DAO Midterm NYU COD 25'
1/265
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
266 Terms
Anterior teeth have how many lobes?
4 total
- 3 facially
- 1 forms cingulum
The middle lobe of canine becomes the ____
labial ridge
In anterior teeth, the mesial contacts are in the ______ and the distal contacts are in the ____
EXCEPT in maxillary incisors and maxillary canines, the distal contact is in the ____
incisal third for both
middle third
cervical line is also called the _____
cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
Cervical line has greatest FACIAL/ LINGUAL curvature on which tooth? what does it curve towards
maxillary central incisor
the apex
Cervical line has greater curvature on than ____ side than the ___ side of the same tooth, and curves _____
mesial greater curvature than distal
incisally
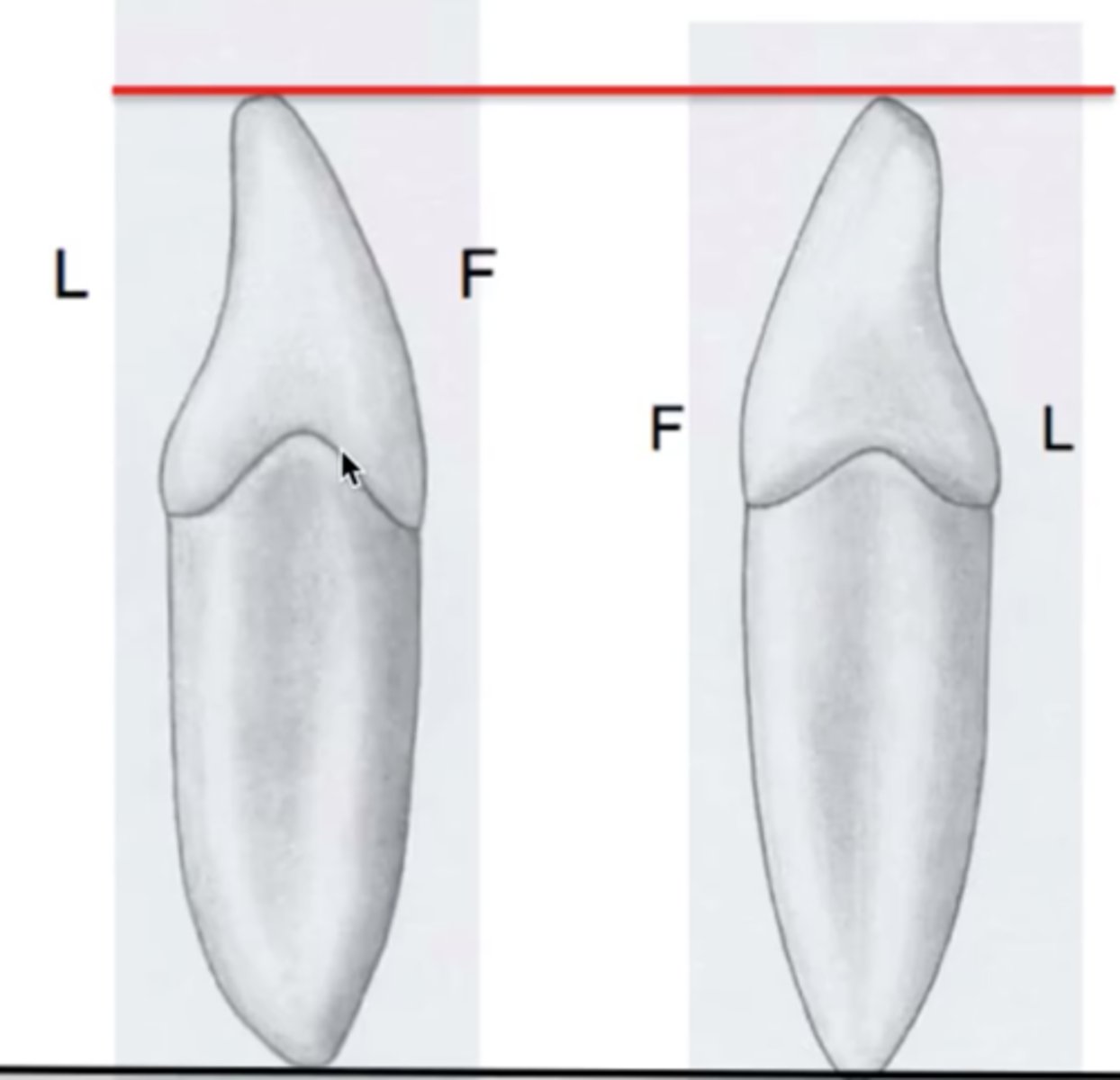
The cervical line curvature becomes ____ pronounced from anterior to posterior
less
What are the functions of the incisors
cut food, enable speech, help support lip, help guide mandible properly during teeth contact
Incisors have a _____ or _____ _____ incisal edge
straight or slightly curved
Incisors have _______ angles that are sharper then the _______ angles of the same tooth, EXCEPT _____ which are symmetrical
mesioincisal sharper than distoincisal
mand. centrals
incisors incisal edge slope _____, EXCEPT _____
cervically toward distal
mand. central (symmetrical)
incisors are _____ in shape from FACIAL perspective, and longer ______ than they are wide ______
rectangular
incisogingivally then mesiodistally
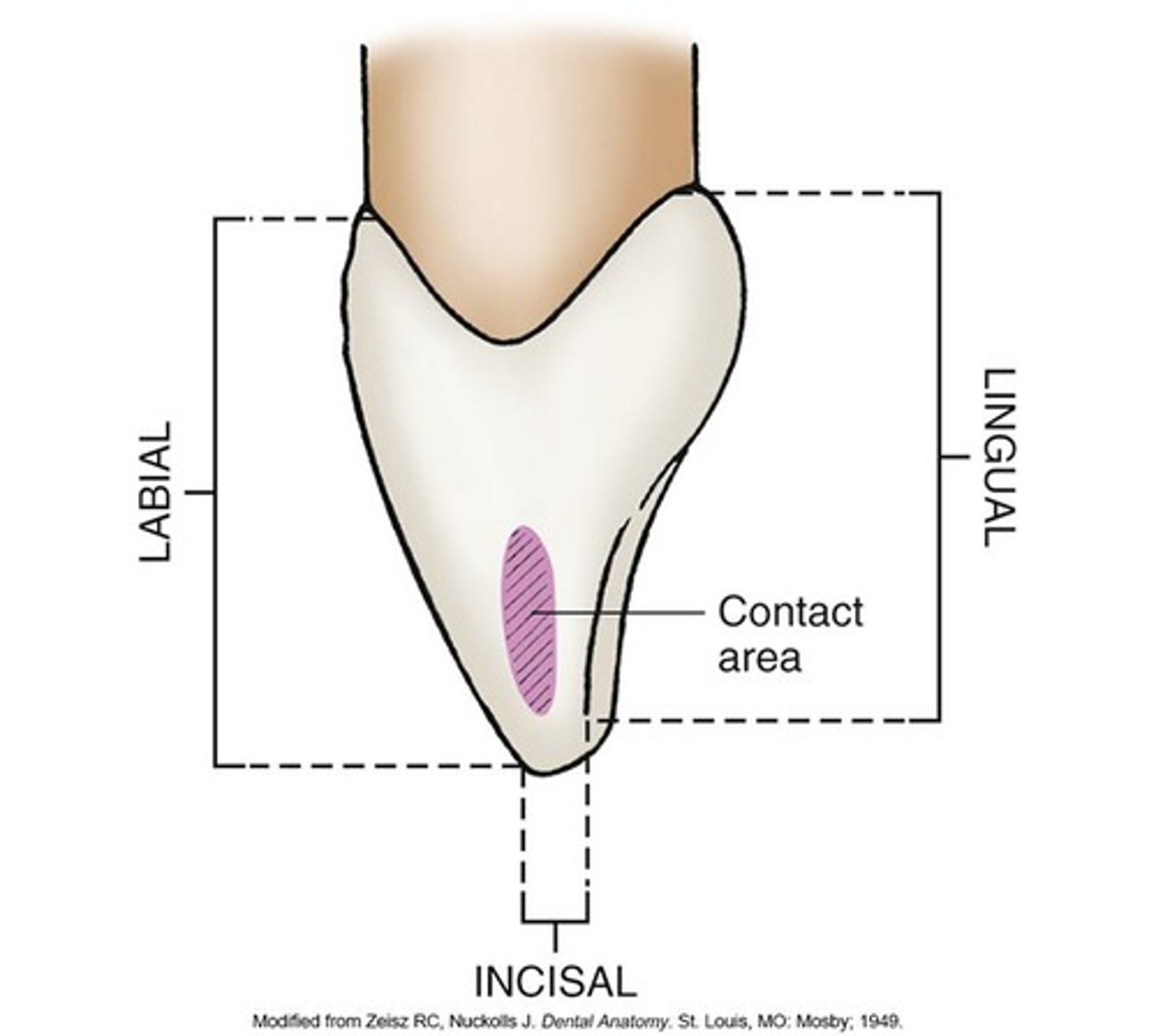
on incisors, the contact areas are at the
greatest proximal height of contour
Incisors: facial HOC is in ___ 3rd, lingual HOC is in ____ 3rd
incisal
cervical (cingulum)
All incisor roots are longer than _____. They are _____ faciolingually then mesiodistally EXCEPT on _____ _______ where they are _____
the crowns
wider
max. centrals where they are equal
Incisor roots may bend in the ______ 3rd, EXCEPT on ____ ____ which are not as likely to bend
apical
max centrals
max incisors are ___ than mand incisors
larger
max incisors are wider _____ than _____
mesiodistally than faciolingually
Max incisors have ___ fossae and ______ ______ marginal ridges than mand incisors
deeper
more pronounced
max incisors have a _____ crown to root ratio then mand incisors
poorer
mand incisors are ____ faciolingually than mesiodistally. in mand centrals, they are almost ____
wider
equal
mand lateral incisors are ____ than mand central incisors
max lateral incisors are ____ than max central incisors
larger
smaller
on max incisors, incisal edge is set more ____
facially
on mand incisors, incisal edge is set more ____
lingually
Which tooth has the longest crown? which tooth has the widest crown mesiodistally?
