Approaches
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:40 PM on 1/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
Key features of a science
* paradigm
* empirical methods
* objectivity
* replicable
* general laws
* empirical methods
* objectivity
* replicable
* general laws
2
New cards
Wundt
* established psychology out of biology and philosophy
* was to use scientific techniques to understand human mind and behaviour
* was to use scientific techniques to understand human mind and behaviour
3
New cards
Introspection
scientific technique used to study mental states by Wundt
* 186 research assistants were trained to observe and report their own thoughts and emotions in an unbiased way
Pps were asked to do this many times and used the enormous amount of data to break down structure of the mind to smaller elements
* 186 research assistants were trained to observe and report their own thoughts and emotions in an unbiased way
Pps were asked to do this many times and used the enormous amount of data to break down structure of the mind to smaller elements
4
New cards
Behaviourist approach
* believe that behaviours are learned from the environment after birth
* only observable behaviour should be studied due to psych being an objective science
* only observable behaviour should be studied due to psych being an objective science
5
New cards
Classical conditioning
when a conditioned stimulus becomes associated with an unrelated unconditioned stimulus in order to produce conditioned response
6
New cards
Pavlov (1902\`\`)
* food = unconditioned stimulus
* salivation = unconditioned response
* by ringing a bell every time food was presented to the dog, the unconditioned response of salivation soon became a conditioned response as the dog began to salivate at just the response of hearing the bell due to its conditioning
* salivation = unconditioned response
* by ringing a bell every time food was presented to the dog, the unconditioned response of salivation soon became a conditioned response as the dog began to salivate at just the response of hearing the bell due to its conditioning
7
New cards
Watson (1920)
* Little Albert initially did not fear the white rat (neutral stimulus)
* after the rat was paired repeatedly with loud noises (unconditioned stimulus), he would get scared (unconditioned response)
* Then, he would cry when the rat was present (now conditioned stimulus and conditioned response)
* his fear also generalised to other fuzzy white objects
* after the rat was paired repeatedly with loud noises (unconditioned stimulus), he would get scared (unconditioned response)
* Then, he would cry when the rat was present (now conditioned stimulus and conditioned response)
* his fear also generalised to other fuzzy white objects
8
New cards
Operant conditioning
behaviour is shaped and maintained by its consequences, such as reinforcements which make behaviour more likely to be repeated and punishments which make behaviour less likely to be repeated
9
New cards
Skinner (1930s)
* hungry rat in a box would move around and accidentally hit a lever which dispensed food
* the rats quickly learnt to go straight to the lever
* consequence of food = **positive reinforcement**
\
* rat in box subjected to electric shocks
* as it moved around it accidentally hit a lever which stopped the electric shocks
* rats learned to go straight to the lever
* consequence of removing shocks = **negative reinforcement**
* the rats quickly learnt to go straight to the lever
* consequence of food = **positive reinforcement**
\
* rat in box subjected to electric shocks
* as it moved around it accidentally hit a lever which stopped the electric shocks
* rats learned to go straight to the lever
* consequence of removing shocks = **negative reinforcement**
10
New cards
negative reinforcement
termination of an unpleasant state following a response
11
New cards
positive reinforcement
behaviour is strengthened by rewards, leading to repetition of desired behaviour
12
New cards
punishment
opposite of reinforcement since it is designed to weaken/eliminate a response rather than increase it
13
New cards
Cognitive approach
* argue that thoughts and other internal mental processes cause behaviour
* processes such as memory, language etc need to be fully understood because they cause behaviour
