Ap Biology Ch. 8
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
What is Metabolism?
The totality of an organism’s chemical reactions; manages the material and energy resources of the cell
2
New cards
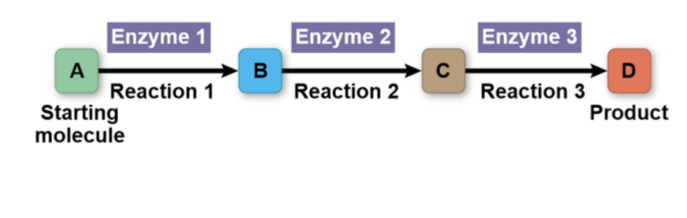
Metabolic pathways begin with…
A specific molecule and ends with a product
3
New cards
A catabolic pathway…
leads the RELEASE energy by the BREAK DOWN complex molecules into similar compounds
4
New cards
Example of a catabolic pathway
Cellular respiration
5
New cards
Anabolic pathways…
CONSUME energy to BUILD complex molecules from similar ones
6
New cards
What is energy?
Capacity to work
7
New cards
What is Kinetic energy(KE)?
Associated with motion; thermal energy & heat
8
New cards
what is potential energy (PE)?
Energy that matter posses because if it’s location or structure; chemical energy
9
New cards
1st law of thermodynamics:
Energy can be transferred and transformed but not created or destroyed
10
New cards
What is thermodynamics?
The study of energy transformations
11
New cards
2nd law of thermodynamics:
In every energy transfer the PE if the final state is less than the PE of the initial state
12
New cards
What is Free energy(🔼G)?
Part of a system’s energy that is able to perform when the temperature of a system is uniform
13
New cards
Exergonic reaction…
Energy is released; occurs spontaneously; 🔼G
14
New cards
Endergonic reaction…
Requires energy; absorb/ require free energy; 🔼G>0
15
New cards
What is ATP
The cell’s energy shuttle; ribose, adenine, and 3 phosphate groups
16
New cards
When ATP transfers one phosphate group through_______, it becomes____
Hydrolysis, ADP
17
New cards
When ADP transfers one phosphate group through_____ it becomes ___
Phosphorylation, ATP
18
New cards
What is a catylsist?
A chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction
19
New cards
Ex of a catalytic protein
Enzyme; ase= enzyme
20
New cards
Activation Energy (EA)
The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction
21
New cards
Enzymes speed up reactions by…
Lowering the EA of the reaction but without altering the 🔼G of the reaction
22
New cards
In catalysis, how do enzymes or other catalysts speed up specific reactions?
By lowering the EA barrier
23
New cards
Enzymes do not affect the change in 🔼G…
They hasten reactions that would occur eventually
24
New cards
What is an Active site?
Region on the enzyme where the substrate binds
25
New cards
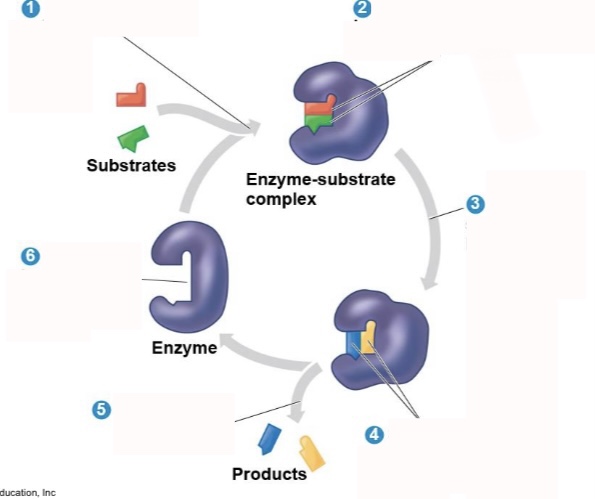
What is step 1 of an enzymatic reaction?
Substrates enter active site
26
New cards
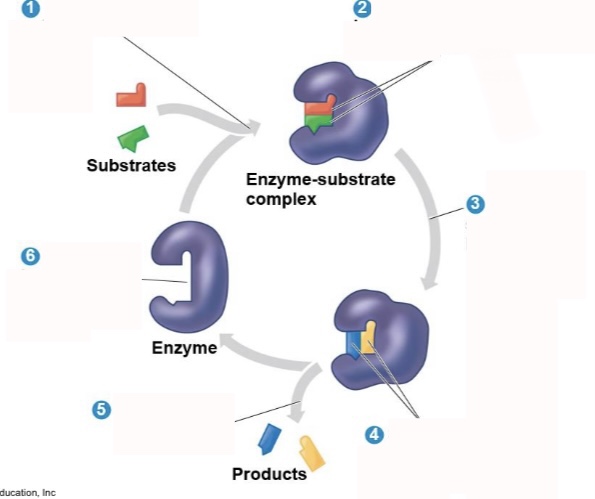
What is step 2 of an enzymatic reaction?
