Opioids or Opiates
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
peptide neurotransmitters are
longer lasting, more diffuse effects
often co-released with conventional small molecule transmitters
opioids are
diverse short peptides from long precursors
t/f opioid receptors are ligand gated ionotropic receptors
FALSE
Opioid receptors are metabotropic receptors (Gi coupled protein coupled receptors)
examples of opioid receptors
All are Gi coupled
Mu (u), Delta (S), and Kappa (K)
Function of the opioid receptor
to alleviate stress and pain
Targeted by analgesics, some general anesthetics and drugs of abuse
Three families of opioid peptides
Enkephalins
Dynorphins
Endorphins
generated from precursor proteins
endogenous opioids role
inhibit neurotransmitter release (glutamate)
inhibit activation of spinal nociceptive neurons
Opioid receptors are __ coupled and are expressed where?
Opioid receptors are Gi coupled GPCRs expressed in brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
Endorphins relationship to
mu, delta, and kappa
Endorphins
Delta - Mu, NO KAPPA
Enkephalins relationship to
mu, delta, and kappa
Delta > mu, NO KAPPA
Dynorphins relationship to
mu, delta, and kappa
ACTIVATE K
sensitize nociceptive signals in the dorsal horn
Endomorphins relationship to
mu, delta, and kappa
u selective
pain target for pain meds
where is the main target for pain meds?
mu receptor
mu, delta, and kappa
expression on presynaptic expression
All three receptor types are expressed presynaptically
Primary afferent
mu, delta, and kappa
post-synaptic expression
mu on spinal nociceptive neurons, peripheral terminals of sensory neurons
spinal cord acts via
pre and post synaptic mechanisms
supraspinal effects in the brain act via
pre and post synaptically
peripheral terminals
post-synaptic mechanisms
examples of opioid agonists at the mu receptor
Endogenous: Endorphins
Natural: Morphine
Synthetic: Fentanyl
opioid peptides bind opioid receptors and activate: ________________
