Chapter 32 - Fungi
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
how do fungi differ from plants
a) lacking plastids (hence they are heterotrophic)
b) storing E in glycogen rather than starch
c) their cell wall which is composed of chitin (N-glucose).
how do fungi differ from animals
inability to capture prey or solid food particles by phagocytosis
absorptive heterotrophs
digest food outside their body and then absorb it
- saprophytes
- parasite
- mutualistic
saprophytes
decomposers, feeding off dead organisms
parasite
feed off living organisms
mutualistic fungi
absorb nutrients from a host organism, but they reciprocate with actions that benefit the host
-associated with living autotrophic organisms but not lethal, Either algae, cyanobacteria or plants!
hypha
A filament of fungal cells.
mycellium
entire mass of hyphae making up the body of a fungus.
mating types in fungi
determined by mating-type gene
- homothallic (selfing)
- heterothallic (outcrossing)
fungal life cycle
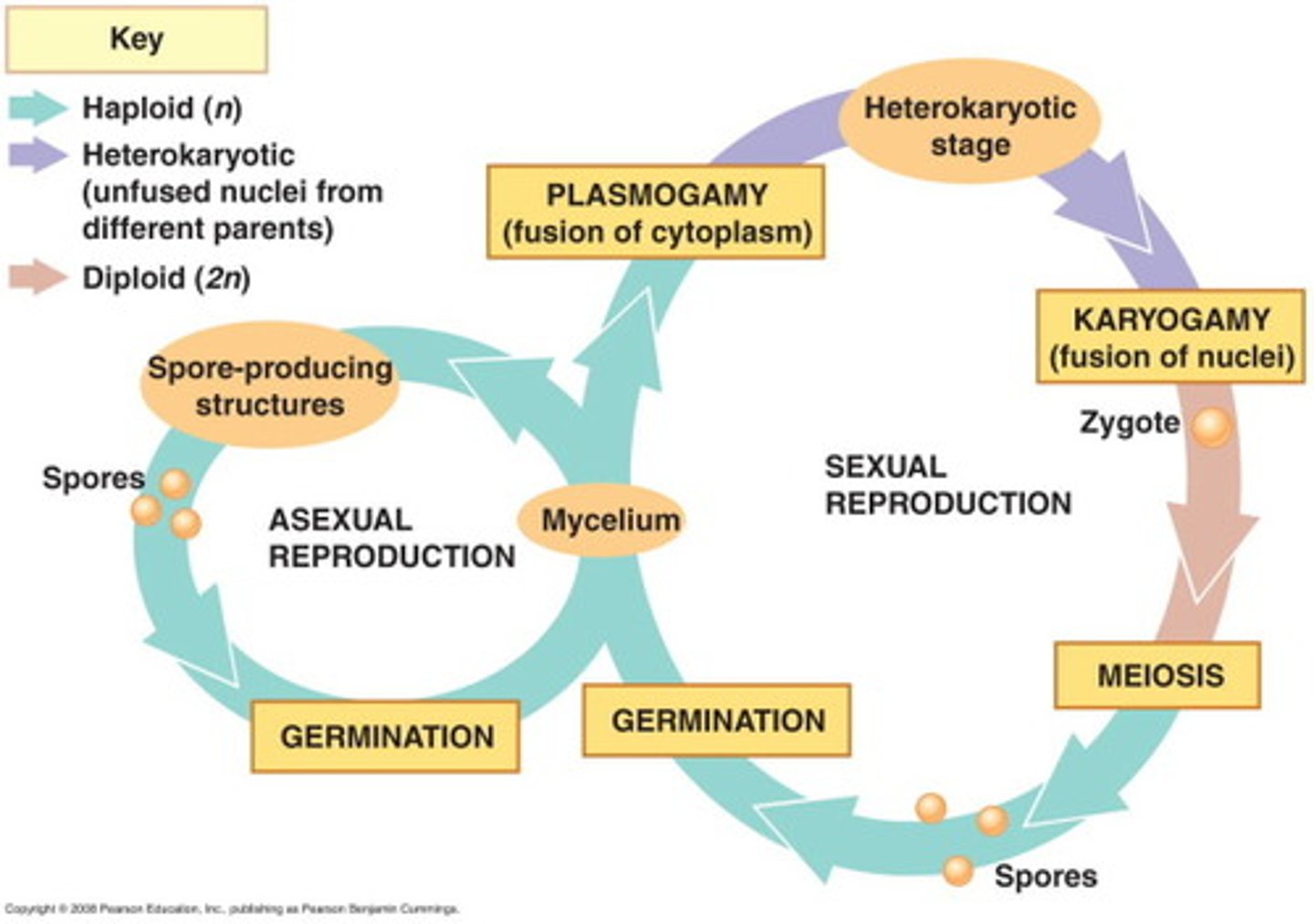
role of fungi
a) Main decomposers of the planet: imagine what the world would look like if none (or less) of the dead organic material was recycled (a giant peatland or dump)!
