Biology Study Guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology Study Guide
Last updated 6:16 AM on 5/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
crossing over
\
**Which event is an important factor in increasing variety among sexually reproducing organisms?**
**Which event is an important factor in increasing variety among sexually reproducing organisms?**
2
New cards
\
produces haploid gametes
produces haploid gametes
\
**Which phrase best describes the process of meiosis?**
**Which phrase best describes the process of meiosis?**
3
New cards
acts as a source of variations within a species never occur
\
**The exchange of segments of DNA between the members of a pair of chromosomes __________.**
**The exchange of segments of DNA between the members of a pair of chromosomes __________.**
4
New cards
\
Pairs of homologous chromosomes exchange segments.
Pairs of homologous chromosomes exchange segments.
\
**Which phrase best describes the process of crossing over?**
**Which phrase best describes the process of crossing over?**
5
New cards
\
Males produce four functional sperm while females produce only one functional egg.
Males produce four functional sperm while females produce only one functional egg.
**How is gametogenesis different in females than in males?**
6
New cards
\
meiosis I
meiosis I
\
**During which of these does the separation of homologous chromosomes occur?**
**A.** mitosis **B.** meiosis I
**C.** meiosis II **D.** fertilization
**During which of these does the separation of homologous chromosomes occur?**
**A.** mitosis **B.** meiosis I
**C.** meiosis II **D.** fertilization
7
New cards
exchange corresponding segments of DNA
**What happens to chromosomes when crossing over takes place?**
8
New cards
They are divided.
**What happens to the sister chromatids in meiosis II?**
9
New cards
anaphase I
**In which phase of meiosis does the chromosome number change from diploid to haploid?**
10
New cards
\
division of homologous chromosomes
division of homologous chromosomes
\
**Which phrase best describes meiosis I?**
**Which phrase best describes meiosis I?**
11
New cards
False
\
**True/False**: Meiosis begins with haploid cells and ends with diploid cells
**True/False**: Meiosis begins with haploid cells and ends with diploid cells
12
New cards
True
\
**True/False**: Meiosis has two cell division stages
**True/False**: Meiosis has two cell division stages
13
New cards
False
\
**True/False**: Meiosis II divides the sister chromatids into four haploid cells
**True/False**: Meiosis II divides the sister chromatids into four haploid cells
14
New cards
False
\
**True/False**: Crossing Over takes place in Telophase II of meiosis
**True/False**: Crossing Over takes place in Telophase II of meiosis
15
New cards
True
\
**True/False:** All gametes formed at the end of meiosis are haploid
**True/False:** All gametes formed at the end of meiosis are haploid
16
New cards
True
\
**True/False:** A zygote formed from the process of fertilization is a diploid cell
**True/False:** A zygote formed from the process of fertilization is a diploid cell
17
New cards
True
**True/False:** Random alignment results in chromosomes that have different combinations of alleles than they had before.
18
New cards
True
**True or False?** The diploid cell that enters meiosis becomes 4 haploid cells at the end of meiosis.
19
New cards
Doubles then divide in half.
**During meiosis, chromosome number**
20
New cards
Two of the above
**During meiosis I,**
a. Homologous chromosomes separate.
b. Each sister chromatid becomes a chromosome.
c. Sister chromatids separate.
d. 4 daughter cells are formed from a single original cell.
e. Two of the above.
a. Homologous chromosomes separate.
b. Each sister chromatid becomes a chromosome.
c. Sister chromatids separate.
d. 4 daughter cells are formed from a single original cell.
e. Two of the above.
21
New cards
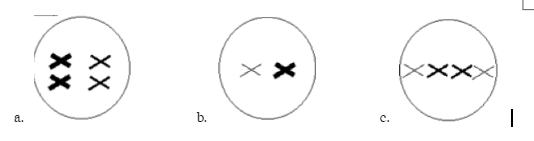
A
\
**Which of these cells is shown during metaphase I of meiosis?**
**Which of these cells is shown during metaphase I of meiosis?**
22
New cards
\
Late Prophase I and Early Metaphase I
Late Prophase I and Early Metaphase I
\
**During meiosis, when does crossing over occur?**
**During meiosis, when does crossing over occur?**
23
New cards
\
Sister chromatids separate.