Thereby inhibiting _________
Opioid peptides bind opioid receptors and activate G-proteins, thereby inhibiting Calcium (Ca++) influx
Opioid receptors mediate postsynaptic inhibition of pain by enhancing
Cl influx and K efflux
What receptor is the primary therapeutic target of opioid analgesics?
mu receptors
analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, dependence
Selective Kappa agonists are effective analgesics can cause
dysphoric reactions (anxiety, panic, delirium)
k receptors are important in
sedative and GI effects s
delta receptors are likely to contribute to
tolerance
Full/STRONG mu OR Agonists
Phenanthrenes: Morphine, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, heroin
Phenylethylamines: methadone
Phenylpiperidines: meperidine, fentanyl, sufentanil, alfentanil, remifentanil
Morphinans: levorphanol, dextromethorphan
Partial/Mild mu OR agonists
Phenanthrenes: codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone
Phenylethylamines: propoxyphene
Phenylpiperidines: diphenoxylate, difenoxin, loperamide
mixed (mu or kappa OR) Agonists/Antagonists
Phenanthrenes: Nalbuphine, Buprenorphine
Morphinans: Butorphanol
Benzomorphans: Pentazocine, dezocine
u OR antagonists
Naloxone, naltrexone
metabolism of phenanthrenes
converted to non-active polar glucuronides in the liver and excreted by kidneys
exception is morphine (full agonist) e
exception of phenanthrene metabolism
morphine (full agonist)
morpgine-3-glucuronide
neurotoxic - seizures
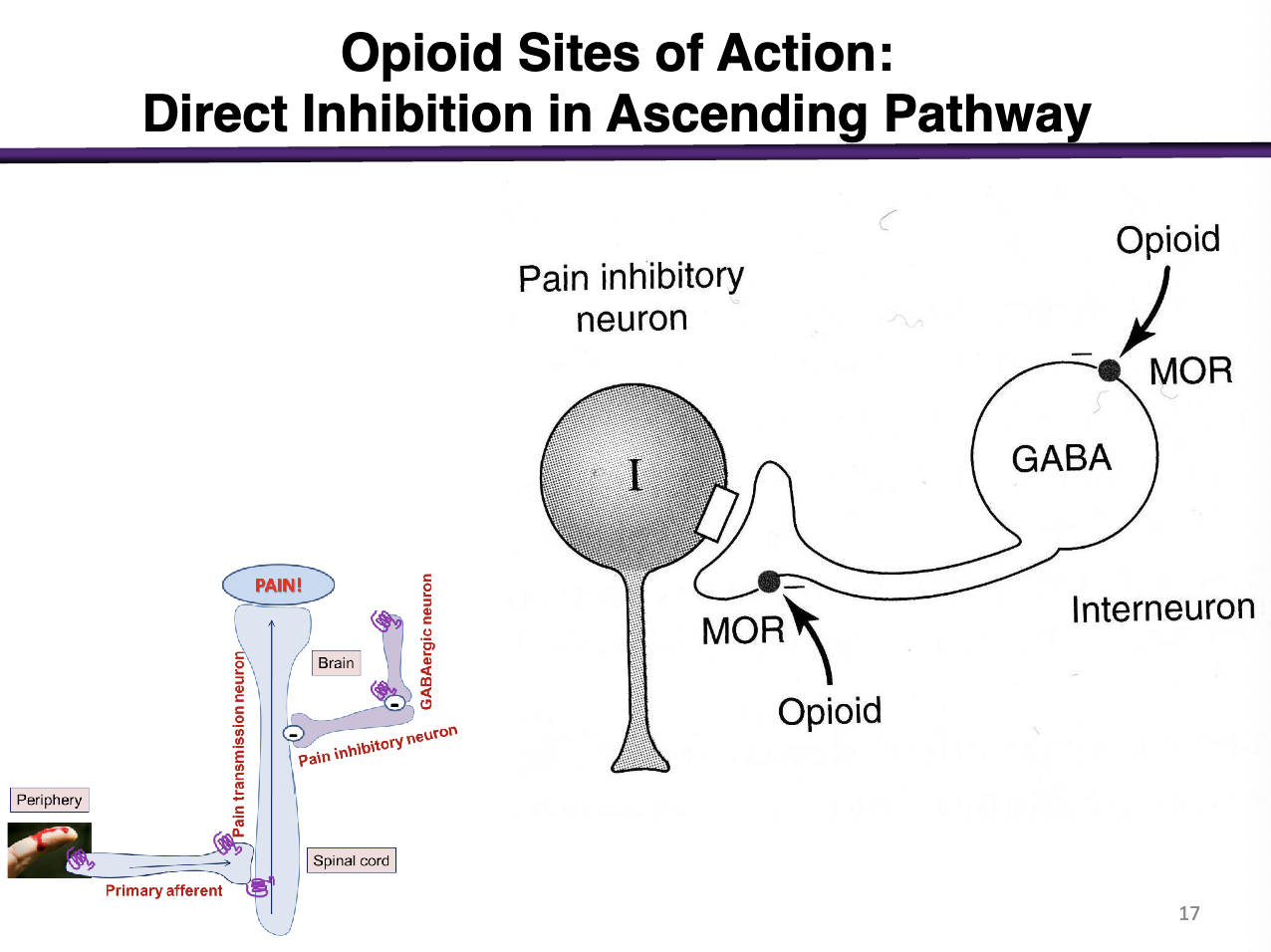
Explain this
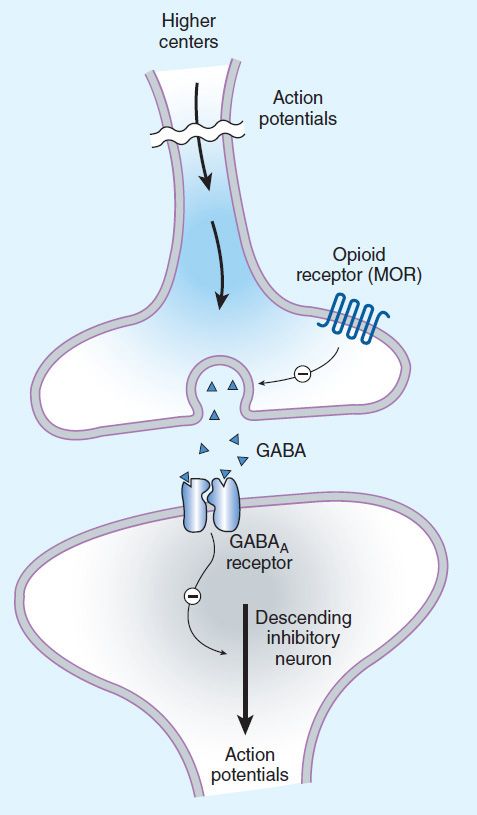
Role of GABA: inhibits descending inhibitory neurons
Opioids bind to the mu opioid receptor. This negatively regulates gaba interneurons. If GABAergic neurons previously NEGATIVELY regulated the pain inhibitory neuron, then taking GABA away allows for the Pain inhibitory neuron (Descending neuron) to REDUCE more pain. This increases the flow of descending pathways by inhibiting the ascending pathway.
