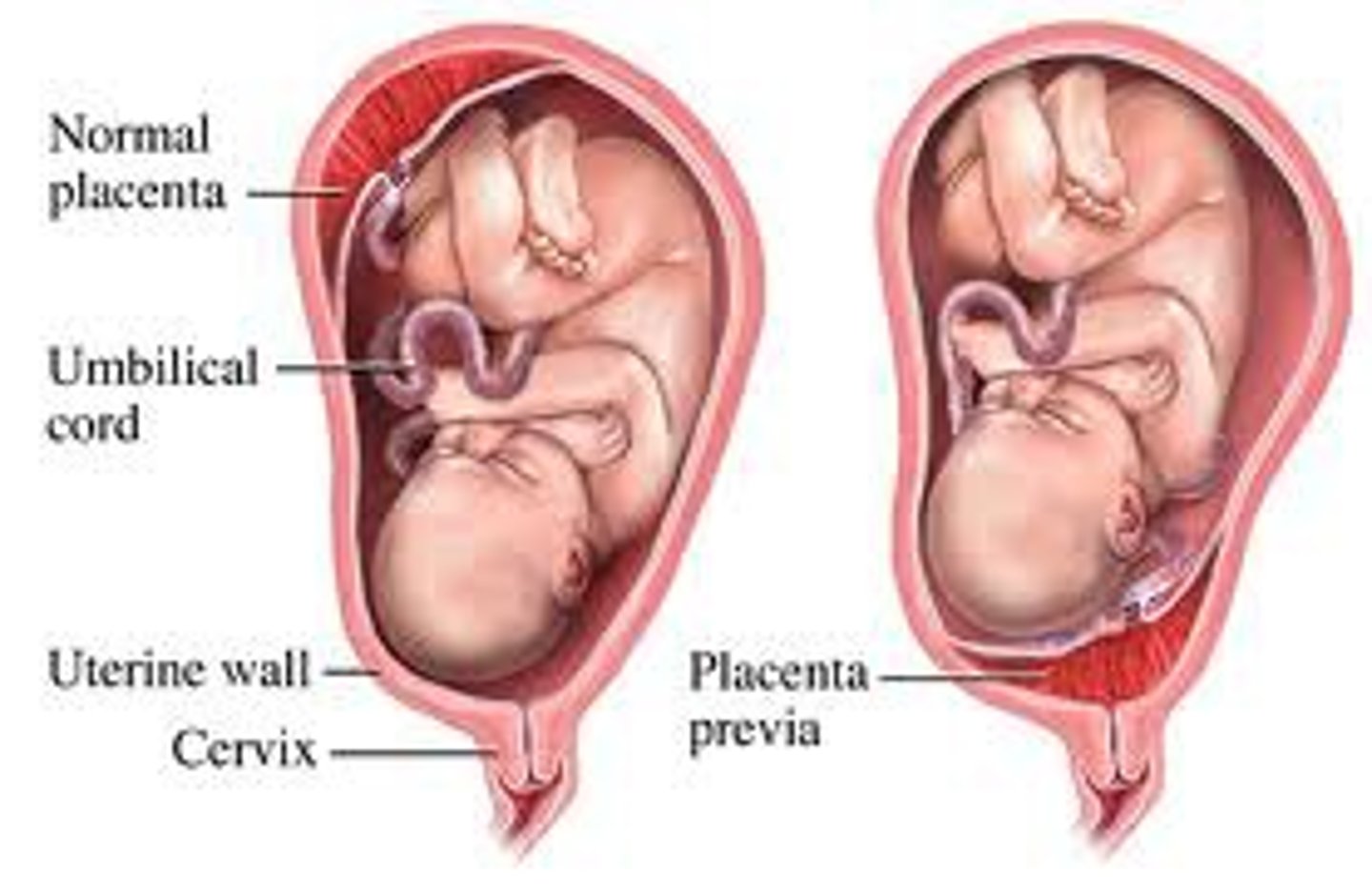
Placenta
> organ that develops in uterus
> provides oxygen and nutrients to growing baby
> removes waste products from baby's blood
> attaches to wall of uterus and baby's umbilical cord arises
> attached to top, side, front or back of uterus
> highly vascular organ
> health depends on: maternal age, waters breaking early, HTN, clotting disorders, multiple pregnancy, substance abuse, uterine surgery