AP Psychology Unit 6 -> Motivation & Emotion
5.0(3)Studied by 112 people
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:01 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
Instinctive Theory
The body follows a set of biologically pre-programmed instinctual urges
2
New cards
Drive Reduction Theory
Our bodies like to be in homeostasis (internal state of balance)
3
New cards
Incentive Theory
Positive or negative environmental stimuli motivate behavior
4
New cards
Arousal Theory (aka Yerkes-Dodson Theory)
Optimum stress is necessary for optimum performance (too much or too little stress is bad, but the right amount is optimal)
5
New cards
Self-Determination Theory
Desire for significant accomplishment (being in control of your life allows you to be more self-directed)
6
New cards
Extrinsic Motivation
Desire to perform a behavior for reward or to avoid punishment
7
New cards
Intrinsic motivation
Desire to perform a behavior for your own sake
8
New cards
Self-Actualization Theory
A true realization of our inner potential (goals & dreams)
9
New cards
Extracellular thrist
Loss of fluids surrounding cells of your body (caused by vomiting & dehydration; need minerals & water to relpenish)
10
New cards
Intracellular thirst
Sodium decreases fluids inside cells from eating salty foods (only water can fix this)
11
New cards
Leptin
Hunger hormone
12
New cards
Set point theory
Your body tries to maintain a particular level of weight (homeostasis)
13
New cards
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs
(Bottom) Physiological, Saftey, Love/belonging, Esteem, Self-actualization, Transcendence (Top)
14
New cards
Type A personality
Competitive, hard-driving, impatient,
15
New cards
Type B personality
Calm, relaxed, non-competitive
16
New cards
Type C
Models Type A but can mirror Type B under stress
17
New cards
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
Process of responding to stressful events
\
* Alarm → immediate (fight or flight) response of the body
* Resistance → Body defenses weaken and stress is reduced
* Exhaustion → Stress becomes persistent
\
* Alarm → immediate (fight or flight) response of the body
* Resistance → Body defenses weaken and stress is reduced
* Exhaustion → Stress becomes persistent
18
New cards
Adaptation Level Phenomenon
Humans adapt to their surroundings and no longer respond to the novelty of certain stimuli after a period of time has passed (Ex: winning the lottery made you happy a year ago, but now you don’t feel the same happiness)
19
New cards
Approach-Approach conflict (conflict motivatoin)
occurs when you must choose between two attractive outcomes
20
New cards
Avoidance-avoidance conflict (conflict motivation)
occurs when you must choose between two unattractive outcomes
21
New cards
Approach-avoidance conflict (conflict motivation
When one event or goal has both attractive and unattractive features (ex: You like the taste of candy but your stomach hurts after eating it)
22
New cards
Catharsis
The process of releasing tension (getting out of a state of tension)
23
New cards
Feel Good, do-good phenomenon
The tendency to help others when your in a good mood
24
New cards
Subjective well-being
Self-measuring your state of well-being (How you feel about your own life)
25
New cards
Relative Deprivation
When you feel worse than the people you associate and compare them to yourself with (ex: you feel sad because all of your friends did well on a test but you didn’t)
26
New cards

James-Lange theory
Our physiological reaction leads us to labeling the emotion
27
New cards
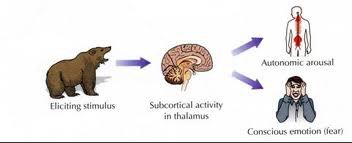
Cannon-Bard theory
Our physiological reaction occurs simultaneously with labeling the emotion
28
New cards
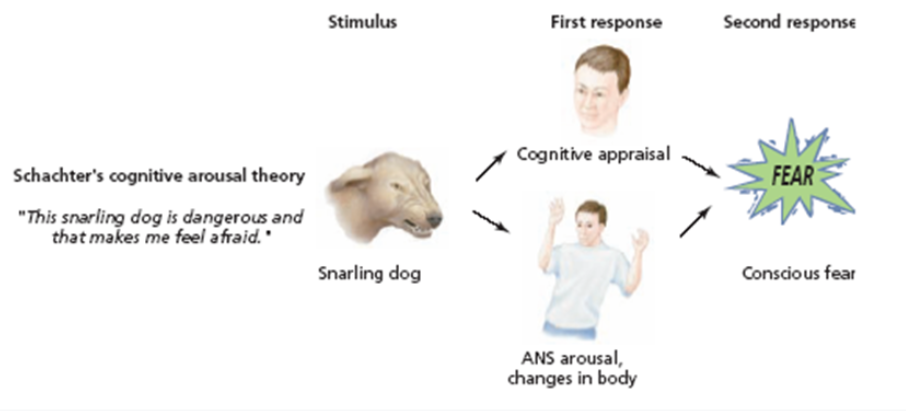
Shachter-Singer “2-factor” theory
Our physiological reaction occurs while we create a cognitive label from the environment; then we experience the emotion
29
New cards
Opponent Process theory
after you feel an emotion you will feel the opposite of said emotion. Also, emotions work in pairs
30
New cards
Leadership Style
Theory X (Task Leadership) vs Theory Y (Social leadership)
31
New cards
Theory X
Constant monitoring of workers, hovers
32
New cards
Theory Y
Gives challenges and freedom; workers are more motivated to demonstrate competence and creativity
33
New cards
Izard Theory
10-basic emotions that are cross cultural (ex: anger, sadness, disgust)
34
New cards
Ekman’s Theory
Facial muscles are used to indicate emotion and are universal
35
New cards
Limbic System
Controls behavioral and emotional responses