Substrates are held in active site by weak interactions
27
New cards
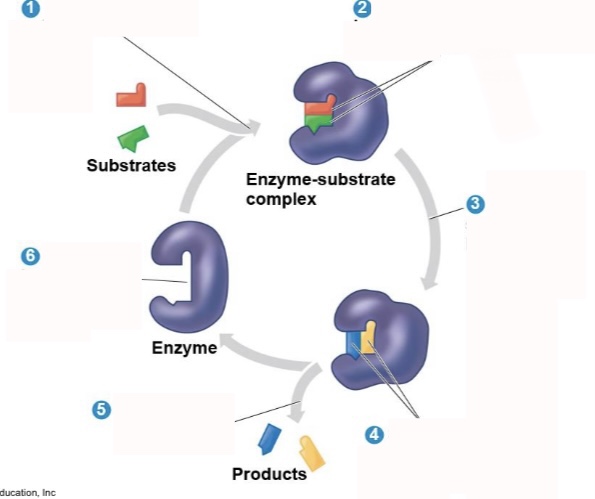
What is step 3 of an enzymatic reaction?
The active site lowers EA
28
New cards
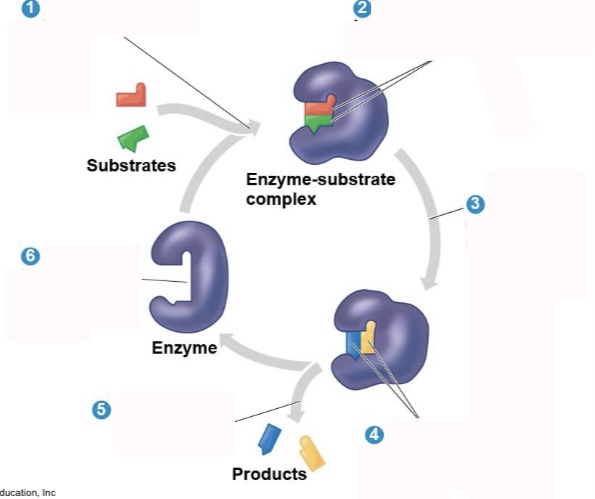
What is step 4 of an enzymatic reaction?
Substrates are converted into products
29
New cards
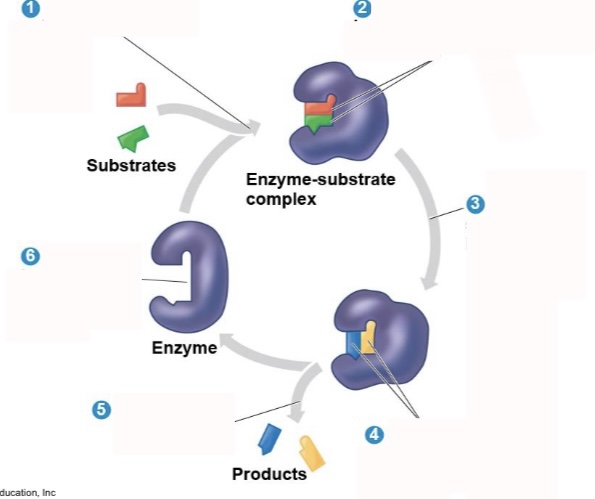
What is step 5 of an enzymatic reaction?
Products are released
30
New cards
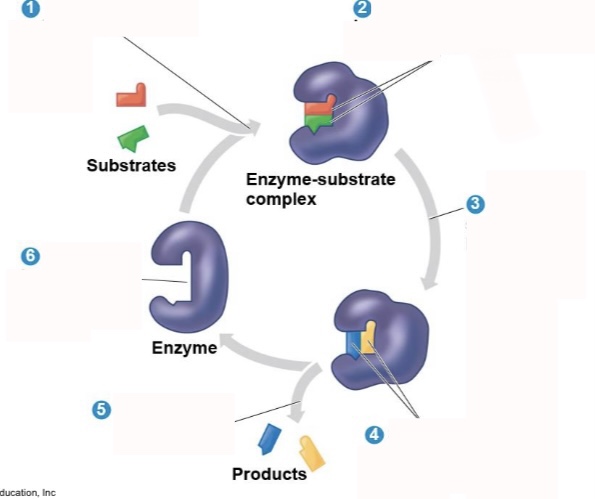
What is step 6 of an enzymatic reaction?
Active site is now available for new substrates
31
New cards
An enzyme has an…
Optimal temperature in which it can function
32
New cards
Each enzyme has an…
Optimal pH in which it can function
33
New cards
As the enzyme loses its precise shape, it’s efficiency decreases until…
It becomes denatured; can no longer function
34
New cards
Many enzymes require
Nonproteins, aka cofactors
35
New cards
If the cofactor is organic…
It is referred to as a coenzyme
36
New cards
What is an example of a cofactor?
