S1M1 - NIST and Technology Frameworks
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Remove barriers to industrial competitiveness and improve access to resources to promote U.S. research capabilities.
Three of the most prolific sets of standardized frameworks promulgated by NIST include the:
Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
Privacy Framework
Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations
CSF is a voluntary framework that includes three primary components to manage cybersecurity risk
Framework Core
Framework Implementation Tiers
Framework Profile
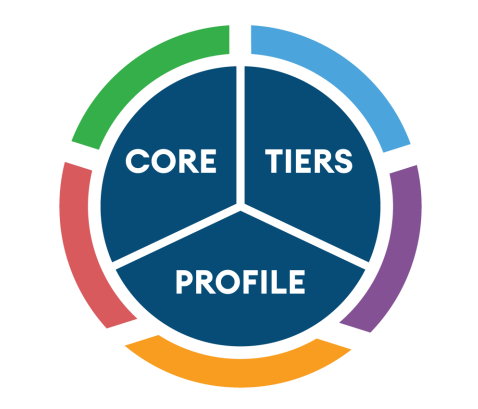
CSF - Framework Core - General
Developing a set of plain language controls for the protection of critical IT infrastructure
Develop a program to identify, assess, and manage cybersecurity risks in a cost-effective and repeatable manner
5 Areas of Focus
CSF - Framework Core - 5 Areas of Focus
Identify
Protect
Detect
Respond
Recover
Identify
Keep records of:
assets of the organization
system users
information process operations and all systems used
Protect
Deploying safeguards and access controls
Performing regular updates to security software
Performing data backups, developing plans for disposing of files or unused devices, and user training
Detect
Deploy tools to:
detect active cyber security attacks
Monitor network access points, user devices, unauthorized personnel access, and high-risk employee behavior or the use of high-risk devices
Respond
Develop response policies addressing how to:
Contain a cybersecurity event
React using planning responses that mitigate losses
Notify all affected parties
Recover
Supporting the restoration of a company’s netowrk to normal operations
Restoring backed up files or environments
Positioning employees to rebound with the proper response
CSF - Implementation Tiers
provides a measure of an organization’s information security infrastructure sophistication in the form of four implementation tiers
an organization must select a tier based on the perception of its own risk given the cybersecurity policies currently in place
inform an organization as to the effectiveness of profiles
What are the implementation tiers? (lowest to highest based on risk)
Tier 1 (Partial)
Tier 2 (Risk-Informed)
Tier 3 (Repeatable)
Tier 4 (Adaptive)
Tiers are subdivided into:
Risk management process
Risk management program integration
External participation
CSF - Framework Profiles - General
Mechanisms by which NIST recommends companies measure cybersecurity risk and how to minimize such risk
determines success of failure of information security implementation
Thought of as implementation guides with insight specific to a particular industry
CSF - Framework Profile - Considerations
organizational goals
industry goals
legal and regulatory requirements
industry best practices
risk management priorities
CSF - Framework Profile - 3 Categories
Current Profile - current state of organizational risk management
Target Profile - desired future state of organizational risk management
Gap Analysis - identifies differences from the above (how an organization can drive change)
Privacy Framework - General
Protect individuals’ data as used in data processing applications
Developed to be industry agnostic
Overlap with CSF
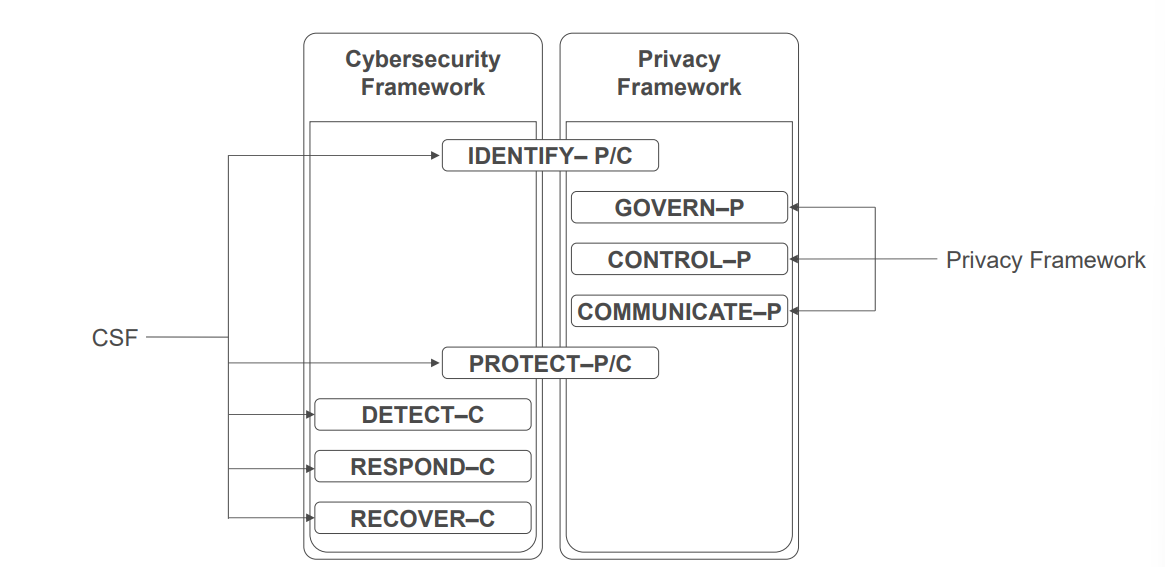
Privacy Framework - Categories
Identify
Govern (not part of CSF)
Control (not part of CSF)
Communicate (not part of CSF)
Protect (access control vs. data policies)
Detect (conceptually the same as CSF)
Respond (conceptually the same as CSF)
Recover (conceptually the same as CSF)
NIST Security and Privacy Controls (SP 800-53)
Set of security and privacy controls applicable to all information systems and now the standard for federal information security systems
designed for protecting information systems against sophistication threats