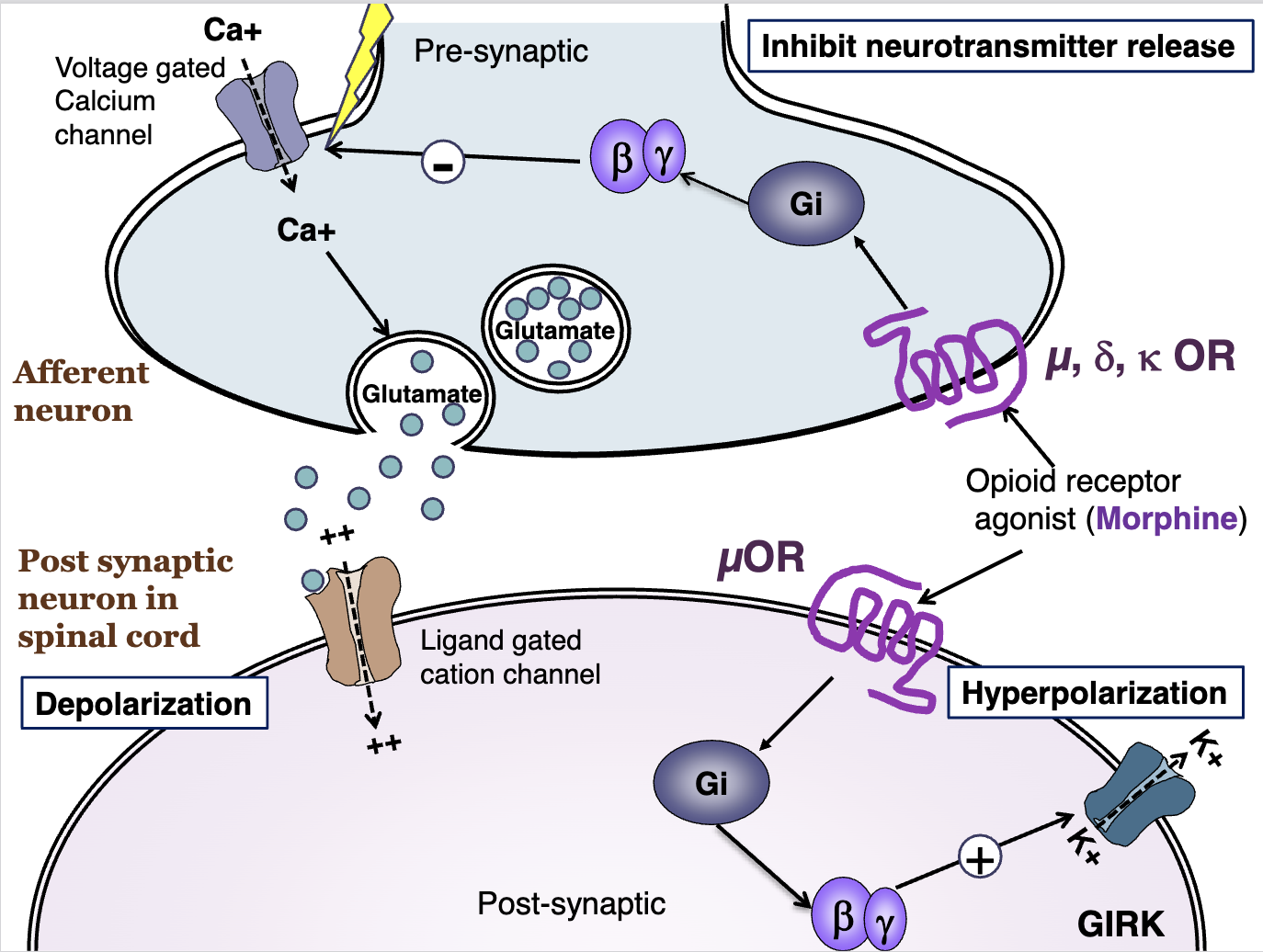
Explain normal action potential
An action potential will cause a membrane voltage change
This will be sensed by voltage gated calcium channels
