Chapter 21 - Electromagnetic Induction
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
varying magnetic field with time, an electric field could be generated, this phenomenon is known as
electromagnetic induction
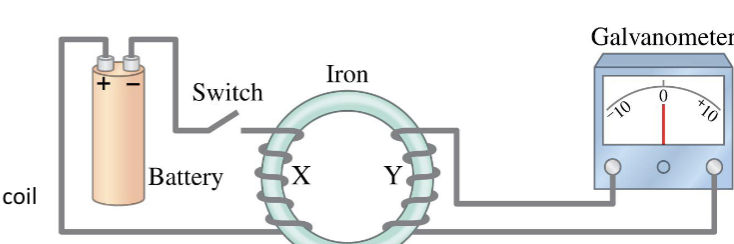
electromagnetic induction - with the switch open
no current through coil X
no magnetic field in Ron core
no current through coil Y
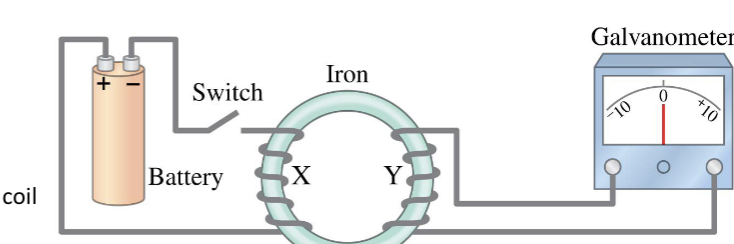
electromagnetic induction - immediately after the switch is closed
a current begins to flow through coil X
this current creates a magnetic field within coil X, the iron core, and also coil Y
a current starts to flow through coil Y
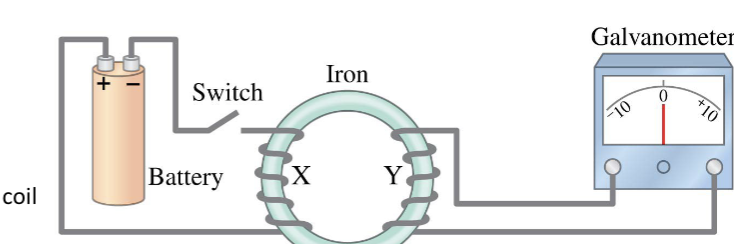
electromagnetic induction - later, after the switch has been closed a while:
a current still flows through coil X
there is still a magnetic field within the coils and iron ocre
current no longer flows through coil Y
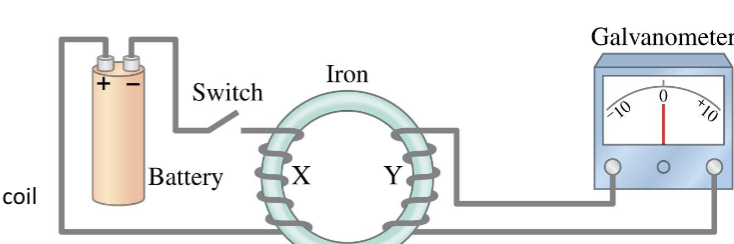
electromagnetic induction - if the switch is now opened:
the current in coil X stops flowing
the magnetic field dies off
for a brief moment, a current flows through coil Y
a constant magnetic field produces no
current in a conductor
a banging magnetic field can produce
an electric current
such a current is called an induced current
when the magnetic field through coil Y changes, a current occurs in Y as if there were a source of electromotive force (emf), meaning electric potential difference, in circuit Y:
a changing magnetic field (not magnetic field itself) induces an emf (a potential difference)
and the faster the field changes, the larger the induced emf
faraday showed that no current is registered in the galvanometer when
bar magnet is stationary which respect to the loop
However, a current is induced in the loop when a
relative motion exists between the bar magnet and the loop
Faraday’s experiment demonstrates that an
electric current is induced in the loop by changing the magnetic field
the coil behaves as if it were connected to a voltage course
experimentally, it is found that the induced voltage depends on
the rate of change of magnetic flux through the coil
to produce an induced current you need
a closed conducting loop
an external magnetic flux through the loop that is changing in time
Faraday’s Law describes the effect:
the magnetitude of the induced emf in the coil is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop
the induced current as a result of the induced emf is proportional to
the resistance of the conductive loop
the minus sign in induced emf equation means that the induced emf always
opposes the change in flux
an induced current produced by an induced emf moves in a direction so that the magnetic field created by that current
opposed the original change in flux
an induced emf is always in a direction that
opposes the original change in flux that caused it
be aware that we are now discussing two distinct magnetic fields:
the changing magnetic field or flux that induces the current and
the magnetic field produced by the induced current
(all current produce a magnetic field)
the second (induced) field opposes the change in the first
the magnetic field due to the induced current
points in the same direction as the external field is the flux is decreasing
points in the opposite direction from the external field if the flux is increasing
is zero if the flux is not changing
when a changing current passes through a coil or solenoid, a
changing magnetic flux is produced inside the coil, and this in turn induces an emf
a changing current in solenoid 1 will induce an
emf in the solenoid 2
the metal inductance is defined as the
proportionally constant between the induced emf and the rate of change of the current
the unit of metal inductance (M) is the
Henry (H)
mutual inductance (M) is a “constant”
it does not depend on I
it depends on “geometric”
size, shape, number of turns, and relative positions of the two coils, and also on whether iron (or other ferromagnetic material) is present
inductance idea applies the same to a
single solenoid
self-inductance, also kwon simply as inductance has the symbol
L and is also measured in Henrys
a device that is designed to have an iductance is known as
inductor
an inductor store energy in its
magnetic field
the magnetic field in an inductor is the source of energy for the
induced emf when the current changes
an inductor can store energy in its magnetic field din the same way a
capacitor stores energy in its electric field
we can also find the energy density in any magnetic field which only depends on
the strength of the magnetic field
the symmetry between the electric and magnetic fields is reflected in the similar roles played by
capacitors and inductors
Air filled parallel plate capacitor
constant electric field
capacitance only depends on geometry
energy stores in electric field
air filled solenoid inductor
uniform magnetic field inside the solenoid
inductance only depends on geometry
energy stored in magnetic field