* internal mental processes should and can be studied scientifically
* using inference and models
* knowledge is constructed through experience = schemas
* processes such as memory, language etc need to be fully understood because they cause behaviour
* internal mental processes should and can be studied scientifically
* using inference and models
* knowledge is constructed through experience = schemas
14
New cards
Computer models in cognitive psychology
suggest that humans are ‘info processors’ and this ability to process and make sense of info from our environment causes our behaviour
* human-computer analogy = human mind works like a computer
* both have input, encode, store info and have output
* human-computer analogy = human mind works like a computer
* both have input, encode, store info and have output
15
New cards
Theoretical models in cognitive psychology
way of explaining how specific mental processes work
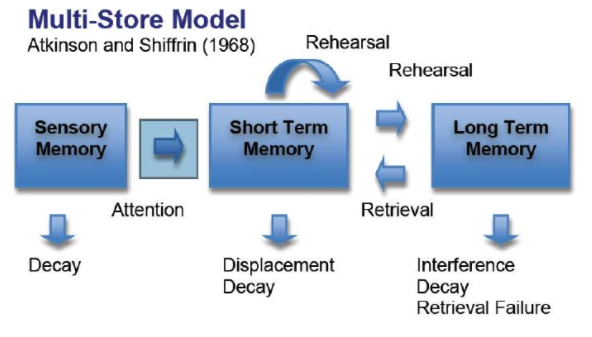
* working memory model, multi store model of memory etc
* working memory model, multi store model of memory etc
16
New cards
schema
cognitive framework that helps organise and interpret info, developed through experience
17
New cards
cognitive neuroscience
assumes all internal mental processes have a physical location within the brain and precisely locates these areas
* Broca’s patient ‘Tan’ = Broca’s area
* fMRIs, PET scans
* Broca’s patient ‘Tan’ = Broca’s area
* fMRIs, PET scans
18
New cards
Social learning theory
* argued that we learn through observation and imitation of other’s behaviour
* mediation processes (mental/cognitive processes) are essential for learning to take place
* imitation of behaviour depends on observed consequencesmedi
* mediation processes (mental/cognitive processes) are essential for learning to take place
* imitation of behaviour depends on observed consequencesmedi
19
New cards
mediational processes
cognitive factors that influence learning and come between stimulus and response
* **attention**: extent to which individual notices the behaviour
* **retention**: how well behaviour is remembered
* **motor reproduction**: ability to perform behaviour
* **motivation:** will to perform behaviour is determined on whether it was rewarded or punished (**vicarious reinforcement**)
* **attention**: extent to which individual notices the behaviour
* **retention**: how well behaviour is remembered
* **motor reproduction**: ability to perform behaviour
* **motivation:** will to perform behaviour is determined on whether it was rewarded or punished (**vicarious reinforcement**)
20
New cards
identification
role model more likely to be imitated if they possess similar characteristics to the observer, have a high status etc
21
New cards
vicarious reinforcement
if the model is observed to be reinforced for their actions, then imitation is more likely
22
New cards
Bandura et al (1961)
Bobo doll study
* lab experiment, 36 girls and 36 boys between 3-6yrs
* 12 girls and 12 boys each group (group 1: shown aggressive model, group 2: non aggressive model, group 3: control group not shown model)
= children shown aggressive model were more aggressive with the toys than the other 2 groups, **supporting SLT**
* lab experiment, 36 girls and 36 boys between 3-6yrs
* 12 girls and 12 boys each group (group 1: shown aggressive model, group 2: non aggressive model, group 3: control group not shown model)
= children shown aggressive model were more aggressive with the toys than the other 2 groups, **supporting SLT**
23
New cards
Bandura and Walters (1963)
repeated Bobo doll experiment but all shown aggressive model (group 1: model was praised, 2: punished, 3: no consequence)
= children in group 1 most aggressive, 2 least aggressive, **demonstrating importance of vicarious reinforcement**
= children in group 1 most aggressive, 2 least aggressive, **demonstrating importance of vicarious reinforcement**
24
New cards
Psychodynamic approach
* initiated by Freud
* argue that important influences on behaviour come from the unconscious
* psychodynamic conflict
* behaviour is motivated by sexual and aggressive drives
* argue that important influences on behaviour come from the unconscious
* psychodynamic conflict
* behaviour is motivated by sexual and aggressive drives
25
New cards