The release of calcium will cause release of glutamate (Excitatory)
Glutamate will bind to the ligand gated cation channel, which will cause a positive influx of cations and depolarize the membrane; enabling more action potentials
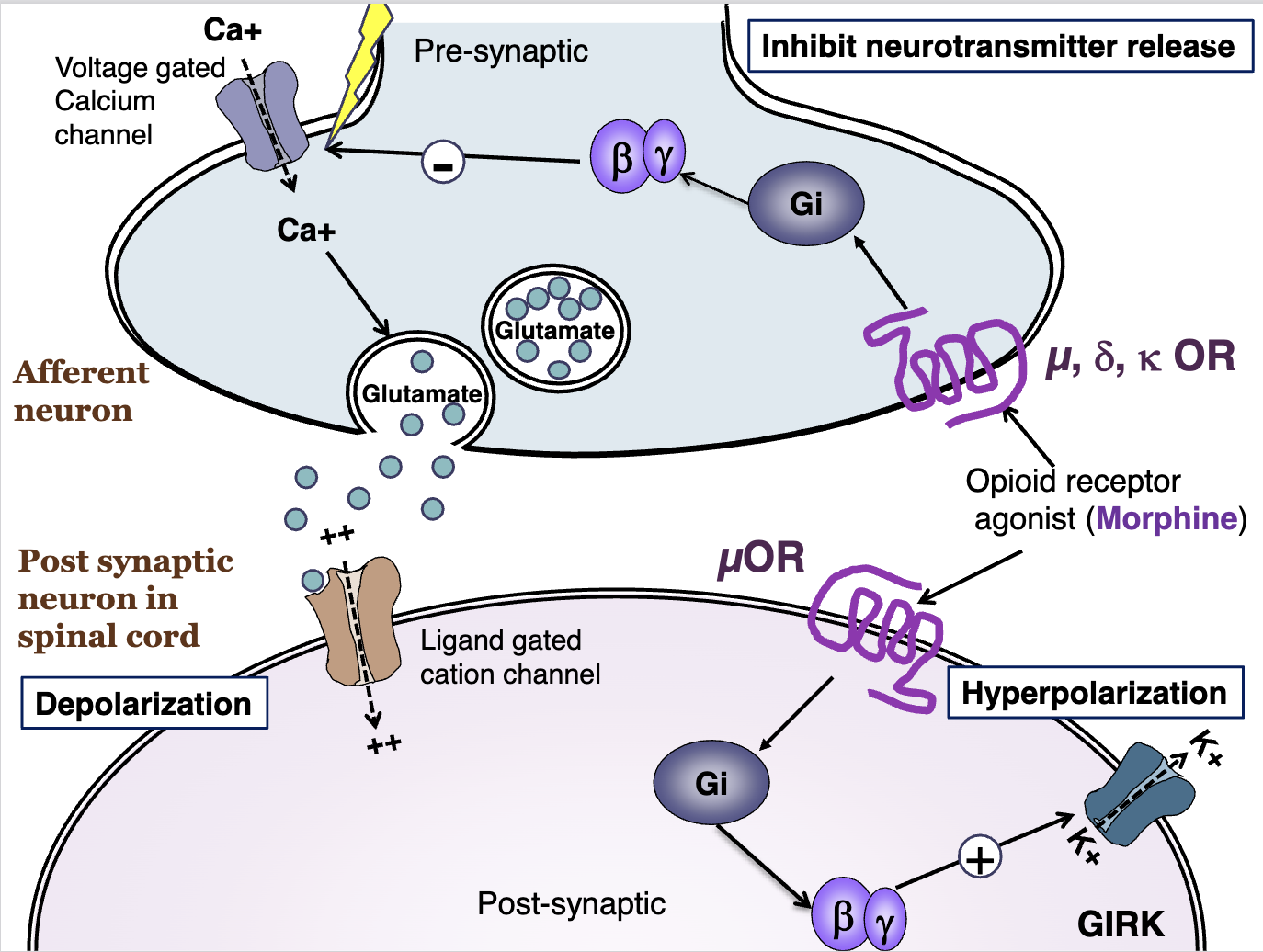
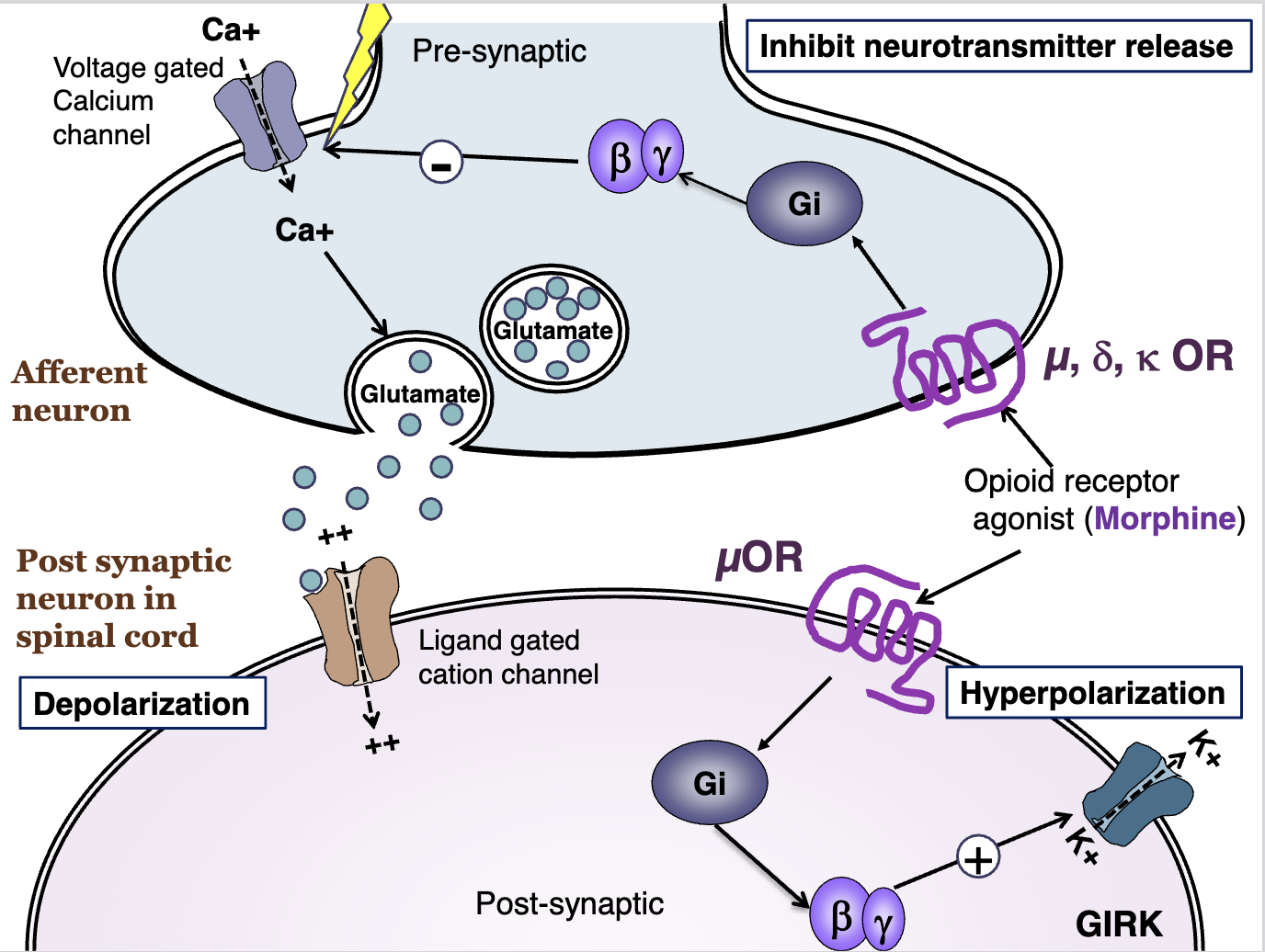
Explain opioid receptors
These opioid receptors are located pre (afferent neuron) and post synaptically (within the spinal cord).