Sister chromatids separate.
\
**Which of the following happens during both meiosis and mitosis?**
a. Crossing over
b. Random alignment of homologous chromosomes
c. Sister chromatids separate.
d. Homologous chromosomes separate
**Which of the following happens during both meiosis and mitosis?**
a. Crossing over
b. Random alignment of homologous chromosomes
c. Sister chromatids separate.
d. Homologous chromosomes separate
24
New cards
\
Sperm and egg
Sperm and egg
\
**Which cells are formed by meiosis?**
**Which cells are formed by meiosis?**
25
New cards
One
**A human female forms how many eggs from one original cell?**
26
New cards
46
\
**How many total chromosomes are there in the karyotype of a normal human?**
**How many total chromosomes are there in the karyotype of a normal human?**
27
New cards
\
interphase
interphase
\
**The division of sex cells is known as**
**The division of sex cells is known as**
28
New cards
interphase
**During which stage of the cell cycle does the cell grow, the DNA replicates, and the organelles are copied?**
29
New cards
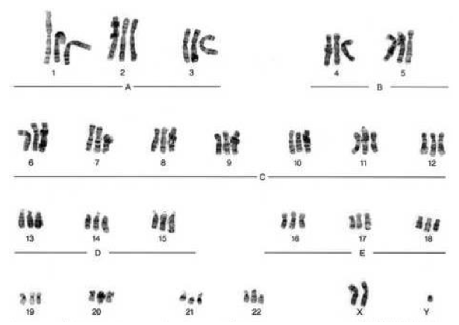
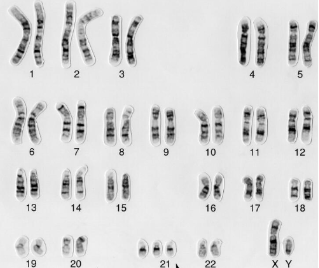
More than 46 chromosomes, miscarriage, male, multiple trisomies (3 chromosomes in a pair), This karyotype resulted from nondisjunction of an entire cell, The haploid number of this person is over 34.
What does the picture indicate?
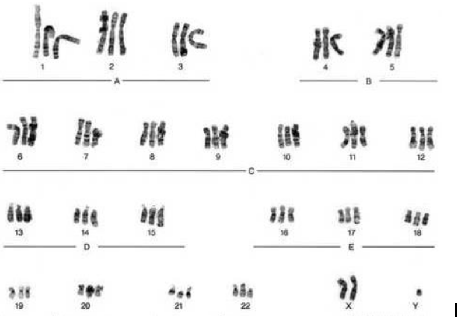
30
New cards
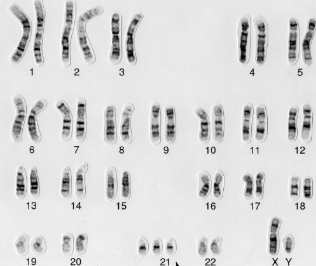
Diploid number 46, Haploid number 23, 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes, 1 trisonomy, male, no birth defects
What does the picture indicate?