mand canine
max central
in max centrals, the cingulum is offset to the ___
distal
The crown to root ratio is the smallest in which tooth
max central
in max centrals, the mesial contact in in the _____ 3rd, and in the _______ for the distal contact
incisal
junction of the incisal and middle third
in max laterals, the _____ is longer than wide
crown
The incisal edge of the max lateral has the greatest ______ of any tooth
curvature
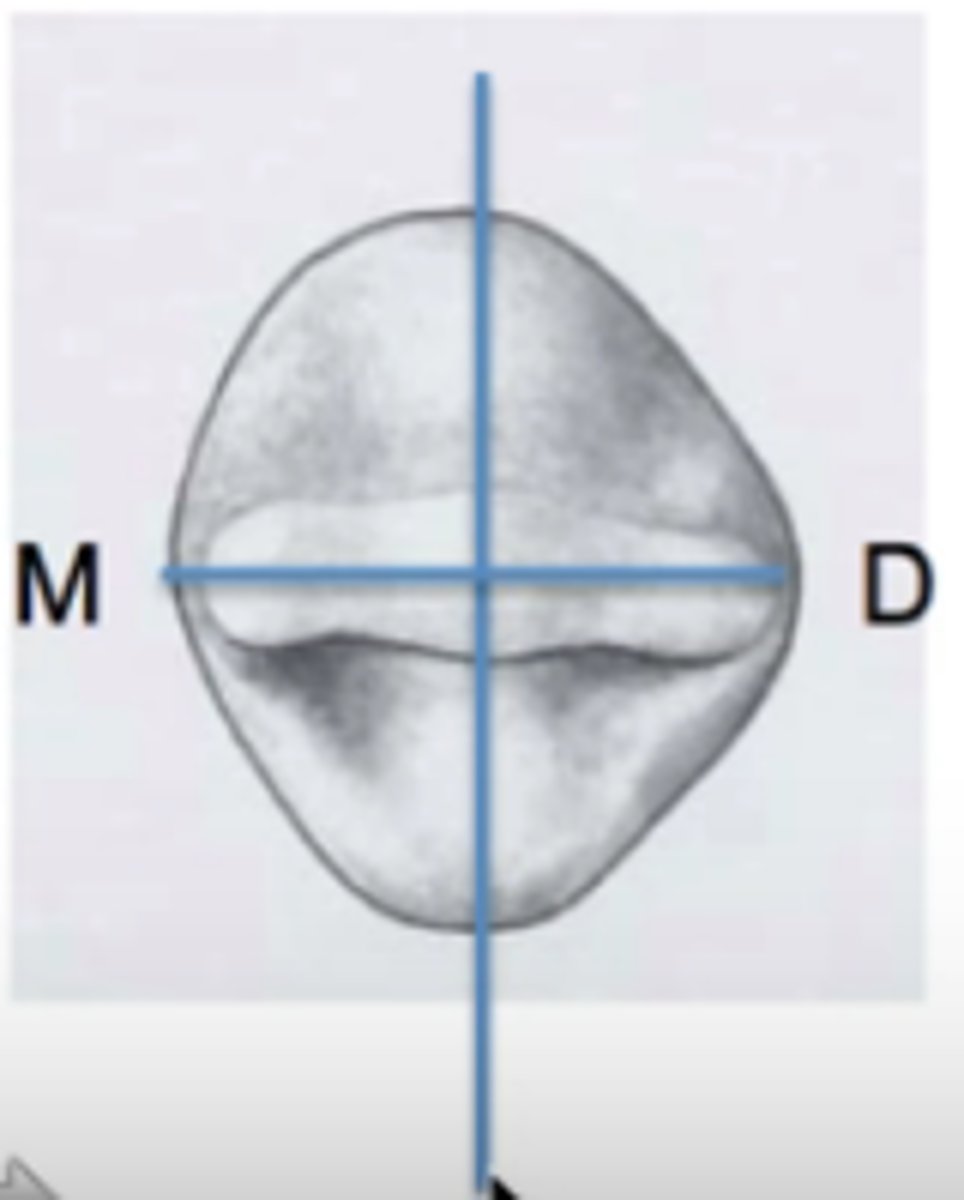
max laterals are likely to have a very deep ____ ____
lingual pit
on max laterals, the cingulum is
centered
Maxillary centrals roots are _____________, with a _____ apex that may have a ______
single, conical, and straight
straight
distal deflection
which tooth has the narrowest crown mesiodistally
mand central
What is the smallest tooth of any dentition?
mand central
in mand central, mesial and distal contacts are in ____
incisal third
on mand centrals, the cingulum is
centered
what is a distolingual twist, and which tooth has it
crown is twisted distally on its root of the distal half of the incisal edge appears more lingual on MAND LATERAL
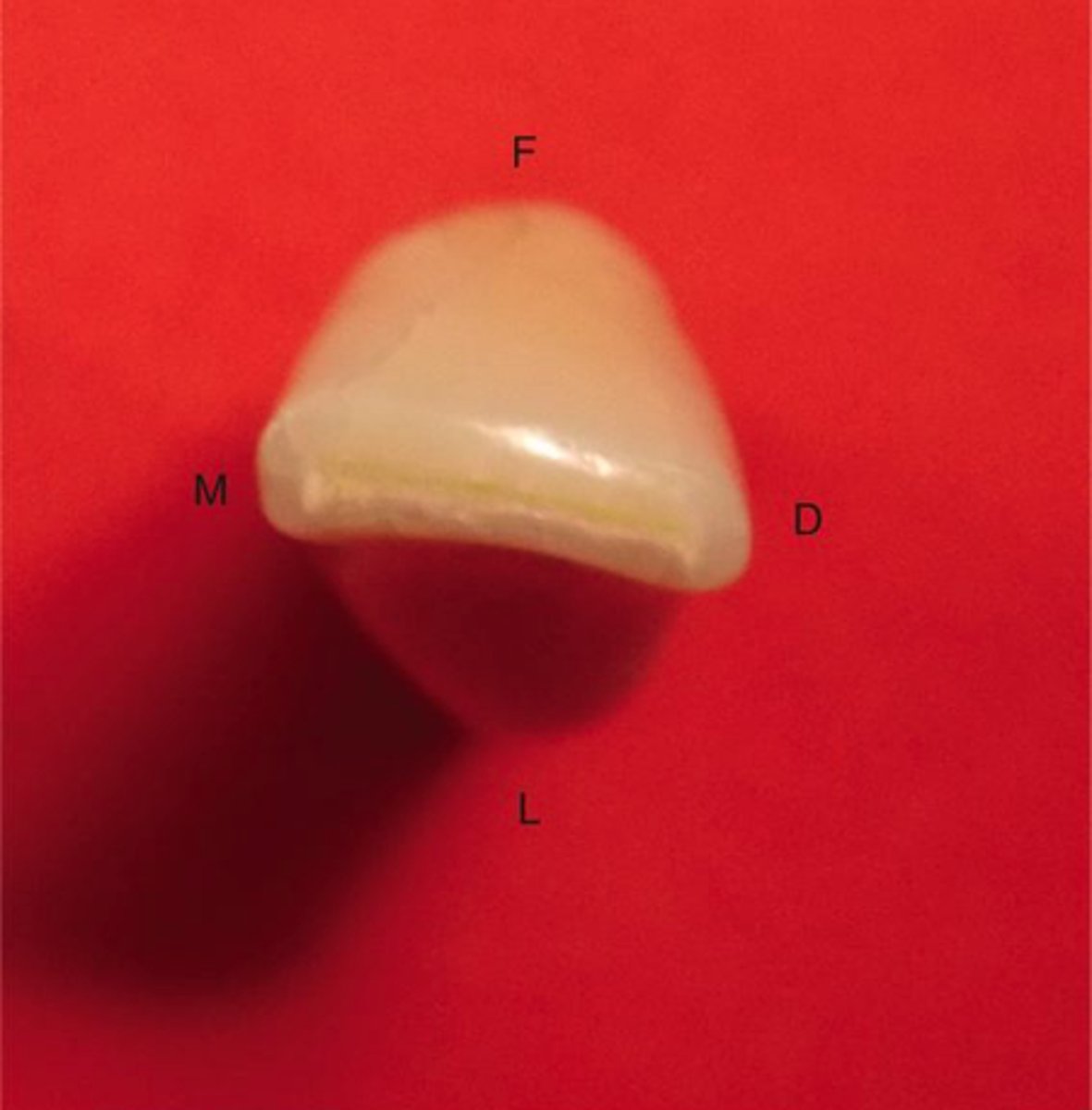
on mand lateral, the cingulum is _____
offset to distal
mand incisor roots are _______. They also may have concavities on the ____ and ______ root surfaces
single, straight, and both longer/wider than max incisor roots
mesial and distal
**they are also wider faciolingually than mesiodistally
What is a canine eminence?