role of the unconscious
**conscious** mind: thoughts and feelings which we are aware of
**subconscious** mind: can be brought into consciousness if you are asked about them
**unconscious**: all repressed ideas and feelings blocked from conscious, its contents can leak out into conscious awareness (Freudian slip, dreams)
**subconscious** mind: can be brought into consciousness if you are asked about them
**unconscious**: all repressed ideas and feelings blocked from conscious, its contents can leak out into conscious awareness (Freudian slip, dreams)
26
New cards
structure of personality
* **id**: source of all basic drives, aims to obtain gratification for our needs
* **superego**: governed by moral constraints, morality principle, in conflict with the id
* **ego**: mediates links with the outside world, reality principle
* **superego**: governed by moral constraints, morality principle, in conflict with the id
* **ego**: mediates links with the outside world, reality principle
27
New cards
defence mechanisms
protect the ego from anxiety
* **repression**
* **denial**
* **displacement**
* **repression**
* **denial**
* **displacement**
28
New cards
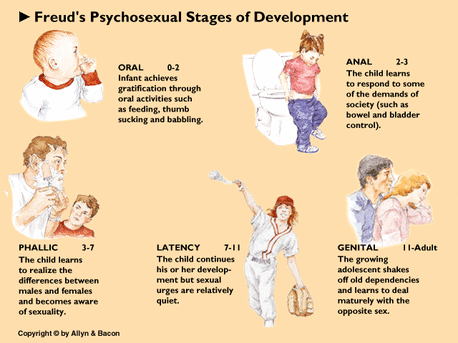
psychosexual stages
**O**ld **A**ge **P**ensioners **L**ove **G**uinness
1. **Oral** (0-2yrs) - mouth is focal point of sensation
2. **Anal** (2-3yrs) - beginning of ego development, major issue is toilet training
3. **Phallic** (3-6yrs) - focus on the genitals, major conflict = Oedipus complex, castration anxiety
4. **Latent** (6-12yrs) - conflicts of previous stages are repressed as children cannot remember much of their early years
5. **Genital** (12+ yrs) - directs us towards sex
1. **Oral** (0-2yrs) - mouth is focal point of sensation
2. **Anal** (2-3yrs) - beginning of ego development, major issue is toilet training
3. **Phallic** (3-6yrs) - focus on the genitals, major conflict = Oedipus complex, castration anxiety
4. **Latent** (6-12yrs) - conflicts of previous stages are repressed as children cannot remember much of their early years
5. **Genital** (12+ yrs) - directs us towards sex
29
New cards
Oedipus complex
* son desires his mother
* father becomes focus of jealousy and rivalry
* this is expressed as fear = castration anxiety
girls = **penis envy**
* father becomes focus of jealousy and rivalry
* this is expressed as fear = castration anxiety
girls = **penis envy**
30
New cards
Freud’s methods of investigation
* case studies
* free association
* dream analysis
* free association
* dream analysis
31
New cards
Humanistic approach
* people have free will
* subjective, conscious experience of the individual is the most important way to understand human behaviour
* subjective, conscious experience of the individual is the most important way to understand human behaviour
32
New cards
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
1. Physiological needs
2. Safety
3. Love and belonging
4. Esteem needs
5. Self-actualisation
33
New cards
unconditional positive regard
where an individual is supported and not judged, regardless of what they do or say
crucial to Roger’s approach
crucial to Roger’s approach
34
New cards
person centred therapy
clients encouraged to focus on current subjective understanding rather than someone else’s interpretation
35
New cards
Biological approach
all behaviour has a physical cause
* **physiological -** explain behaviour in terms of structures and processes
* **ontogenetic** - try capture development of particular behaviour
* **evolutionary** - locate a particular structure in evolutionary context
* **functional** - explain behaviour in terms of the purpose it serves
* **physiological -** explain behaviour in terms of structures and processes
* **ontogenetic** - try capture development of particular behaviour
* **evolutionary** - locate a particular structure in evolutionary context
* **functional** - explain behaviour in terms of the purpose it serves
36
New cards
genotype
* a person’s actual genetic makeup
* unique to the individual
* unique to the individual
37
New cards
phenotypes
product of genotype’s interaction with the environment
38
New cards
Evaluation of biological approach
\- reductionist
\- deterministic
\+ supporting evidence
\+ highly scientific
\- deterministic
\+ supporting evidence
\+ highly scientific