Vitamins
37
New cards
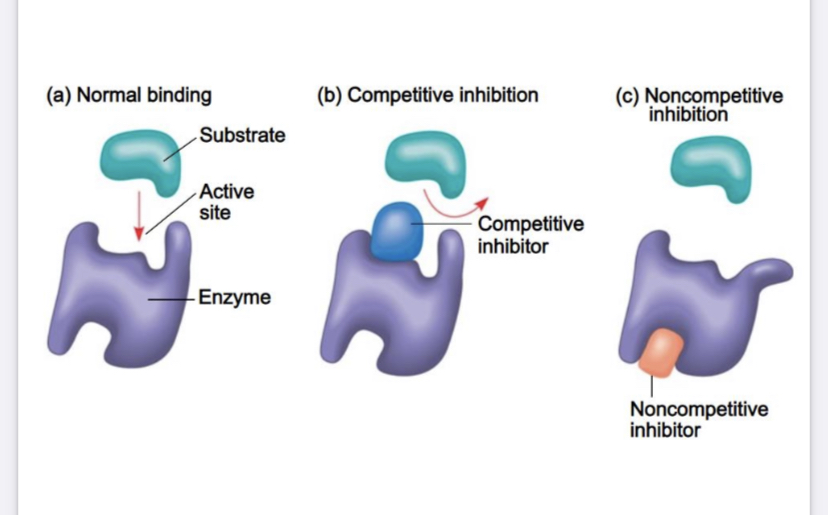
What are Competitive inhibitors?
Molecules that compete with the substrate for the active site on the enzyme; may bind reversible or irreversibly to the active site.
38
New cards
What is an example of a competitive inhibitor
Poisons
39
New cards
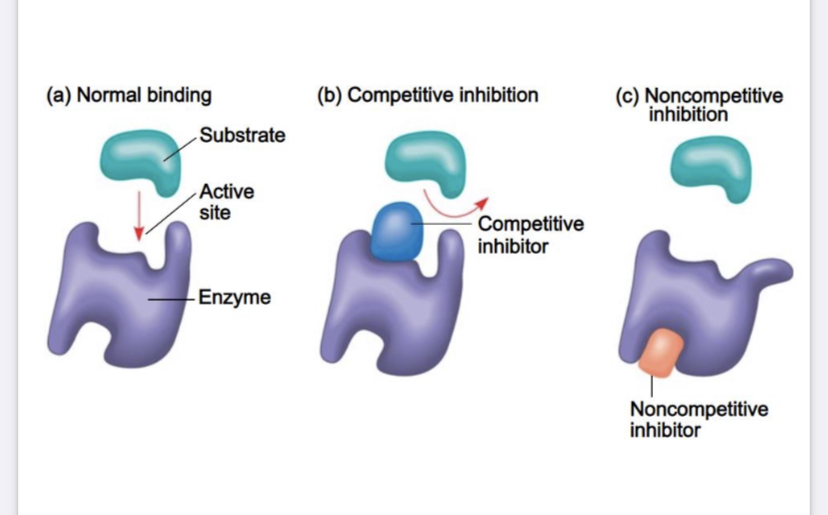
What are non competitive inhibitors?
Molecules that don’t directly compete with the substrate molecule to bind at the active site; they impede enzyme activity by binding to another part of the enzyme. This causes the enzyme to change shape, often rendering the active site nonfunctional.
40
New cards
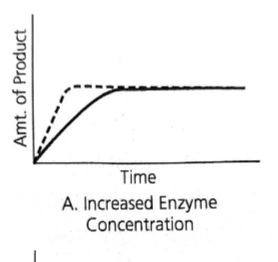
Assuming abundant substrate, An increase in enzyme concentration will lead to…
An increase in production of the final product
41
New cards
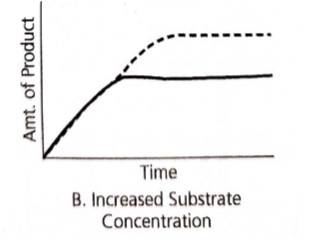
If the enzyme concentration is held constant and the substrate concentration is increased, the rate of the reaction will
increase until the enzyme is saturated (functioning at maximum efficiency) and the production of the final product is constant.
42
New cards
Many enzyme regulators bind to…
Allosteric sites on the enzyme; which is a specific binding site but NOT the active site
43
New cards
Once bound, the shape of the enzyme is changed and can stimulate…
Enzyme activity(allosteric activator) or inhibit enzyme activity(allosteric inhibitor)
44
New cards
What happens during feedback inhibition?
The end product of a metabolic pathway shuts down the pathway by binding to the allosteric site of the enzyme in the pathway
45
New cards
Feedback inhibition…
Increases the efficiency of the pathway by turning it off when the end product accumulated in the cell.
46
New cards
ATP powers cellular work by…
coupling energy releasing (exergonic) reactions to energy requiring (endergonic) reactions.
47
New cards
Enzymes catalyze the conversion…
of a substrate to a final product by lowering the energy of activation.
48
New cards
Enzymes are specific in the reactions they catalyze…
because of the molecular shape and charge of their active sites.
49
New cards
Factors that change the shape of the active site of enzymes…
influence enzyme activity.
50
New cards
enzymes regulate biological activities
by the rate of their reactions, often governed by feedback inhibition and activation.
51
New cards
enzyme and substrate concentrations can affect
the rate of reactions.