The thick facial plate of bone overlying the canine root that causes a bone projection below the gingiva
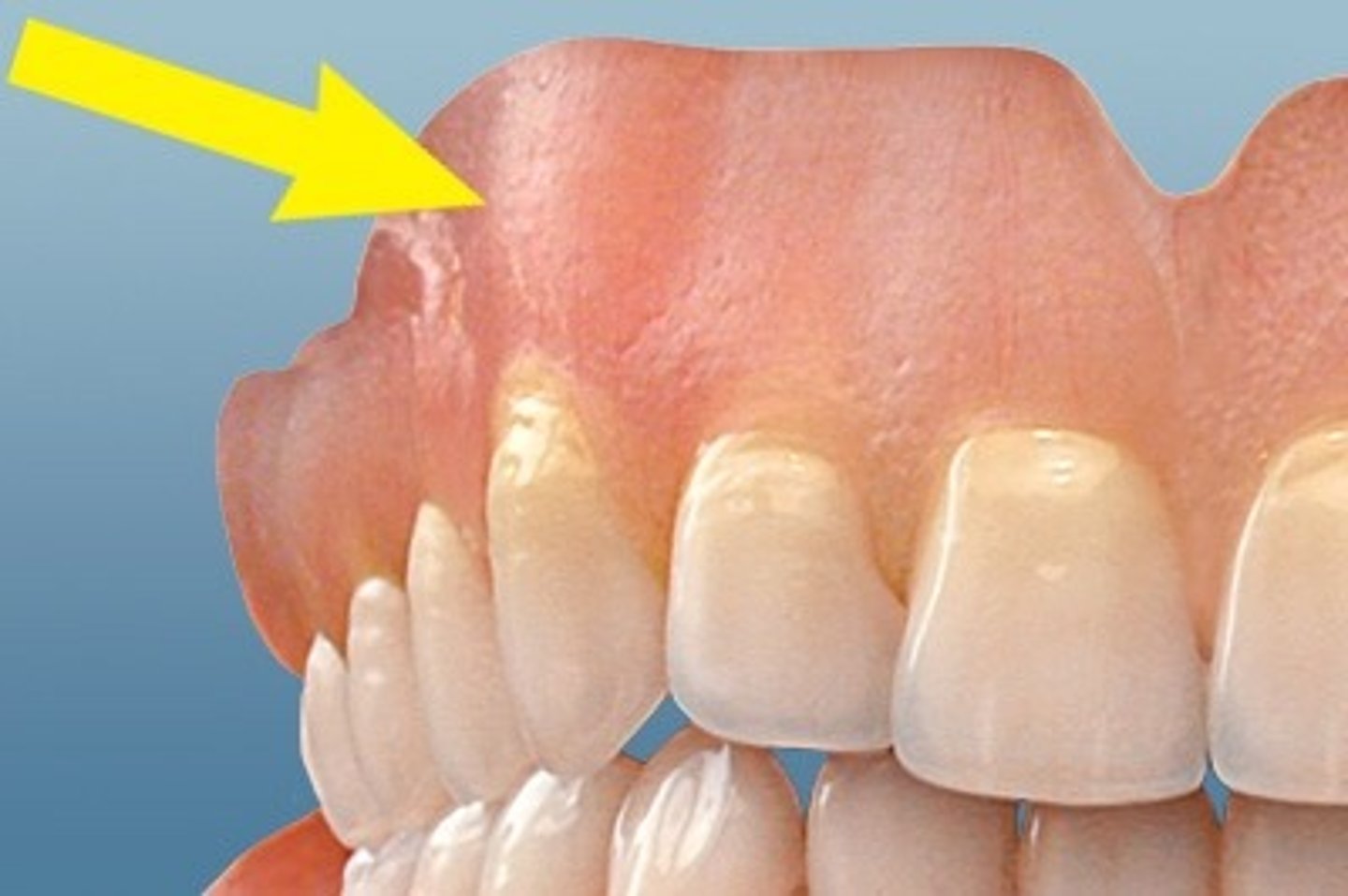
the canine is known as the
cornerstone of the arches
When smiling, only the ______ half of the canine is visible
mesial
Which tooth is often the last to be lost from decay/periodontal disease?
canine
Which is the longest tooth (crown & root)
max canines
Which tooth has the longest crown
mandibular canine
on the canines, the _____ incisal slope is shorter
mesial
Which tooth has a prominent labial ridge
canine
