Roman republic lesson
2.3(3)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:30 PM on 9/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
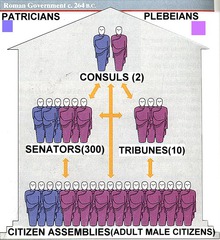
Patricians
Wealthy, land-holding, upper-class, group of powerful Romans. They were basically the rich people of Rome.

2
New cards
Plebeians
The common, regular people of Rome, that were made up of farmers, artisans, and merchants who had little wealth or power. They elected tribunes to represent them in government. They were basically the poor people of Rome.

3
New cards
Senate
The law-makers of Rome that were made up of 300 members from the Patricians and they served for life.

4
New cards
Consuls
Two officials who headed the Roman Republic government. They were elected by the Senate. One managed the government and the other commanded the army.

5
New cards
Tribunes
People who represented the Plebeians in government.
6
New cards
veto
"I forbid" - to forbid/prevent a law from going into effect. Consuls could veto each other's laws.

7
New cards
dictator
A person who was given total power in times of crisis, but the power was temporary.

8
New cards
triumvirate
It is a government by three (tri-) people with equal power, specifically referring to Caesar, Pompey and Crassus.

9
New cards
Julius Caesar
He was made dictator (absolute ruler) in 45BCE. He realized Rome needed reforms, so he gave land to the poor and increased the Senate to 900 members. By increasing the number of Senators, he weakened the Senate's power. He was assassinated by some senators in 44BCE.

10
New cards
gladiator
A prisoner, criminal, or slave who served as a professional fighter in Rome. The most famous place they fought at was the Colosseum.

11
New cards
Tiber River
The river where Rome was founded.

12
New cards
Twelve Tables
The earliest written collection of Roman laws, drawn up by patricians. These twelve codes became the foundation of Roman law. The laws talked about property, crime, family, theft, marriage and inheritance. They were engraved on tablets of metal and put on display at the Forum in the city of Rome, so that everyone could see them.

13
New cards
The Etruscans
Lived in a region just north of Rome called Etruria. Conquered the Romans in 616BC. Introduced the arch and army structure to the Romans.

14
New cards
Republic
A government where some citizens have the right to elect their leaders.

15
New cards
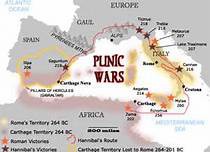
Punic Wars
A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage (264-146 B.C.); Rome won all 3 wars and Carthage was destroyed. Rome became the dominant power in the western Mediterranean.
16
New cards
Hannibal
Carthaginian military commander in the 2nd Punic War. Attempted a surprise attack on Rome by crossing the Alps with a large group of soldiers, horses, and elephants.

17
New cards
peninsula
Land surrounded by water on three sides. Greece and Italy are both peninsulas.
18
New cards
Pax Romana
207 year period of peace in Rome.

19
New cards
Constantine
Emperor of Rome (280-337 CE) who adopted the Christian faith in 313 CE and stopped the persecution of Christians.

20
New cards
emperor
The ruler of an empire.

21
New cards
caesar
The title given to a Roman ruler.

22
New cards
barbarians
A word that Romans used to refer to anyone outside the empire who did not share in the Greek or Roman cultures. Some barbarian tribes were the Vandals, the Visogoths, the Ostrogoths, the Huns.

23
New cards
polytheism
The belief in or worship of many gods and goddesses.

24
New cards
persecute
To punish people for their religious beliefs.

25
New cards
Jesus
A Jewish leader who taught God's law, who spoke of one true God and died upon a crucifix.

26
New cards
Christianity
A religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus.

27
New cards
Augustus Caesar
The first emperor of the Roman Empire after Julius Caesar was assassinated, who brought peace and order to Rome and started Pax Romana.

28
New cards
Diocletian
He divided the Roman Empire into 2 parts because it had gotten too big to manage

29
New cards
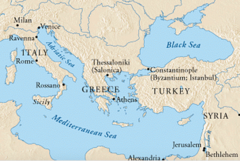
Constantinople
the name given to Byzantium after it was made the new capital of the Roman Empire; it was the capital of the Eastern Empire
30
New cards
Latin
The official language of Rome; named for the people who settled the city.

31
New cards
aqueduct
A Roman engineering feat that brought fresh water from up to a hundred miles away to Roman cities.

32
New cards
Colosseum
An amphitheater that was used for gladiator fights and other types of entertainment.

33
New cards
Pantheon
A Roman temple dedicated to all the Roman gods.

34
New cards
Forum
An open area near government buildings where Romans would go to express their ideas and discuss politics.
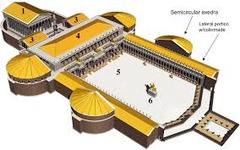
35
New cards
concrete
A Roman invention that enabled buildings to be built quickly while still remaining strong.

36
New cards
Rome
Capital of the Roman Empire.

37
New cards
Tyrrhenian Sea
Protected Rome from the West
38
New cards
Alps Mountains
Protected Rome from the North
39
New cards
Adriatic Sea
Protected Rome from the East
40
New cards
Ionian Sea
Protected Rome from the South
41
New cards
Britain
Farthest northern area conquered by Rome.
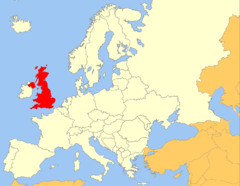
42
New cards
Israel/Palestine
This is where Christianity was founded during the Pax Romana.
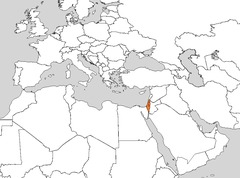
43
New cards
Carthage
Phoenician city-state that went to war with Rome in the Punic Wars.
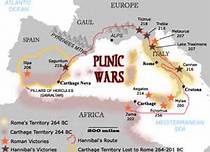
44
New cards
Clovis
5th century Frankish leader of a large kingdom who converted to Christianity.

45
New cards
Byzantine Empire
(330-1453) The eastern half of the Roman Empire, which survived after the fall of the Western Empire at the end of the 5th century C.E. Its capital was Constantinople, named after the Emperor Constantine.
46
New cards
Justinian I
Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565; he reunited the parts of the Roman empire, simplified Roman laws with Justinian's Code, and ordered Hagia Sophia built.

47
New cards
Justinian Code
The body of Roman law collected by order of the Byzantine emperor, Justinian around A.D. 534 and lasted about 900 years.

48
New cards
schism
(n.) a formal split within a religious organization; any division or separation of a group or organization into hostile factions

49
New cards
Roman Catholic Church
A branch of Christianity based in Rome. The original Christian church.

50
New cards
Orthodox Church
Eastern church which was created in 1053 after the schism from the western Roman church; its head is the patriarch of Constantinople, also called the Byzantine Church.

51
New cards
mosaic
A picture or pattern produced by arranging together small colored pieces of hard material, such as stone, tile, or glass.
