Unit 10 - Redox Reactions and Hydric Soils
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Redox Reactions - Oxidation / Reduction reactions (redox) are widely considered the ____
most important chemical reactions on Earth
Redox Reactions - The most common reaction is CO2 + H2O + energy = ____
CH2O (carbohydrate) + O2 (when left to right, it’s photosynthesis)
Redox Reactions - ___ requires energy in the form of sunlight
photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a ____ because elements are gaining and losing electrons
redox reaction
The oxidation state of carbon in CO2 is ___
+4
The oxidation state of O in H2O and CO2 is ___
-2
The redox reaction is in the transfer of ____ to e^4+ in CO2
4e’s from O2-
The oxidation state of O in O2 is ___
0
The oxidation state of C in organic matter is ____
0
When the photosynthesis reaction goes right to left, it’s called
respiration
Respiration releases ___ in organic matter
energy stored
The oxidation of organic matter is also called ___
mineralization, decomposition, or decay
Organic matter is ____
electron rich
Microbial decay of soil organic matter releases ___
4e- per C atom
CH2O (om) + H2O = ____
CO2 (g) + 4e- + 4H+
The most common electron acceptor in nature is
elemental oxygen (O2)
Redox Ladder - Many microorganisms can take advantage of ____ in the absence of O2
alternative electron acceptors
The relative order in which these alternative electron acceptors are used is called the ____
“redox ladder”
O2 (ag) + 4e- + 4H+ > 2H2O
Anoxia equation:
NO3- (ag) + 5e- + 6H+ > ½N2 (g) + 3H2O
Denitrification equation:
Mn O2 (g) + 2e- + 4H+ > Mn2+ (ag) + 2H2O
Reductive dissolution of manganese dioxide:
Fe OOH (s) + e- + 3H+ > Fe2+ (ag) + 2H2O
Reductive dissolution of goethite:
SO4^2- (ag) + 8e- + 10H+ > H2S (g) + 4H2O
Sulfate reaction:
2CH2O (om) > CH4 (g) + CO2 (g)
Methane Production
Electron Activity - The electron activity of a solution can be measured using a ____ coupled with a reference electrode
Pt electrode
The Pt electrode measurement is called the ____ of the solution
“redox potential” (Eh)
Large positive Eh values indicate ___ and low e- activity
oxidizing conditions
Eh ranges for redox reactions in soils: Fully aerated water, saturated with dissolved oxygen
(+600 to +450 mV)
Eh ranges for redox reactions in soils: Denitrification
(+200 to -100 mV)
Eh ranges for redox reactions in soils: Reductive Dissolution of FeOOH
(+170 to -100 mV)
Eh ranges for redox reactions in soils: Sulfate reduction
(-100 to -200 mV)
Eh ranges for redox reactions in soils: Methane Production
(-150 to -3,000 mV)
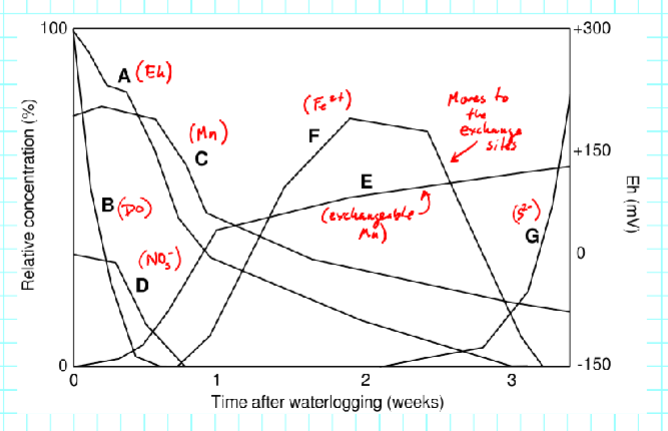
Eh ranges for redox reactions in soils:
______ form under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding
Hydric soils
Hydric Soils - The saturated conditions need to be long enough during the growing season to ____, especially in the upper part of the soil
develop anaerobic conditions
Hydric Soils - These soils support the growth of ____ under natural conditions
hydrophytic vegetation
Hydric soils exhibit properties that can be easily observed in the field known as
redoximorphic features
Accumulation of iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn) nodules
Zones of iron accumulation on pore surfaces and root channels
Zones of iron depletion > gray mottles or gley colors
Indicator tests positive for Fe2+ in soil solution
Examples of redoximorphic features
Eh measurements with Pt electrodes and pH are
Time consuming and difficult
Use of alpha - alpha - dipyridyl will
React with ferrous iron (Fe2+) and forms a pink color
Difficult to obtain (hazardous)
IRIS tubes
Indicator of Reduction In Soils
PVC tubes are coated with ferrihydrate paint
Fe3+ > Fe2+
Organic matter accumulation is favored in soils that are ____ (hydric soil conditions)
perennially wet
Organic Soils - _____, very common in peatlands
Histosols
Organic matter decomposition rates are low because of the lack of e- acceptors
(no O2, NO3, MnO2, Fe2 oxides, sulfates)
High organic matter content
Dark brown or black in color
Low bulk density
High water holding capacity
High CEC (lots of humus)
Corpse preservation
Peat can be harvested for fuel
properties of organic soils
Organic soil subside when drained due to
Shrinkage as the material dries
Consolidation because of a loss of groundwater buoyancy
Compact from tillage or traffic
Wind erosion, burning, oxidation
Microbial decomposers take advantage of the energy stored in organic C bonds, thereby altering the ____
original organic matter
____ results from decomposing organic matter
Humus
Anaerobic, decompositions processes are found in
Flooded soils
Anaerobic processes are found in
Well-drained upland soils
75% water
25% dry matter
45% cellulose
20% lignin
18% hemicellulose
8% protein
5% sugars and starches
2% fats and waxes
2% polyphenols
Typical composition of organic matter
Sugars, starches, simple proteins (easy to decompose)
Crude proteins
Hemicellulose
Cellulose
Fats and waxes
Lignins and phenolic compounds (hard to decompose)
Rate of decomposition
____ decomposition is complicated and slow
The reactions are carried out by fungi
Lignin
Residue particle size
The smaller the particles, the more rapid the decomposition
Temperature
The colder the temperature, the slower the decomposition
Soil water content
Too much water, too little water
Carbon : Nitrogen ratio
Factors controlling rates of decomposition and mineralization