An opioid receptor agonist will bind to these receptors.
On the presynaptic, mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors will cause a G inhibatory effect on the voltage gated calcium channel
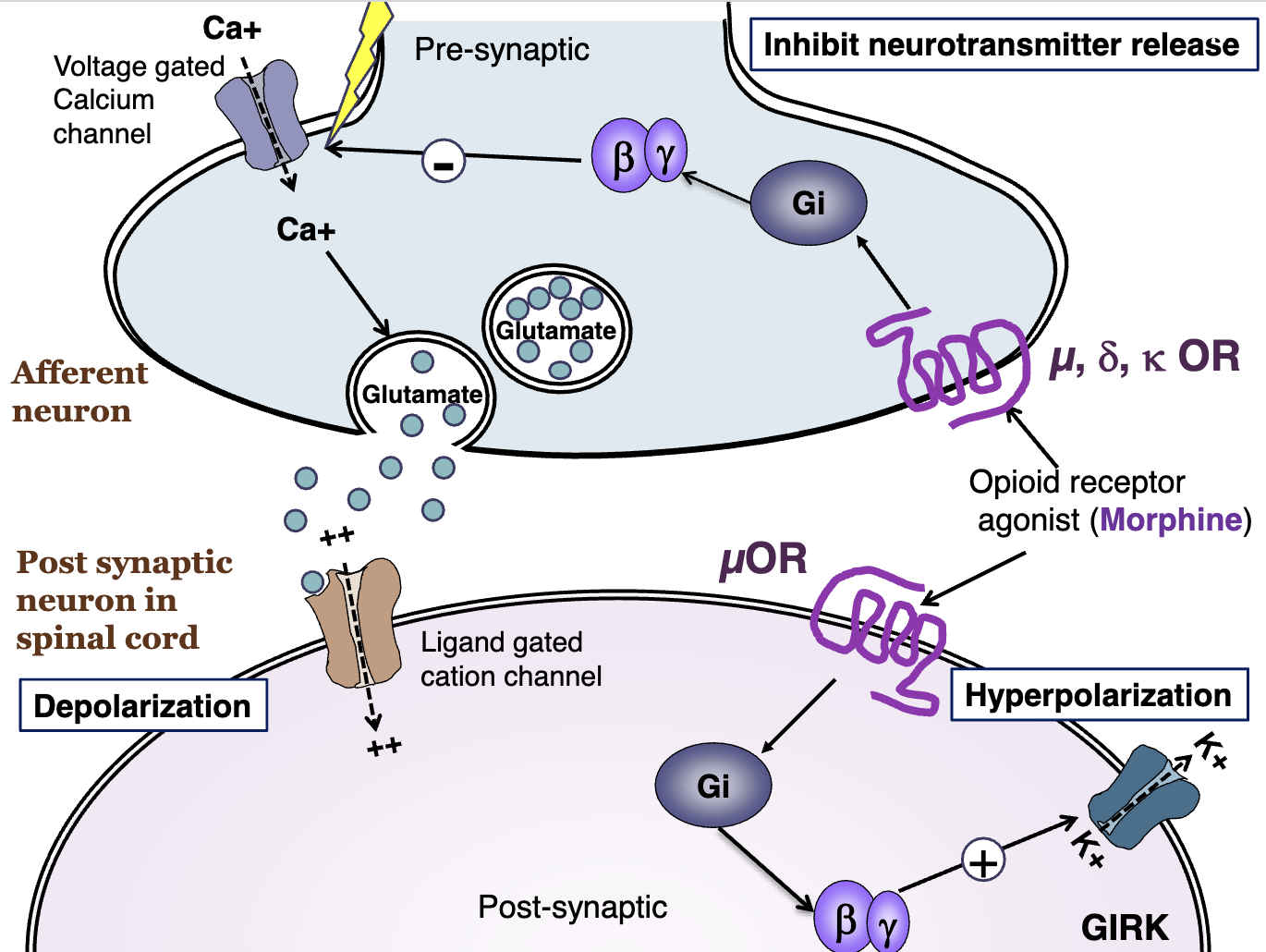
On the postsynaptic, the opioid receptor agonist will activate Gi and enhance GIRK channels to release Potassium (Depolarization)
Presynaptic activation of opioid receptors
On the presynaptic, mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors will cause a G inhibitory effect on the voltage gated calcium channel,
Post synaptic activity of opioid receptors
On the postsynaptic, the opioid receptor agonist (via mu) will activate Gi and enhance GIRK channels to release Potassium (Depolarization)
what is the primary therapeutic target of opioid analgesics
u receptors, responsible for Analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, dependence
what are side effects of selective kappa receptor agonists
effective analgesics but can cause dysphoric reactions (anxiety, panic, delirium)
activation of mu opioid receptors stimulate what
release of endogenous opioids that activate all three opioid types
kappa receptors are important in
sedative and gi effectsd
delta receptors likely contribute to
tolerance (mu also)
4 major classes of opioids
Full/strong mu opioid receptor agonists
Partial/mild mu opioid receptor agonists
Mixed (u or kappa opioid receptor) agonist/antagonist
u opioid receptor antagonists:
Examples of full agonists of u receptors
Morphine, Hydromorphone, Oxymorphone, Heroin
Methadone
Meperidine, fentanyl, sufentanil, alfentanil, remifentanil
Levorphanol, dextromethorphan
example of partial mu opioid receptor agonists
codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone
propoxyphene
diphenoxylate, difenoxin, loperamide
mixed (u and kappa) opioid agonist/antagonist
nalbuphine, buprenorphine
butorphanol
pentazocine, dezocine
mu opioid receptor antagonists
naloxone, naltrexone
morphine metabolism
morphine-3-glucuronide and M6G
Neurotoxic = seizures
meperidine metabolism
demethylated to form normeperidine (can cause seizures)
what 2 drugs are full agonists that can trigger seizures
meperidine and morphine
absorption of opioids
significant first pass metabolism in the liver
*can cross the placental barrier
Opioid effects on the CNS
Analgesia - reduced sensory and emotional pain
Euphoria - pleasant, floating, reduced anxiety
Rarely: dysphoria, possible via kappa receptor
Sedation
Cough suppression via unknown mechanism (codeine; not via OR)
Respiratory depression. Contraindicated in Asthma, COPD, intracranial pressure
Miosis, truncal rigidity, N/V
Opioid major contraindication
