Slides - 5. Inventory & COGS
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Purchase merchandise for resale, Sell Merchandise and Deliver to Customer, Receive cash from Customer Toward Accounts Receivable
Operating Cycle
Draw Expenditures included in inventory
y
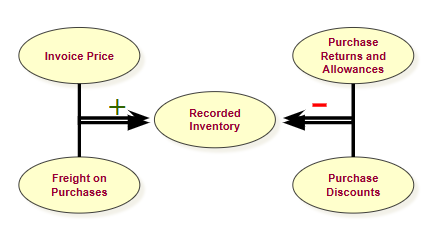
Purchase transactions are recorded directly in an inventory account.
Perpetual inventory
is always being updated every time a purchase/sale is made
Perpetual inventory
Sales require two entries to record: (1) the retail sale and (2) the cost of goods sold.
Perpetual inventory
No up-to-date record of inventory is maintained during the year.
Periodic Inventory
is only updated at the end of the period
Periodic Inventory
Sales require one entry to record the retail sale. Cost of goods sold is calculated.
Periodic Inventory
Beginning Inventory + Purchases =
Goods Available for Sale
Goods Available for Sale =
Beginning Inventory + Purchases
Goods Available for Sale - Ending Inventory =
COGS
COGS =
Goods Available for Sale - Ending Inventory
Inventory Cost Flow Assumptions
1. Specific Identification
2. First-in, First-out (FIFO)
3. Last-in, First-out (LIFO)
4. Weighted-Average Cost
When units are sold, the specific cost of the unit sold is added to cost of goods sold
specific identification
Most commonly used in businesses that have low sales volume of high dollar items
specific identification
Impractical when large quantities of similar items are stocked.
Specific identification
like putting new produce at the back with oldest produce in the front
FIFO
Best approximates physical flow for many businesses
FIFO
The newest stuff that we bought we are going to assume that is sold and then we are going to build our inventory based on older stuff
LIFO
Each unit in cost of goods sold and each unit in ending inventory has the (BLANK) average cost.
same
Weighted Average Cost =
Cost of Goods Available for Sale/Number of Units Available for Sale
Specific Identification or FIFO inventory values are the (BLANK) regardless of whether computed on a perpetual or periodic basis
same
In periods of rising prices, (BLANK) LIFO yields lower taxes than (BLANK) LIFO
periodic, perpetual
Weighted average perpetual inventory (BLANK) the weighted average cost after each inventory purchase
recalculates
In periods of rising prices, results in higher net income
FIFO
In periods of rising prices, results in lower taxes
LIFO
Smooths out effects of price changes.
Weighted Average
If using LIFO for tax, must also use for financial reporting
LIFO Conformity Rule
Ending inventory is reported at the
lower of cost or net realizable value (LCNRV)
Net Realizable Value =
Selling Price - Cost to sell
causes the recognition of ‘holding loss’ when inventory value drops prior to sale
Conservatism
Overstatement of ending inventory
Understates COGS, Overstates net income
Understatement of ending inventory
Overstates COGS, understates net income
Inventory turnover ratio =
COGS/Average Inventory
Days’ sales in inventory =
365/inventory turnover
the (BLANK) the inventory turnover ratio the better
higher
the (BLANK) the days’ sales in inventory the better
lower
LIFO Reserve =
Ending inventory (FIFO) - Ending Inventory (LIFO)
FIFO COGS =
LIFO COGS - the change in the LIFO reserve
Required disclosure if company reports using LIFO
LIFO Reserve
Useful in comparing companies using LIFO vs. FIFO
LIFO Reserve