1.) 1.1 Interaction of Heredity and Environment & 1.2 Overview of the Nervous System (#1-7)
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.) #1-7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Epigenetics
the study of the relative effects of our genes and how experience can influence genetic expression
changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence
Example: a mother using drugs prenatal, and neglecting child postnasal can influence the child’s genetic expression as he or she grows up.
plasticity
humans’ enormous capacity to learn and adapt
nature vs nurture debate
the nature vs nurture debate is the biggest and most persistent debate in psychology debating if human traits are resent at birth (nature) or if they are developed through experience (nurture).
evolutionary perspective
the evolutionary perspective considers many different behaviors and traits like memory, perception, and language as the result of natural selection.
natural selection
The principle that the inherited traits that better enable an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will, in competition with other trait variations most likely be passed on to succeeding generations.
Natural selection explains how human behaviors, emotions, and traits evolve to provide adaptive advantages.
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind using principles of natural selection. (Focuses on how humans are alike because of their shared biology and history)
behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior. (How humans differ because of their differing genes and environments.)
the study of the environmental factors that affect how our genes are expressed
mutations
random errors in gene relocation that leads to change
heredity
the genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring
survival of the fittest
adapted traits, including psychological traits, that can and are more likely to be passed on to help with survival and reproduction of successful generations (natural selection).
Evolutionary psychology uses this to explain why certain traits and behaviors evolved to help humans survive by natural selection
adaptation
the process by which a species becomes fitted to its environment through natural selection
eugenics
selectively breeding humans to promote certain characteristics
theorists used evolutionary principles in racist ways such as selectively breeding humans to promote certain characteristics (ex: white facial features)
twin studies
research designs used in psychology to measure the influence of genetic factors on human behavior by comparing identical (monozygotic) twins with fraternal (dizygotic) twins.
researching twins can find the nature of how their behaviors, traits, and personalities are alike or different because of their same/identical genes, and how their behaviors are nurtured through their environmental influences or epigenetics.
adoption studies
a research method that compares adopted children to their biological and adoptive parents to determine the effects of genes and environment on behavior and mental processes.
family studies
looks at traits across biological relatives to see how succeeding traits are passed down through generations (natural selection) and which is more common with closer genetic relatedness. They can support nurture if the family members share a common environment.
genome
humans’ common set of genes
no more than 5% of genetic differences among humans arise from population group differences
hereditability
the proportion of observed differences on a trait among individuals of a population that are due to genetic differences.
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
a complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
gene
smallest unit of heredity
small segments of the giant DNA molecules
molecular genetics
the subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes
environment
every nongenetic influence surrounding a person
can trigger genetic expression
genetically influence traits that can influence the experiences we seek and the responses we evoke from others
breakdown the nervous system
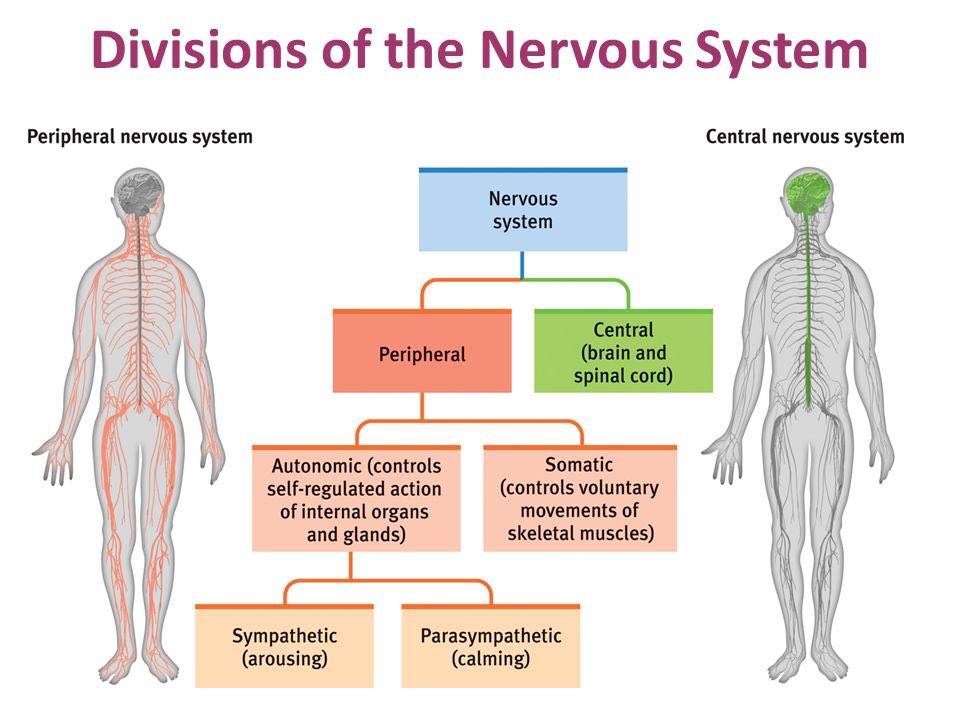
nervous system
the body’s fast, electrochemical communication network (neurotransmitters), consisting of all nerve cells and is divided into several smaller systems based on function
Central Nervous System (CNS)
In the brain and spinal cord
The body’s decision maker
Nerves link the CNS with the body’s sensory receptors, muscles, and glands
acts as the body’s main hub for managing esverything it does, from your thoughts and feelings to your movement
Peripheral nervous system
responsible for gathering information and for transmitting CNS decisions to other body parts
sensory and motor neurons that connect to brain and spinal cord
two main PNS divisions: autonomic and somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
controls involuntary functions like: heartbeat, digestion, breathing, etc.
controls our glands and internal organ muscles, in means of its sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
both work together to regulate homeostasis
how does the sympathetic system act on the body?
fight or flight
Pupils dilate (enlarge) and inhibits/restricts tear production
heart rate increases
restriction digestion
bladder relaxes
release of adrenaline + noradrenaline
how does the parasympathetic system act on the body?
the aftermath of a stressful evet
pupils constrict (stress) and stimulates tear production
heart rate decreases
stimulates digestion
bladder contracts
stimulates elimination in sexual arousal
spinal cord
a two way information highway connecting the peripheral nervous system and the brain.
Ascends neural fibers send up sensory neurons/info and descending fibers send back motor neurons to the body.
reflexes
our automatic response to stimuli, which illustrate the spinal cord’s work
motor (EFFERENT) neurons
motor neurons that carry OUTgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
sensory (AFFERENT) neurons
afferent nerves of sensory neurons that carry INcoming information from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that serve as mediators between sensory and motor neurons; carry info around the brain for processing
reflex arc
a simple spinal reflex pathway is composed of a single sensory neuron and a single motor neuron; communicates through a spinal cord interneuron