Asthma, COPD, intracranial pressure
Peripheral effects of opioids
Cardiovascular effects
bradycardia (not meperidine)
slight hypotension
GI tract
constipation
tolerance does not develop in the colon
Uterus
reduce uterine tone to prolong baby delivery
Renal and other effects of opioids
Renal: increased bladder tone, urinary retention, reduces renal function
Pruritus (itchiness)
triggered by mu opioid receptor agonists
Immune responses
inhibits NK cells, lymphocytes
clinical use of opioids for analgesia
Opioids are usually indicated in severe acute pain
most effective against severe constant pain
considerations for opioid analgesic use
maximal efficacy
pain experience is self-reported
duration of action/duration of therapy
Route of administration
Side effects/adverse reactions
individual history with opiates and opioids
considerations used in chronic pain
tolerance and depedence
limited efficacy
considerations for regional analgesic use of opioids via epidural delivery
reduced supraspine adverse effects
Usually morphine or combined fentanyl with local anesthetics
Respiratory depression may still occur
Rare “epidural HA”
Fetus should be monitored for respiratory depression
use of opioids in acute pulmonary edema
causes dyspnea (difficult or labored breathing)
can be alleviated by morphine
acute pulmonary edema is a complication of heart failure
opioids used for cough supression
codeine and dextromethorphan
unknown mechanism, distinct from analgesia
all full agonists have high potential for
physical dependence and addiction
rapid acting full agonists of the fentanyl type
Alfentanil and Remifentanil: rapid action, short T1/2
Meperidine considerations
antimuscarinic activity; can increase heart rate
avoid in tachycardia
avoid in decreased renal function
demethylated for normeperidine → potential for seizures
use of methadone
longer acting, used to treat Opioid Use Disorder (OUD)
primarily used for detox, lessens withdrawal severity
Maintenance/relapse prevention: blocks rewarding effects of heroin
Increasingly used as a therapeutic analgesic
potent agonist of mu opioid receptors, blocks NMDA receptors
effective in neuropathic pain, morphine-resistant pain
Partial agonists used for diarrhea
diphenoxylate, difenoxin, loperamide are used for diarrhea. Low solubility, low CNS distribution
considerations of partial agonists
Do NOT give partial agonists to patients receiving full agonists
partial agonist dose response curve
will never reach full efficacy
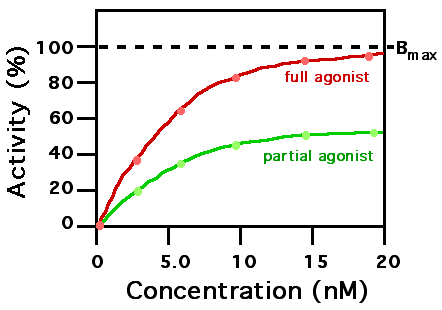
partial agonists examples
codeine, oxycodone, dihydrocodeine, hydrocodone
combined with aspirin or acetaminophen
used for less severe pain
less addictive