canine facial HOC in_____ and lingual HOC in ____
cervical 3rd for both
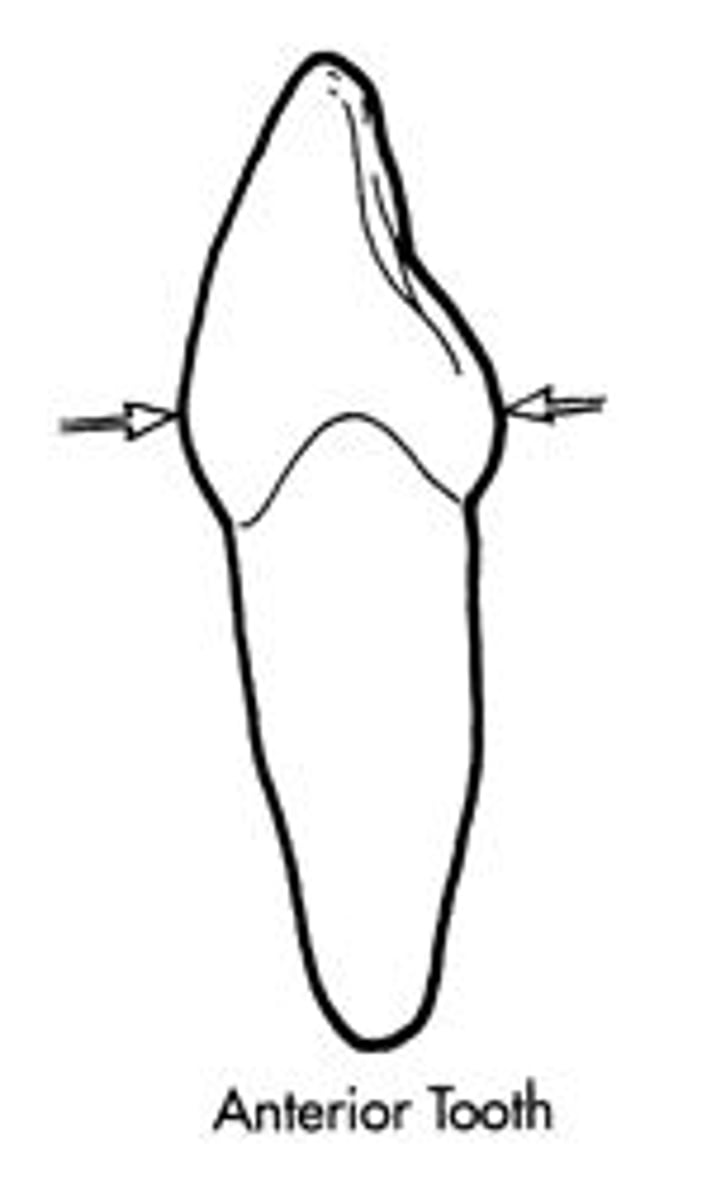
canine distal HOC in _____ and mesial HOC in _____
middle 3rd
junction of incisal and middle
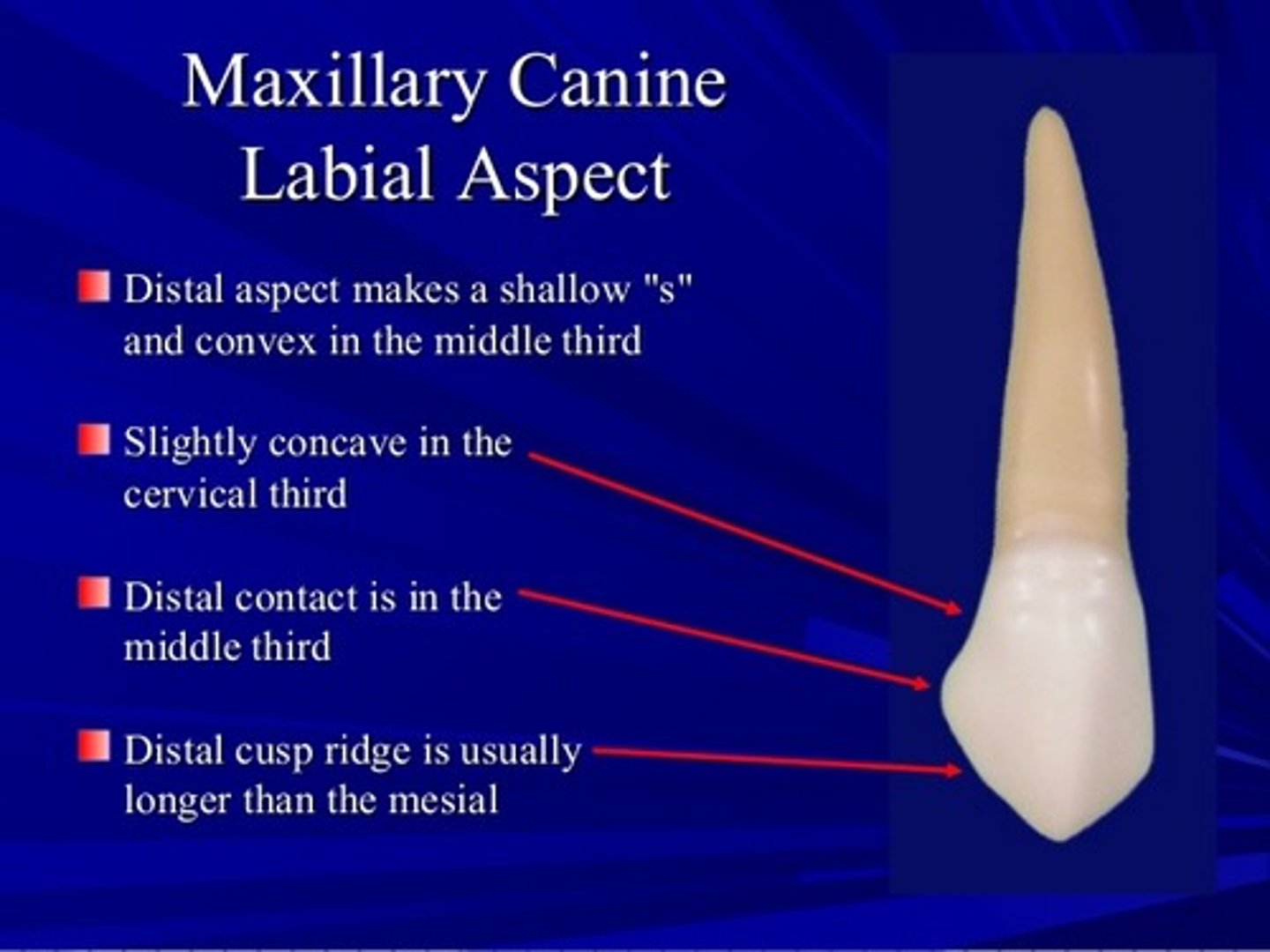
Which tooth has the longest root
max canine
When the max canine is viewed from the incisal, the mesial half is ____ and the distal is _____
convex
concave
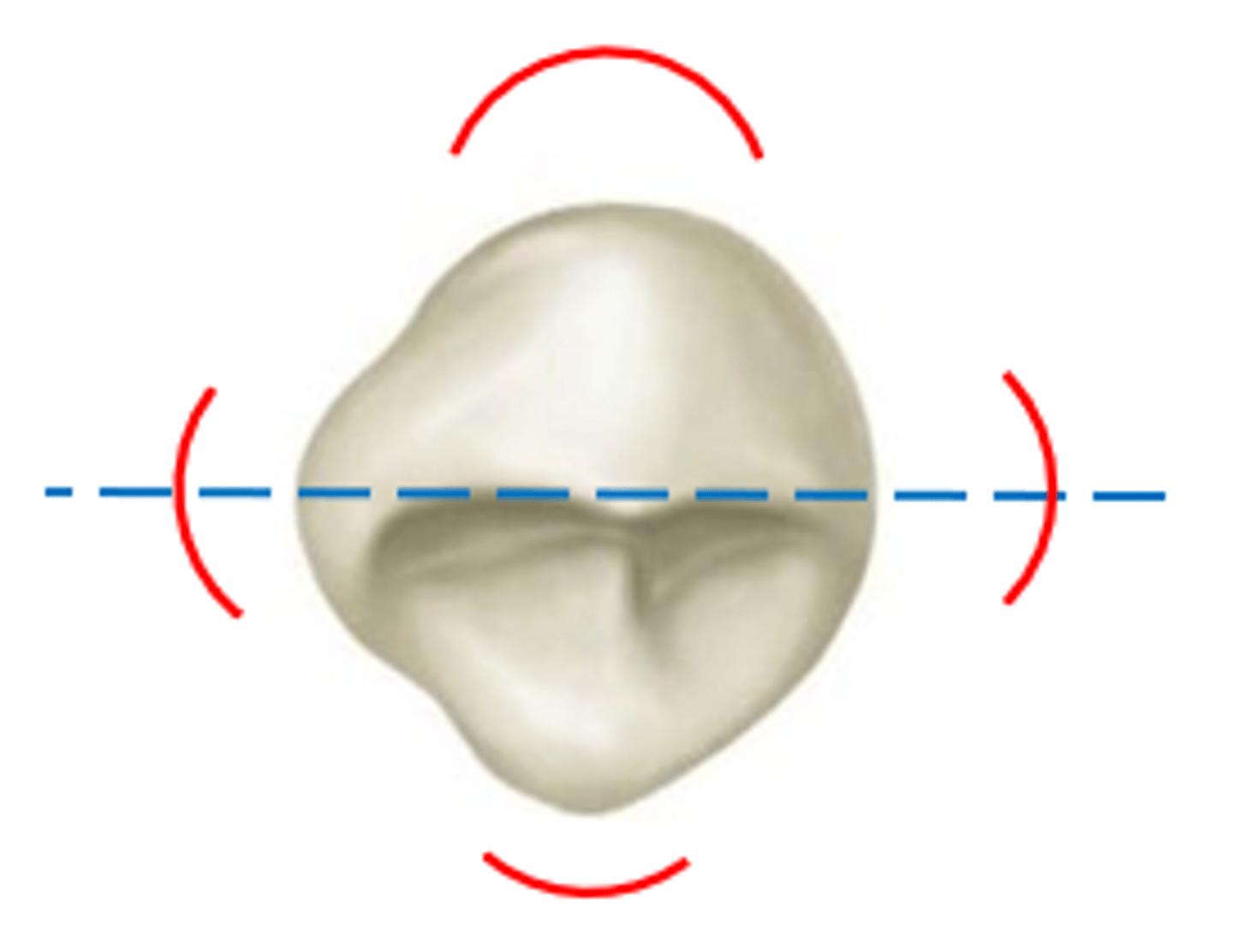
in the max canine, the cingulum is ____
centered
in the mand canine, the cingulum is ____
distal
Which tooth is the thickest faciolingually?