31
New cards
The age of an individual
**The karyotype can tell us about all of the following facts except ONE**
The gender of an individual The species the individual belongs
\
The age of an individual The disorder the individual has
The gender of an individual The species the individual belongs
\
The age of an individual The disorder the individual has
32
New cards
Down syndrome
**An individual was diagnosed with Trisomy 21 (extra chromosome in the 21st set), the patient is likely to have what type of syndrome**
33
New cards
Patau syndrome
**An individual was diagnosed with Trisomy 13 (extra chromosome in the 13th set), the patient is likely to have what type of syndrome**
34
New cards
Down Syndrome
**An individual was diagnosed with Trisomy 21 (extra chromosome in the 21st set), the patient is likely to have what type of syndrome**
35
New cards
autosomes are arranged from largest to smallest
**In karyograms, _______.**
36
New cards
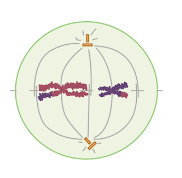
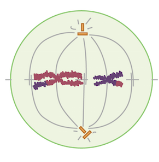
Metaphase II
**Which stage of meiosis II is the cell in?**
37
New cards
karyotype
**A picture that shows all of a cell's chromosomes, matched up into pairs is called a ________.**
38
New cards
female, male
**If a person's sex-determining chromosomes consist of two X chromosomes (XX), that person is ________, whereas if they consist of an X and a Y (XY), that person is ________.**
39
New cards
gametes
**Sex cells are also termed ________.**
40
New cards
fertilization, a zygote
**When a sperm cell unites with an ovum (egg), it is called ______ and leads to the formation of ______.**
41
New cards
both parents
**Offspring born through sexual reproduction receive genes from ________.**
42
New cards
True
**In humans and most other animals, meiosis occurs in the testes of females and in the ovaries of males.**
43
New cards
False
**Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes within a cell by one-half.**
44
New cards
stomata cells and somatic cells
**Body cells are also called ________.**
45
New cards
2
**Humans contain how many sex chromosomes.**
46
New cards
diploid (or 2n)
**A cell containing the full complement of chromosomes is said to be a ________ cell.**
47
New cards
haploid (1n)
**A cell containing one-half of the normal complement of chromosomes is said to be a ________ cell.**
48
New cards
True
**In meiosis, two nuclear divisions yield a total of 4 haploid cells.**
49
New cards
tetrad
**Synapse forms a chromosome complex known as a ________.**
50
New cards
increases genetic diversity
**Crossing over ________**
51
New cards
when homologous chromosomes are paired up
**If crossing over occurs, it occurs ________.**
52
New cards
sister chromatids
**The two chromatids making up a chromosome are ________.**
53
New cards
non-sister chromatids
**Chromatids found on different chromosomes in a homologous pair are _________.**
54
New cards
non-sister chromatids
During crossing over, ________ exchange portions of DNA.
55
New cards
that carries DNA from both parents
**Crossing over results in a chromosome ________.**
56
New cards
microtubules that form spindles
**Extending from the centrioles are ________.**
57
New cards
False
**In meiosis I, all stages come to a clear stop before the cell enters the next stage.**
58
New cards
each chromosome in the homologous pair becomes attached to a different centriole
**At the start of metaphase I, ________.**
59
New cards
metaphase plate
**At the end of metaphase I, all chromosomes have been aligned at the equator of the cell, known as the ________.**
60
New cards
move towards different centrioles
**In anaphase I, chromosomes in the homologous pair _________.**
61
New cards
briefly move to the outside of the cell
**In telophase I, the spindles ________.**
62
New cards
1n
**At the end of telophase I, each pole of the cell is ________.**
63
New cards
double helix
**Which of the following best describes a DNA molecule?**
A. double helix B. contains ribose
\
C. made of amino acids D. contains Uracil
A. double helix B. contains ribose
\
C. made of amino acids D. contains Uracil
64
New cards
nucleotides
**Which of the following units are repeatedly joined together to form a strand of DNA?**
65
New cards
it serves as the blueprint for traits of all living things
**Why is DNA important?**
66
New cards
deoxyribose sugar and phosphate
**Which 2 molecules form the sides (backbone) of the DNA ladder?**
67
New cards
hydrogen bonds
**Nitrogenous bases are joined by which type of bond?**
68
New cards
sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base
**What are the three components of a nucleotide?**
69
New cards
Single Strand
**RNA is**
70
New cards
A-T and C-G
**Base pair for DNA is**
71
New cards
U-A and C-G
**Base pair for RNA is**
72
New cards
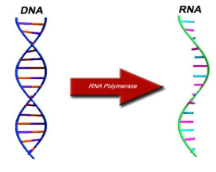
Transcription
\
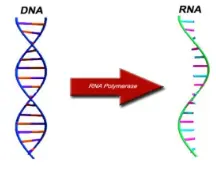
73
New cards
DNA-RNA-protein
**Genetic info flows in one direction. Which best represents this flow?**
74
New cards
5’-TACGGTA-3’
**What is the complementary base pair to the DNA strand below:** 5'-ATGCCAT-3'
75
New cards
helicase
**Enzyme that unwinds the DNA**
76
New cards
DNA polymerase I
The enzyme that adds nucleotides to the newly synthesized strand of DNA
77
New cards
Hershey & Chase
**Experiment that radioactively labeled the proteins and DNA of bacteriophages to determine if DNA or protein was the transforming agent**
78
New cards
each one with one new strand and one original strand
**DNA replication results in two DNA molecules,**
79
New cards
32% cytosine, 32% adenine, 18% thymine
**If a DNA molecule is 18% Guanine which of the following is correct**
18% cytosine, 32% adenine, 32% thymine
32% cytosine, 18% adenine, 32% thymine
18% cytosine, 64% adenine, 64% thymine
32% cytosine, 32% adenine, 18% thymine
18% cytosine, 32% adenine, 32% thymine
32% cytosine, 18% adenine, 32% thymine
18% cytosine, 64% adenine, 64% thymine
32% cytosine, 32% adenine, 18% thymine
80
New cards
Nucleus
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells?