b) Fungi as food
c) Fungi as producers of medicines: antibiotics
five phyla of fungi
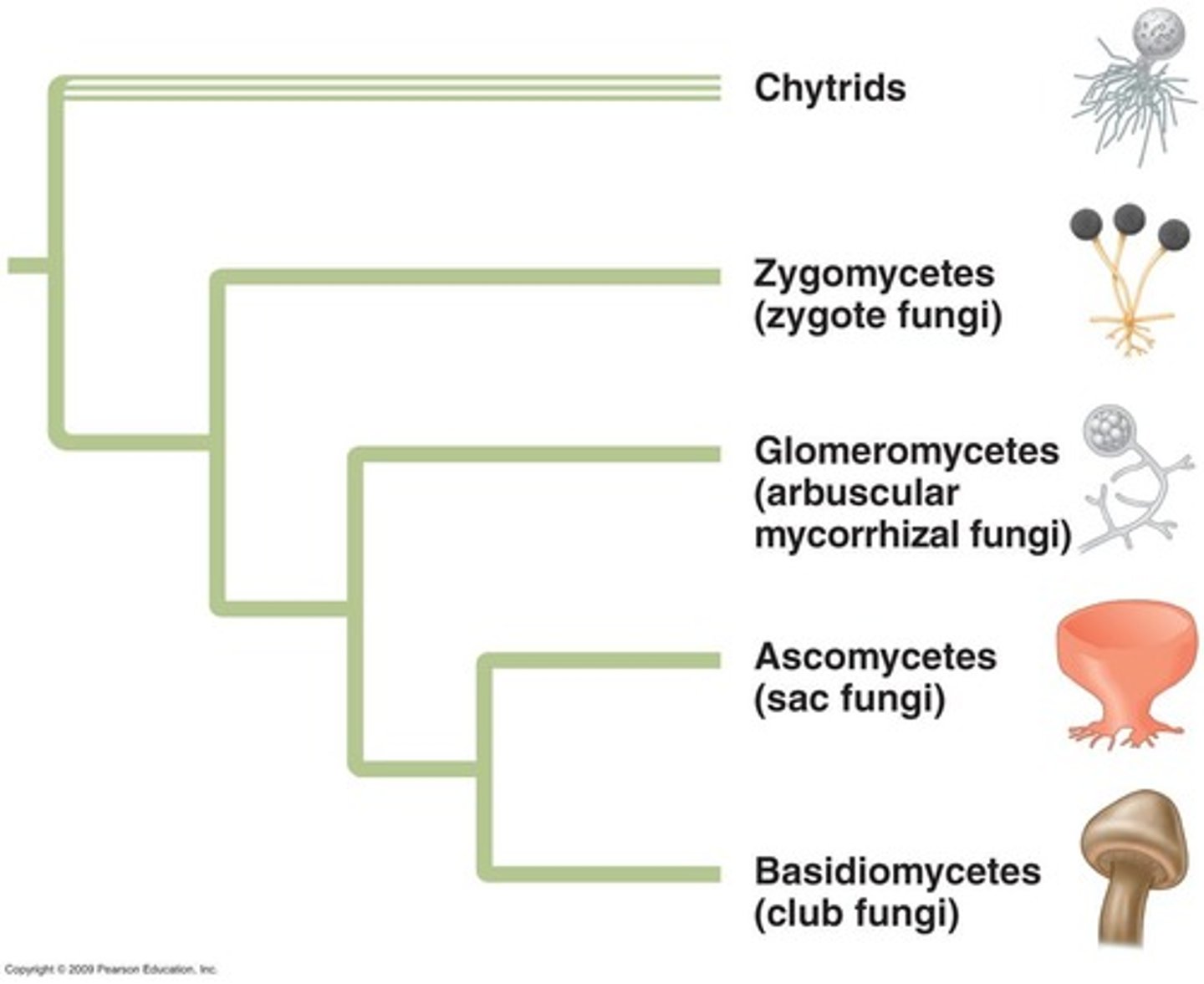
chytrids
mostly aquatic fungi with flagellated zoospores that represent an early-diverging fungal lineage.
zygomycetes
molds found on meat, cheese, and bread
glomeromycota
arbuscular mycorrhizae, e fungal hyphae form little "trees" (arbuscules) inside root cells, providing a large surface area for transfer of food, water and minerals
Mycorrhizal symbiosis
An association between the roots of most plant species and certain fungi. The plant provides organic compounds to the fungus, while the fungus provides water and nutrients to the plant.
Ascomycetes
sac fungi; produce spores in a sac called an ascus; most are multicellular except the yeasts
- penicillin, cheeses, athlete's foot, etc
lichens
Lichens are mutualistic associations between an ascomycete fungus and a green alga (or cyanobacterium).
- alga provides food to the fungus, and the fungus provides protection, water and minerals for the alga. Yeast association also.
three types of lichens

Predatory ascomycetes
- Cordyceps lloydii devours Camponotus ants, from the inside out!
- Arthrobotrys traps roundworms in the soil with loops that are triggered to swell when something touches their inner surface
Basidiomycetes
Club fungi. Produce mushroom like thallus, spore bearing structure (basidiocarp), many mushrooms/fungi of the woods in this group. ex- Bradiospores, Basidia, Toadstool, etc.
Ectomycorrhizae
mycorrhizae in which the fungal hyphae do not penetrate the root cells of the plant