max canine
Which canine has a more pronounced labial ridge
max canine
when the mand canine is viewed from the facial, the mesial outline is ____
flat, and parallel to root
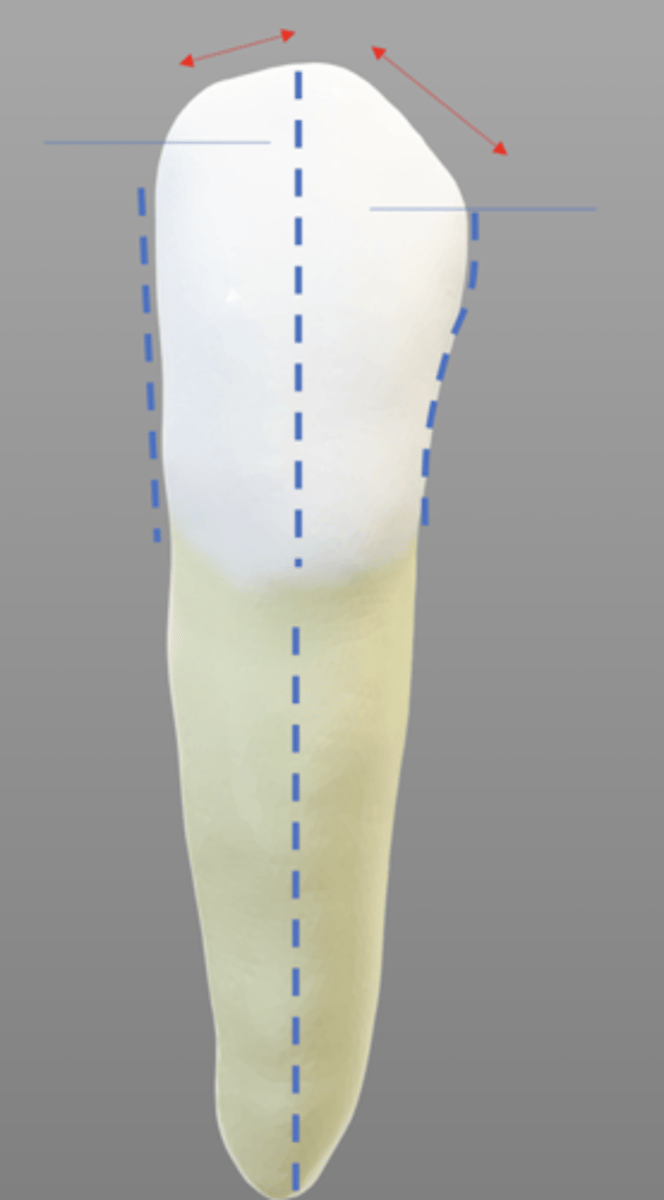
When viewed from the proximal, the mand canine crown and root makes a
C shape
the mand canine cingulum is
distal
the max canine roots are ______, having root depressions on the ___ and ____, where the _____ one is more pronounced.
Apex is _____ and may have a distal deflection
long, slender, conical
mesial and distal (more pronounced)
pointed/sharp
the mand canine roots are ______, having root depressions on the ___ and ____, where the _____ one is more pronounced.
Apex is _____
long (but shorter than max canine) and straight
mesial and distal (more pronounced)
blunt/ rounded
What is outline form?
outer shape or perimeter of the restoration
What is resistance form?
The internal shape of a prep that prevents fracture of the remaining tooth
What is retention form?
Internal shape that best prevents the filling material from falling out
Ex: grooves, slots, undercuts
What is margination
finishing the external preparation of the walls
also called cavosurface finishing
Class I Outline Form:
how far into dentin?
how far into tooth overall?
FL width?
What shape/ pattern should it follow?
0.5 mm into dentin
1.7-2 mm into tooth
1 mm FL width
follows central groove, and slightly extends major grooves
maintain marginal and oblique ridge integrity
Class I Resistance Form:
What kind of pulpal floors?
What angle should the M and D walls be with pulpal floor?
smooth, flat, pulpal floor, perpendicular to long axis of tooth
6 degrees
Class I Retention Form:
What degree should FL walls be to pulpal floor?
90 degrees
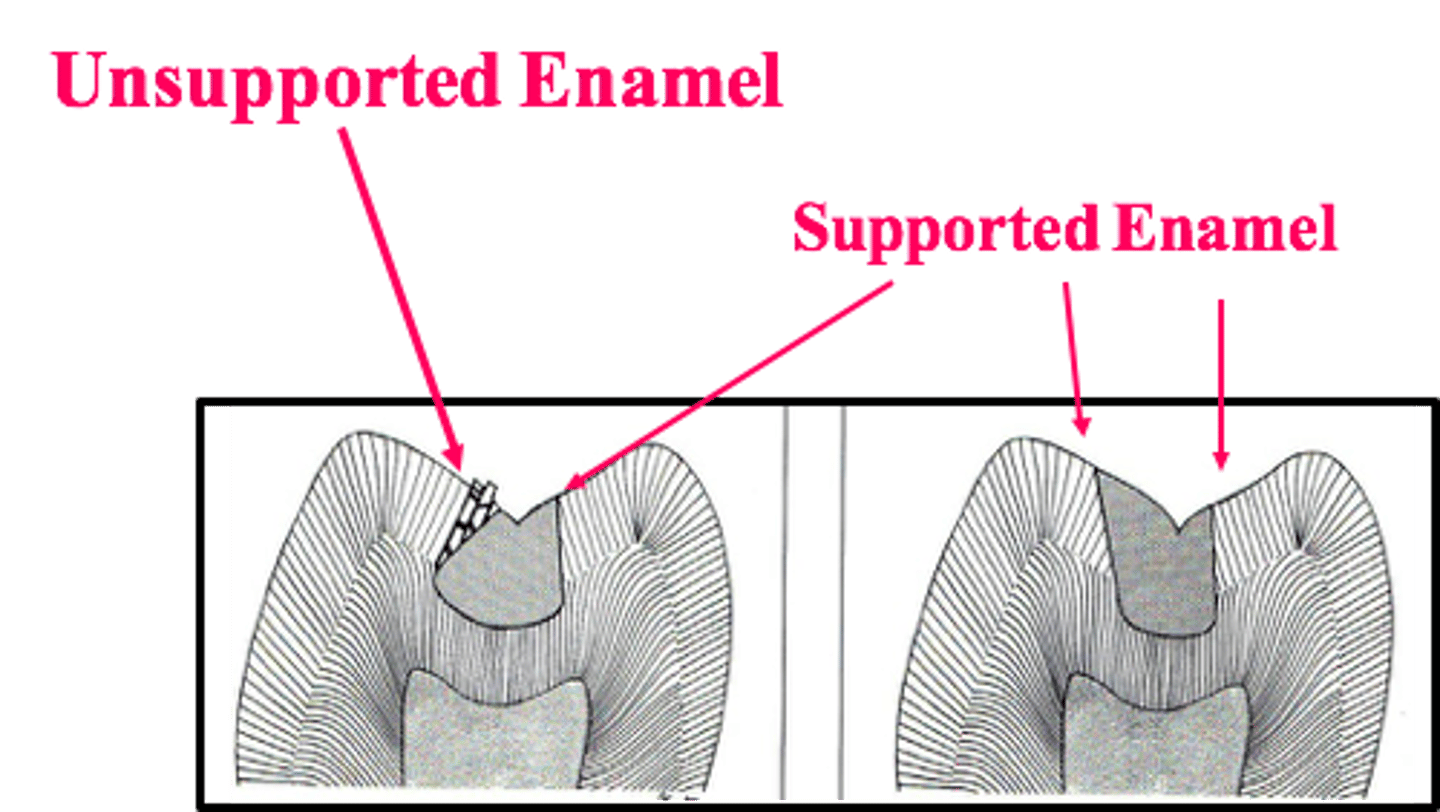
Class I and II Margination:
_____ unsupported enamel
remove
What degree should the burr enter the enamel for a mandibular first premolar? Why?
45 degrees
to match the occlusal surface, maintain transverse ridge
Class II Outline Form:
how far into tooth overall?
FL width?
What shape/ pattern should it follow?
Which way does the box converge?
1.7-2 mm into tooth
1 mm FL width
follows central groove, and slightly extends major grooves
maintain marginal and oblique ridge integrity
box converges slightly towards the occlusal
break gingival contact, open embrasures sometimes
Class II Resistance Form:
What kind of pulpal floors?
What angle should the M and D walls be with pulpal floor?
What is the axial depth?
The axiopulpal line angle is ________.
Axial wall is _____, following the contour of the _________.
smooth, flat, pulpal floor, perpendicular to long axis of tooth
6 degrees
1 mm in pre-molars and 1.3 mm in molars
- rounded
- convex, gingival cavo-surface margin
Class II Retention Form:
What degree should FL walls be to pulpal floor?