81
New cards
UAC
**What is the complementary tRNA anticodon to the following mRNA codon: AUG**
82
New cards
\
**AUA GGC UGA**
**AUA GGC UGA**
\
Transcribe the following DNA sequence: TAT GGC ACT
Transcribe the following DNA sequence: TAT GGC ACT
83
New cards
Met-Asn-Cys-Stop
**Translate the following RNA sequence:** *AUG AAU UGU UGA*
84
New cards
UAG UUA GCA AUC
**What is the complementary RNA sequence for the following:** ATC AAT CGT TAG
85
New cards
Gly-Ala-His-His
**What is the amino acid sequence for the following:** GGG GCA CAT CAC
86
New cards
Either insertion or deletion of a base.
A frameshift mutation could result from
87
New cards
complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon.
**The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is**
88
New cards
Insertion
**Original: ATC CAT**
**Mutation: ATC GCAT**
**What mutation occurred?**
**Mutation: ATC GCAT**
**What mutation occurred?**
89
New cards
substitution
**What type of mutation has occurred here?**
T-G-A-C-C-A
T-G-A-G-C-A
T-G-A-C-C-A
T-G-A-G-C-A
90
New cards
it allows a gene to be transcribed
**What does a promoter do?**
91
New cards
A stop codon would be inserted
In the mRNA sequence: AUGUGGAACAGAUAC, what would happen if in the last codon, Guanine was substituted with Cytosine?
92
New cards
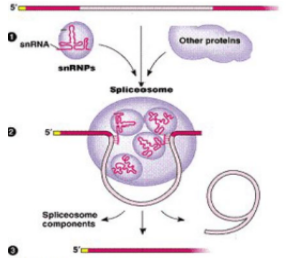
mRNA
**What product gets made at the end of the process pictured?**
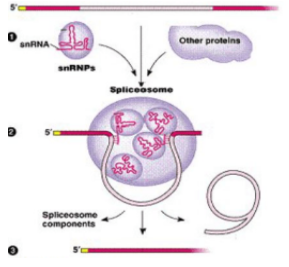
93
New cards
Introns
**The segments of RNA that are cut out are called.**
94
New cards
Exon
**In RNA processing, the coding sequence that remains in the final mRNA.**
95
New cards
ribose
**RNA contains the sugar**
96
New cards
\
**Which of the following is a base that is NOT contained in DNA?**
1. Adenine B. Thymine
C. Uracil D. Guanine
**Which of the following is a base that is NOT contained in DNA?**
1. Adenine B. Thymine
C. Uracil D. Guanine
**Uracil**
97
New cards
mutation
**Permanent change in a cell's DNA**
98
New cards
Ribosomal RNA
**A type of RNA that associates with proteins to form ribosomes.; Intron**
99
New cards
Transfer RNA
**The type of RNA that transports amino acids to the ribosomes is called**
100
New cards
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that regulates RNA synthesis