Diphenoxylate, difenoxin, and loperamide are used for diarrhea
mixed agonists
all mixed agonists have the potential for negative psychotogenic effects (delusion and hallucination)
mixed agonist examples
nalbuphine: kappa agonist, mu antagonist
butorphanol: kappa agonist, partial agonist at mu receptor
pentazocine: Kappa agonist, weak mu antagonist
buprenorphine characteristics
high potency, long-acting partial mu agonist
antagonist at delta and kappa receptors
used for detox and maintenance for addictions (lower respiratory risk than methadone, full mu agonist)
Functions as an analgesic on its own
Naloxone resistant
tramadol
serotonergic analgesic (SERT Blocker)
Weak mu opioid receptor agonist
Chronic neuropathic pain
No respiratory effects
Seizures, nausea
tapentadol
adrenergic analgesic NET blocker
weak mu opioid receptor agonist
partial agonists may ____ ____ _____ in patients receiving full agonists
Partial agonists may precipitate withdrawal symptoms in patients receiving full agonists
similar to lowering the dose
pre-existing intracranial pressure of head injury considerations for opioids
Opioids should NOT be used in patients with pre-existing intracranial pressure of head injury
contraindications for opioid use
pre-existing pulmonary impairments - respiratory depression compounded
impaired renal or hepatic function: dosage should be reduced due to longer half life
hypothyroidism or low adrenal activity: opioid effects are exaggerated
opioid antagonists characteristics
high affinity for u receptors
inert in the absence of agonist
Used for management of acute opioid overdose
completely reverse morphine effects
Can also induce withdrawal due to mu receptor blocking “abstinence syndrome”
opioid antagonist examples
naloxone: short acting
major clinical use: reverse acute CNS and respiratory effects
naltrexone: long acting
maintenance drug for addicts
taked qid to block all heroin effects
decreases craving for alcohol in alcoholics (reduces alcohol dependence)
what receptor is important for the development and maintenance of tolerance and dependence
mu opioid receptor is important in the development and maintenance of tolerance and dependence
chronic opioid administration may lead to
hyperalgesia
increased sensitivity to feeling pain and an extreme response to pain
limited tolerance develops with
mixed-type opiates and opioid rotation
major symptoms of dependence
Rhinorrhea, lacrimation, hyperventilation, hyperthermia, anxiety
antagonist-precipitated withdrawal
immediate symptoms following administration of naloxone (mu receptor blocker)
abrupt discontinuance of mixed agonist also produces
some withdrawal symptoms but less severe