Mesial and distal walls are _______
Facial and lingual walls _______
90 degrees
-Parallel or tapering towards the occlusal
-facing each other, converging slightly towards occlusal
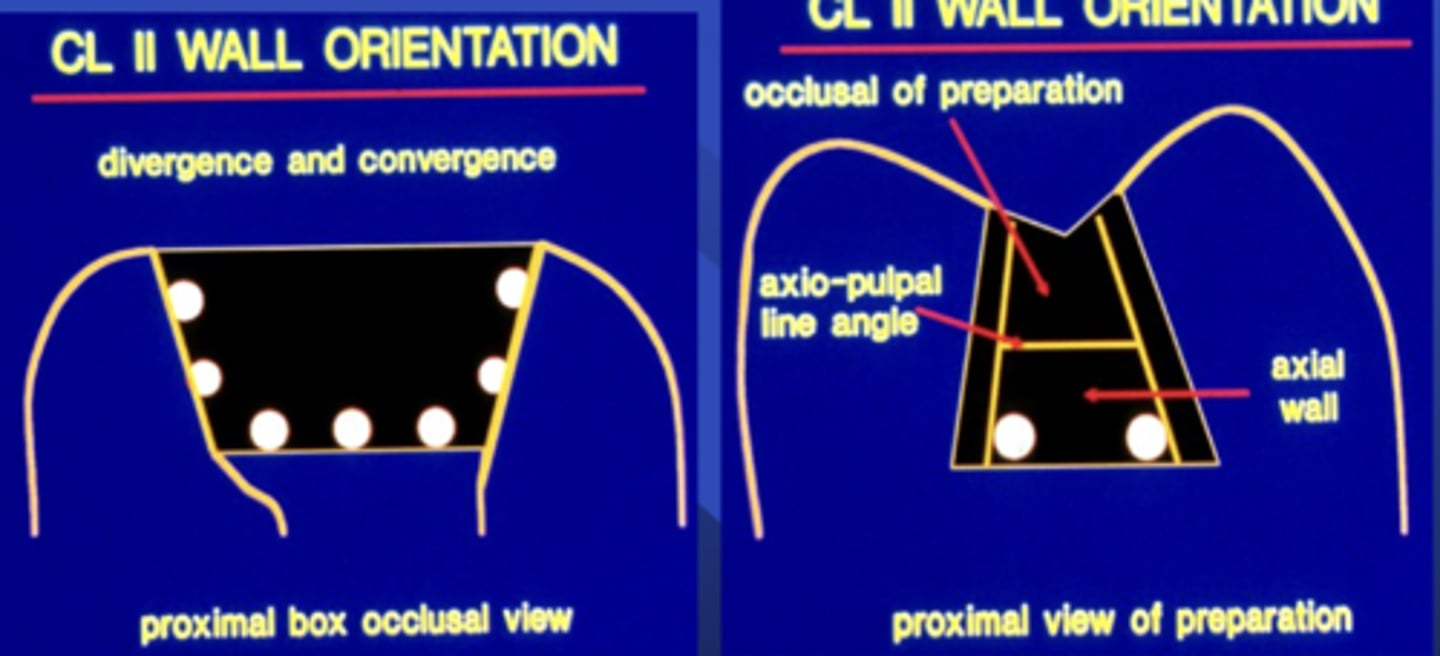
What is a proximal box?
the axial depth on the M or D side of a class II restoration
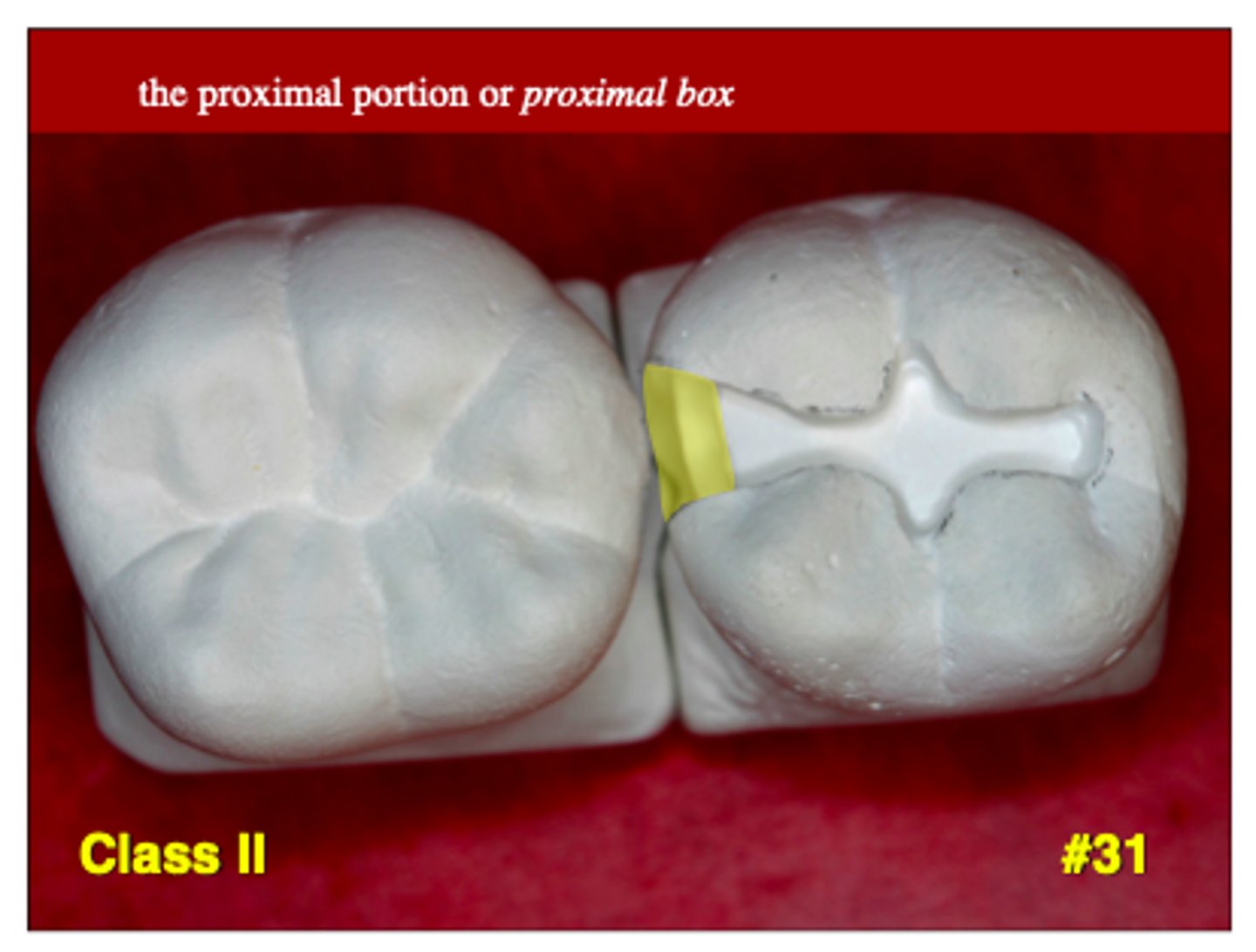
The proximal box should be centered on the ____
contact area
What can be used as an interproximal protector?
pre wedge, interproximal guard, Tofflemire matrix
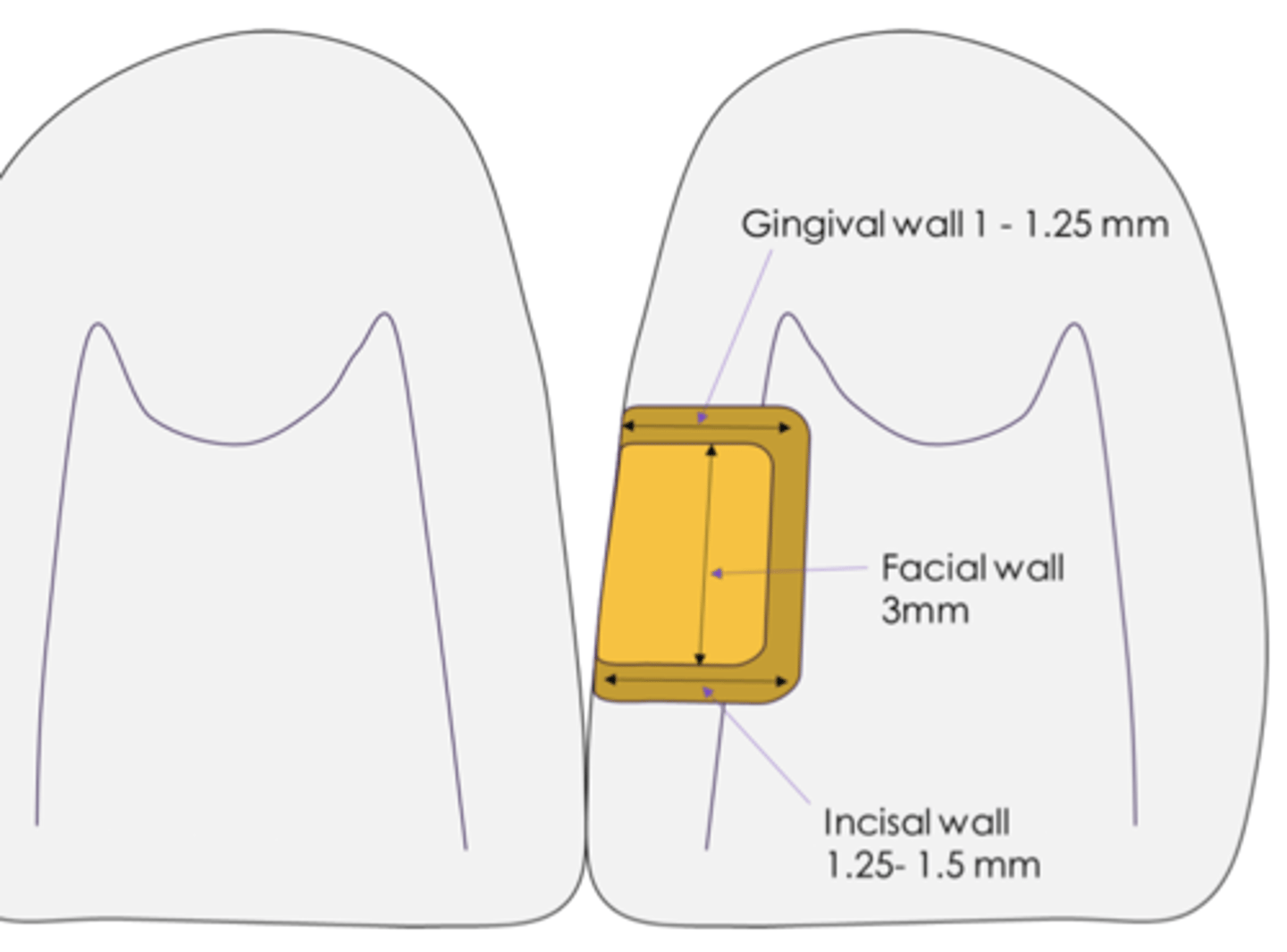
Class III Outline Form:
What approach is preferred?
___1___ contact should be broken, ___2__ contact should not be broken
MD width should be within the ____3___
The incisal and gingival walls converge towards the __4__ and face __5___
Begin at and extend below the ___6____, without breaking ____7_____
Keep gingival width ___8____ and ___9__
Lingual approach
1. gingival
2. incisal margin
3. marginal ridge
4. access
5. face each other
6. contact point
7. facial contact
8. 1 mm FL
9. 1.5 mm axially
Class III Resistance Form:
Internal wall are ______
Preserve ____ edge
smooth
incisal
Class III Retention Form:
for composite, use ____
etch
Class III Margination Form:
All cavosurface margins meet the tooth surface at ____ degrees, with no ____
90 degrees
no bevels *except facial approach or broken facial contact
What bur is used for a Class III?
330 carbide burr (pear-shaped)
What classes are 1556 carbide burs used for (per the lecture)? What is their cutting length?
Class I, II, and V
3.8 mm
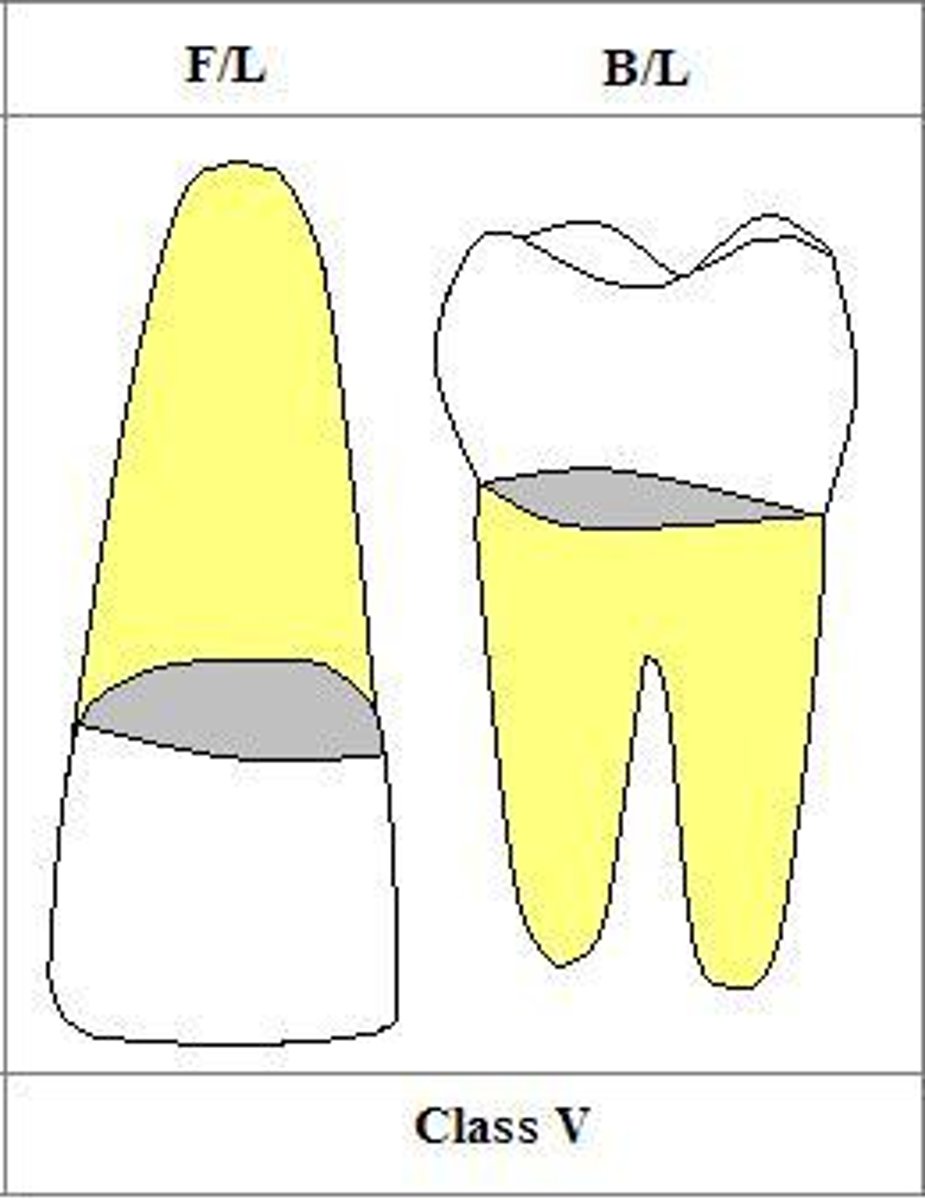
Class V Outline Form:
Shape should be proportional to ____1___, following contour of the ___2__
- more curved in the ____3__, straighter __4___
preparation is limited to ___5___ incisogingivally, and __6___mesiodistally
Gingival depth is __7___ axially
Incisal depth is __8__ axially
1. meso-distal diameter
2. CEJ
3. anterior
4. posterior
5. gingival 1/3
6. two middle fourths mesio-distally
7. 1 mm
8. 1.5 mm
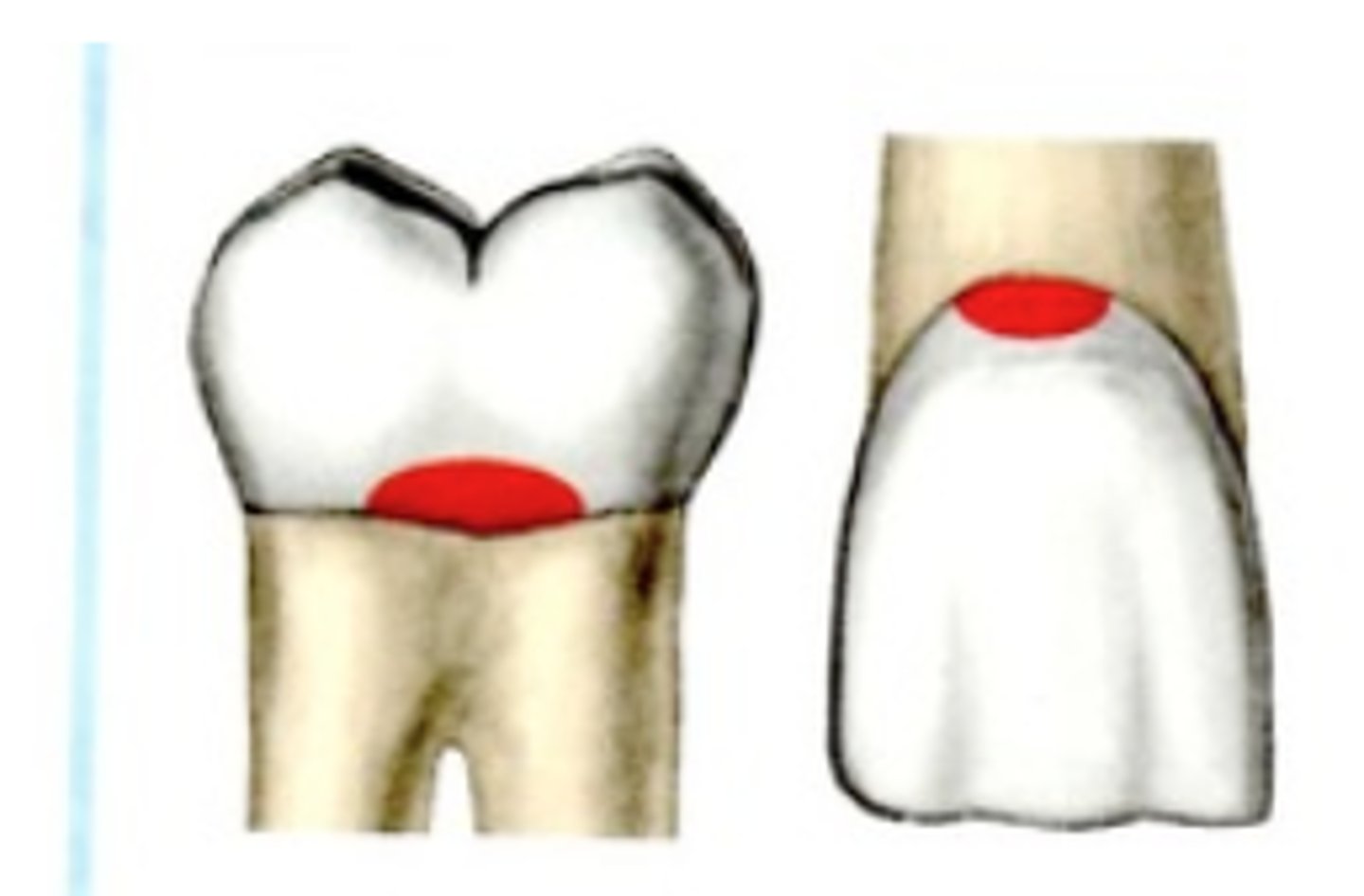
Class V Resistance Form:
the contour of the axial wall must follow the _______
M&D walls are at ________
contour of the facial surface
right angles
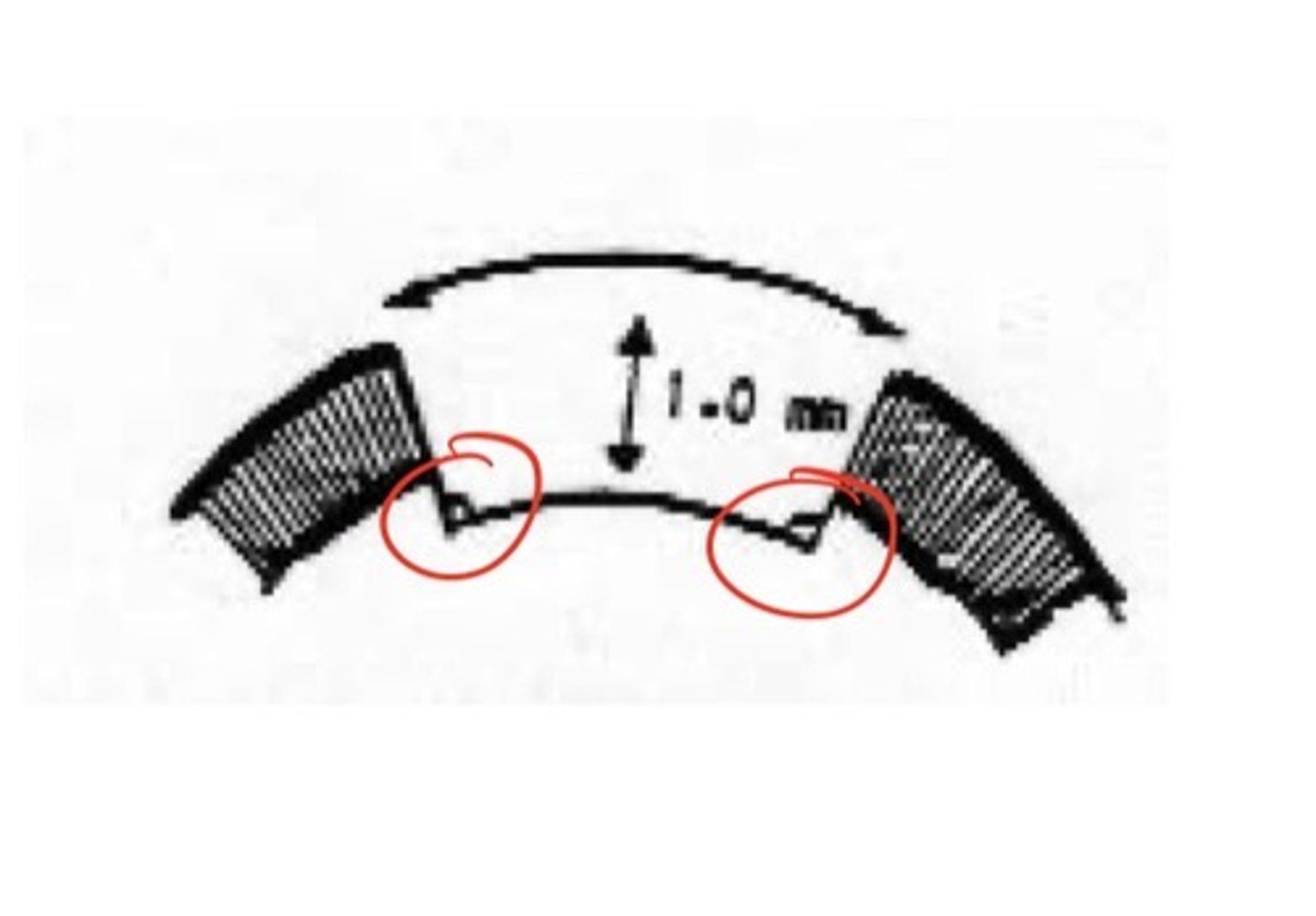
Class V Retention Form:
Composite, use ____
Amalgam, retention grooves are placed both _____ and ____ in dentin using a _____
etch
incisally, gingivally, using a #1/2 round bur
Class V Margination Form:
Composite:
- if preparation is entirely on enamel, all Cavo surface margins are ___1___, ___2__, and at __3___
- if prep is half enamel/ half cementum, ____4_____
- if prep is all cementum, _____5_____
Amalgam: ___6____
1. beveled
2. 0.5 mm deep
3. at 45 degrees
4. Only that portion of the enamel receives a bevel
5. "butt joints all around"
6. no bevels
On class V's, enamel is beveled using only ___ burs
diamond
Why isolate with rubber dams?
improve vision, produce dry field, protect patient, infection control, more time efficient (by about 40%)
What are methods of controlling the operating field?
- rubber dams
- drugs (antisialogogues, epinephrine, liquid hemostatic agents)
- dri-angles (blocks stensons duct)
-cotton rolls
- vacuum devices
Anterior isolation is used from ___ to ___, on classes ______, using __ clamps
first PM to first PM
classes III, IV, and V
2 clamps, one on each PM
Posterior quadrant isolation is used from ___ to ____, with clamp on ____
second molar to one tooth past the midline
clamp on 2nd molar
Single tooth isolation is used in _____
endo
What is posterior 3-tooth isolation?
clamp tooth distal to the one being restored and ligate tooth anterior to the one being restored
How far away should holes be in rubber dams?
1.5-2.0 mm
Rubber dam clamp #9 is for ______
anterior teeth class V (butterfly clamp)
Rubber dam clamp #2A is for ______
smaller pre-molars
Rubber dam clamp #7 is for ______
mandibular molars
Rubber dam clamp #14 is for ______
maxillary molars
Rubber dam clamp #12A is for ______
mand right and max left molars
Rubber dam clamp #13A is for ______
mand left and max right molars